Key Points
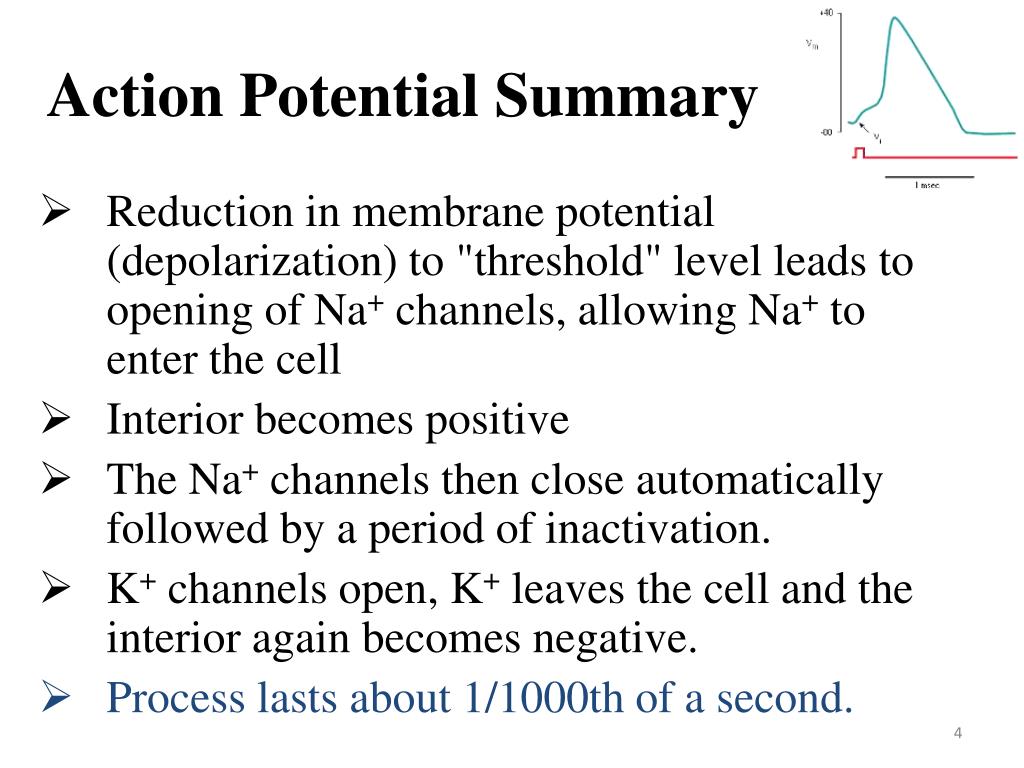
- Action potential is a brief reversal of membrane potential in which the membrane potential changes from -70mV to +30mV
- The action potential has three main stages: depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization.
- Depolarization is caused when positively charged sodium ions rush into a neuron with the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels.
What are the 5 steps of an action potential?
Mar 13, 2022 · An action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. It consists of four phases: depolarization, overshoot, and repolarization. An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button.
What are the steps of an action potential?
Sep 26, 2019 · An action potential is a predictable change in membrane potential that occurs due to the open and closing of voltage gated ion channels on the cell membrane. Electrically Active Cell Membranes Most cells in the body make use of charged particles ( ions) to create electrochemical charge across the cell membrane.
What are the four phases of an action potential?
A neuron (a nerve cell) is the basic building block of the nervous system. When neurons transmit signals through the body, part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. This process, which occurs during the firing of the neurons, allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon (a portion of the neuron that carries nerve …
What are the steps in the generation of an action potential?
May 30, 2020 · An action potential is part of the process that occurs during the firing of a neuron. During the action potential, part of the neural membrane opens to allow positively charged ions inside the cell and negatively charged ions out. When the charge reaches +40 mv, the impulse is propagated down the nerve fiber.

What are the 7 steps of an action potential?
7 Cards in this SetSTEP 1Threshold stimulus to -55mvStimulusSTEP 4At +30mv, Na channels close and K ions channels openK ionsSTEP 5K floods out of the cellOut of cellSTEP 6Hyperpolarization to -90mvHyperSTEP 7K channels close and tge resting potential is re-established at -70Re-established2 more rows
What are the 5 steps of an action potential?
What Are The 5 Steps Of An Action Potential?Resting potential.Threshold.Rising phase.Falling phase.Recovery phase.
What is action potential in simple terms?
The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current. This means that some event (a stimulus) causes the resting potential to move toward 0 mV. When the depolarization reaches about -55 mV a neuron will fire an action potential. This is the threshold.
