Focal spot is the area of the anode surface which receives the beam of electrons from the cathode. It is the apparent source of x-rays. Size and shape of the focal spot is determined by the size and shape of the electron beam when it strikes the anode 1. Size and shape of the electron beam is determined by:
What is focal spot in X-ray?
Focal spot. A.Prof Frank Gaillard ◉ ◈ and Dr Aditya Shetty ◉ et al. Focal spot is the area of the anode surface which receives the beam of electrons from the cathode. It is the apparent source of x-rays. Size and shape of the focal spot is determined by the size and shape of the electron beam when it strikes the anode 1.
How to calculate the apparent focal spot size of a tube?
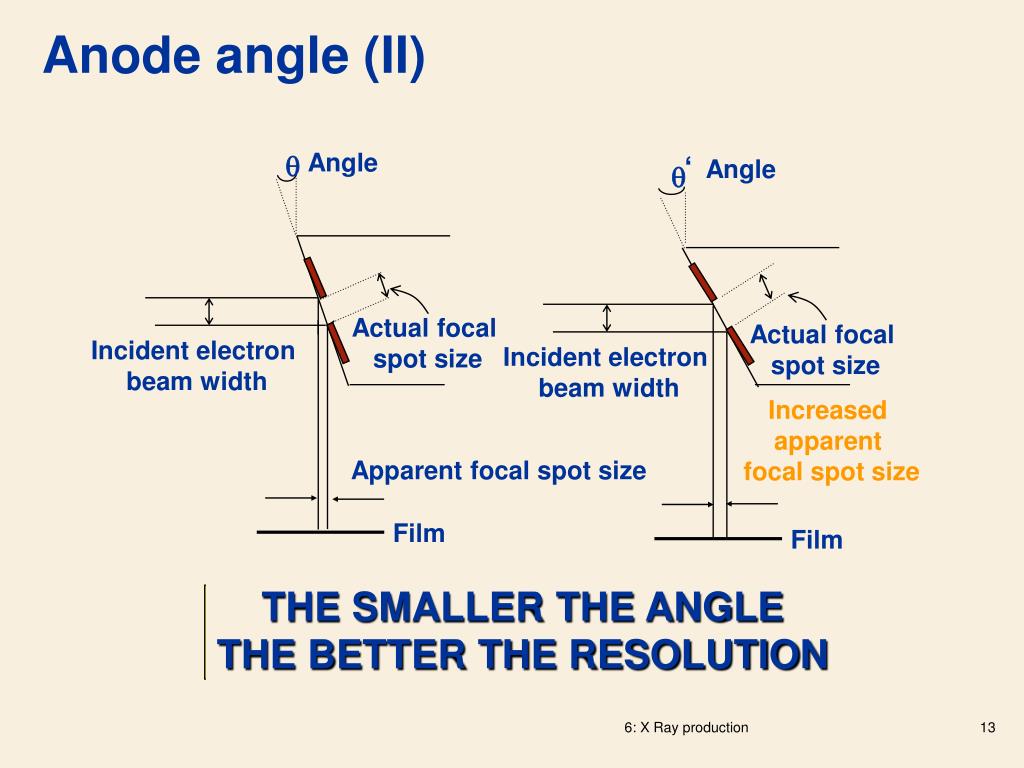
The apparent focal spot (projected focal spot) size can be determined by the sine of the angle of the anode surface (apparent focal spot size = real focal spot size * sin anode angle). The angle varies as per tube design with a range value of 6 degrees to about 20 degrees. Limitation of the principle
What is the meaning of focal spot in anode?
Focal spot. Focal spot is the area of the anode surface which receives the beam of electrons from the cathode.
What is the focal spot of an electron beam?
The focal spot is the area of the target upon which the electron beam impinges. The energy of the electrons in the electron beam is mostly converted into heat (approximately 99%, which is why materials such as tungstenare used due to their high melting-points) and dissipated uniformly across the focal spot and anode surface.
What is the electric field created between the cathode and anode?
What is the focal spot of an anode?
What determines the size of an electron beam?
Why are focal spots important?
See 1 more
About this website

What is focal spot in radiography?
The focal spot is the origin of X-rays used to produce a radiograph. The area of the anode target hit by electrons is described as the actual focal spot area, whereas the rectangular area projected downwards to produce an X-ray field is known as the effective focus.
What is the difference between actual and effective focal spot?
2:246:21Focal Spot & Line Focus Principle - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNotice how the width of the effective focal spot. Changes when you select a small filament versusMoreNotice how the width of the effective focal spot. Changes when you select a small filament versus the large filament. The smaller filament produces a smaller effective focal spot and the larger
What is meant by focal spot?
Focal spot is the area of the anode surface which receives the beam of electrons from the cathode. It is the apparent source of x-rays.
What is the actual focal spot controlled by?
