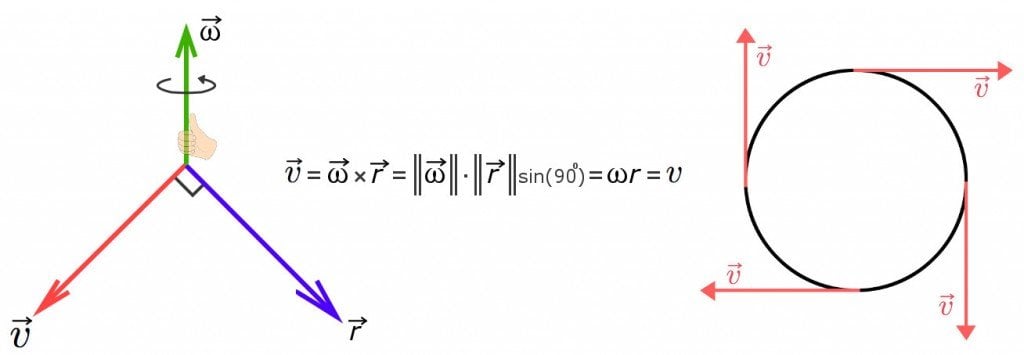
What is the formula used for calculate acceleration?
What is the formula for calculating acceleration? The formula for acceleration is given as a = (v2 – v1) / (t2 – t1), where “a” denotes the acceleration, “v2” indicates the final velocity, “v1” represents the initial velocity and “t2 – t1” is the time interval between the final and initial velocities.
What are the tangential and normal components of acceleration?
The tangential component of acceleration and the normal component of acceleration are the scalars aT a T and aN a N that we obtain by writing the acceleration as the sum of a vector parallel to T T and a vector orthogonal to N. a → = a T T → + a N N →.
What is the difference between centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration?
centripetal and tangential acceleration
- centripetal and tangential acceleration Definition. Centripetal acceleration is defined as the movement of an object towards the central point of circle whereas in tangential acceleration the movement of object is ...
- Overview of Centripetal And Tangential Acceleration. ...
- Centripetal Acceleration. ...
- Tangential acceleration. ...
What is tangential and normal acceleration used for?
The normal (or centripetal) acceleration is the component normal to the velocity, the tangential and normal accelerations add vectorially to give the whole acceleration. I'll have to think more on how to view the vector equation for that. one parallel to ##vec V## and the other (the rest of ##vec A##) perpendicular to ##vec V##.
How do you find the tangential acceleration example?
0:106:50Tangential Acceleration Introduction with Example Problem - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThat is correct tangential acceleration equals radius times alpha or angular acceleration.MoreThat is correct tangential acceleration equals radius times alpha or angular acceleration.
What is the formula of tangential force?
Σ F = m a the equation shows how an unbalanced force must be acting to cause negative acceleration or deceleration. The force produced is called a tangential force.
What is tangential acceleration in rotational motion?
Tangential acceleration is the rate at which a tangential velocity varies in the rotational motion of any object. It acts in the direction of a tangent at the point of motion for an object. The tangential velocity also acts in the same direction for an object undergoing circular motion.
How do you find tangential acceleration from centripetal acceleration?
2:1813:54Non-Uniform Circular Motion Problems, Centripetal ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo that's how you can calculate the tangential acceleration. And a centripetal acceleration. YouMoreSo that's how you can calculate the tangential acceleration. And a centripetal acceleration. You know it's simply v squared divided by the radius of the circle.
What is the value of tangential acceleration?
The direction of tangent acceleration is toward the tangent. The tangential acceleration is zero for uniform circular motion. In a uniform circular motion, angular velocity remains constant thus tangential acceleration = 0.
How do you find tangential and normal acceleration?
0:2013:54tangential and normal components of the acceleration vector ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe're going to take the dot product of the first and second derivative. And over here for the normalMoreWe're going to take the dot product of the first and second derivative. And over here for the normal component we're going to take the cross product of the first and second derivative.
