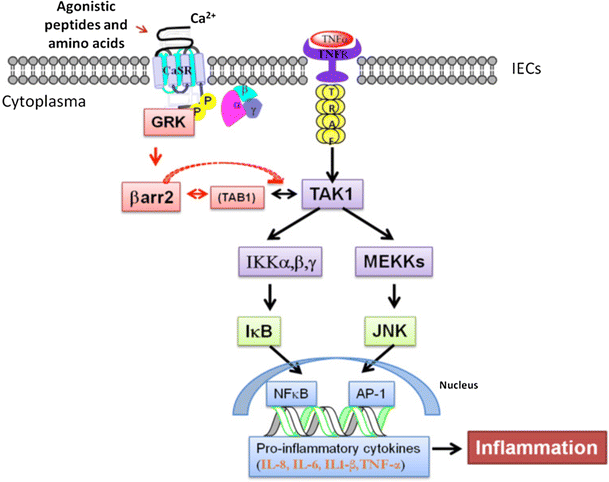
| Full Name | Abbreviation (3 Letter) | Abbreviation (1 Letter) |
| Glutamate | Glu | E |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glutamate or Glutamine | Glx | Z |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
What is glutamine used for?
Glutamine is used to: Treat weakness and loss of muscle mass caused by cancer treatment. Treat neuropathy (numbness or tingling hands and feet) caused by chemotherapy. Treat nausea (feeling like you’re going to throw up), vomiting (throwing up), and diarrhea (loose, watery bowel movements) due to cancer treatments.
Where to buy L glutamine?
Shop for Glutamine in Protein & Fitness. Buy products such as NOW Supplements, Glutathione 500 mg, With Milk Thistle Extract & Alpha Lipoic Acid, Free Radical Neutralizer*, 60 Veg Capsules at Walmart and save.
Is glutamine acidic or basic?
Glutamine (data page) Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid.
What is glutamine function?
the functions of glutamine are many and include: substrate for protein synthesis, anabolic precursor for muscle growth, acid-base balance in the kidney, substrate for ureogenesis in the liver, substrate for hepatic and renal gluconeogenesis, an oxidative fuel for intestine and cells of the immune system, inter-organ nitrogen transport, precursor …
See more
What is glutamate abbreviation?
Glu EFull NameAbbreviation (3 Letter)Abbreviation (1 Letter)GlutamateGluEGlutamineGlnQGlutamate or GlutamineGlxZGlycineGlyG18 more rows
What is the three letter abbreviation for glutamine?
gln QAnnex 4 - Amino acids, one and three letter codesAmino acidThree letter codeOne letter codeglutamineglnQglutamine or glutamic acidglxZglycineglyGhistidinehisH18 more rows
What symbol is glutamine in one letter?
Q GlnTable 5. The One-Letter SymbolsOne-letter symbolThree-letter symbolAmino acidQGlnglutamineRArgarginineSSerserineTThrthreonine20 more rows
Does Glu stand for glutamate?
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins.
Does the body produce L glutamine?
Essential amino acids can only be acquired through food, while nonessential ones, like L-glutamine, are produced by the body. Under normal conditions, your body can produce enough L-glutamine to meet most of its needs.
How do you abbreviate amino acids?
IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides. Eur. J....Amino Acid Codes.Abbreviation1 letter abbreviationAmino acid nameArgRArginineAsnNAsparagineAspDAspartic acidCysCCysteine23 more rows
What does the R in amino acids stand for?
radicalR is an abbreviation for radical, when the term radical applied to a portion of a complete molecule (not necessarily a free radical), such as a methyl group. Should not be confused with R (the gas constant), R (the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid arginine) or R (a designation of absolute configuration).
How do you remember Q glutamine?
It's helpful that the three-letter abbreviations for asparagine (N) and glutamine (Q) are Asn and Gln, respectively–the fact that both contain the letter “n” reminds me of the nitrogen atom found in their amino side chains.
What is the one letter code for amino acids?
The simplest, and smallest, amino acid is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen (H)....Amino acid abbreviations.Amino acidAbbreviationSingle letter abbreviationAsparagineAsnNAspartic acidAspDCysteineCysCGlutamineGlnQ23 more rows•Sep 26, 2019
Is glutamate the same as glutamine?
Glutamate and glutamine are not the same. Glutamate is a nonessential amino acid and glutamine is a conditional amino acid. Only those who are instructed to do so by a physician should supplement with glutamate.
Is glutamine and glutamic acid the same?
Glutamine is a derivative of glutamic acid and is formed in the body from glutamic acid and ammonia in an energy requiring reaction catalyzed by glutamine synthase. It also possesses anticancer activity.
Is glutamic acid and glutamate the same thing?
Glutamic acid is an amino acid used to form proteins. In the body it turns into glutamate. This is a chemical that helps nerve cells in the brain send and receive information from other cells.
Is Glutamate the same as glutamic acid?
"Glutamic Acid" is sometimes referred to as "Glutamate" or a negative ion form. Glutamic acid is a nonessential amino acid that functions as an important metabolic intermediate.
