What are the 5 steps of glycolysis?
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps Step 1: Hexokinase. Step 2: Phosphoglucose Isomerase. Step 3: Phosphofructokinase. Step 4: Aldolase. Step 5:
What is the ultimate end result of glycolysis?
What is the end result of glycolysis? Results of Glycolysis Glycolysis creates 2 ATP, 2 NADH, as well as 2 pyruvate particles: Glycolysis, or the cardiovascular catabolic failure of sugar, creates power in the kind of ATP, NADH, as well as pyruvate, which itself goes into the citric acid cycle to generate even more power.
How is glucose broken down in anaerobic respiration?
What is glucose broken down into during anaerobic respiration? Glycolysis breaks down glucose (6-C) into two molecules of pyruvate (3C) , and also produces: Hydrogen carriers (NADH) from an oxidised precursor (NAD + ) A small yield of ATP (net gain of 2 molecules)
How many ATP are needed to break glucose in glycolysis?
The Energy-Requiring Steps of Glycolysis. In the first half of glycolysis, energy in the form of two ATP molecules is required to transform glucose into two three-carbon molecules. The energy to split glucose is provided by two molecules of ATP.

What is the anaerobic energy system?
The Anaerobic System provides the body with explosive short term energy without the need for oxygen. Stored in the cells in the chemical adenosine triphosphate(ATP), the energy the anaerobic system delivers powers the working muscle cells when the blood is unable to provide them with oxygen quickly enough.
What are some examples of anaerobic glycolysis?
Examples of training that focus primarily on the anaerobic glycolytic system are:3 sets of 10 repetitions of any resistance exercise performed relatively slowly (5 seconds per rep) with 2.5 minutes rest between sets. ... Gym circuit class with 45 seconds on each station and 15 seconds rest to move to the next station.More items...
Why is it called anaerobic glycolysis?
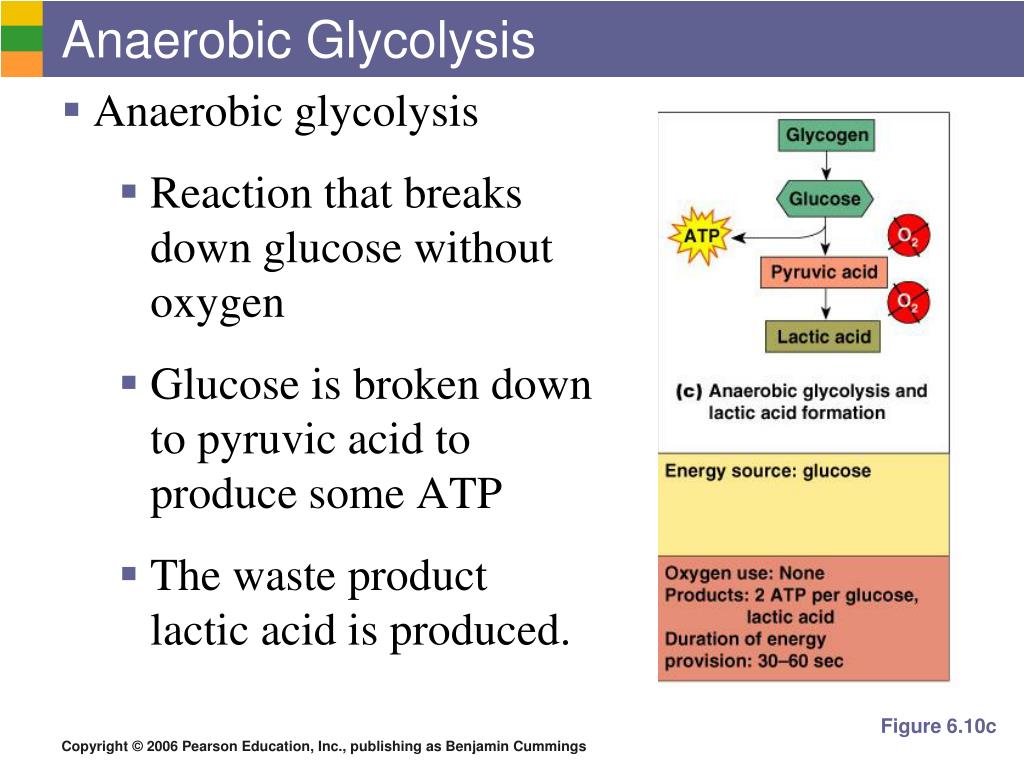
The conversion of glucose to lactate is known as anaerobic glycolysis, since it does not require oxygen.
What happens in the anaerobic system?
The anaerobic energy system (also called the lactic acid system) is the body's way of creating energy in the form of ATP quickly. Primarily using glucose as fuel, this energy system powers the muscles anywhere from ten to thirty seconds for intense efforts.
What's the difference between aerobic and anaerobic glycolysis?
Glycolysis via aerobic glycolysis occurs when oxygen and hydrogen atoms bond together to break down glucose, and facilitate an exchange of energy. Anaerobic glycolysis, on the other hand, occurs when glucose is broken down without the presence of oxygen.
What is the end product of anaerobic glycolysis?
