Do enzymes have active sites?
Usually, an enzyme molecule has only two active sites, and the active sites fit with one specific type of substrate. An active site contains a binding site that binds the substrate and orients it for catalysis.
What is the function of active site?
The active site is usually a groove or pocket of the enzyme which can be located in a deep tunnel within the enzyme, or between the interfaces of multimeric enzymes. An active site can catalyse a reaction repeatedly as residues are not altered at the end of the reaction (they may change during the reaction, but are regenerated by the end).
What is the activation site of an enzyme?
The enzyme’s active site is the small region, which seems like a cleft or cavity composed of nearly 10-15 amino acid residues. According to the term, we can define it as a site that activates the complex enzyme to bind with the particular substrate, induces the substrate’s transition state and stabilize the product formation .
What is a substrate and active site?
What is a substrate and active site? Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme, depending on the particular chemical reaction. In some reactions, a single-reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. The enzyme’s active site binds to the substrate.

What is the active site and what is its function?
The active site refers to the specific region of an enzyme where a substrate binds and catalysis takes place or where chemical reaction occurs. It is a structural element of protein that determines whether the protein is functional when undergoing a reaction from an enzyme.
What is the active site in an enzyme?
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the active site (since that's where the catalytic “action” happens). A substrate enters the active site of the enzyme. This forms the enzyme-substrate complex.
What is the active site of an enzyme quizlet?
the active site of an enzyme is the region that binds the substrates(and cofactor if any) The interaction of the enzyme and substrate at the active site promotes the formation of the transition state. the enzyme changes shape on substrate binding.
How active site of an enzyme can be determined?
The activity of an enzyme is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure. Substrates bind to the active site of the enzyme in order to specifically accelerate a particular chemical reaction. The active site of an enzyme comprises a substrate binding site and a catalytic site.
What is an example of an active site?
For example, stringing together nucleotides and amino acids to make DNA and proteins, breaking down sugar and fat into energy, and breaking down toxins in the liver. Thus, enzymes are some of the most important molecules in biology.
How do you identify the active site of a protein?
In general, structure-based methods proposed to identify active sites in proteins are based on graphs, where nodes represent atoms in the amino acid side chain and neighbour atoms are connected with edges, weighted by their distances.
What is the active site of an enzyme Brainly?
In enzyme, the active site refers to a particular place in the enzyme. This is the place where substrate molecules bind to the receptor of the enzyme and then they undergo various types of chemical reaction depending on the type of enzyme and the substrate.
What is the active site of an enzyme BBC Bitesize?
Enzymes are folded into complex 3D shapes that allow smaller molecules to fit into them. The place where these molecules fit is called the active site . In the lock and key hypothesis , the shape of the active site matches the shape of its substrate molecules. This makes enzymes highly specific.
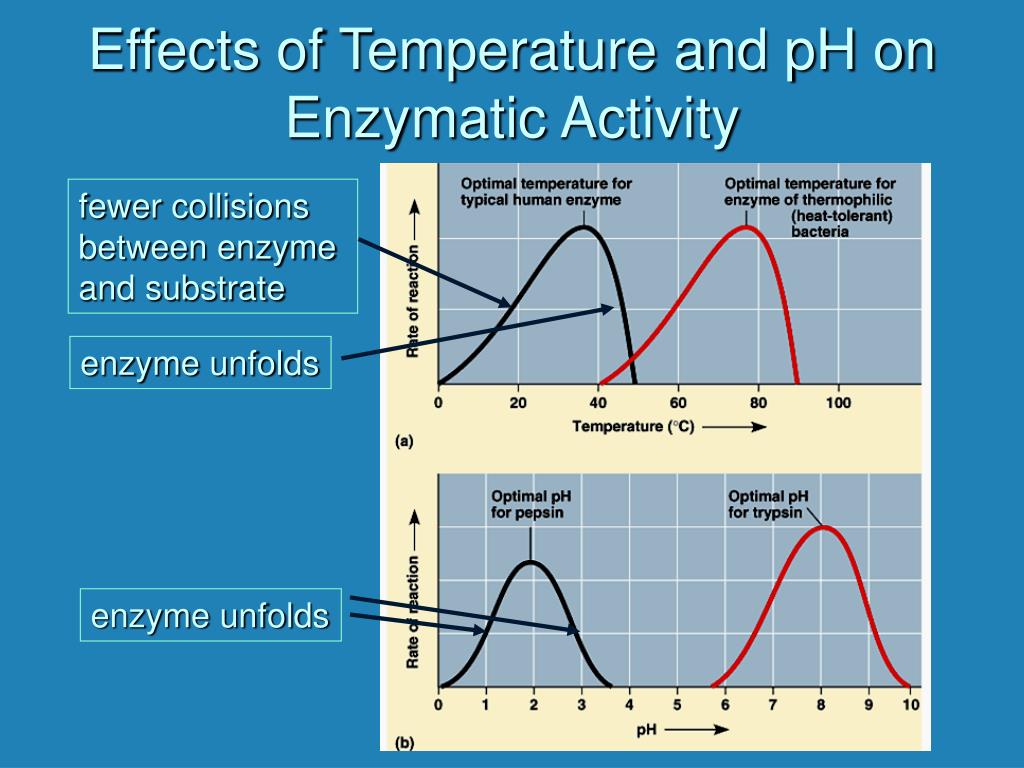
How does pH affect enzymes?