What does the R in amino acids stand for?
radicalR is an abbreviation for radical, when the term radical applied to a portion of a complete molecule (not necessarily a free radical), such as a methyl group. Should not be confused with R (the gas constant), R (the one-letter abbreviation for the amino acid arginine) or R (a designation of absolute configuration).
Which amino acid is Glu?
Glutamic AcidAmino AcidAbbreviationGlutamic AcidGluEGlutamineGlnQGlycineGlyGHistidineHisH17 more rows
What are the two main types of abbreviations for amino acids?
Amino acid abbreviationsAmino acidAbbreviationSingle letter abbreviationAspartic acidAspDCysteineCysCGlutamineGlnQGlutamic acidGluE23 more rows•Sep 26, 2019
What is glutamine used for?
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid.
Why is glutamine prescribed?
Glutamine is marketed as medical food and is prescribed when a medical professional believes a person in their care needs supplementary glutamine due to metabolic demands beyond what can be met by endogenous synthesis or diet.
What is the most abundant amino acid in the human body?
Glutamine is the most abundant naturally occurring, nonessential amino acid in the human body, and one of the few amino acids that can directly cross the blood–brain barrier. Humans obtain glutamine through catabolism of proteins in foods they eat.
What are the functions of glucose?
Glutamine plays a role in a variety of biochemical functions: Protein synthesis, as any other of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids. Lipid synthesis, especially by cancer cells. Regulation of acid-base balance in the kidney by producing ammonium. Cellular energy, as a source, next to glucose.
What foods contain glutamine?
The dietary sources of glutamine includes especially the protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso .
How is glutamine made?
Glutamine is produced industrially using mutants of Brevibacterium flavum, which gives ca. 40 g/L in 2 days using glucose as a carbon source. Glutamine is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia. The most relevant glutamine-producing tissue is the muscle mass, accounting for about 90% of all glutamine synthesized. Glutamine is also released, in small amounts, by the lungs and brain. Although the liver is capable of relevant glutamine synthesis, its role in glutamine metabolism is more regulatory than producing, since the liver takes up large amounts of glutamine derived from the gut.
Where is glutamine released?
Glutamine is also released, in small amounts, by the lungs and brain. Although the liver is capable of relevant glutamine synthesis, its role in glutamine metabolism is more regulatory than producing, since the liver takes up large amounts of glutamine derived from the gut.
What is glutamic acid?
Glutamic Acid. Glutamic acid is an acidic, hydrophilic amino acid. As the amino acid, glutamic acid has important roles as a neurotransmitter and a flavor component. In peptides, glutamic acid residues may be utilized to form cyclic structures through amide bond formation with a lysine residue side chain.
What is the only amino acid that incorporates the Î-amine into a ring?
Proline is the only natural amino acid that incorporates the α-amine into a ring. Because of this unique structure, proline residues introduce a “kink†into the backbone structure of peptides. Proline disrupts β-sheet formation and promotes turn formation. This property of the proline residue is exploited in pseudoproline derivatives utilized to disrupt peptide aggregation and product higher yield and higher purity peptides with difficult sequences. (See the Pseudoproline Dipeptide section for AAPPTec’s pseudoproline products). Since proline does not contain a primary amine, Kaiser test (ninhydrin test) results may give false positive results when testing coupling to proline. Alternative tests, such as the 2,4,6-trinitobezoic acid test, should be considered.
What is arginine amino acid?
Arginine is a basic, hydrophilic amino acid . The guanidinium group in the sidechain is strongly basic and is protonated in most conditions. Arginine is a common component of cell-penetrating peptides which are utilized to transport larger molecules and particles into cells. In proteins, arginine can play a regulatory role. Arginine residues may be mono- or di-methylated on the sidechain or may be converted to citrulline. Regulatory modifications of arginine residues are often observed in histone proteins. AAPPTec offers a variety of high purity Fmoc or Boc protected arginine derivatives for solid phase peptide synthesis. AAPPTec also provides many high quality arginine derivatives for solution phase synthesis.
Which amino acid is a nucleophile?
Histidine. Histidine is a mildly basic, moderately hydrophobic amino acid. Histidine residues often play important roles in enzymes. The histidine side chain can activate serine, threonine or cysteine residues as nucleophiles by abstracting a proton.
Is alanine a hydrophobic amino acid?
Alanine is the simplest optically active amino acid. It is nonpolar and contributes a hydrophobic character when incorporated into a peptide, although the unprotected amino acid is water soluble. Alanine is a strong α-helix forming amino acid and does not significantly contribute to turn or β-sheet formation. AAPPTec provides Fmoc, Boc, and Z protected alanine as well as alanine esters with 99+% purity. High purity amino acid derivatives from AAPPTec produce higher peptide yields and purer peptides.
Is glycine a peptide?
Glycine is the simplest amino acid. It lacks a sidechain, thus is achiral. As a free amino acid, glycine is very water soluble due to its small size and strong hydrogen bonding ability of the acid and amine functions. Incorporated into a peptide, glycine contributes a small hydrophobic character to the peptide.
Does glutamine cyclize?
As an N-terminal residue, glutamine can cyclize to form pyroglutamic acid. Glutamine, like aspargine, is susceptible to nitrile formation by dehydration. As with asparagine, side-chain protection blocks this side reaction in increases the solubility of the derivative in organic solvents.