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is assigned as the end-product of the pathway, while under anaerobic conditions, lactate is the end product.
How many ATP are produced in anaerobic glycolysis?
It is a method for rapidly transferring a huge amount of energy. Anaerobic glycolysis produces 2 ATP molecules.
What happens during anaerobic glycolysis quizlet?
During Anaerobic Glycolysis, lactate accumulates due to lack of oxygen.
What enzyme regulates anaerobic glycolysis?
Regulation of glycolysis Several steps in glycolysis are regulated, but the most important control point is the third step of the pathway, which is catalyzed by an enzyme called phosphofructokinase (PFK).
What is the main function of anaerobic respiration?
Definition. Anaerobic respiration is the type of respiration through which cells can break down sugars to generate energy in the absence of oxygen. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy.
What is the process of anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is when an athlete is exercising too vigorously there's not enough oxygen delivery into the muscle. So what happens is that the glucose is reacting and there's a by-product from that which is called lactic acid.
What is anaerobic respiration short answer?
Anaerobic respiration usually occurs in lower plants and microorganisms. In the absence of oxygen, the glucose derived from food is broken down into alcohol and carbon dioxide along with the production of energy. Further Reading: Fermentation: Anaerobic Respiration. Glucose → Alcohol + Carbon dioxide + Energy.
What are the examples of glycolytic system?
Glycolytic Pathway400-meter sprint.Lifting weights for short periods.Sports requiring quick bursts of speed, such as basketball.High-intensity interval training programs.
Is citric acid cycle aerobic or anaerobic?
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the Krebs or citric acid cycle, is the main source of energy for cells and an important part of aerobic respiration.
Which of the following is a common product of anaerobic metabolism?
Lactic acid is a by-product of anaerobic glycolysis and anaerobic metabolism, which occur during strenuous exercise.
What happens during anaerobic glycolysis quizlet?
During Anaerobic Glycolysis, lactate accumulates due to lack of oxygen.
What are the products of anaerobic glycolysis?
During high intensity exercise the products of anaerobic glycolysis namely pyruvate and H+ accumulate rapidly.
What are the steps of glycolysis?
Steps of the anaerobic glycolytic system: 1 Initially stored glycogen is converted to glucose. Glucose is then broken down by a series of enzymes. 2 2 ATP are used to fuel glycolysis and 4 are created so the body gains 2 ATP to use for muscular contraction. 3 The breakdown of glucose to synthesise ATP results in the creation of a substance called 'pyruvate' and hydrogen ions. The muscle becomes increasingly acidic as more hydrogen ions are created. 4 Because this system is ‘anaerobic’ there isn’t enough oxygen to break down pyruvate and synthesise anymore ATP.
Why is pyruvate binding with hydrogen ions?
Because this system is ‘anaerobic’ there isn’t enough oxygen to break down pyruvate and synthesise anymore ATP. This results in pyruvate binding with some of the hydrogen ions and converting them into a substance called lactate (completely different to 'lactic acid').
How is glucose broken down?
Glucose is then broken down by a series of enzymes. 2 ATP are used to fuel glycolysis and 4 are created so the body gains 2 ATP to use for muscular contraction. The breakdown of glucose to synthesise ATP results in the creation of a substance called 'pyruvate' and hydrogen ions. The muscle becomes increasingly acidic as more hydrogen ions are ...
What is the purpose of training the ATP system?
Training this system is aimed at increasing tolerance to lactate, the removal of lactate and improving the rate at which glycolysis produces ATP.
How many steps are involved in the glycolytic system?
There are four key steps involved in the anaerobic glycolytic system. However they take longer to be carried out compared to the steps in the ATP-PC system. This is why it doesn’t start working as quickly and as these steps are more complex than the ATP-PC system, energy isn't produced as quickly.
What is the breakdown of glucose?
Glycolysis simply means the breakdown (lysis) of glucose and consists of a series of chemical reactions that are controlled by enzymes.
What is the end product of the anaerobic glycolytic system?
If glucose is used, it generates 2 ATPs, while if glycogen is used, it forms 3 ATPs. The end product of this energy system is lactic acid.
How long does ATP last in the body?
This system provides ATP for up to 2 – 3 minutes. If exercise continues beyond 2 – 3 minutes, either the intensity of exercise should be decreased or the body would switch to aerobic systems to use oxygen to produce ATP.
How much ATP does anaerobic glycolysis produce?
Although anaerobic glycolysis produces only about 5% of the ATP provided during the catabolism of glucose, there are a number of reasons why it is necessary:
Which is more efficient, aerobic glycolysis or anaerobic glycolysis?
Aerobic glycolysis is more efficient; however, the price needed to maintain this system is high: it requires functional mitochondria, a functioning circulatory system with a constant oxygen supply, and the ability to eliminate carbon dioxide. It is used as the main supply of energy during sustained, dynamic forms of exercise such as walking, but if short bursts of energy are needed, the system is often overwhelmed and anaerobic glycolysis takes over.
How does lactate form during anaerobic glycolysis?
