What is the difference between telencephalon and diencephalon?
Furthermore, depending on the structures each part consists, the functionality of both telencephalon and diencephalon also varies. Telencephalon is important for sensory recognition, olfaction, language, speech, learning and memory. Meanwhile, diencephalon is important for homeostasis, sensory recognition and visual detection.
What is the telencephalon?
The telencephalon is the scientific name for the largest region of the brain better known as the cerebrum. The word telencephalon comes from the Greek root words "telos," meaning end, and "enkephalos," meaning brain. Telencephalon literally translates to endbrain.
Where is the diencephalon located?
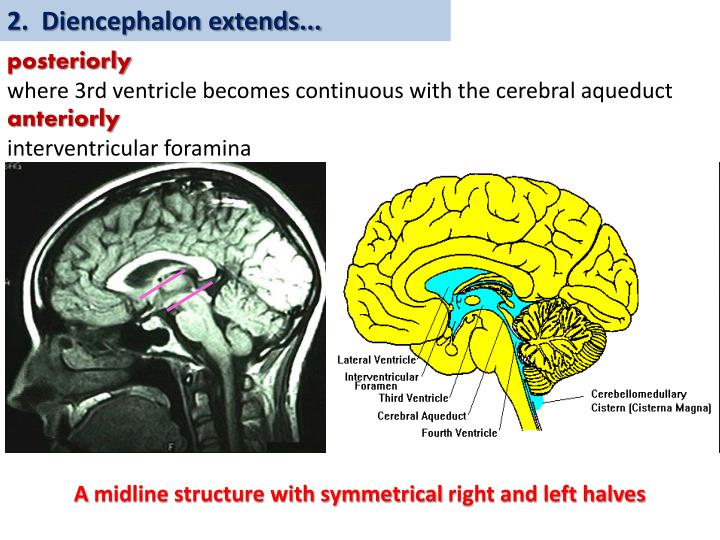
The diencephalon is a division of the forebrain (embryonic prosencephalon), and is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic mesencephalon). It consists of structures that are on either side of the third ventricle, including the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus and the subthalamus.
What is the function of thalamus and diencephalon?
The diencephalon encloses a cavity called third ventricle. Thalamus serves as a relay centre for sensory and motor impulses from Spinal cord and medulla oblongata to cerebrum. It recognizes sensory impulses of heat, cold, pain, pressure etc. The floor of the third ventricle is called hypothalamus.

What is a diencephalon?
The diencephalon connects the midbrain to the forebrain. It is located deep within the brain and comprises the epithalamus, thalamus, subthalamus and hypothalamus.
Is the diencephalon part of the telencephalon?
The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic prosencephalon), and is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic mesencephalon). The diencephalon has also been known as the 'tweenbrain in older literature.
What is telencephalon and its function?
The telencephalon is too large an area of the brain to try to link it with a function or short list of functions. It plays a role in most of our brain activity and thus is more analogous to an entire division of the nervous system than to a particular delimited brain structure.
What does telencephalon mean in anatomy?
Telencephalon - Telencephalon The cerebrum or telencephalon is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb.
Where is the diencephalon?
the brainIn adults, the diencephalon is centrally located within the brain sitting at the top of the brain stem above the midbrain and under the cerebrum. It is part of the third ventricle of the brain. Along with the cerebrum, the diencephalon is part of the forebrain.
What is metathalamus?
The metathalamus is composed of the medial and lateral geniculate bodies, or nuclei. Fibres of the optic nerve end in the lateral geniculate body, which consists of six cellular laminae, or layers, folded into a horseshoe configuration.
What lobe is the telencephalon?
What lobes are in the telencephalon? There are four lobes in the telencephalon. They are the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe is found on both hemispheres of the brain.
What develops from the telencephalon?
From the telencephalon derive the cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampal formation, amygdala and olfactory bulb. From the diencephalon the thalamus and surrounding nuclei, hypothalamus, retina and optic nerve. The mesencephalon gives rise to the midbrain structures, and the metencephalon the pons and cerebellum.
What nuclei are found in the telencephalon?
caudate nucleus. caudothalamic groove.corpus striatum.lentiform nucleus. globus pallidus. putamen.neostriatum.nucleus accumbens.
What is the insula?
The insula (or insular cortex) is a thin ribbon of gray matter tissue that lies just deep to the lateral brain surface, separating the temporal lobe from the inferior parietal cortex.
What is the center of your brain called?
Brainstem. The brainstem (middle of brain) connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. The brainstem includes the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
What are the cerebrum’s functions?
The cerebrum has many functions. The most important functions include: sensorial function, olfactive function (smell), communication and language f...
Which part of the brain is called telencephalon?
