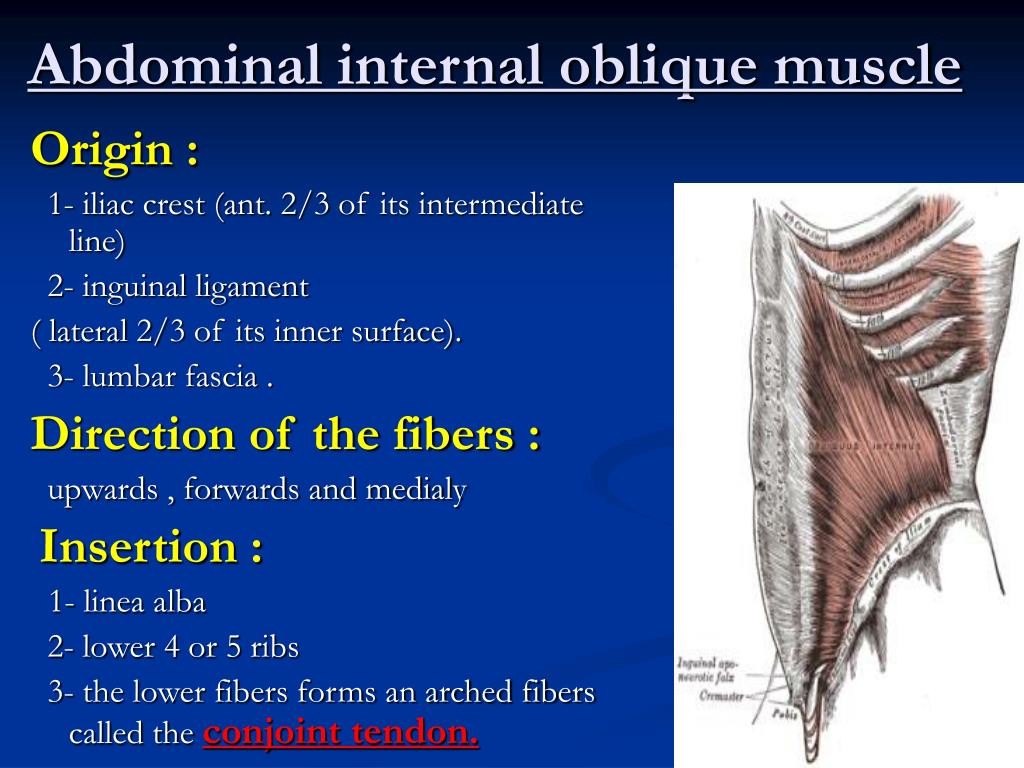
Abdominal internal oblique muscle actions
Bilateral: Compresses abdomen
Unilateral: ipsilateral trunk rotation
What is the primary action of external oblique?
The main action of the external obliques is to move the spinal column and back in several different directions. These directions include: The external obliques are wide, thin muscles that run diagonally down each side of the abdomen.
What is the function of the internal oblique muscle?
The main functions of the internal oblique muscles are to support the abdominal wall, help with forced respirations, provide stability to the spine, and aid with trunk rotation. When exhaling, the internal obliques contract and push the organs of the abdomen into the chest cavity. This reduces the size of the lungs to force the air out.
What do internal obliques do?
What two muscles can be found on the dorsal side of the rat?
- Biceps brachii – located on the anterior surface of the humerus.
- Triceps brachii – located on the sides and back of the upper arm.
- Spinotrapezius – located across the dorsal thoracic region of the rat.
What causes tight external obliques?
Pain in the side of the waist area, low abs and pelvis can be caused by the oblique muscles. Pain can also occur in the following areas: Activities such rowing, raking leaves, chronic or persistent coughing, lifting heavy loads, using shovels or pitchforks and even sitting for long periods of time can bring on muscle pain in the external obliques.
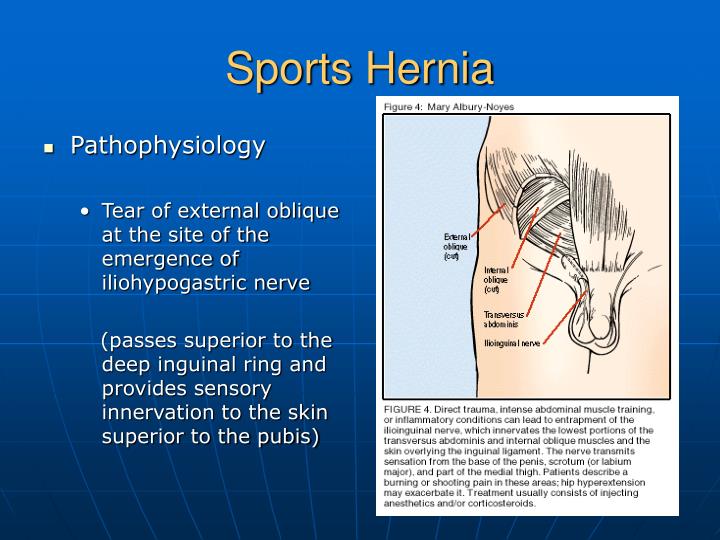
What is the action of the oblique muscles?