Chapter 6 Study QuestionsQuestionAnswerWhich anodes have a greater heat-loading capacity?high-speed anodesWhat is the effective focal spot controlled by?--1.actual focal spot--2.target angleWhat is the actual focal spot controlled by?--1.filament size--2.angle of anode113 more rows
Where is actual focal spot located?
anodeThe actual focal spot is the area of the focal spot on the radiographic target (anode) as viewed at right angles to the plane of the target.
What does the actual focal spot size measure?
The actual dimension of the focal spot shall be determined as the value related to the Line Spread Function, measured at 15% of the peak value.
What are the types of focal spot?
In a usual x-ray tube, there are two focal spot sizes (large and small) and two directions of the focal spot (length: the focal spot size along the anode–cathode direction, width: the one along perpendicular to the anode–cathode direction).
Why fine or broad focal spots are used in radiography?
The point to having small and large focal spots in your x-ray tube is that it gives the machine the versatility to image something as small as a finger and something as large as the side of the lumbar spine.
Why small focal spot is used in mammography?
Focal Spots: The typical x-ray tube for mammography has two selectable focal spots. The spots are generally smaller than for other x-ray procedures because of the requirements for minimal blurring and good visibility of detail to see the small calcifications.
What is heel effect in radiology?
In radiography, the “heel effect” causes less X-ray fluence and higher mean radiation energy in the anode direction due to the absorption of low-energy photons by the anode heel [15]. The non-uniform distribution of X-ray fluence may result in non-uniform image quality, especially in the anode-cathode direction.
What is inverse square law in radiology?
The inverse square law in Radiography describes the fact that x-rays are divergent and spread out as they leave the focal spot like 1/R^2. To maintain constant exposure at the image receptor the inverse square law formula is: mAs_new = mAs * (SID_new/SID)^2, where SID is the source to image distance.
How is the actual focal spot affected by the position of the filament in the focusing Cup?
position of the filament in the focusing cup. the electric field created between the cathode and anode: focal spot enlarges as current increases due to the repulsion of adjacent electrons (blooming effect)
What is the advantage of a small effective focal spot?
"An X-ray tube with a smaller focal spot enables the operator to optimize setup to reduce exposure time or gain in image quality, or in most cases, accomplish both". "The focal spot of an X-ray tube is one of the most critical parameters when using X-rays for NDT applications.
How does focal spot size affect image quality?
The focal spot is the area on the anode in which x-rays are produced. This variable ONLY affects recorded detail. The smaller the focal spot, the sharper the recorded detail or the more recorded detail increases.
Does focal spot size affect magnification?
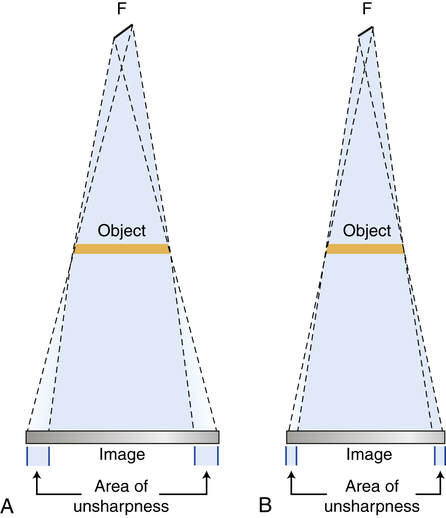
With decrease of the focal spot-object distance and/or increase of the object-film distance, both radiographic image and penumbra are magnified, but not in the same degree. The size of the penumbra is determined only by the relative distances involved and the focal spot size, and is independent of the size of object.
Effective focal spot | definition of effective focal spot by Medical ...
spot [spot] a circumscribed area or place, usually distinguished by its color; see also macula and tache. actual focal spot the section of a focal spot on which there is intersection of an electron beam with an anode of an x-ray tube. Bitot's s's foamy gray triangular spots of keratinized epithelium on the conjunctivae, a sign of vitamin A deficiency ...
Impact of focal spot size on radiologic image quality: A visual grading ...
The size of this penumbra can be characterized by psychophysical techniques such as line and edge spread functions.2, 3, 4 The importance of focal spot sizes on this penumbra and apparent direct relationship with visible image degradation is evidenced by the continuing effort by X-ray manufacturers to produce increasingly smaller X-ray foci. 5 On the other hand, to minimize X-ray tube damage ...
The larger the focal spot the greater the - Columbia University
The larger the focal spot the greater the penumbra and this detracts from the detail because the outline of the images become blurred. The size of the effective focal spot is a function of the angulation.
Relevance of the Focal Spot in High-Resolution CT - NDT
Relevance of the Focal Spot in High-Resolution CT Bärbel KRATZ1, Frank HEROLD1, Wilhelm NIEMANN1 1YXLON International GmbH, Essener Bogen 15, 22419 Hamburg, Germany Phone: +49 40 52729 764, e-mail: [email protected], [email protected],
Why is a large focal spot important?