pH. pH can also affect enzyme function. Active site amino acid residues often have acidic or basic properties that are important for catalysis. Changes in pH can affect these residues and make it hard for substrates to bind. Enzymes work best within a certain pH range, and, as with temperature, extreme pH values (acidic or basic) can make enzymes denature.
How does an enzyme catalyze a reaction?
To catalyze a reaction, an enzyme will grab on (bind) to one or more reactant molecules. These molecules are the enzyme's substrates. In some reactions, one substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates come together to create one larger molecule or to swap pieces.
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
Because active sites are finely tuned to help a chemical reaction happen, they can be very sensitive to changes in the enzyme’s environment. Factors that may affect the active site and enzyme function include: 1 Temperature. A higher temperature generally makes for higher rates of reaction, enzyme-catalyzed or otherwise. However, either increasing or decreasing the temperature outside of a tolerable range can affect chemical bonds in the active site, making them less well-suited to bind substrates. Very high temperatures (for animal enzymes, above or ) may cause an enzyme to denature, losing its shape and activity. 2 pH. pH can also affect enzyme function. Active site amino acid residues often have acidic or basic properties that are important for catalysis. Changes in pH can affect these residues and make it hard for substrates to bind. Enzymes work best within a certain pH range, and, as with temperature, extreme pH values (acidic or basic) can make enzymes denature.
How does an enzyme-substrate complex lower activation energy?
The enzyme-substrate complex can also lower activation energy by bending substrate molecules in a way that facilitates bond-breaking, helping to reach the transition state. Finally, some enzymes lower activation energies by taking part in the chemical reaction themselves.
What happens when an enzyme binds to its substrate?
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, we know it lowers the activation energy of the reaction, allowing it to happen more quickly . But, you may wonder, what does the enzyme actually do to the substrate to make the activation energy lower?
What does it mean when a cleaner is enzymatic?
As I would later learn, all that “enzymatic” meant was that the cleaner contained one or more enzymes, proteins that catalyzed particular chemical reactions – in this case, reactions that broke down the film of eye goo that accumulated on my contacts after a week of use. (Presumably, the reason it stung when I got it in my eyes was that the enzymes would also happily break down eye goo in an intact eye.) In this article, we’ll look in greater depth at what an enzyme is and how it catalyzes a particular chemical reaction.
What is the part of an enzyme where the substrate binds?
The part of the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the active site (since that’s where the catalytic “action” happens). A substrate enters the active site of the enzyme. This forms the enzyme-substrate complex.The reaction then occurs, converting the substrate into products and forming an enzyme products complex.
What happens to amino acids in the active site of an enzyme?
In the active site, amino acids of the enzyme protein will bind to the substrate. The substrate fits perfectly into the active site of an enzyme, meaning that enzymes are specific for their substrates and not any others. Lactase cannot break down any other disaccharide besides lactose.
How does lactase start its reaction?
Lactase starts its reactions by binding to its substrate. A substrate is the substance or molecule on which an enzyme functions. So, the substrate for lactase is lactose. Together with enzymes, substrates form an enzyme-substrate complex. Enzymes like lactase are block-like, globular proteins with pockets.
What is the active site of lactase?
These pockets contain the active site, which is the area of an enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reaction takes place. In the active site, amino acids of the enzyme protein will bind to the substrate.
What happens when enzymes bind to a substrate?
When binding to a substrate, enzymes may undergo an induced fit. This is the change in enzyme shape to accommodate and bind to a substrate. Although it's true all substrates are specific for their enzymes, you can imagine this is just like a little tweak to the enzyme-substrate complex to make the reaction occur.
