The abdominal wall:
- Forms a firm, yet flexible boundary which keeps the abdominal viscera in the abdominal cavity and assists the viscera in maintaining their anatomical position against gravity.
- Protects the abdominal viscera from injury.
- Assists in forceful expiration by pushing the abdominal viscera upwards.
What are the layers of the abdominal wall?
- External oblique abdominal muscle
- Internal oblique abdominal muscle
- Rectus abdominis
- Transverse abdominal muscle
- Pyramidalis muscle
What organs are attached to the abdominal wall?
The supracolic compartment contains:
- stomach
- liver
- spleen
What causes abdominal wall weakness?
These factors include:
- Aging
- Chronic coughing
- Collagen vascular disease
- Frequent heavy lifting
- Genetic defects
- History of previous hernias
- Infection (especially following surgery)
- Injuries to the abdominal area
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
What does the stomach wall contain?
The stomach wall has 5 layers: The stomach wall is made up of several layers of mucous membrane, connective tissue with blood vessels and nerves, and muscle fibers (see Figure 5). The innermost layer is the mucosa. This is where stomach acid and digestive enzymes are made. Most stomach cancers start in this layer.

What is the abdominal wall called?
Rectus abdominis: This pair of muscles goes down the middle of your abdomen from your ribs to the front of your pelvis. The muscles hold your internal organs in place and keep your body stable during movement. The rectus abdominis may form bumps sometimes called a “six-pack” when someone has a trim, fit abdomen.
Where is the abdominal wall located in the body?
The abdominal wall surrounds the abdominal cavity, providing it with flexible coverage and protecting the internal organs from damage. It is bounded superiorly by the xiphoid process and costal margins, posteriorly by the vertebral column and inferiorly by the pelvic bones and inguinal ligament.
Is abdominal wall same as stomach?
They both differ in terms of their functionality and anatomy. The abdominal wall is split into the posterior (back), lateral (sides) and anterior (front) walls. Whereas the Stomach, a “J” shaped organ, is split in Anterior wall, curvature, cardiac, angular notch, pyloric canal, gastric canal and rugal fold.
What is the function of the abdominal wall?
The major functions of the abdominal wall include: Providing a durable and flexible covering to prevent the abdominal viscera from leaving the abdominal cavity. Protecting internal abdominal organs from trauma/injury. Maintaining the anatomical position of the abdominal organs.
What is abdominal wall pain?
Most commonly, abdominal wall pain is related to cutaneous nerve root irritation or myofascial irritation. The pain can also result from structural conditions, such as localized endometriosis or rectus sheath hematoma, or from incisional or other abdominal wall hernias.
How thick is your abdominal wall?
The thicknesses of the rectus abdominis muscle were measured as follows: MXR, 9.58±2.11 mm; MXL, 9.73±2.06 mm; MUR, 10.26±1.83 mm; and MUL, 10.26±1.85 mm. The thickness of the subcutaneous fat tissue at the umbilicus level was measured as follows: FUR, 24.31±8.04 mm; and FUL, 23.39±7.92 mm (Table 2).
What organs are in the abdominal wall?
The abdominal cavity contains the greater part of the digestive tract, the liver and pancreas, the spleen, the kidneys, and the adrenal glands located above the kidneys.
How can I strengthen my abdominal wall?
Abdominal crunches are a classic core-strength exercise:Lie on your back and place your feet on a wall so that your knees and hips are bent at 90-degree angles. Tighten your abdominal muscles.Raise your head and shoulders off the floor. ... Return to the start position and repeat.
What is abdominal wall made of?
The abdominal wall is composed of 5 paired muscles: 2 vertical muscles (the rectus abdominis and the pyramidalis) and 3 layered, flat muscles (the external abdominal oblique, the internal abdominal oblique, and the transversus abdominis muscles).
What muscle moves the abdominal wall?
rectus abdominis – slung between the ribs and the pubic bone at the front of the pelvis. When contracting, this muscle has the characteristic bumps or bulges that are commonly called 'the six pack'. The main function of the rectus abdominis is to move the body between the ribcage and the pelvis.
How many layers are cut during C section?
At the beginning of a caesarean section, six separate layers of the abdominal wall and uterus are opened individually. Once the baby is delivered the uterus is closed with a double layer of stitching.
What layers are cut in C section?
The uterus consists of the serosal outer layer (perimetrium), the muscle layer (myometrium), and the inside mucosal layer (endometrium). All three of these layers are incised to make the uterine incision or hysterotomy.
How can I strengthen my abdominal wall?
Abdominal crunches are a classic core-strength exercise:Lie on your back and place your feet on a wall so that your knees and hips are bent at 90-degree angles. Tighten your abdominal muscles.Raise your head and shoulders off the floor. ... Return to the start position and repeat.
What are the 3 layers of abdominal wall?
Classically the anterolateral abdominal wall has been described as separate layers from superficial to deep as follows: Skin. Subcutaneous tissues (further divided into the more superficial Camper's fascia and the deeper Scarpa's fascia) External oblique muscle.
What is safest site for abdominal incision?
In general, for abdominal surgery, the midline incision is versatile and allows access to most organs.
What is abdominal wall made of?
The abdominal wall is composed of 5 paired muscles: 2 vertical muscles (the rectus abdominis and the pyramidalis) and 3 layered, flat muscles (the external abdominal oblique, the internal abdominal oblique, and the transversus abdominis muscles).
What is the abdominal wall?
In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.
What are the three layers of the abdominal wall?
In medical vernacular, the term 'abdominal wall' most commonly refers to the layers composing the anterior abdominal wall which, in addition to the layers mentioned above, includes the three layers of muscle: the transversus abdominis (transverse abdominal muscle), the internal (obliquus internus) and the external oblique (obliquus externus).
What are the layers of the abdominal wall?
It is composed of several layers, including skin, superficial fascia, subcutaneous fat, anterolateral and midline muscle groups, transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat and peritoneum. The anatomy is well demonstrated on CT and MRI. Ultrasound is useful in evaluating focal masses in the anterior abdominal wall but does not demonstrate ...
What is the rectus abdominis?
The rectus abdominis (commonly called the “sit-up” muscles) are paired paramedian strap muscles that extend from the ventral lower thorax to the pubis, separated from each other by the linea alba. These muscles are narrow and thick inferiorly, becoming broader and thinner superiorly.
Which tendinous sheet medially contributes to the rectus sheath and linea alba?
The aponeurosis forms a strong tendinous sheet which medially contributes to the rectus sheath and linea alba.
Where is the transversalis fascia?
The spermatic cord in the male, or round ligament in the female, passes through the transversalis fascia at the deep inguinal ring.
Where do the posterior fibres of the iliac crest and pubic tubercle insert?
Insertion: iliac crest and pubic tubercle: The posterior fibres, from the lower ribs, pass vertically to insert into the anterior half of the liac crest. The middle and upper fibres pass anteriorly and forwards to end in the muscle’s aponeurosis.
Which layer of the thigh is thick and contains areolar tissue and variable amounts of fat?
The superficial layer is thick and contains areolar tissue and variable amounts of fat. It passes over the inguinal ligament to fuse with the underlying fascia of the thigh.
Which is thinner, the internal oblique or the external oblique?
The internal oblique lies internal to the external oblique and is thinner and less bulky than the external oblique
What is the purpose of the abdominal wall?
The wall that encases the cavity of the abdomen has a number of things it is responsible for, including: 1 Keeping the abdominal viscera from being injured 2 Creating the wall that will keep the abdominal viscera within the cavity of the abdomen 3 Helping to keep the abdominal viscera in the proper position against gravity 4 Increasing intra-abdominal pressure that is used in actions such as vomiting or coughing 5 Working in a forceful manner to help push the abdominal viscera in an upward position
Which muscle is the largest in the abdominal wall?
External Oblique . This is the largest of the flat muscles that line the wall of the abdomen. The fibers meet in the middle and create a flat broad tendon. The aponeuroses of the flat muscles intertwine with each other and create the linea alba which runs from the sternum to the middle of the public bones.
What nerves run between the muscles of the abdominal wall?
In the layers of abdominal wall, there are a large number of nerves that go between the skin and muscles of the abdomen. They include: Thoracoabdominal nerves – There are five pair of these nerves and they run between the muscles of the abdominal wall to the muscles of the anterolateral wall of the abdomen. The cutaneous, lateral, and anterior ...
What are the muscles in the abdomen?
Muscles. There are two groups of five muscles that are located in the wall of the abdomen. The groups consist of vertical muscles and flat muscles. The Flat Muscles. These muscles laterally flex and rotate the trunk.
What is the layer above the umbilicus?
If it is above the umbilicus, it is made up of a single sheet of tissue; if it is below the umbilicus, it has two layers – the superficial layer that is fatty and the deep layer which has a lot of membranes. There are superficial nerves and vessels that go between these two layers. 5. Skin.