A large focal spot is therefore useful to protect the tungsten target as the heat accumulates and dissipates within the area of focal spot. However, a small focal spot is required to achieve good radiographic image quality. Thus the line focus principle helps resolve this issue by stating that angulation of the anode surface will result in an ...
What is the focal spot of an electron beam?
The focal spot is the area of the target upon which the electron beam impinges. The energy of the electrons in the electron beam is mostly converted into heat (approximately 99%, which is why materials such as tungsten are used due to their high melting-points) and dissipated uniformly across the focal spot and anode surface.
How to determine focal spot size?
The apparent focal spot (projected focal spot) size can be determined by the sine of the angle of the anode surface (apparent focal spot size = real focal spot size * sin anode angle). The angle varies as per tube design with a range value of 6 degrees to about 20 degrees.
What is the focal track of an anode?
Focal Track: The portion of the anode where the high-voltage electron stream will impact. When discussing a rotating anode this describes the circular path that will be impacted by the electron beam
Why is the anode on the right rotating?
The anode on the right is a rotating anode because the anode rotates during an exposure. What are X-ray tubes typically immersed in to help with heat disipation. X-ray tubes are usually immersed in oil for electrical insulation and for aiding heat. dissipation by convection.
What is focal spot size?
Focal spot size is a result of the filament shape, focusing cup, and electric field cre-ated between the cathode and anode.
How is heat transferred from the focal spot?
Heat is transferred from the focal spot by RADIATION to the tube housing and CONDUCTION into the anode.
What is the angle of the focal spot?
The angle of the focal spot is one way to control the size of the effective focal spot. The larger the angle the larger the effective focal spot
What is the effective focal spot?
Note that the effective focal spot is the apparent source of X-rays FROM the tube.
Which side of the anode is the radiation intensity greater?
Due to the geometry of the angled anode target, the radiation intensity is greater on the cathode side.
What is the system blurring?
The system blurring is dependent upon the size of the focal spot, and the system geometry. The unsharpness (U) due to the penumbra is U=f*OID/SOD, where OID is the object to image distance and SOD is the source to object distance. Thus the unsharpness in the image directly relates to f (focal spot size) and the ratio of the object to image distance divided by the source to object distance.
What are the different types of radiography?
At a high level these clinical radiography scenarios have a low magnification as it is typically desirable to have the detector fairly close to the patient: 1 Chest Radiography 2 Mammography 3 Abdominal Radiography
What is the blurring region of an x-ray?
That blurring region is typically called the penumbra of the x-ray beam, and the region that is fully blocked behind the object is termed the umbra.
What are geometric effects in x-ray radiography?
To conclude we have discussed geometric effects in x-ray radiography including magnification and rotation effects. These effects are similar to the example that we mentioned at the onset of making shadow puppets on the wall with your fingers. So, feel free to ‘study’ at home by making your own shadows on the wall and change the position and orientation of your fingers to see how it affects the projection on the wall.
Why does a magnified object appear larger on a x-ray?
By Brian Nett, PhD / Physics, X-Ray. Magnification occurs in x-ray imaging because the x-rays are divergent or spread out from the x-ray source. Therefore, the object will appear larger on the detector than the true object size. Magnification in radiography is defined as (Image Size/Object Size) and is equal to the ...
What is the magnification of an image?
The definition of the magnification is the relationship between the object plane and the image plane. The magnification is defines as the (Image Size)/ (Object Size). Since the x-rays are spreading out (i.e. diverging) the magnification will always be a number that is greater than 1 (i.e. the image size will always be larger than the object size).
Why is reading a radiograph so difficult?
There are several factors which make reading radiographs difficult including overlapping anatomy and difficulty distinguishing low contrast structures. Additionally, the dependence of the radiograph on the rotation of the objects makes image interpretation more challenging. As you can see from the figure if two objects are rotated, they could project either the same or very differently depending on the direction of the rotation.
What is the electric field created between the cathode and anode?
the electric field created between the cathode and anode: focal spot enlarges as current increases due to the repulsion of adjacent electrons (blooming effect)
What is the focal spot of an anode?
Focal spot is the area of the anode surface which receives the beam of electrons from the cathode. It is the apparent source of x-rays .
What determines the size of an electron beam?
Size and shape of the electron beam is determined by: To produce sharp images, focal spots need to be small but able to withstand heat loading without melting the anode target. A small focal spot is used when spatial resolution is important, while a large focal spot is employed when a short exposure time is the priority.
Why are focal spots important?
To produce sharp images, focal spots need to be small but able to withstand heat loading without melting the anode target. A small focal spot is used when spatial resolution is important, while a large focal spot is employed when a short exposure time is the priority. The focal spot sizes commonly employed are: