What does the ADA2 gene do?
The ADA2 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called adenosine deaminase 2. This enzyme breaks down molecules called adenosine and 2'-deoxyadenosine. Because this enzyme functions in the spaces between cells, it is described as extracellular.
What chromosome is adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency on?
The enzyme adenosine deaminase is encoded by a gene on chromosome 20 . ADA deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 20 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent)...
What is the function of ADA enzyme?
Adenosine deaminase (also known as adenosine aminohydrolase, or ADA) is an enzyme ( EC 3.5.4.4) involved in purine metabolism. It is needed for the breakdown of adenosine from food and for the turnover of nucleic acids in tissues. Its primary function in humans is the development and maintenance of the immune system.
Is ADA genetic or autosomal recessive?
Genetics. ADA deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 20 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder.

What does ADA gene stand for?
The ADA gene makes an enzyme called adenosine deaminase, which helps protect lymphocytes from harmful substances in the body. Also called adenosine deaminase-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency.
What is ADA gene mutation?
Mutations in the ADA gene reduce or eliminate the activity of adenosine deaminase and allow the buildup of deoxyadenosine to levels that are toxic to lymphocytes. Immature lymphocytes in the thymus are particularly vulnerable to a toxic buildup of deoxyadenosine.
What is the ADA enzyme?
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is an enzyme of the purine metabolism which catalyzes the irreversible deamination of adenosine and deoxyadenosine to inosine and deoxyinosine, respectively. This ubiquitous enzyme has been found in a wide variety of microorganisms, plants, and invertebrates.
How do you cure ADA?
Although it doesn't cure the disease, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) may help your immune system work better and prevent infections. In this therapy, you get injections of healthy enzymes, usually from a cow. The only way to cure ADA-SCID is with a stem cell transplant.
How is ADA deficiency inherited?
ADA deficiency is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 20 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder.
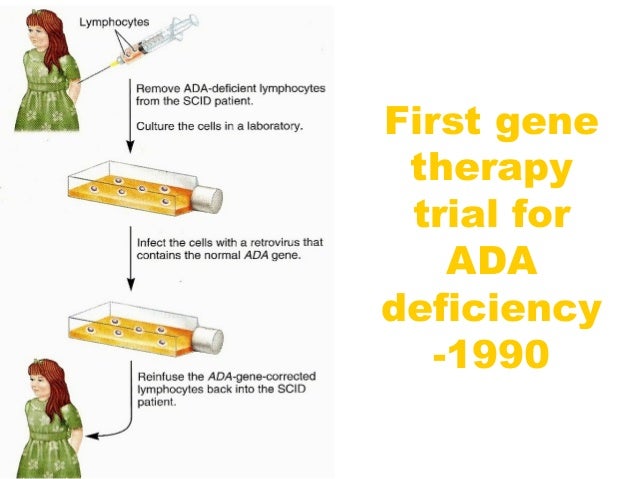
How does ADA deficiency cure gene therapy?
Treatment includes gene therapy. In this, lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in a culture in vitro. A functional ADA cDNA is introduced into these lymphocytes using a retroviral vector. These lymphocytes are introduced back into the patient.
How is ADA deficiency diagnosed?
Diagnosis. Diagnosis of ADA-deficiency is established by biochemical and molecular genetic testing. Biochemical testing demonstrates absent or greatly reduced ADA activity (< 1% of normal) and marked elevation of the metabolite dATP or total dAdo nucleotides (the sum of dAMP, dADP and dATP) in erythrocytes.
What is ADA in blood?
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is a protein that is produced by cells throughout the body and is associated with the activation of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that plays a role in the immune response to infections.
What type of mutation is ADA deficiency?
Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease, due to mutations of ADA gene, the purine salvage enzyme, located on chromosome 20q12-q13.
Why is ADA High in TB?
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) has been developed and widely used for the diagnosis of TB. ADA is an enzyme that increases in TB because of the stimulation of T-cell lymphocytes by mycobacterial antigens.
What is ADA in blood?
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) is a protein that is produced by cells throughout the body and is associated with the activation of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that plays a role in the immune response to infections.
What is meant by ADA deficiency How is gene therapy a solution to this problem?
Children with ADA deficiency are cured by bone marrow transplantation or enzyme replacement therapy where ADA is given by injection. By using gene therapy techniques Iymphocytes are taken from the patients bone marrow and the normal gene for ADA is introduced into the lymphocytes using retrovirus.
Which genotype has lower ADA1 activity?
activity of ADA isoenzymes and distribution of ADA1 G22 A genotypes were different among fertile and infertile men and more likely the GA genotype, which had lower ADA1 activity and was higher in fertile men is a protective factor against infertility.
What is ADA in HIV?
diagnostic value of serum adenosine deaminase (ADA) activity as a useful tool to differentiate HIV mono- and co-infection, was investigated.
What is the mechanism that decreases the level of adenosine?
Adenosine deaminases ADA1 and ADA2 (ADAs) decrease the level of adenosine by converting it to inosine, which serves as a negative feedback mechanism. These results suggest the existence of a new mechanism, where the activation and survival of immune cells is regulated through the activities of ADA2 or ADA1 anchored to the cell surface.
What is adenosine deaminase used for?
Suggest that adenosine deaminase can be used to distinguish between tuberculous and malignant pleural effusions. the primary mechanism in men with ischemic stroke might involve the reduction of ADA1 activity. Observational study of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction.
What are the neurological alterations in Adenosine Deaminase?
These included motor dysfunction, EEG alterations, sensorineural hypoacusia, white matter and ventricular alterations in MRI as well as a low mental development index or IQ.
What is the role of EADA in vascular protection?
Inhibition of eADA blocked endothelial activation suggesting a crucial role of this enzyme in the control of vascular inflammation. This supports the concept of eADA targeted vascular protection therapy
Is ADA higher in schizophrenia?
ADA levels were found to be higher among patients, and revealed a possible link between evening rise and severity of auditory hallucinations as well as morning rise and severity of avolition-apathy in patients with schizophrenia.
What is the ADA gene?
This gene encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of adenosine to inosine in the purine catabolic pathway. Various mutations have been described for this gene and have been linked to human diseases related to impaired immune function such as severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) which is the result of a deficiency in the ADA enzyme. In ADA-deficient individuals there is a marked depletion of T, B, and NK lymphocytes, and consequently, a lack of both humoral and cellular immunity. Conversely, elevated levels of this enzyme are associated with congenital hemolytic anemia. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2019]
What is adenosine deaminase?
Adenosine Deaminase as a Biomarker of Tenofovir Mediated Inflammation in Naive HIV Patients.
How many tissues are there in RNA-seq?
Description: RNA-seq was performed of tissue samples from 95 human individuals representing 27 different tissues in order to determine tissue-specificity of all protein-coding genes
Does ADA increase polycystic ovary syndrome?
ADA levels were found to be increased in polycystic ovary syndrome patients compared to controls.
What is the function of ADA2?
Normal Function. The ADA2 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called adenosine deaminase 2. This enzyme breaks down molecules called adenosine and 2'-deoxyadenosine. Because this enzyme functions in the spaces between cells, it is described as extracellular.
What is the other form of adenosine deaminase?
Another form of the enzyme, adenosine deaminase 1, breaks down the same molecules inside cells. This other version of the enzyme is produced from the ADA gene. Researchers are still working to determine the functions of adenosine deaminase 2.
Where is the genetics home reference?
Genetics Home Reference has merged with MedlinePlus. Genetics Home Reference content now can be found in the "Genetics" section of MedlinePlus. Learn more
Where is ADA1 found?
ADA1 is found in most body cells, particularly lymphocytes and macrophages, where it is present not only in the cytosol and nucleus but also as the ecto- form on the cell membrane attached to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (aka, CD26). ADA1 is involved mostly in intracellular activity, and exists both in small form (monomer) and large form (dimer).
What is the active site of the ADA?
The ADA active site contains a zinc ion, which is located in the deepest recess of the active site and coordinated by five atoms from His15, His17, His214, Asp295, and the substrate. Zinc is the only cofactor necessary for activity.
What is the hydrogen bond between ribose and Asp19?
The 3'-OH of the substrate ribose forms a hydrogen bond with Asp19, while the 5'-OH forms a hydrogen bond with His17. Two further hydrogen bonds are formed to water molecules, at the opening of the active site, by the 2'-OH and 3'-OH of the substrate.
How many helices are in the ADA?
In addition to the eight central β-barrels and eight peripheral α-helices, ADA also contains five additional helices: residues 19-76 fold into three helices, located between β1 and α1 folds; and two antiparallel carboxy-terminal helices are located across the amino-terminal of the β-barrel.
What causes adenosine deaminase to not be expressed?
Some mutations in the gene for adenosine deaminase cause it not to be expressed. The resulting deficiency is one cause of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), particularly of autosomal recessive inheritance. Deficient levels of ADA have also been associated with pulmonary inflammation, thymic cell death, and defective T-cell receptor signaling.
What enzyme deaminates adenosine?
Adenosine. Inosine. Inosine can then be deribosylated (removed from ribose) by another enzyme called purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP), converting it to hypoxanthine .
How many hydrogen bonds are there between adenosine and Glu217?
The substrate, adenosine, is stabilized and bound to the active site by nine hydrogen bonds. The carboxyl group of Glu217, roughly coplanar with the substrate purine ring, is in position to form a hydrogen bond with N1 of the substrate.
What is ADA deficiency?
Adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA deficiency) is an inherited condition that damages the immune system and is a common cause of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). People with SCID due to ADA deficiency are unable to fight off most types of infections, including bacterial, viral and fungal infections.
How is ADA deficiency caused?
ADA deficiency is caused by mutations in the ADA gene and is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [1] [2] Diagnosis may be suspected by newborn screening or symptoms and confirmed by blood and genetic test results.
When does adenosine deaminase deficiency start?
The symptoms of adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA deficiency) usually begin before 6 months of age. [1] [2] Babies with ADA deficiency usually develop serious lung infections and chronic diarrhea. They have trouble gaining weight and do not grow very well.