Which peritoneum is used for nerves?
While the visceral peritoneum shares the blood that is used by the nerves and lymphatic vessels of the organs of the abdomen, the parietal peritoneum utilizes the nerve supply and circulation from the layers of abdomen wall. 2.
How to keep abdominal viscera in proper position?
Helping to keep the abdominal viscera in the proper position against gravity. Increasing intra-abdominal pressure that is used in actions such as vomiting or coughing . Working in a forceful manner to help push the abdominal viscera in an upward position.
What are the layers of the abdominal wall?
Layers of the abdominal wall as seen on high frequency ultrasound. Fat (F); external oblique muscle (EO); internal oblique muscle (IO); transversus abdominis muscle (TA); rectus abdominis (RA); peritoneum (arrow); aponeurosis of external oblique (white arrowhead) and anterior part of the aponeurosis of internal oblique contributing to the rectus sheath (black arrowhead).
What is the most important component of the anterior abdominal wall?
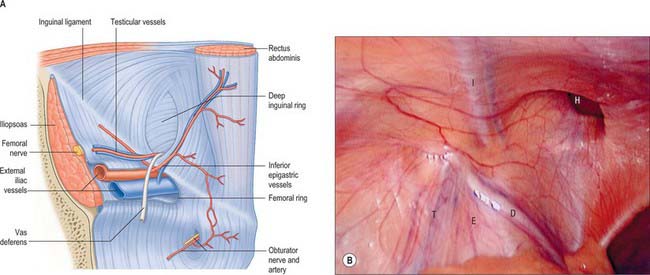
At its most inferior aspect the aponeurosis of external oblique folds back on itself to form the inguinal ligament and inguinal canal. This is an important component of the anterior abdominal wall since it contains two potential openings for the development of hernias. The first opening is the deep inguinal ring traditionally described as lying immediately lateral to the inferior epigastric artery, though in several studies (1,2,3) this has been shown to be variable. The second opening is the superficial inguinal ring located just superolateral to the pubic tubercle.
What is the posterior margin of the rectus abdominis?
The anterior margin of the sheath is formed by the external oblique aponeurosis and the anterior part of the internal oblique aponeurosis. The posterior margin is formed from the posterior part of the internal oblique aponeurosis and the transversus abdominis aponeurosis. The posterior layer ends at the arcuate line or linea semicircularis equidistant from the pubic symphysis and umbilicus. Additionally, the sheath ends superiorly at the superior insertions of the contributing muscles. The linea semilunaris indicates the most lateral extent of the rectus abdominis.
What are the three flat muscles in the abdominal wall?
MR anatomy of the abdominal wall demonstrating the three flat muscles (short arrow); the linea semilunaris (open arrow); rectus abdominis (black arrowhead); the linea alba (open arrowhead); the epigastric vessels (long arrow); the quadratus lumborum muscle (black arrow) and the erector spinae (white arrowhead).
What is the transversus abdominis plane?
Transversus abdominis muscle (TA); the transversus abdominis plane (arrowhead); internal oblique (IO); and external oblique (EO).The transversus abdominis plane is important in the anaethetisation of the abdominal wall post operatively since this is the plane through which the the intercostal and subcostal nerves pass.
Which muscle splits to cover the rectus abdominis anteriorly and posteriorly?
Axial CT image demonstrating the internal oblique muscle (arrow) and its aponeurosis (arrowhead) which splits to cover rectus abdominis anteriorly and posteriorly.
Which muscle is the outermost muscle of the lateral abdominal wall?
External oblique muscle. The outermost muscular layer of the lateral abdominal wall is made up from the external oblique muscle s. These two muscles arise from the outer parts of the lower 7 to 8 ribs on either side and extends anteroinferiorly to the anterior aspect of the iliac crests, pubic tubercle and to the linea alba in the midline.
What is the abdominal wall made of?
Abdominal wall hernias are commonly seen by general surgeons. The abdominal wall is made up of muscles and the tissues , which attach the muscles together or attach the muscles to bone. In areas where there is a weakness or natural opening in the abdominal wall, the abdomen’s internal contents can push through, and that is what is called a hernia. The abdominal contents (frequently fat or bowels) can push through the abdominal wall and then fall back inside the abdomen (reducible hernia) or sometimes they can get stuck (incarcerated hernia).
How to prevent a hernia from developing?
Maintaining a healthy body weight, avoiding heavy lifting and not straining to urinate or pass stool helps prevent a hernia from developing. You can also exercise regularly to strengthen your abdominal wall muscles. If you already have a hernia it will not go away, but it may improve with weight loss down to a healthy weight.
