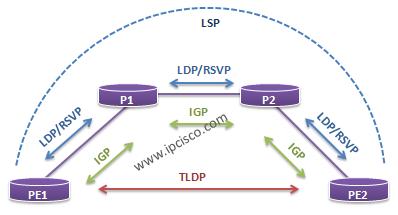
Targeted LDP is for exchanging messages with a distant, non-adjacent peer. Targeted LDP can allow routers to use LDP-signaled LSPs to reach next-hops connected to each-other by sending traffic through the data-plane with an additional, inner label which is signaled using tLDP.
What is an MPLS LDP targeted session?
This is called extended discovery. An MPLS LDP targeted session is a label distribution session between routers that are not directly connected. When you create an MPLS traffic engineering tunnel interface, you need to establish a label distribution session between the tunnel headend and the tailend routers.
What is targettargeted LDP and when to use it?
Targeted LDP is used when we have non-directly connected routers and we need to have LDP neighborship between them. We commenly see this in cases of traffic-engineering tunnels and L2VPN scenarios.
What is the MPLS LDP neighbor targeted command?
You can use the mpls ldp neighbor targeted command to set up a targeted session when other means of establishing targeted sessions do not apply, such as configuring mpls ip on a traffic engineering (TE) tunnel or configuring Any Transport over MPLS (AToM) virtual circuits (VCs).
What is Label Distribution Protocol LDP?
The Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is a protocol for distributing labels in non-traffic-engineered applications. LDP allows routers to establish label-switched paths (LSPs) through a network by mapping network-layer routing information directly to data link layer-switched paths.

What is LDP used for?
The Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is used to establish MPLS transport LSPs when traffic engineering is not required. It establishes LSPs that follow the existing IP routing table, and is particularly well suited for establishing a full mesh of LSPs between all of the routers on the network.
What is an MPLS LDP targeted session?
This is an LDP session between LSRs that are not directly connected. Examples in which the targeted LDP session is needed are AToM networks and TE tunnels in an MPLS VPN network. In the case of AToM, an LDP session must exist between each pair of PE routers.
What is LDP in router?
Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is a protocol in which routers capable of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) exchange label mapping information. Two routers with an established session are called LDP peers and the exchange of information is bi-directional.
What are two types of LDP messages?
LDP Messages Announce and maintain LSRs on networks. Hello messages are discovery messages. Establish, maintain, and terminate sessions between LDP peers. Initialization and Keepalive messages are session messages.
How does MPLS LDP work?
LDP is a protocol that automatically generates and exchanges labels between routers. Each router will locally generate labels for its prefixes and will then advertise the label values to its neighbors. It's a standard, based on Cisco's proprietary TDP (Tag Distribution Protocol).
Is LDP TCP or UDP?
LDP and tLDP discovery runs on UDP port 646 and the session is built on TCP port 646. During the discovery phase hello packets are sent on UDP port 646 to the 'all routers on this subnet' group multicast address (224.0.
What are LDP four major functions?
LDP allows routers to establish LSPs through a network by mapping network-layer routing information directly to data link LSPs....4.2. 4. Execution Flow4.1. Initialization. MPLS must be enabled when LDP is initialized. ... 4.2. Session Lifetime. ... 4.2. Adjacency Establishment. ... 4.2. Session Establishment.
What is the difference between MPLS and LDP?
2 commonly used terms in MPLS are LDP and RSVP-TE. While the former relates to easy provisioning in MPLS setup, the latter i.e. RSVP-TE is related to guarantee bandwidth for traffic communication. LDP setups LSPs based on routing data, whereas RSVP setups additional traffic engineered LSPs.
What is LDP Tunneling?
LDP over RSVP-TE allows tunneling of user packets using an LDP LSP inside an RSVP LSP. The main application of this feature is for deployment of MPLS based services, for example, VPRN, VLL, and VPLS services, in large scale networks across multiple IGP areas without requiring full mesh of RSVP LSPs between PE routers.
What is LDP how is it prepared?
LDP is prepared by polymerization of ethylene under high pressure (1000 – 2000 atm) and temperature (350 – 570 K) in presence of traces of O2 or peroxide as initiator. The mechanism of this reaction involves free radical addition and H-atom abstraction. The latter results in branching.
How is LDP session established?
Process of Establishing an LDP Session Two LSRs exchange Hello messages. After receiving the Hello messages carrying transport addresses, the two LSRs use the transport addresses to establish an LDP session. The LSR with the larger transport address serves as the active peer and initiates a TCP connection.