What is tangential and angular acceleration?
Angular acceleration is the change in angular velocity divided by time, while tangential acceleration is the change in linear velocity divided by time.
What is centripetal and tangential acceleration?
The centripetal acceleration is due to the change in the direction of tangential velocity, whereas the tangential acceleration is due to any change in the magnitude of the tangential velocity.
What is the formula for acceleration in circular motion?
The centripetal acceleration ac has a magnitude equal to the square of the body's speed v along the curve divided by the distance r from the centre of the circle to the moving body; that is, ac = v2/r.
Is tangential acceleration the same as velocity?
The tangential acceleration is a measure of the rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity vector, i.e. speed, and the normal acceleration are a measure of the rate of change of the direction of the velocity vector.
Is tangential acceleration parallel to velocity?
The direction of the tangential acceleration vector is always parallel to the tangential velocity, and perpendicular to the radius vector of the circular motion.
How do you find the tangential acceleration of a vector?
2: Tangential and Normal Components of Acceleration. a⇀N=⇀a⋅⇀N=||⇀v×⇀a||||⇀v||=√||⇀a||2−(a⇀T)2. ⇀a(t)=a⇀T⇀T(t)+a⇀N⇀N(t). Here ⇀T(t) is the unit tangent vector to the curve defined by ⇀r(t), and ⇀N(t) is the unit normal vector to the curve defined by ⇀r(t).
How do you find tangential?
Tangential velocity is equal to the circumference of the circle divided by the time it takes to make one full rotation: 2*pi*r/t. It is also related to angular velocity by the formula V = w * r, where w (omega ) is the angular velocity of the rotating object and r is the radius of the circle.
What is the net tangential force?
3:394:45Centripetal vs. Tangential Acceleration and Net ForceYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipKeep in mind the net forces cause accelerations accelerations are the rate of change of velocityMoreKeep in mind the net forces cause accelerations accelerations are the rate of change of velocity centripetal net force causes a change in direction the tangential net force causes a change in speed.
What is the formula for the tangential braking force on the wheel?
Determine the tangential force using the formula. F = T/R = 9 Newton-meters/0.3 metres = 30 Newtons.
How do you find the tangential force of a wheel?
Use the fact that if an object is pinned at a point and you apply a force F at a distance R from the pin at an angle θ relative to a line to the center, then F_r = R∙cos(θ) and F_t = F∙sin(θ).
Q.1. What do you mean by tangential acceleration?
Ans: The rate of change speed of the particle in the circular path is known as tangential acceleration. It is equal to the product of angular accel...
Q.2. What is the formula of centripetal acceleration and tangential acceleration?
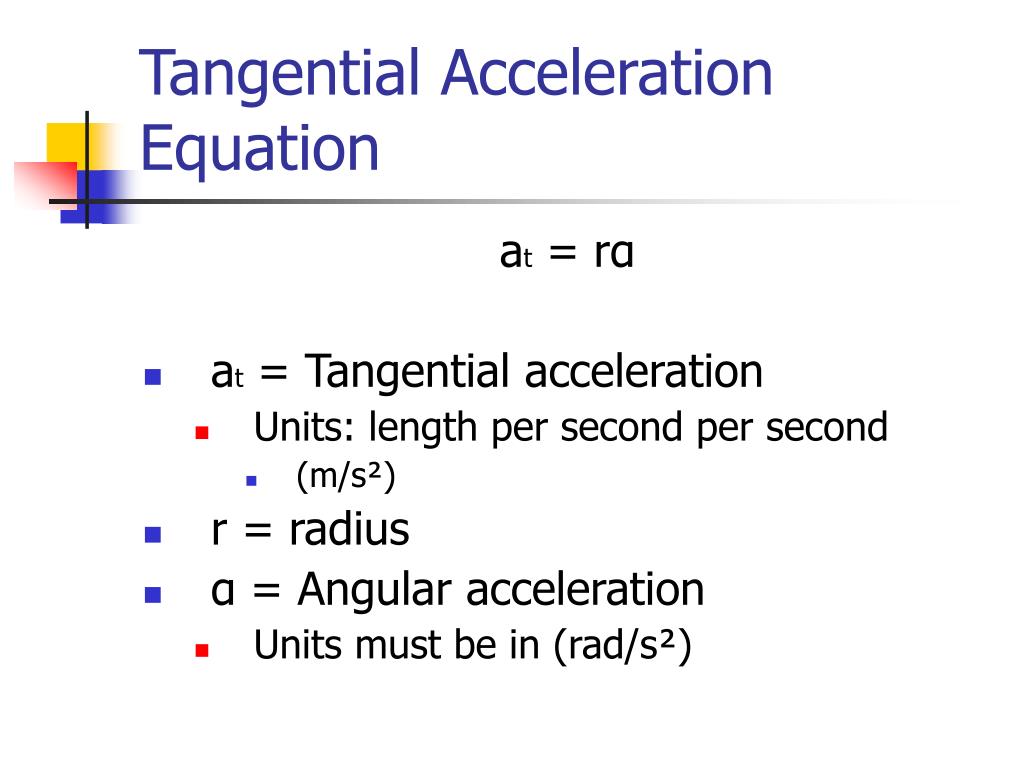
Ans: (i) We can find tangential acceleration with the help of the tangential acceleration formula, which is given as: at=dvdt or at=rα (ii) And, we...
Q.3. In which direction the tangential acceleration works?
Ans: A tangential acceleration works in the direction of a tangent at the point of circular motion. Its direction is always in the perpendicular di...
Q.4. What force causes tangential acceleration?
Ans: The tangential force component will create tangential acceleration, which will cause the object to accelerate along the tangent. Then, the obj...
Q.5. Give an example of both centripetal and tangential acceleration.
Ans: Suppose you are holding a thread to the end of which is tied to a stone. Now when you start whirling it around, you will notice that two force...
Q.6. What is Centripetal Acceleration?
Ans: Centripetal Acceleration can be defined as the component of acceleration in the radial direction (towards the centre).
Q.7. What is the difference between centripetal and tangential acceleration?
Ans: Tangential acceleration is in the direction of the tangent to the circle, whereas centripetal acceleration is in the radial direction of the c...
1. Why do we study the rotational motion and what does the centripetal acceleration specify?
Rotational mechanics is one of the important topics of mechanics that requires great imagination and intuitive power. It helps us understand the me...
2. Why do we study tangential acceleration? What is a tangential velocity vector?
When an object makes a circular motion, it experiences both tangential and centripetal acceleration. Components of acceleration for a curved motion...
3. What can be a suitable example to study tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is a term used for the objects which are in the rotational motion where tangential acceleration is used to measure how quic...
4. How can we relate tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration?
Centripetal acceleration refers to the acceleration that causes any object to take a turn, or move along a circular path and it is also referred to...
5. How is tangential acceleration in a projectile motion described?
Tangential acceleration is associated with the rotational motion of an object that measures the change in the tangential velocity and is thus often...
What is tangential acceleration?
Tangential acceleration is the measure of how quickly the speed of a body changes when an object moves in a circular motion. Let us consider a particle ( (P)) that is moving in a circle of radius ( (r)) and centre (O,) as shown in the figure below. The position of the particle (P) at a given instant may be described by the angle (theta) between (OP) and (OX.) This angle (theta) is called the angular position of the particle with respect to (OX,) and it changes as the particle moves on the circle. Let us assume the point rotates an angle (∆θ) in the time interval of (∆t.) The rate of change of angular position is known as the angular velocity (left ( omega right).)
What is the difference between tangential and centripetal acceleration?