How do enzymes help break molecules apart?
Enzymes can break molecules apart, build or add molecules, and even rearrange them. In lowering the activation energy of a reaction, enzymes decrease the barrier to starting a reaction. It's important to note, however, that the change in energy remains the same between the start and end of a chemical reaction.
What is an enzyme?
Lesson Summary. In summary, enzymes are proteins that lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction.
Why are enzymes important in chemical reactions?
The presence of enzymes is analogous to decreasing the size of the hill in your backyard. Enzymes make things easier for your cell and help chemical reactions occur.
What is the second part of an active site?
The second part of an active site is called the catalytic site . The catalytic site is point at which the enzyme actually works to catalyze a reaction. In other words, the amino acids in the catalytic site function is such a way that when a substrate molecule is present, the amino acids reduce the activation energy of the forthcoming reaction.
How does the substrate interact with the active site?
The substrate, attracted by interactions with the amino acids within the active site, pushes into the enzyme, changing its shape. This forces the enzyme around the substrate, introducing forces which hold the substrate in the enzyme and allow catalytic processes to take place.
What is enzyme specificity?
This is known as enzyme specificity, and each enzyme has a different degree of specificity for the molecules it acts on. The active site of some enzymes is so specific ...
What are the chemical properties of amino acids?
The chemical properties of the individual amino acids yield a structure which has the ability to specifically bind to certain molecules. This ability is largely due to the amino acids present within the active site. The active site of an enzyme can have a number of structures, which determine the resulting function of the protein.
How does an active site affect the substrate?
First, an active site increases the concentration of the substrate being acted on. It does this by isolating the substrate molecule from the surrounding water environment. As the hydrogen bonds of the water molecules no longer affect the substrate inside the active site, it is hidden from these forces.
What is binding site?
The binding site, consists of a number of specific amino acids, which have various properties. In combination, these various amino acids create a three dimensional space with very specific electrical and chemical properties. In effect, only a very small number of molecules will match the shape of the space, let alone have ...
Why is the active site important?
First, an active site increases the concentration of the substrate being acted on.
Why are enzymes important?
If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process. Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. They bind to molecules and alter them in specific ways. They are essential for respiration, digesting food, muscle and nerve function, among thousands of other roles.
What are enzymes used for?
They are essential for respiration, digesting food, muscle and nerve function , among thousands of other roles. In this article, we will explain what an enzyme is, how it works, and give some common examples of enzymes in the human body.
What is an inhibitor that binds to an enzyme and permanently inactivates it?
The products leave the active site less easily, and the reaction is slowed down. Irreversible inhibitors – an irreversible inhibitor binds to an enzyme and permanently inactivates it.
What are some examples of enzymes?
There are thousands of enzymes in the human body, here are just a few examples: Lipases – a group of enzymes that help digest fats in the gut. Amylase – helps change starches into sugars. Amylase is found in saliva. Maltase – also found in saliva; breaks the sugar maltose into glucose.
What enzyme breaks down starch into sugars?
The basics. The enzyme amylase (pictured), breaks down starch into sugars. Enzymes are built of proteins folded into complicated shapes; they are present throughout the body. The chemical reactions that keep us alive – our metabolism – rely on the work that enzymes carry out.
How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
of an enzyme and is converted into products. Once the products leave the active site , the enzyme is ready to attach to a new substrate and repeat the process.
Why do enzymes need to be slowed down?
To ensure that the body’s systems work correctly, sometimes enzymes need to be slowed down. For instance, if an enzyme is making too much of a product, there needs to be a way to reduce or stop production.
How many active sites does an enzyme have?
Usually, each subunit of an enzyme has one active site capable of binding substrate. The characteristics of an enzyme derive from the sequence of amino acids, which determine the shape of the enzyme (i.e., the structure of the active site) and hence the specificity of the enzyme.
What is the role of the active site?
The role of the active site. That the compound on which an enzyme acts (substrate) must combine in some way with it before catalysis can proceed is an old idea , now supported by much experimental evidence. The combination of substrate molecules with enzymes involves collisions between the two.
What forces attract the substrate to the surface of an enzyme?
The forces that attract the substrate to the surface of an enzyme may be of a physical or a chemical nature . Electrostatic bonds may occur between oppositely charged groups—the circles containing plus and minus signs on the enzyme are attracted to their opposites in the substrate molecule.