Function. The external oblique functions to pull the chest downwards and compress the abdominal cavity, which increases the intra-abdominal pressure as in a valsalva maneuver.
What is the function of the internal oblique muscle of the abdomen?
It is broad and thin. it forms one of the layers of the lateral abdominal wall along with external oblique on the outer side and transverse abdominis on the inner side. Its fibers are obliquely oriented hence the name. It helps maintain the abdominal pressure and movements of the trunk along with the other muscles.
Which action do the external obliques and internal obliques perform?
The external and internal oblique muscles rotate and side bend the trunk.
What is the main action of the external oblique?
External abdominal oblique muscleOriginExternal surfaces of ribs 5-12InsertionLinea alba, pubic tubercle, anterior half of iliac crestActionBilateral contraction - Trunk flexion, compresses abdominal viscera, expiration Unilateral contraction - Trunk lateral flexion (ipsilateral), trunk rotation (contralateral)2 more rows•May 11, 2020
What is the difference between internal and external obliques?
External oblique is an opposite side rotation muscle, while internal oblique is a same side rotation muscle. They work together.
What is the origin insertion and action of the internal oblique?
Abdominal internal oblique muscleOriginInguinal ligament, Iliac crest and the Lumbodorsal fascia.InsertionLinea alba, Pectineal Line of Pubis (via Conjoint tendon) and ribs 10-12.ArterySubcostal arteries.NerveThoracoabdominal nn. (T7-T11), Subcostal n. (T12), Iliohypogastric n. (L1) and Ilioinguinal n. (L1)10 more rows
What is the action of the external oblique muscle quizlet?
Terms in this set (14) what is the action of the external oblique, and internal oblique ? bilateral : flexes vertebral column and compresses abdominal wall.
What is the general function of the external and internal oblique muscles as well as the transversus abdominis?
The main function of the rectus abdominis is to move the body between the ribcage and the pelvis. external oblique muscles – these are on each side of the rectus abdominis. The external oblique muscles allow the trunk to twist, but to the opposite side of whichever external oblique is contracting.
How do you contract internal obliques?
0:291:29Internal External Oblique Exercises on Mat - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipInstead focus on pushing only your knees upward. Towards the ceiling. In the second phase of thisMoreInstead focus on pushing only your knees upward. Towards the ceiling. In the second phase of this exercise. Place one leg over the other leg. Then push your left knee.
What is the job of the internal obliques?
Its main job is to pull the chest downwards and compress the abdominal cavity. The internal obliques, on the other hand, have two main jobs. First, it counteracts the diaphragm (the muscle that contracts excessively when you hiccup) so that you can exhale. Second, it allows you to rotate and bend from your trunk.
What is the function of the external oblique?
The external oblique functions to pull the chest downwards and compress the abdominal cavity, which increases the intra-abdominal pressure as in a valsalva maneuver.
What is the function of the transversus abdominis muscle?
It is involved in moving the trunk, but also stabilizes the vertebral column, creates tension of the anterior body wall and increases the intraabdominal pressure upon contraction.
What is the function of the rectus abdominis?
The main action for rectus abdominis is flexion of the trunk (flexion of thoracic and lumber spine), while it works by drawing symphysis and Sternum toward each other. Also, it works on posterior pelvic tilt with other abdominal muscles.
What muscles are involved in front plank?
The plank strengthens the abdominals, back and shoulders. Muscles involved in the front plank include : Primary muscles: erector spinae, rectus abdominis (abs), and transverse abdominis.
Where is the rectus abdominis located?
The rectus abdominis muscle is the muscle that is located at the front of the abdomen; it is most often referred to as the ''abs. '' The action of this muscle pulls the rib cage and the pelvic bone towards the middle of the abdomen, just like the movement when a person performs a sit-up or crunch.
Where are the obliques located?
They are located on the sides of the abdominals (six-pack muscles) running from the hips to the rib cage. The internal obliques are located directly under the external obliques, and the muscle fibers travel perpendicular to each other.