What is action potential example?
The most famous example of action potentials are found as nerve impulses in nerve fibers to muscles. Neurons, or nerve cells, are stimulated when the polarity across their plasma membrane changes. The polarity change, called an action potential, travels along the neuron until it reaches the end of the neuron.Sep 28, 2014
How does action potential occur?
Going down the length of the axon, the action potential is propagated because more voltage-gated Na + channels are opened as the depolarization spreads. This spreading occurs because Na + enters through the channel and moves along the inside of the cell membrane. As the Na + moves, or flows, a short distance along the cell membrane, its positive charge depolarizes a little more of the cell membrane. As that depolarization spreads, new voltage-gated Na + channels open and more ions rush into the cell, spreading the depolarization a little farther.
Where does action potential propagate?
The action potential must propagate from the trigger zone toward the axon terminals. Propagation, as described above, applies to unmyelinated axons. When myelination is present, the action potential propagates differently, and is optimized for the speed of signal conduction.
Why do skeletal muscles contract?
For skeletal muscles to contract, due to excitation–contraction coupling, they require input from a neuron. Both muscle and nerve cells make use of a cell membrane that is specialized for signal conduction to regulate ion movement between the extracellular fluid and cytosol.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
The functions of the nervous system—sensation, integration, and response —depend on the functions of the neurons underlying these pathways. To understand how neurons are able to communicate, it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals. The basis of this process is the action potential.
Why do ligand-gated channels open?
A ligand-gated channel opens because a molecule, or ligand, binds to the extracellular region of the channel ( Figure 12.5.2 ).
What is the role of the cell membrane?
As you learned in the chapter on cells, the cell membrane is primarily responsible for regulating what can cross the membrane. The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, so only substances that can pass directly through the hydrophobic core can diffuse through unaided.
What is the sodium potassium pump?
The sodium/potassium pump requires energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), so it is also referred to as an ATPase pump. As was explained in the cell chapter, the concentration of Na + is higher outside the cell than inside, and the concentration of K + is higher inside the cell than outside.
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
The resting potential of the neuron refers to the difference between the voltage inside and outside the neuron. The resting potential of the average neuron is around -70 millivolts, indicating that the inside of the cell is 70 millivolts less than the outside of the cell.
What is the role of sodium channels in the cell?
The sodium channels play a role in generating the action potential in excitable cells and activating a transmission along the axon. Action potentials either happen or they don't; there is no such thing as a "partial" firing of a neuron. This principle is known as the all-or-none law .
What is the basic building block of the nervous system?
A neuron (a nerve cell) is the basic building block of the nervous system. When neurons transmit signals through the body, part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. This process, which occurs during the firing of the neurons, allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon ...
Which atoms have a positive charge?
Electrically charged atoms known as ions maintain the positive and negative charge balance. Calcium contains two positive charges, sodium and potassium contain one positive charge, and chloride contains a negative charge. When at rest, the cell membrane of the neuron allows certain ions to pass through while preventing or restricting other ions ...
Who is Kendra Cherry?
Kendra Cherry, MS, is an author, educational consultant, and speaker focused on helping students learn about psychology. Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, is an award-winning physician-scientist and clinical development specialist. A neuron (a nerve cell) is the basic building block of the nervous system.
What is the all or none law?
This principle is known as the all-or-none law . This means that neurons always fire at their full strength. This ensures that the full intensity of the signal is carried down the nerve fiber and transferred to the next cell and that the signal does not weaken or become lost the further it travels from the source.
Who is Shaheen Lakhan?
Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, is an award-winning physician-scientist and clinical development specialist. A neuron (a nerve cell) is the basic building block of the nervous system. When neurons transmit signals through the body, part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential.
What is the action potential of a cell?
The Action Potential. Resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell, which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. Without any outside influence, it will not change. To get an electrical signal started, the membrane potential has to change.
Why do voltage-gated channels open?
Voltage-gated channels open when the transmembrane voltage changes around them. Amino acids in the structure of the protein are sensitive to charge and cause the pore to open to the selected ion.
What are the functions of the nervous system?
The functions of the nervous system—sensation, integration, and response— depend on the functions of the neurons underlying these pathways. To understand how neurons are able to communicate, it is necessary to describe the role of an excitable membrane in generating these signals. The basis of this communication is the action potential, ...
How do muscle cells work?
Both of the cells make use of the cell membrane to regulate ion movement between the extracellular fluid and cytosol.
What is the role of the cell membrane?