The telencephalon is more commonly known as the cerebrum. It is located in the forebrain and makes up the largest part of the brain.
What is the difference between telencephalon and diencephalon?
While they are both part of the forebrain, the telencephalon is larger and located at the anterior. The diencephalon is small and located inside or...
What lobes are in the telencephalon?
There are four lobes in the telencephalon. They are the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe. Each lobe is found on both...
Which part of the diencephalon controls motivation?
Parts of the diencephalon. Thalamus – The thalamus has 2 lobes, and is responsible for sensory relay in your brain. Essentially, it is the “traffic cop” that directs information. It does NOT help with recognition. Hypothalamus – The hypothalamus controls motivated behavior by regulating the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
What are the two types of neurons?
However, there are 2 types of basic neurons: Star-shaped cells (small interneurons with no tail) and triangular cells (large multipolar neurons). There are 4 lobes in the cerebral cortex: Frontal lobe – The frontal lobe is associated with personality, conscience (right/wrong/consequences), planning and is the source of inhibitions.
What are the two parts of the forebrain?
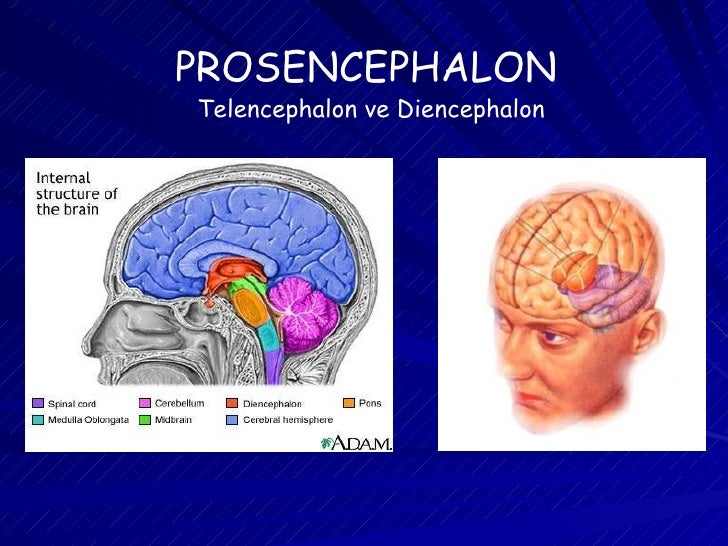
The forebrain is split into 2 sections: The telencephalon and the diencephalon.
Which lobe of the brain processes visual memory?
Occipital lobe – The occipital lobe processes visual memory, and is associated with migraine headaches. Temporal lobe – Auditory and language processing occurs in the temporal lobe; about 90% on the left side. Corpus callosum – The white matter in the brain that connects the left and right hemispheres. Split brain occurs when the connection in the ...
What are the abnormalities in the hippocampus?
Abnormalities in development of the hippocampus are associated with schizophrenia. Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) – In PTSD, there is lower activity and fewer neurons in the the anterior cingulate cortex. Amygdala -The amygdala is shaped like an almond, and located on the fatter end of the hippocampus.
What Is the Telencephalon?
The telencephalon is the scientific name for the largest region of the brain better known as the cerebrum. The word telencephalon comes from the Greek root words "telos," meaning end, and "enkephalos," meaning brain. Telencephalon literally translates to endbrain.
Telencephalon Parts
Because the telencephalon includes the majority of the brain, it has many different parts. The main telencephalon structures include:
Telencephalon Function
The telencephalon composes a large portion of the brain and includes a variety of functions.
The Macroscopic Structure of the Telencephalon
The telencephalon has two hemispheres: right and left. They are connected by the corpus callosum in order to communicate and exchange information with each other.
What are the parts of the diencephalon?
The diencephalon is comprised of the: Epithalamus. Thalamus. Subthalamus. Metathalamus. Hypothalamus. In the following article, we will explore the anatomy of different parts of the diencephalon as well as their function. Key facts about the diencephalon. Parts.
What are the structures that make up the diencephalon?
These include the epithalamus, thalamus, subthalamus, metathalamus, hypothalamus, hypophysis cerebri and the third ventricle as its cavity.
What is the short posterior wall of the thalamus?
The short posterior wall is formed by the stalk of the pineal gland, posterior commissure and the Habenular commissures. The lateral walls are of the cavity are formed by the medial walls of each thalami. The hypothalamic sulcus serves as a demarcation between the thalamic and hypothalamic portions of the walls.
What is the function of the tela choroidea?
These are the choroid plexuses of the third ventricle which functions as a point of production of the cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF).
Where is the ependyma of the third ventricle reflected from?