How early can you tell if you have ADA?
[2] [4] Approximately 10-15% of people with ADA deficiency do not develop symptoms until later in childhood, often between ages 1 and 10, or even into adulthood.
What are the early symptoms of ADA?
The earliest symptoms of ADA deficiency include pneumonia, chronic diarrhea, widespread skin rashes, slowed growth, and/or developmental delay. Some people with ADA deficiency will develop symptoms later in life. The symptoms in the late-onset form are typically milder than in the form that occurs in infancy.
What is related disease?
Related diseases are conditions that have similar signs and symptoms. A health care provider may consider these conditions in the table below when making a diagnosis. Please note that the table may not include all the possible conditions related to this disease.
Can ADA cause lung damage?
However, over time, people with the milder form of ADA deficiency may develop chronic lung damage, malnutrition, and other health problems. [1] [2] There are some people who have partial ADA deficiency. People with this condition have low amount of ADA enzyme in some cells, but have normal immune systems.
What are the genes that are associated with type 1 diabetes?
For example, most white people with type 1 diabetes have genes called HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4, which are linked to autoimmune disease. If you and your child are white and share these genes, your child's risk is higher.
What is the antibody test for diabetes?
An antibodies test can be done for children who have siblings with type 1 diabetes. This test measures antibodies to insulin, to islet cells in the pancreas or to an enzyme called glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). High levels can indicate that a child has a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Do white people have diabetes?
In most cases of type 1 diabetes, people need to inherit risk factors from both parents. We think these factors must be more common in white people because white people have the highest rate of type 1 diabetes. Because most people who are at risk do not get diabetes, researchers want to find out what the environmental triggers are.
Do twins have the same genes?
Identical twins have identical genes. Yet when one twin has type 1 diabetes, the other gets the disease, at most, only half the time. When one twin has type 2 diabetes, the other's risk is three in four at most.
Is type 2 diabetes genetic?
Type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes has a stronger link to family history and lineage than type 1, and studies of twins have shown that genetics play a very strong role in the development of type 2 diabetes. Race can also play a role. Yet it also depends on environmental factors.
When was the ADA gene discovered?
ADA deficiency was discovered in 1972 by Eloise Giblett, a professor at the University of Washington. The ADA gene was used as a marker for bone marrow transplants. A lack of ADA activity was discovered by Giblett in an immunocompromised transplant candidate.
What is ADA2 mutation?
Adenosine deaminase deficiency ( ADA deficiency) is a metabolic disorder that causes immunodeficiency. It is caused by mutations in the ADA gene.
How many copies of the defective gene do parents carry?
The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder. Age of onset and severity is related to some 29 known genotypes associated with the disorder.
What is ADA SCID?
ADA deficiency or ADA-SCID. Specialty. Immunology. Adenosine deaminase deficiency ( ADA deficiency) is a metabolic disorder that causes immunode ficiency. It is caused by mutations in the ADA gene. It accounts for about 10–15% of all cases of autosomal recessive forms of severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) among non- inbred populations.
How do you know if you have ADA deficiency?
Affected children also grow much more slowly than healthy children and some have developmental delay. Most individuals with ADA deficiency are diagnosed with SCID in the first 6 months of life.
When was gene therapy first used?
Gene therapy. In September 1990 , the first gene therapy to combat this disease was performed by Dr. William French Anderson on a four-year-old girl, Ashanti DeSilva, at the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A.
Where is the defective gene located?
This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 20 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder.
How many years ago did the Y chromosomes start?
And in a study detailed in March in the American Journal of Human Genetics, Hammer's group showed that several men in Africa have unique, divergent Y chromosomes that trace back to an even more ancient man who lived between 237,000 and 581,000 years ago.
Who is Tia from Wired?
Tia is the assistant managing editor and was previously a senior writer for Live Science. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Wired.com and other outlets. She holds a master's in bioengineering from the University of Washington, a graduate certificate in science writing from UC Santa Cruz and a bachelor's in mechanical engineering from the University of Texas at Austin. Tia was part of a team at the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel that published the Empty Cradles series on preterm births, which won multiple awards, including the 2012 Casey Medal for Meritorious Journalism.
How does the Y chromosome work?
The Y chromosome is passed down identically from father to son, so mutations, or point changes , in the male sex chromosome can trace the male line back to the father of all humans. By contrast, DNA from the mitochondria, the energy powerhouse of the cell, is carried inside the egg, so only women pass it on to their children.
Do gene studies always rely on DNA?
Gene studies always rely on a sample of DNA and, therefore, provide an incomplete picture of human history. For instance, Hammer's group sampled a different group of men than Bustamante's lab did, leading to different estimates of how old common ancestors really are.
Can DNA reveal the maternal lineage?
The DNA hidden inside mitochondria, therefore, can reveal the maternal lineage to an ancient Eve. But over time, the male chromosome gets bloated with duplicated, jumbled-up stretches of DNA, said study co-author Carlos Bustamante, a geneticist at Stanford University in California.