What is the amino acid L-glutamine?
Trusted Source. ). Summary Glutamine is an important amino acid. L-glutamine is the form found in foods, supplements and the human body. It is part of the proteins in your body and involved in immune function and intestinal health.
What is the purpose of glutamine?
Glutamine is an amino acid. Amino acids are molecules that play many roles in the body. Their main purpose is to serve as building blocks for proteins. Proteins are crucial to the organs. They also serve other functions, such as transporting substances in the blood and fighting off harmful viruses and bacteria ( 1 ).
What is glutamine? What function does it serve?
Glutamine is an important amino acid with many functions in the body. It is a building block of protein and critical part of the immune system. What’s more, glutamine has a special role in intestinal health. Your body naturally produces this amino acid, and it is also found in many foods. Yet, you may be unsure if you need extra glutamine ...
Does glutamine affect the body?
Adding glutamine to a regular diet may cause a variety of changes in the way the body absorb s and processes amino acids. Yet, the long-term effects of these changes are unknown ( 25 ).
Is glutamine a bad amino acid?
Dosage, Safety and Side Effects. Since glutamine is an amino acid that is naturally produced in the body and found in many foods, there is no concern that it’s harmful in normal quantities.
Can glutamine be taken long term?
Therefore, more information is needed concerning long-term supplementation , particularly when high doses are used. It is possible that glutamine supplements may not have the same effects if you eat an animal-based, high-protein diet, compared to a plant-based, lower-protein diet.
Does glutamine help with muscle gain?
Due to its role as a building block of protein, some researchers have tested whether taking glutamine as a supplement improves muscle gain or exercise performance. In one study, 31 people took either glutamine or a placebo during six weeks of weight training ( 29.
What is glutamine?
Glutamine is an amino acid that affects the processes of growth and function of cells in the stomach and intestines.
How should I take glutamine?
Use exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by your doctor. Do not use in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
What should I avoid while taking glutamine?
Follow your doctor's instructions about any restrictions on food, beverages, or activity.
What other drugs will affect glutamine?
Other drugs may interact with glutamine, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell each of your health care providers about all medicines you use now and any medicine you start or stop using.
How long does glutamine help with sickle cell anemia?
Usual Adult Dose for Sickle Cell Anemia: In a clinical study of 7 patients after 4 weeks of therapy with glutamine at 30 g orally per day, there was clinical benefit in reducing the oxidative susceptibility of sickle red blood cells.
How to dissolve glutamine?
Dissolve your dose of glutamine oral powder in at least 8 ounces of hot or cold liquid. You may also mix the powder with a soft food such as pudding, applesauce, or yogurt. Stir the mixture and eat or drink all of it right away. Do not pour dry glutamine powder directly into a tube feeding formula.
Is glutamine a part of a diet?
Glutamine may be only part of a complete program of treatment that may also include a special diet, tube feedings, and IV fluids. It is very important to follow the diet and medication plan created for you by your doctor or nutrition counselor. Store at room temperature away from moisture and heat.

Overview
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. It is non-essential and conditionally essential in humans, meaning the body can usually synthesize sufficient amounts of it, but in some instances …
Functions
Glutamine plays a role in a variety of biochemical functions:
• Protein synthesis, as any other of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids
• Lipid synthesis, especially by cancer cells.
• Regulation of acid-base balance in the kidney by producing ammonium
Production
Glutamine is produced industrially using mutants of Brevibacterium flavum, which gives ca. 40 g/L in 2 days using glucose as a carbon source. Glutamine is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia. The most relevant glutamine-producing tissue is the muscle mass, accounting for about 90% of all glutamine synthesized. Glutamine is also released, in small amounts, by the lungs and brain. Although the liver is capable of relevant glutamine synt…
Uses
Glutamine is the most abundant naturally occurring, nonessential amino acid in the human body, and one of the few amino acids that can directly cross the blood–brain barrier. Humans obtain glutamine through catabolism of proteins in foods they eat. In states where tissue is being built or repaired, like growth of babies, or healing from wounds or severe illness, glutamine becomes conditionally essential.
Safety
Glutamine is safe in adults and in preterm infants. Although glutamine is metabolized to glutamate and ammonia, both of which have neurological effects, their concentrations are not increased much, and no adverse neurological effects were detected. The observed safe level for supplemental L-glutamine in normal healthy adults is 14 g/day.
Adverse effects of glutamine have been prescribed for people receiving home parenteral nutritio…
Structure
Glutamine can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, L-glutamine and D-glutamine. The L-form is found in nature. Glutamine contains an α-amino group which is in the protonated −NH3 form under biological conditions and a carboxylic acid group which is in the deprotonated −COO form, known as carboxylate, under physiological conditions.
Research
Glutamine mouthwash may be useful to prevent oral mucositis in people undergoing chemotherapy but intravenous glutamine does not appear useful to prevent mucositis in the GI tract.
Glutamine supplementation was thought to have potential to reduce complications in people who are critically ill or who have had abdominal surger…
See also
• Isoglutamine