What are the attractive forces between substrate and enzyme?
The attractive forces between substrate and enzyme may also involve so-called hydrophobic bonds , in which the oily, or hydrocarbon, portions of the enzyme (represented by H-labelled circles) and the substrate are forced together in the same way as oil droplets tend to coalesce in water. The role of the active site in the lock-and-key fit ...
What is the region of contact between enzymes?
Because of the difference in size between the two, only a fraction of the enzyme is in contact with the substrate; the region of contact is called the active site. Usually, each subunit of an enzyme has one active site capable of binding substrate.
How do modifications in the structure of amino acids affect the enzyme's activity?
Modifications in the structure of the amino acids at or near the active site usually affect the enzyme’s activity, because these amino acids are intimately involved in the fit and attraction of the substrate to the enzyme surface. The characteristics of the amino acids near the active site determine whether or not a substrate molecule will fit ...
What are Enzymes?
Enzymes are mostly proteins except for ribozymes, made of RNA. Enzymes are produced by living cells to speed up the biochemical reactions in and outside the cells of the body. Enzymes are also called biocatalysts.
How do enzymes form products?
Enzymes have active sites to bind to the substrate (enzyme-substrate complex), forming products by allowing the formation of bonds between the substrates. While in some, a single reactant is broken down into different products. Products leave the active site of the enzyme, and again that enzyme is ready to bind another substrate.
What is the surface configuration of an enzyme?
The surface configuration of the active site is such as to allow the particular substrate molecules to be held over it. This concept was given by biologist Emil Fisher in his lock and key structure model.
What are the reactants of enzymes?
The reactants in the reaction catalysed by enzymes are called substrates, while the substances produced in the reaction are called products.
What happens when products have different structural configurations?
The products having different structural configuration does not fit the last conformation of the active site and thus are released from the enzyme molecule or active site.
How does amino acid sequence affect protein structure?
So, a change in the sequence of amino acids changes the structure of the enzyme and its active site. Thus changing its function too.
How does the activation complex lower the activation energy?
This complex lowers the activation energy by bringing the reactant close to each other and orienting in such a way that allows easy interaction between the substrates.
What happens to chemical bonds in catabolic reactions?
A.) Catabolic reactions remove chemical bonds and result in larger substances being broken down into smaller ones.
What increases the activation energy of some enzymes?
A.) The presence of a cofactor increases the activation energy of some enzymes.
What are the benefits of whole grains?
A.) Some processed whole grains have reduced fiber, which is the single most important factor for improved healthfulness of a grain-based food . B.) Some processed whole grains have had their protein and lipids removed , which are important micronutrients to human health.
What happens to anabolic reactions?
D.) Anabolic reactions add chemical bonds and result in smaller molecules being built up into larger ones.
How does enzyme affect the activation energy of a reaction?
How does an enzyme affect the activation energy of a reaction? A.) It lowers the energy of activation, which makes the reaction it catalyzes less likely to occur and slows down the production of the chemical product. B.) It increases the energy of activation, which decreases the likelihood of undesirable side reactions and increases the yield ...
What determines what substrate the active site can bind?
C.) Enzyme shape determines what substrate the active site can bind.
Which neurochemical increases the likelihood of drowsiness?
A.) Tryptophan is a precursor molecule for dopamine, a neurochemical associated with pleasure, which increases the likelihood of drowsiness. B.) Tryptophan is a precursor molecule for serotonin, a neurochemical associated with increased relaxation, which increases the likelihood of drowsiness.
Active Site Definition
Structure of The Active Site
- An active site has two main components, as seen in the image below. The binding site, consists of a number of specific amino acids, which have various properties. In combination, these various amino acids create a three dimensional space with very specific electrical and chemical properties. In effect, only a very small number of molecules will match the shape of the space, le…
Function of The Active Site
- An active site in an enzyme has several general functions which all revolve around lowering the activation energy needed for a biological reaction. Consider the reaction of the breakdown of glucose, one of the most important cellular sugars. Glucose breaks down naturally into the products needed by cells, in the course of thousands of years. Cells cannot wait that long. They …
Induced Fit vs Lock-And-Key
- Historically, it was assumed that the active site of a protein was a perfectly designed shape, matched to the substrate. This was supported by the fact that most enzymes operate only on a specific substrate, and by the fact that molecules of similar shape and chemical properties could act as an enzyme inhibitor. This “perfect shape” hypothesis is known as the “Lock-and-Key” hypo…