What is LSP in MPLS?
A label-switched path (LSP) is a path through an MPLS network, set up by the NMS or by a signaling protocol such as LDP, RSVP-TE, BGP (or the now deprecated CR-LDP). The path is set up based on criteria in the FEC.
How is LDP session established?
Process of Establishing an LDP Session Two LSRs exchange Hello messages. After receiving the Hello messages carrying transport addresses, the two LSRs use the transport addresses to establish an LDP session. The LSR with the larger transport address serves as the active peer and initiates a TCP connection.
What is the default value for session hold time and keep alive time in LDP?
The default value of a Keepalive hold timer is 45, in seconds. The smaller value between two configured Keepalive hold timers on both ends of the LDP session takes effect.
Why BGP core free is good or not please explain?
Why Should You Care? There's a simple reason to build a BGP-free core network: the core routers (or switches) don't need to support the number of routes you're carrying around in BGP (above 900.000 entries if you're carrying the full Internet routing table), which means they could be cheaper, or faster, or both.
What is LDP in a network?
LDP is a signaling protocol that runs on a device configured for MPLS support. The successful configuration of both MPLS and LDP initiates the exchange of TCP packets across the LDP interfaces. The packets establish TCP-based LDP sessions for the exchange of MPLS information within the network. Enabling both MPLS and LDP on the appropriate interfaces is sufficient to establish LSPs.
How does LDP work?
You must configure LDP for each interface on which you want LDP to run. LDP creates LSP trees rooted at each egress router for the router ID address that is the subsequent BGP next hop. The ingress point is at every router running LDP. This process provides an inet.3 route to every egress router. If BGP is running, it will attempt to resolve next hops by using the inet.3 table first, which binds most, if not all, of the BGP routes to MPLS tunnel next hops.
How to configure LDP-signaled LSPs?
To configure LDP-signaled LSPs, you must enable the MPLS family on all transit interfaces in the MPLS network and include all the transit interfaces under the [ protocols mpls] and [ protocols ldp] hierarchy levels.
What is label distribution protocol?
The Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) is a protocol for distributing labels in non-traffic-engineered applications. LDP allows routers to establish label-switched paths (LSPs) through a network by mapping network-layer routing information directly to data link layer-switched paths.#N#These LSPs might have an endpoint at a directly attached neighbor (comparable to IP hop-by-hop forwarding), or at a network egress node, enabling switching through all intermediary nodes. LSPs established by LDP can also traverse traffic-engineered LSPs created by RSVP.#N#LDP associates a forwarding equivalence class (FEC) with each LSP it creates. The FEC associated with an LSP specifies which packets are mapped to that LSP. LSPs are extended through a network as each router chooses the label advertised by the next hop for the FEC and splices it to the label it advertises to all other routers. This process forms a tree of LSPs that converge on the egress router.
What is LDP signaling?
It’s common for service providers to use the LDP signaling protocol with MPLS transport at the edges of their networks. LDP offers the advantage of being simple, but LDP lacks traffic engineering (TE) and sophisticated path repair capabilities that are often desired in the network’s core. Many service providers are migrating from RSVP to segment routing traffic engineering (SR-TE) in the core. SR-TE is also referred to as source routing in packet networks (SPRING).
What happens when LDP routers become neighbors?
When LDP routers become neighbors, they establish an LDP session to exchange label information. If per-router labels are in use on both routers, only one LDP session is established between them, even if they are neighbors on multiple interfaces. For this reason, an LDP session is not related to a particular interface.
What is LDP message?
LDP uses the message types described in the following sections to establish and remove mappings and to report errors. All LDP messages have a common structure that uses a type, length, and value (TLV) encoding scheme.
What is LDP in MPLS?
LDP provides a standard methodology for hop-by-hop, or dynamic label, distribution in an MPLS network by assigning labels to routes that have been chosen by the underlying Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) routing protocols.
What is MPLS LDP?
MPLS LDP provides the means for LSRs to request, distribute, and release label prefix binding information to peer routers in a network. LDP enables LSRs to discover potential peers and to establish LDP sessions with those peers for the purpose of exchanging label binding information.
What is extended discovery?
The nondirectly connected LSR responds to the Hello message and the two routers begin to establish an LDP session. This is called extended discovery.
Can you enable authentication between two LDP peers?
You can enable authentication between two LDP peers, which verifies each segment sent on the TCP connection between the peers. You must configure authentication on both LDP peers using the same password; otherwise, the peer session is not established.