As you learned in the chapter on cells, the cell membrane is primarily responsible for regulating what can cross the membrane and what stays on only one side. The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer, so only substances that can pass directly through the hydrophobic core can diffuse through unaided.
What is the membrane of a cell?
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and has many transmembrane proteins, including different types of channel proteins that serve as ion channels. The sodium/potassium pump requires energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), so it is also referred to as an ATPase.
What are hydrophilic amino acids?
Hydrophilic amino acids are exposed to the fluid environments of the extracellular fluid and cytosol. Additionally, the ions will interact with the hydrophilic amino acids, which will be selective for the charge of the ion. Channels for cations (positive ions) will have negatively charged side chains in the pore.
What is Action Potential
An action potential is the rapid rise and fall in membrane potential, or voltage, across the cellular membrane. Also known as 'nerve impulses' or 'spikes', action potentials are seen in neurons, which are the main cell type in the brain.
What Triggers an Action Potential
When neurons are not firing action potentials, they are said to be at rest. This denotes that the intracellular potential of the neuron is negative when compared to the extracellular potential. The difference in intracellular and extracellular potentials is achieved by the movement of charged ions in and out of the cell.
Refractory Period
The refractory period is when the cell can no longer fire action potentials due to being in a hyperpolarization state. The absolute refractory period is the first part of this period, during which the cell is incapable of firing.
What is the action potential of a neuron?
In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse, and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. Sometimes called a propagated potential because a wave of excitation is actively transmitted along the nerve or muscle fibre, an action potential is conducted at speeds that range from 1 to 100 metres ...
What happens when sodium is depolarized?
Depolarization activates sodium channels in adjacent parts of the membrane, so that the impulse moves along the fibre. If the entry of sodium into the fibre were not balanced by the exit of another ion of positive charge, an action potential could not decline from its peak value and return to the resting potential.
Who won the Nobel Prize for Physiology in 1963?
Subscribe Now. The Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine was awarded in 1963 to Sir A.L. Hodgkin, Sir A.F. Huxley, and Sir John Eccles for formulating these ionic mechanisms involved in nerve cell activity.
What is the polarization of a neuron?
Before stimulation, a neuron or muscle cell has a slightly negative electric polarization; that is, its interior has a negative charge compared with the extracellular fluid. This polarized state is created by a high concentration of positively charged sodium ions outside the cell and a high concentration of negatively charged chloride ions ...
What is an encyclopedia editor?
Encyclopaedia Britannica's editors oversee subject areas in which they have extensive knowledge, whether from years of experience gained by working on that content or via study for an advanced degree. ...
What is the first phase of action potential?
The first phase of the action potential is the rising phase called ‘depolarization ’, which occurs due to a stimulus and causes the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels. The stimulus could be in the form of a neurotransmitter released by the presynaptic cell that eventually binds to receptors on the postsynaptic cell membrane. The opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels causes an influx of sodium ions and increases the voltage. At this depolarization stage, the low membrane potential ceases, and the state of the voltage-gated sodium ions changes from a deactivated (closed) state to an activated (open) state. However, an action potential can only occur when depolarization reaches a threshold value of between -40 and -55 mV.
What is the period after an action potential is generated?
This period is known as the relative refractory period.
What is the action potential of a cell membrane?
Action_Potential. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer structure that usually does not allow electrical ions to pass through freely. Therefore, there is a difference in ion concentration maintained across the cell membrane, causing it to be polarized.
How are cardiac cells linked?
All cardiac cells are linked to each other through gap junctions that allow propagation of the action potential. However, there is a clear distinction between the cells that are capable of producing an action potential and cells that can only conduct it (i.e. ventricular myocytes).
Where are glomus cells located?
Glomus cells are located in the peripheral chemoreceptor organs called carotid bodies These cells are interoceptors that are capable of transducing a stimulus within the body into an action potential. More specifically, they respond to changes such as a decreased partial pressure of oxygen (hypoxia), increased partial pressure of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia), or a decreased pH (acidity).
What is the membrane potential?
The maintenance of a potential across the cell membrane is called ‘membrane potential’. Usually, the inside of the cell is more negative than the outside, and the membrane potential is typically at -70 mV (millivolts). This is also described as the state of a normal resting membrane potential.
What happens when sodium channels are opened?
The opening of the voltage-gated sodium channels causes an influx of sodium ions and increases the voltage. At this depolarization stage, the low membrane potential ceases, and the state of the voltage-gated sodium ions changes from a deactivated (closed) state to an activated (open) state.