What is the ABCDE A-E approach?
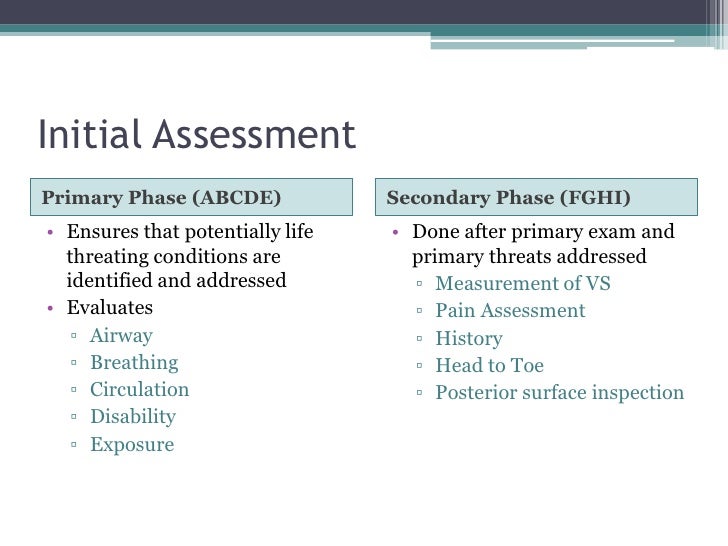
Despite what might seem like chaos, the team uses a systematic method for managing all acutely ill patients called the ABCDE (A-E) approach. It is a way of systematically assessing each of a patient’s vital systems—airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure.
What is the ABCDE approach to assessing patient deterioration?
Take an interactive journey through the approach to assessing patient deterioration The ABCDE approach to identifying patient deterioration enables clinicians to prioritise interventions that will often prove lifesaving. These assessments are frequently made under pressure, but ABCDE helps nurses to order their decisions quickly.
What is the ABCDE approach to critical illness?
The approach to all deteriorating or critically ill patients is the same. The underlying principles are: Use the Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure (ABCDE) approach to assess and treat the patient. Do a complete initial assessment and re-assess regularly.
What is the ABCDE in a trauma evaluation?
For the trauma patient, ABCDE is included in the primary survey, the initial evaluation, and management of injuries. A primary survey is the initial evaluation used to identify and manage life-threatening injuries in a trauma patient. The components of the primary survey are: Establish airway patency.

Why is ABCDE important?
Crucially, it allows them to communicate clinical priorities clearly and at speed across the multidisciplinary team too.
How many stages of ABCDE are there?
Find out how working through the five stages of ABCDE in sequence can give you the best chance of optimising the patient’s outcomes by detecting even subtle changes in their condition. And discover how nurses across a variety of settings apply the ABCDE approach to their practice.
What is an ABCDE?
The airway, breathing, and circulation, disability and exposure (ABCDE) assessment is the mainstay management approach used in managing critically ill patients. The ABCDEs are the essential 1st steps to perform in many situations including unresponsive patients, cardiac arrests, and critical medical or trauma patients. For the trauma patient, ABCDE is included in the primary survey, the initial evaluation, and management of injuries.
What is the goal of disability assessment?
The goal of disability assessment is to determine and manage the presence of neurologic injury.
What is the next step after the airway has been deemed adequate?
Breathing is the next step after the airway has been deemed adequate.
Who is the author of Initial Management of the Critically Ill Adult with an Unknown Overdose?
Sivilotti, M. Initial management of the critically ill adult with an unknown overdose. (2019). UpToDate. Retrieved November 22, 2020 from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/initial-management-of-the-critically-ill-adult-with-an-unknown-overdose
What is the ABCDE approach?
The underlying principles are: Use the Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure (ABCDE) approach to assess and treat the patient. Do a complete initial assessment and re-assess regularly. Treat life-threatening problems before moving to the next part of assessment. Assess the effects of treatment. Recognise when you will need extra help.
How to assess conscious level?
Make a rapid initial assessment of the patient’s conscious level using the AVPU method: Alert, responds to Vocal stimuli, responds to Painful stimuli or Unresponsive to all stimuli. Alternatively, use the Glasgow Coma Scale score. A painful stimuli can be given by applying supra-orbital pressure (at the supraorbital notch).
What is the aim of A-E assessment?
The aim of the assessment is to identify and stabilise the patient’s most life threatening problems first, before moving on to the next vital system to achieve some clinical improvement to buy time for further treatment and making a diagnosis. 1 Once the team has completed an A-E assessment, it repeats the steps to reassess each system to determine if clinical features are improving or deteriorating.
When should repeat assessment be done?
Whenever an intervention, such as intravenous fluids, is given, repeat assessment from A to E should be done to assess the effectiveness of the intervention—for example, blood pressure should be checked again.
How is A-E performed?
In reality, the A-E process is performed simultaneously, rather than in a linear fashion—that is, establishing intravenous access, administering high flow oxygen and fluids, and checking blood glucose levels are often done at the same time by various members of the team. However, a team leader (usually a senior doctor) should have a clear overview of what the team is doing and continue to think through the A-E approach in a systematic, logical way. This ensures nothing important is missed and simplifies what patients require in an emergency situation, focusing on dealing with the most important issues first.
What is the role of a cardiologist in an acute situation?
They are often among the first at the bedside in an acute situation. They might carry out the initial A-E assessment and perform practical tasks such as establishing intravenous access , obtaining arterial blood gases, and carrying out catheterisation. They also prescribe necessary drugs and fluids and request investigations such as chest radiography.
What is the ABCDE rule for skin cancer?
Updated on July 15, 2020. The ABCDE Rule of skin cancer is an easy-to-remember system for determining whether a mole or growth may be cancerous. They describe the physical condition and/or progression of any skin abnormality that would suggest the development of a malignancy. 1:50.
Is melanoma an ABCDE?
The following photo is an example of melanoma that meets most of the ABCDE criteria. However, every case of skin cancer is unique, and a different individual's malignancy could look quite different.
What is A-E assessment?
The A-E assessment; Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure (ABCDE) approach is a systematic approach to the immediate assessment and treatment of critically ill or injured patients[1], it has become widely adopted as a way of documenting the assessment of respiratory patients. This systematic approach should allow you to determine if the patient has one of the following problems: 1 Sputum retention 2 Loss of lung volume 3 Increased work of breathing (breathlessness) 4 Respiratory failure
When referring to evidence in academic writing, should you always try to reference the primary source?
When refering to evidence in academic writing, you should always try to reference the primary (original) source. That is usually the journal article where the information was first stated. In most cases Physiopedia articles are a secondary source and so should not be used as references.