When is the abbey pain scale best used?
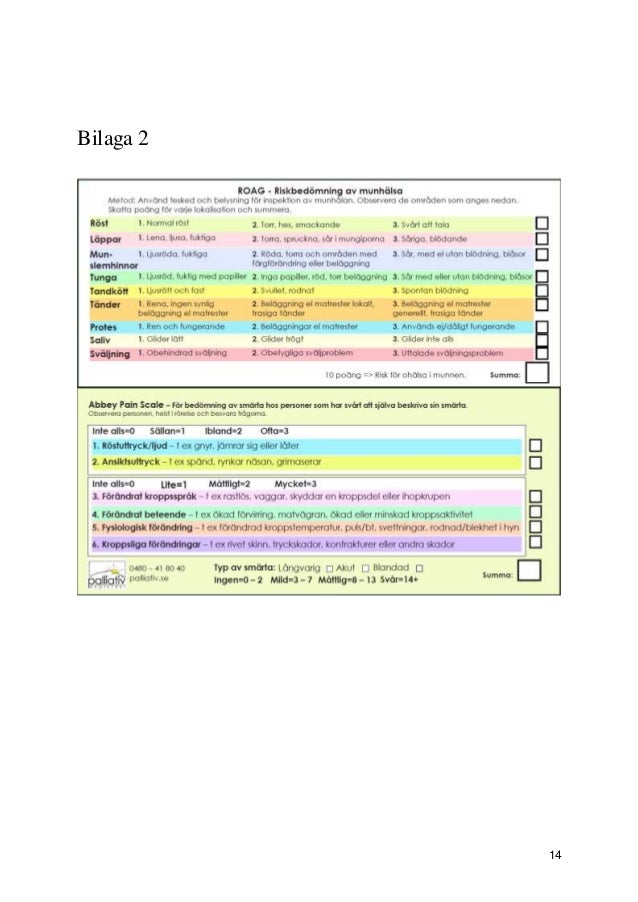
The Abbey Pain Scale is best used as part of an overall pain management plan. Objective The Pain Scale is an instrument designed to assist in the assessment of pain in patients who are unable to clearly articulate their needs. Ongoing assessment
What is the pain scale?
The Pain Scale is an instrument designed to assist in the assessment of pain in patients who are unable to clearly articulate their needs.
What is the abbey pain scale for end-stage dementia?
As a result, the Abbey Pain Scale (APS) was designed to assist in the assessment of pain in the nonverbal individual suffering from end-stage dementia. Like many pain scales for use with people with dementia, there is not a lot of evidence regarding the APS. This is probably because of the nature of the group the scale is designed for.
What is the best measure of pain in dementia?
Currently the only two behavioural pain assessment scales that take account of all six areas identified by the AGS are The Assessment of Discomfort in Dementia Protocol (19), and The Abbey Pain Scale (22). Observational behavioural pain assessment measures therefore require to be more widely researched.

Is the abbey pain scale used in the UK?
PAINAD and Doloplus-2 scales continue to show positive results in terms of reliability and validity. There has been no recent evaluation of the Abbey pain scale although it is widely used throughout the UK.
Why do we use the Abbey pain scale?
The Abbey Pain Scale is an instrument designed to assist in the assessment of pain in patients who are unable to clearly articulate their needs, for example, patients with dementia, cognition or communication issues.
How do you use the Abbey pain scale?
How to use the scaleQ1. Vocalisation. eg: whimpering, groaning, crying. ... Q2. Facial expression. eg: looking tense, frowning, grimacing, looking frightened. ... Q3. Change in body language. eg: fidgeting, rocking, guarding part of body, withdrawn. ... Q4. Behavioural change. ... Q5. Physiological change. ... Q6. Physical changes.
What are the 3 pain scales?
Using the Pain Scale0 – Pain Free. Mild Pain – Nagging, annoying, but doesn't really interfere with daily living activities. ... 3 – Pain is noticeable and distracting, however, you can get used to it and adapt. ... 6 – Moderately strong pain that interferes with normal daily activities.
What are the different types of pain scales?
Pain Assessment ScalesNumerical Rating Scale (NRS)Visual Analog Scale (VAS)Defense and Veterans Pain Rating Scale (DVPRS)Adult Non-Verbal Pain Scale (NVPS)Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale (PAINAD)Behavioral Pain Scale (BPS)Critical-Care Observation Tool (CPOT)
What pain assessment tool is used for dementia patients?
The Pain Assessment in Advanced Dementia Scale (PAINAD) is a reliable assessment tool for dementia patients. It can be used in both nonverbal and verbal patients.
What is the 0 to 10 pain scale called?
Numeric rating scales (NRS) This pain scale is most commonly used. A person rates their pain on a scale of 0 to 10 or 0 to 5. Zero means “no pain,” and 5 or 10 means “the worst possible pain.” These pain intensity levels may be assessed upon initial treatment, or periodically after treatment.
What pain scale is used for nonverbal adult patients?
Quantifies pain in patients unable to speak (due to intubation, dementia, etc). One can also use the Behavioral Pain Scale (BPS) for Intubated Patients as an alternative to the NVPS.
What is the 1/10 pain scale?
There are many different kinds of pain scales, but a common one is a numerical scale from 0 to 10. Here, 0 means you have no pain; one to three means mild pain; four to seven is considered moderate pain; eight and above is severe pain.
What are the 6 types of pain?
Types of painAcute pain.Chronic pain.Neuropathic pain.Nociceptive pain.Radicular pain.
What is the most common pain assessment tool?
The Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) is designed for anyone over age 9. It is one of the most commonly used pain scales in health care.
What is the best pain assessment tool?
The best choice for assessing pain intensity include: the Iowa Pain Thermometer (IPT), the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS), and the Faces Pain Scale-Revised (FPS-R).
When using the abbey pain tool which are the symptoms of pain?
The Abbey Pain Scale, devised in nursing homes in Australia, comprises six categories (vocalisation, facial expression, change in body language, behavioural change, physiological change, and physical changes) and has a score range of 0-24 (Abbey et al, 2004).
What pain scale is used for nonverbal adult patients?
Quantifies pain in patients unable to speak (due to intubation, dementia, etc). One can also use the Behavioral Pain Scale (BPS) for Intubated Patients as an alternative to the NVPS.
Which tool should be used to identify the likelihood that a person may be experiencing some pain?
Common tools include the numerical rating scale (NRS), which involves asking the patients to rate their pain intensity on a scale of 0-10, in which 0 means no pain at all and 10 is the worst pain they have ever experienced or the worst imaginable pain.
How do you score Mcgill pain questionnaire?
The MPQ is composed of 78 words. Respondents choose those that best describe their experience of pain. Scores are tabulated by summing values associated with each word; scores range from 0 (no pain) to 78 (severe pain). Qualitative differences in pain may be reflected in respondent's word choice (Melzack, 1975).
Q4. Behavioural change
eg: increased confusion, refusing to eat, alteration in usual patterns.
Q6. Physical changes
eg: skin tears, pressure areas, arthritis, contractures, previous injuries.
What are behavioural pain scales?
There are a number of behavioural indicator pain assessment scales available (18–23). However, the evidence for using these scales in the acute postoperative setting remains contradictory (20,24,25). While debate concerning the reliability and validity of observational pain scales remains ongoing, the American Geriatrics Society (4) have outlined six areas that they consider should be incorporated into behavioural pain assessment charts (Table 1). Currently the only two behavioural pain assessment scales that take account of all six areas identified by the AGS are The Assessment of Discomfort in Dementia Protocol (19), and The Abbey Pain Scale (22) . Observational behavioural pain assessment measures therefore require to be more widely researched.
How many areas are required to be incorporated into behavioural pain assessment charts?
Six areas required to be incorporated into behavioural pain assessment charts
How to improve pain management for cognitively impaired elderly?
Improving pain management with cognitively impaired older people requires healthcare professionals to reflect on reactions, values and beliefs surrounding pain and how these have the potential to influence the care provided. Arguably the Acute Pain Team (APT) can offer some direction and leadership in this area. MacKintosh and Bowles (34) propose that the clinical nurse specialist (CNS) within the APT promotes good practice, has increased awareness of what good pain management entails and influences healthcare professionals' decision-making. Indeed, Thompson et al (35) argue that nurses value the advice or guidance of a CNS. Therefore the challenge for the CNS/APT is to adopt multiple approaches to changing pain assessment practices with cognitively impaired older people, in an attempt to effect a sustainable change upon the culture and context of individual wards.
What are the symptoms of pain?
The four most commonly displayed behaviours of pain and distress exhibited by patients in study by Kovach et al (19): 1 Tense muscles 2 Sad facial expression 3 Fidgeting 4 Increased &/or sudden &/or repetitive verbalisation
Why is pain assessment important?
It is well documented that pain assessment is an important first step to any pain management process. Despite the literature advocating that the patient's description of their pain is the most reliable and accurate indicator, pain assessment continues to pose difficulties for the healthcare team.
Why do older people have pain?
The high prevalence of pain in older people is associated with chronic underlying health disorders (e.g. arthritis, peripheral vascular disease) and acute pain conditions such as cancer and surgical procedures.
Can a pain scale be verbalized?
However, it is generally agreed that once it has become impossible for a patient to verbalise their pain, pain scales utilised for older people with cognitive impairment should incorporate observational behavioural components .