Where is the internal oblique located?
The internal oblique is an abdominal muscle located beneath the external abdominal oblique.
Which muscle is located closer to the skin than the transverse abdominal muscle?
The internal abdominal oblique muscle is located closer to the skin than the transverse abdominal muscle. This muscle supports the abdominal wall, assists in forced respiration, aids in raising pressure in the abdominal area, and rotates and turns the trunk with help from other muscles.
What muscle is the opposite of the diaphragm?
The internal abdominal oblique muscle is an opposing force to the diaphragm, reducing upper chest cavity volume during exhalation. As the diaphragm contracts, the chest cavity is pulled down to increase lung size.
What are the actions of the internal oblique?
Action of the Internal Oblique. Description. Flexion of the trunk. Bending the trunk forward, such as when you bend over to pick something up off the ground.
Where does the internal oblique run?
From these points of origin, the internal oblique runs diagonally up the side of the body and inserts onto the costal cartilage of the eighth through twelfth ribs and the linea alba. The costal cartilage are the sections of cartilage that extend from the front ends of the ribs, and the linea alba is a band of connective tissue that runs up the middle of the abdomen.
What muscle is used to exhale?
The internal oblique muscles assist with forced exhalation, such as when a person blows out birthday candles. The internal oblique muscle is a diagonal muscle that is found at each side of the body, just lateral to the abdomen. This muscle has several different points of origin, which include:
Where does the oblique muscle insert?
This muscle has several different points of origin, which include: From these points of origin, the internal oblique runs diagonally up the side of the body and inserts onto the costal cartilage of the eighth through twelfth ribs and the linea alba.
Which ribs are inserted into the internal oblique?
Insertion of the Internal Oblique. The internal oblique inserts onto the costal cartilages of the eighth through twelfth ribs and the linea alba. Costal cartilage is the section of cartilage that extends from front ends of the ribs, and the linea alba (Latin for 'white line') is a band of connective tissue that runs up the middle of the abdomen.
Where is the internal oblique muscle located?
The internal oblique muscle is a muscle that is found at each side of the body, just lateral to the abdomen. The word 'oblique' means 'diagonal' or 'slanted', which is a reference to the slanted direction that the muscle fibers of this muscle run up the sides of the body.
What muscle is used to celebrate birthdays?
The internal oblique is very important muscle when celebrating your birthday. Find out why, as well as the action and origin of this muscle, by reading the rest of this lesson. Updated: 02/22/2021
What are the functions of the internal oblique muscles?
The main functions of the internal oblique muscles are to support the abdominal wall, help with forced respirations, provide stability to the spine, and aid with trunk rotation. When exhaling, the internal obliques contract and push the organs of the abdomen into the chest cavity. This reduces the size of the lungs to force the air out. The internal obliques also work with the external obliques on the opposite side of the body during rotation of the trunk.
Where is the internal oblique located?
The internal oblique begins at the lumbar fascia, the outer two-thirds of the inguinal ligament, and the front two-thirds of the iliac crest. The lumbar fascia is a connective tissue that covers the lower back. The inguinal ligament is a ligament located on the bottom-outer edge of the pelvis. The iliac crest is the upper-outside portion of the pelvis.
What muscles are involved in the abdominal wall?
The internal obliques are one of the four abdominal muscles. They start at the lumbar fascia, inguinal ligament, and iliac crest and end at the costal margin, aponeurosis of the rectus sheath, and pubic crest. Therefore, any action of the internal obliques causes a feeling of contraction right below the rib cage. The main functions of the internal obliques are to support the abdominal wall, stabilize the spine, aid in exhaling during respirations, and rotation of the torso or trunk.
What are the four abdominal muscles?
They are the rectus abdominis, the transverse abdominis, the external obliques, and the internal obliques. There are two sets of internal oblique muscles that are located on each side of the body. They are below the rectus abdominis and just inside the hip bones. The internal obliques control the movement on the same side of the body. This means that if Mark twists to right, the right side internal obliques are contracting. Therefore, they are sometimes referred to as 'same side rotators'.
What is Mark's pain?
Mark is a golfer who has developed a sharp pain around his rib cage, especially when twisting his upper body to the left. He has also noticed some bruising and tenderness in the same area. Mark is now wondering what he has injured and how it will affect his daily life.
Does Mark have pain when he twists his body?
Mark understands that doing any movement that involves moving his torso will cause him discomfort until his left internal obliques are healed. This means that he may feel pain while sitting or standing anytime he twists his body from side to side. Since the internal obliques are also involved with breathing, there may also be pain when taking deep breaths, sneezing, or coughing. Ice, rest, and anti-inflammatory medication will help Mark remain comfortable while he heals.
