What is a land food chain?
Land food chains, also known as terrestrial food chains, usually start with a plant as a producer. Water food chains, or aquatic food chains, can start with an aquatic plant as a producer, but there are also microscopic free-floating cells called phytoplankton that can use sunlight to make their own food as well.
What are facts about food chains?
What Did You Learn?
- What is the food chain? The food chain is a chain is when organisms eat other organisms in order to live and get energy.
- What is the food web? The food web is a more complicated way to explain the food chain.
- What are animals called that do not get eaten? ...
- How do people harm the food chain? ...
- How many levels do scientists use to describe the food web? ...
What is the basic food chain?
food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. Plants, which convert solar energy to food by photosynthesis, are the primary food source. In a predator chain, a plant-eating animal is eaten by a flesh-eating animal.
What is a desert food chain?
The desert food chain is a diagram showing the transfer of energy between organisms in the desert biome. The desert food chain includes producers, organisms that make their own food, and consumers, or organisms that must eat to get energy. There are three different types of consumers:

What is an example of a terrestrial food chain?
For example, the common kingfisher is part of the terrestrial environment and feeds on small fish that belong to the aquatic environment. Another example is that of archer fish. These fish hunt insects that fly over and land on plants that are located near the surface of the water.
What is terrestrial food chain Class 10?
A chain that consists of a group of organisms where there is a transfer of food energy through a series of repeated eating and being eaten is called a food chain. In terrestrial ecosystems, the carnivorous level does not go beyond the fifth trophic level and this level is called top carnivores.
What is terrestrial and aquatic food chain?
Terrestrial and Aquatic food chain. A simple food chain that links producers and consumers in a linear fashion illustrates how energy and matter move through the trophic levels of an ecosystem. Less. AP Environmental Science.
Is a terrestrial food web?
A terrestrial food web is a diagram showing the transfer of energy between different species in a land ecosystem. Terrestrial ecosystems include grasslands, forests, mountains, and any other habitat that is land based. Food webs are organized into layers called trophic levels.
What is terrestrial animal short answer?
Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land (e.g. cats, dogs, ants, spiders), as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water (e.g. fish, lobsters, octopuses), and amphibians, which rely on a combination of aquatic and terrestrial habitats (e.g. frogs ...
What is terrestrial in biology?
Terrestrial biology encompasses any environmental issue that occurs on land, including spills, permitting, construction, wildlife, and restoration.
What is the difference of terrestrial and aquatic?
Terrestrial ecosystems are ecosystems found only in land; these include tropical rainforests, deserts, grasslands, deciduous forests, tundra, and taiga. Aquatic ecosystems are ecosystems found in bodies of water; these include lakes, rivers, ponds, wetlands, oceans, and seas.
What is aquatic food chain?
Phytoplankton and algae form the bases of aquatic food webs. They are eaten by primary consumers like zooplankton, small fish, and crustaceans. Primary consumers are in turn eaten by fish, small sharks, corals, and baleen whales.
What is the difference between terrestrial and marine?
Marine ecosystems are found in a body of water whereas terrestrial ecosystems are ecosystems that are found only on landforms. Generally, the marine ecosystems are biologically more diversified than their equivalent terrestrial ecosystems.
What is example of terrestrial?
Examples of terrestrial ecosystems include the tundra, taigas, temperate deciduous forests, tropical rainforests, grasslands, and deserts.
What are terrestrial give two examples?
Terrestrial habitats are ones that are found on land, like forests, grasslands, deserts, shorelines, and wetlands. Terrestrial habitats also include man made habitats, like farms, towns, and cities, and habitats that are under the earth, like caves and mines.
What kind of animal is terrestrial?
Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land, as compared with aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water, or amphibians, which rely on a combination of aquatic and terrestrial habitats.
What is food chain Class 10 short answer?
The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism. It begins with the producer organism, follows the chain and ends with the decomposer organism.
What is food chain give two examples Class 10?