Why do people get abdominal wall hernias?
However, the risk of developing a hernia tends to increase as you age. Most abdominal wall hernias are caused by an area of weakness in the abdominal walls. A number of different factors can contribute to the development of that weakness.
What is a hernia in the abdominal area?
A hernia occurs when an organ protrudes through the wall of muscle that encircles it. There are several different types of hernias that can occur in the abdominal and surrounding areas. These include umbilical hernias, epigastric hernias, incisional hernias, and others. For more information on these specific types of hernias, ...
What is an incisional hernia?
Incisional Hernia. A hernia that occurs in the area of a previous surgery is known as an incisional hernia. These hernias may occur when the abdominal wall has been weakened by surgery, or when a surgical incision becomes infected, further weakening the area. Incisional hernias are relatively common because surgical incisions weaken ...
Why do umbilical hernias need surgery?
Because they tend to grow bigger over time, umbilical hernias require treatment. Treatment typically involves surgery, but your doctor will discuss all your options with you in detail. Without treatment, you are at risk of developing a strangulated hernia, which means that blood supply to the tissue has been cut off.
What is the term for a lump in the belly button?
An umbilical hernia occurs when a weak spot in the belly allows a bit of fat, fluid, or intestine to push through, creating a lump or bulge near the belly button.
What does a hernia look like?
Symptoms. Abdominal wall hernias are generally visible: they will look like a lump or bulge beneath the skin. These hernias don’t usually cause any other symptoms except for mild pain or discomfort, usually when you are straining (for instance, lifting something heavy).
How to tell if you have a hernia?
In most cases, your doctor will be able to determine whether you are in fact suffering from a hernia simply by looking and by gently palpating the affected area. If for some reason a diagnosis isn’t immediately apparent, your doctor may decide to order an imaging test, such as an abdominal ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
What is the abdominal wall made of?
The abdominal wall (or the belly) is made up of skin, several layers of tissue, including fat and muscle. It protects the abdominal organs, such as the stomach, the liver and others and helps maintain posture while supporting the spine. The abdominal wall also assists in important body functions such as coughing, urination, and defecation.
Why is abdominal wall reconstruction done?
The indications for reconstruction of the abdominal wall can be symptomatic (for example, pain relief of certain pains or for structural defects. Large abdominal defects can lead to significant herniation (abnormal protrusion of an organ or other body structures through a defect or natural opening in the body).
How long does it take to repair an abdominal wall?
Depending on the extent of defect or infection, the surgery can take anywhere between two to eight hours. Abdominal wall is reconstructed using the following: Graft harvesting the patient’s own tissue (autograft). The method of reconstruction is decided by the surgeon based on experience and nature of defect.
What is the best material for abdominal reconstruction?
Polypropylene mesh is the most used synthetic prosthetic material in abdominal reconstruction. It is ideal for clean defects with enough soft tissue coverage. Prostheses are superior to grafts due to the following: Higher tensile strength. Easy availability.
Where are the abdominal muscles located?
They’re located toward the front of your body, between your ribs and your pelvis.
What muscle is located in the lower abdomen?
Pyramidalis: This vertical muscle is small and shaped like a triangle. It’s located very low, in your pelvis. It helps maintain internal pressure in your abdomen.
What are the main muscles of the abdominal region?
There are five main muscles: pyramidalis, rectus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques, and transversus abdominis. Ab strains and hernias are common, but several strategies can keep your abs safe and healthy.
What are the external obliques?
External obliques: The external obliques are a pair of muscles, one on each side of the rectus abdominis. They are the largest of the flat muscles and at the bottom of the stack. They run from the sides of your body toward the middle. The external obliques allow the trunk to twist side to side.
Which abdominal muscles are deepest?
Transversus abdominis: The transversus abdominis is at the bottom of the stack. This pair of muscles is the deepest of the flat muscles. They stabilize the trunk and help maintain internal abdominal pressure.
Where are the internal obliques located?
Internal obliques: The internal obliques are a pair of muscles on top of the external obliques, just inside your hip bones. Like the external obliques, they are on the sides of the rectus abdominis, running from the sides of your trunk toward the middle. They work with the external oblique muscles to allow the trunk to twist and turn.
How many muscles are there in the abdomen?
There are five main muscles in your abdomen. Two are vertical (up and down) muscles located toward the middle of your body. Three are flat muscles stacked on top of each other, situated toward the sides of the trunk.