At the junction of the medial and lateral surfaces of the thalamus the ependyma of the third ventricle is reflected from the lateral wall to the roof. The line of reflection is marked by a line called the taenia thalami, underneath which there is a narrow bundle of fibres called the stria medullaris thalami.
What is the name of the brain that occupies the central region of the brain?
Diencephalon. The human brain can be subdivided by many classification systems. One particular nomenclature that refers to the duality of the brain is the diencephalon. It is the caudal part of the forebrain (prosencephalon) that occupies the central region of the brain. The diencephalon is comprised of the:
What is the third ventricle?
The third ventricle is a narrow vertical midline cleft between and below the two lateral ventricles and in between left and right thalami. The lateral ventricles communicate with the third ventricle via the interventricular foramen of Monro. It also communicates with the fourth ventricle posteroinferiorly via the cerebral aqueduct of Sylvius.
What does telencephalon mean?
The word telencephalon comes from two Greek roots: telos, meaning 'end,' and enkephalos, meaning 'brain.'. So, telencephalon literally means the 'endbrain, ' and in two ways, it is. First, the telencephalon is the last subdivision of the brain to develop in the human embryo. Second, it was the last part of the brain to evolve in humans.
Which part of the brain is affected by the telencephalon?
This, in turn, decreases the ability of the basal ganglia to do its job. Lesson Summary. The telencephalon, a subdivision of the forebrain, is comprised of the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, amygdala, olfactory bulb, and basal ganglia. The cerebral cortex is the wrinkled outer covering of the brain. The hippocampus is within the folds of the ...
What are the three parts of the brain?
The brain can be subdivided into three geographical parts: the hindbrain, the midbrain, and the forebrain. The forebrain can be further subdivided into the diencephalon and the telencephalon. In this lesson, you will learn about the telencephalon and the structures that comprise it: the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, the amygdala, ...
What is the division of the forebrain called?
Lesson Transcript. Paul has taught psychology for over 10 years. In this lesson, you'll learn about a division of the forebrain called the telencephalon. You'll learn about the functions of its structures and disorders that can result when these areas are damaged.
How many nerve cells are in the telencephalon?
What Is the Telencephalon? The human brain is made of over 100 billion nerve cells that make trillions of connections. Yet out of this complexity, scientists who study the brain have been able to identify distinct structures, and they have even begun to see how these structures are organized into systems.
Which area of the brain controls voluntary movement?
These cell clusters form connections with each other, and they also have connections with the cerebral cortex. The basal ganglia is one of the many areas of the brain that control movement, especially voluntary movement. As you might expect, damage to the basal ganglia impairs movement.
What is the first thing you notice about the human brain?
The first thing you might notice about the human brain is its wrinkled outer surface. This surface is the cerebral cortex. One misconception about the brain is that the surface of a healthy brain should be smooth, and if a brain is wrinkled, it is diseased or from a very old person.
What are the structures of the diencephalon?
The diencephalon consists of the following structures: Thalamus. Hypothalamus including the posterior pituitary. Epithalamus which consists of: Anterior and Posterior Paraventricular nuclei. Medial and lateral habenular nuclei. Stria medullaris thalami.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the anterior forebrain structure?
The diencephalon is the region of the embryonic vertebrate neural tube that gives rise to anterior forebrain structures including the thalamus, hypothalamus, posterior portion of the pituitary gland, and the pineal gland. The diencephalon encloses a cavity called the third ventricle.
What is the name of the division of the forebrain?
Diencephalon. The diencephalon (or interbrain) is a division of the forebrain (embryonic prosencephalon ), and is situated between the telencephalon and the midbrain (embryonic mesencephalon ). The diencephalon has also been known as the ' tweenbrain in older literature.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the sensory and motor impulses?
The diencephalon encloses a cavity called the third ventricle. The thalamus serves as a relay centre for sensory and motor impulses between the spinal cord and medulla oblongata, and the cerebrum. It recognizes sensory impulses of heat, cold, pain, pressure etc.
Which vesicles are located on either side of the third ventricle?
It consists of structures that are on either side of the third ventricle, including the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the epithalamus and the subthalamus . The diencephalon is one of the main vesicles of the brain formed during embryogenesis.
Where is the telencephalon?
The telencephalon highlighted red. The telencephalon not only includes the cerebral cortex (visible here) but also a large number of subcortical structures, pathways, etc.
What is the telencephalon and what does it do?
The telencephalon begins to emerge in embryonic development at about 5 weeks. At this time, the nervous system consists of tube-shaped piece of tissue called the neural tube. The neural tube begins to develop swellings (called vesicles ) that will later develop into important structures in the nervous system.
References
Haines DE. Fundamental Neuroscience for Basic and Clinical Applications. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2013.