The organisms in the food chain are dependent on each other and if any organism's ecosystem is harmed, it will affect the whole food chain. An example of food chain is: Eagles->birds->worms->decaying plants. In this food chain eagles consume other smaller birds while these birds consume worms as thier food.
What are the steps in the terrestrial food chain?
Steps of a terrestrial food chain of four trophic level:Level 1: Plants and algae are involved in this group and they make their own food.Level 2: Next level is herbivores who eat plants. ... Level 3: Next level is carnivores who eat herbivores. ... Level 4: Last level is carnivores that eat other carnivores.
What is the detritus food chain?
Detritus Food Chain: The detritus food chain includes dead organic matter. It includes species of organisms and plants like algae, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, mites, insects, worms, and so on. In this food chain, the dead organic matter of plants and animals is broken down by decomposers and detritivores that are further eaten by smaller organisms ...
What are phytoplankton eaten by?
For example, phytoplanktons are eaten by zooplanktons, zooplanktons are eaten by fishes and small fishes by large fishes.
What are trophic levels in food chain?
The trophic levels of the food chain can be easily understood as: As per the trophic levels, here is an example: Often we encounter animals consuming dead and decaying matter, such chains that begin with the consumer eating dead organic matter are known as Detritus Food Chain (DFC).
What is the process of making food in the aquatic system?
Autotrophs: They are the ones who can make their own food from inorganic sources. The process is usually done by Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis in the aquatic system begins from wide variety of autotrophs or producers which ranges from microscopic single-celled organisms to large aquatic plants.
What is a consumer in the food chain?
A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. A consumer is also called a heterotroph. Consumers are usually predatory animals such as meat-eaters but also the herbivorous consumers that eat plants. For example, a tiger and a deer are both consumers.
What are some examples of carnivores?
Examples of carnivores are maggots, frogs, snakes, and more, whereas detritivores are fungi, bacteria, or protozoans that feed on detritus. Grazing Food Chain: It begins with autotrophs that include green plants, passes through herbivores, and then to carnivores.
What is the primary consumer?
Further, the organisms which consume the primary producers are known as primary consumers. As per the terrestrial ecosystem, herbivores like cows, goats, man, etc can be primary consumers. But whenever a human being consumes any herbivorous animal, they become a Secondary Consumer.
What are the main parts of the food chain?
The food chain consists of four major parts, namely: 1 The Sun: The sun is the initial source of energy, which provides energy for everything on the planet. 2 Producers: The producers in a food chain include all autotrophs such as phytoplankton, cyanobacteria, algae, green plants. This is the first stage in a food chain. The producers make up the first level of a food chain. The producers utilise the energy from the sun to make food. Producers are also known as autotrophs as they make their own food. Producers are any plant or other organisms that produce their own nutrients through photosynthesis. For example, green plants, phytoplankton and algae are some examples of producers in a food chain. 3 Consumers: Consumers are all organisms that are dependent on plants or other organisms for food. This is the largest part of a food web, as it contains almost all living organisms. It includes herbivores which are animals that eat plants, carnivores which are animals that eat other animals, parasites are those organisms that live on other organisms by harming them and lastly the scavengers, which are animals that eat dead animals’ carcasses.
What happens when one organism consumes another organism?
This occurs when one organism consumes another organism. It begins with producer organism, follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism. After understanding the food chain, we realise how one organism is dependent upon another species for survival.
How do decomposers help the food chain?
Decomposers complete a life cycle. They help in recycling the nutrients as they provide nutrients to soil or oceans, that can be utilised by autotrophs or producers. Thus, starting a whole new food chain.
What is the food chain?
Food Chain: Introduction. A food chain explains which organism eats another organism in the environment. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism. It begins with producer organism, ...
What is the food chain that starts with green plants, passes through herbivores and then to carni?