Net acceleration: Tangential acceleration is in the direction of the tangent to the circle, whereas centripetal acceleration is in the radial direction of the circle pointing inwards to the centre. These two components are mutually perpendicular, as shown in the figure below. Thus, a particle in a circular motion having centripetal acceleration as well as tangential acceleration has a net acceleration equals to their vector sum, which is given as:
What are the two accelerations of a particle in circular motion?
Like the velocity, a particle in circular motion has two accelerations that are angular and linear acceleration . Where Angular acceleration (left ( alpha right)) is the rate of change of angular velocity. Thus, we can write that
What is the component of acceleration in the radial direction?
Centripetal acceleration: The component of acceleration in the radial direction (towards the centre) is called radial or centripetal acceleration. This component changes the direction of the linear velocity. As the direction continuously keeps on changing. So, this component can never be zero, and the value of this component is given as:
Is angular acceleration a vector quantity?
Angular acceleration (left ( alpha right)) is also a vector quantity. The direction of (left ( alpha right)) is also perpendicular to the plane of the circle, either parallel or antiparallel to (omega .) If the angular speed of the particle is increasing, then (left ( alpha right)) is parallel (omega ) to and if angular speed is decreasing, then (left ( alpha right)) is antiparallel to (omega .) If angular speed (or angular velocity) is constant then, angular acceleration will be zero.
What are the possibilities for the Value of Tangential Acceleration?
The result of tangential acceleration may have the following three possibilities:
What is the subscript for tangential acceleration?
So, we denote the tangential acceleration with a subscript ‘ct’ along with the English letter ‘a’.
What are the components of acceleration for a curved object?
Components of acceleration for a curved motion are radial and tangential acceleration. The tangential component occurs because of the change in the speed of traversal.
How does tangential velocity work?
A tangential velocity works in the direction of a tangent at the point of circular motion. Henceforth, it always acts in the perpendicular direction to the centripetal acceleration of a rotating object. It always equals the product of angular acceleration with the radius of the rotation.
What are the two types of accelerations in circular motion?
For an object exhibiting a circular motion, there are always some parameters to describe its nature. If we talk about a particle’s velocity, which is an angular velocity, that remains constant throughout the motion; however, angular acceleration makes two types of components and they are tangential and radial acceleration.
Which acceleration acts towards the centre of the circle along which the body or a particle is creating a circular motion?
If we talk about the narrow gap between the centripetal acceleration, which is an acceleration that acts towards the centre of the circle along which the body or a particle is creating a circular motion.
Can angular velocity be written?
We also know that the angular velocity can be written , so we can rewrite the above equation (1) to get the Tangential Acceleration Formula Circular Motion in a new form:
What is tangential acceleration?
In the rotational motion of any object, tangential acceleration is the measure of how quickly a tangential velocity changes. Here tangential velocity will work in the direction of a tangent at the point of motion. Therefore it always acts in the perpendicular direction to the centripetal acceleration of a rotating object.
When the velocity vector decreases with time, the magnitude of the velocity vector remains constant?
Less than zero: When the body has slowed or decelerated motion, that is, the magnitude of the velocity vector decreases with time. Equal to zero: When the body has uniform motion, that is, the magnitude of the velocity vector remains constant.
Is tangential acceleration linear or tangential?
Tangential acceleration is similar to the linear acceleration, but it is specific to the tangential direction. This is related to circular motion. Therefore, the rate of change of the tangential velocity of a particle in a circular orbit is known as Tangential acceleration. It always directs towards the tangent to the path of the body.
Angular Acceleration and Tangential Acceleration
In order to understand angular acceleration or tangential acceleration, it is useful to review certain definitions that are important in describing the motion of an object.
Radial Acceleration
Radial Acceleration refers to the acceleration toward the axis of a rotating object. When an object is rotated around a fixed point there is an inward and outward force caused by the acceleration and the mass of the object.
The Radial Acceleration Formula
The formula used to develop the equation for the radial acceleration of an object moving at a constant speed in a circular path includes the use of the radius of the circle and the tangential velocity of the object at a given point. The vector representing the tangential velocity is perpendicular to the radius.