What is the Internal Oblique Muscle?
The abdominal muscles are divided into two compartments, the posterolateral and anterolateral abdominal walls. The posterolateral compartment is located closest to the internal organs of the stomach, while the anterolateral compartment consists of the most superficial muscles of the stomach.
Internal Abdominal Oblique Muscle
The Internal abdominal oblique muscle derives its name from the orientation of its muscle fibers. In this case, oblique refers to the diagonal direction in which the muscle fibers run along the ribs. Humans have two internal oblique muscles, one located on each side of the abdomen along the ribs.
Internal Oblique Origin and Insertion
All muscles have points of attachment known as the origin and the insertion. The origin represents the attachment of a muscle to the stable bone of a joint. A joint refers to the location where two or more bones meet. The insertion of a muscle is located on the mobile bone of a joint. Some muscles have more than point of origin and insertion.
Internal Oblique Action
The internal oblique performs a number of important actions in the body, including:
Innervation and Blood Supply
Innervation refers to the nerves which enable a muscle to perform an action. The internal oblique is innervated by the ilioinguinal nerve and the intercostal nerves. The ilioinguinal nerve is derived from the first lumbar nerve and innervates several muscles in the abdominal region.
What is the function of internal obliques?
The internal obliques can function bilaterally, which means both sides working together. Bilaterally they flex the trunk and compress its contents. They can also function unilaterally, which means one-sided. Unilaterally, they laterally flex the trunk and rotate it to the same side.
What is the external obliques?
External means outside and oblique, as we said, means a slanting orientation, which refers to the muscle fiber direction.
What do the names of the external and internal oblique muscles, mean?
Internal means inside and oblique comes from the Latin word obliquus, which means a slanting orientation. So, the name internal obliques refers to the location and shape of the muscle. The slanting direction refers to the direction of the fibers of this muscle. The fiber direction of the internal obliques is in the direction of reaching across your body. As in, if you place your hand on the opposite side of your abdomen, your fingers represent the direction of the fibers.
Which obliques rotate the trunk to the opposite side?
Unilaterally, they laterally flex the trunk and rotate it to the same side. Like the internal obliques, the external obliques function bilaterally to flex the trunk and compress its contents. However, they function unilaterally to laterally flex the trunk and rotate the trunk to the opposite side.
Where do internal obliques originate?
The internal obliques originate on the inguinal ligament, which is a ligament that runs from the anterior iliac spine to the pubic bone. Additionally they originate on the anterior iliac crest. The external obliques, however, originate on the lower eight ribs.
Which side of the external obliques is lengthened?
If we look at the twisting motion of marichyasana C, as we twist to the right, we are going to find the right side of the external obliques lengthening with the left side of the internal obliques.
Why do the abdominals do isometric contractions?
If we look at a posture such as navasana, we see that all of the abdominals will be doing an isometric contraction in order to help stabilize the trunk. This helps keep it rigid so that the hip flexors can do their work.
What is the function of the internal oblique?
The internal oblique performs two major functions. Firstly as an accessory muscle of respiration, it acts as an antagonist (opponent) to the diaphragm, helping to reduce the volume of the chest cavity during exhalation. When the diaphragm contracts, it pulls the lower wall of the chest cavity down, increasing the volume of the lungs which then fill with air. Conversely, when the internal obliques contract they compress the organs of the abdomen, pushing them up into the diaphragm which intrudes back into the chest cavity reducing the volume of the air-filled lungs, producing an exhalation.
What happens when the internal obliques contract?
Conversely, when the internal obliques contract they compress the organs of the abdomen, pushing them up into the diaphragm which intrudes back into the chest cavity reducing the volume of the air-filled lungs, producing an exhalation. Secondly, its contraction causes ipsilateral rotation and side-bending.
What is the oblique muscle?
(T12), Iliohypogastric n. (L1) and Ilioinguinal n. (L1) The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle .
What is the purpose of the diagram of a transverse section of the posterior abdominal wall?
Diagram of a transverse section of the posterior abdominal wall, to show the disposition of the lumbodorsal fascia.
Where is the internal oblique muscle located?
The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle .
Which muscle is attached to the internal oblique?
In males, the cremaster muscle is also attached to the internal oblique.
Where are the iliac crest and inguinal ligament?
Structure. Its fibers run perpendicular to the external oblique muscle, beginning in the thoracolumbar fascia of the lower back, the anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest (upper part of hip bone) and the lateral half of the inguinal ligament. The muscle fibers run from these points superiomedially ...