Grazing food chain: The grazing food chain is a type of food chain that starts with green plants, passes through herbivores and then to carnivores. In a grazing food chain , energy in the lowest trophic level is acquired from photosynthesis. In this type of food chain, the first energy transfer is from plants to herbivores.
What is the order of events in an ecosystem?
A food chain refers to the order of events in an ecosystem, where one living organism eats another organism, and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism. The flow of nutrients and energy from one organism to another at different trophic levels forms a food chain.
How are food webs connected?
But a food web shows different paths, where plants and animals are connected. A food web comprises several food chains. In a food chain, an organism eats a single item, whereas in a food web an organism consumes multiple items. In a food chain, there is a singular path for energy flow and in a food web, there are different paths for energy flow.
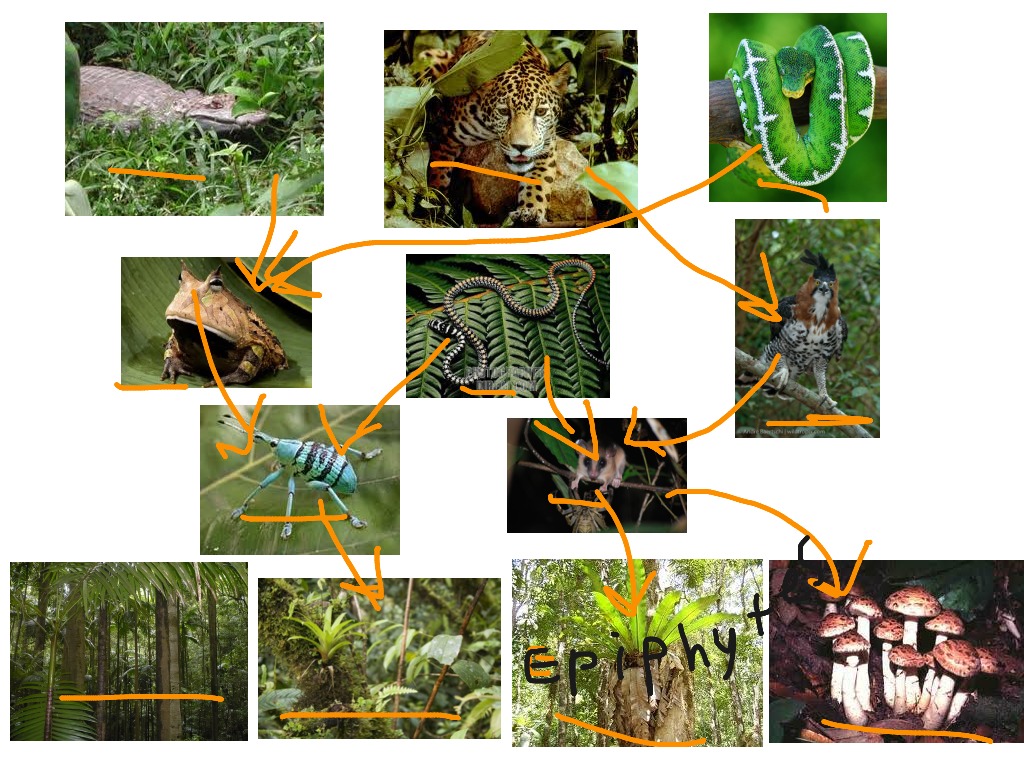
What is Terrestrial Food Chain
The terrestrial food chain or trophic chain indicates the process by which energy and essential nutrients are transmitted from one living being to another.
Links in the terrestrial food chain
The terrestrial food chain is made up of links that indicate how, in general terms, this process is carried out among living beings.
Types of consumers
There are different types of consumers depending on the order in which they are located in the food chain.
Marine food chain
The marine food chain occurs in the seas and oceans. It differs from the terrestrial food chain in that the cycle is more extensive, some producers are microscopic, producers are the fundamental food of predators, which are characterized by their large sizes.
Examples of food chain
These are some examples that demonstrate how the food chain works through different organisms.