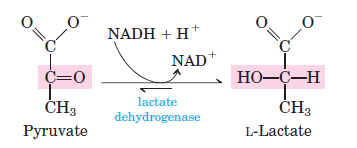
Lactate formed during anaerobic glycolysis enters the gluconeogenic pathway after oxidation to pyruvate by lactate dehydrogenase. After intense exercise, the lactate produced diffuses from the muscle into the blood and is taken up by the liver to be converted into glucose and glycogen.
How many protons are produced for every glucose molecule converted to lactate molecules by glycolysis?
Thus, two protons are produced for every glucose molecule converted to lactate molecules by glycolysis. Since glycolysis produces two ATPs per glucose, the equation seems incomplete, and in one sense it is incomplete. Expanding the equation to include ADP, Pi, and ATP in their predominant ionization states at physiological pH yields
What is the main metabolic pathway used in the setting of limited oxygen supply during exercise?
Anaerobic glycolysis is the main metabolic pathway used in the setting of limited oxygen supply during exercise. It is used during high-intensity, sustained, isometric muscle activity.1 It is inefficient from an energetic standpoint and produces only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule, which is 19 times less than the full energy potential of a glucose molecule. Despite its inefficiency, it is a rapid process, approximately 100 times faster than oxidative phosphorylation. The final step in the pathway is conversion of pyruvate to lactate, which leads to accumulation of lactic acid.
Which enzyme is responsible for supplying the cell with both ATP and nicotinamide adenine?
Anaerobic glycolysis is the main pathway responsible for supplying the cell with both ATP and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced) (NADH), a cofactor for methaemoglobin reductase, the enzyme that catalyses the reduction of methaemoglobin to functional haemoglobin (see Fig. 27.2).
What is the process of producing ATP?
ATP can also be produced by the adenylate kinase reaction , which catalyzes the conversion of two adenosine diphosphate (ADP) molecules into one ATP and one adenosine monophosphate (AMP); however its clinical significance is limited.
How does anaerobic glycolysis produce ATP?
In poorly oxygenated tissue, glycolysis produces 2 ATP by shunting pyruvate away from mitochondria and through the lactate dehydrogenase reaction .[1] In rapidly contracting skeletal muscle cells with energy demand exceeding what can be produced by oxidative phosphorylation alone, anaerobic glycolysis allows for the more rapid production of ATP.[3] ( Glycolysis is approximately 100 times faster than oxidative phosphorylation.) In cells lacking mitochondria altogether, pyruvate cannot undergo oxidative phosphorylation regardless of oxygen levels.
How does glycolysis work?
The steps of glycolysis are as follows: 1 Glucose gets phosphorylated by hexokinase, forming glucose-6-phosphate. This step requires one molecule of ATP. 2 Glucose-6-phosphate is isomerized by phosphoglucose isomeraseto form fructose-6-phosphate. 3 Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated by phosphofructokinaseto form fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. This step requires one molecule of ATP. 4 Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is split into two separate sugar molecules, dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, by aldolase. 5 The molecule of dihydroxyacetone phosphate is isomerized by triosephosphate isomeraseto form a second glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. 6 Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is phosphorylated by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenaseto form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. This step requires NAD+ as a cofactor. 7 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is converted to 3-phosphoglycerate by phosphoglycerate kinase. This step involves the transfer of a phosphate molecule to ADP to form 1 molecule of ATP. 8 3-phosphoglycerate rearranges to form 2-phosphoglycerate by the enzyme phosphoglycerate mutase. 9 2-phosphoglycerate is dehydrated to produce phosphoenolpyruvate by the enzyme enolase. 10 Phosphoenolpyruvate is converted to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase. This step involves the transfer of a phosphate molecule to ADP to form 1 molecule of ATP.
What is the process of glycolysis in erythrocytes?
In erythrocytes and oxygen-deprived tissue, pyruvate remains within the cytoplasm and converts to lactate, a process referred to as anaerobic glycolysis. This final reaction allows for the regeneration of NAD+, a cofactor that must be available in high enough intracellular concentrations for the earlier reactions of glycolysis to remain favorable. Compared to oxidative phosphorylation, however, anaerobic glycolysis is significantly less efficient, providing a net production of only 2 ATP per glucose molecule (versus 32 ATP per glucose molecule produced during oxidative phosphorylation). [1]
What is the process of breaking down glucose into ATP?
Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is broken down within the cytoplasm of a cell to form pyruvate. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate can diffuse into mitochondria, where it enters the citric acid cycle and generates reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and FADH2. These reducing equivalents then enter the electron transport chain, leading to the production of 32 ATP per molecule of glucose. Because the electron transport chain requires oxygen as the final electron acceptor, inadequate tissue oxygenation inhibits the process of oxidative phosphorylation.
What enzyme converts pyruvate to lactate?
Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate has a different fate. Instead of entering mitochondria, the cytosolic enzyme lactate dehydrogenaseconverts pyruvate to lactate. Although lactate itself is not utilized by the cell as a direct energy source, this reaction also allows for the regeneration of NAD+ from NADH.
Why do cancerous cells shift away from oxidative metabolism?
To combat the inadequate tissue perfusion and oxygenation, cancerous cells shift away from oxidative metabolism and instead rely heavily on anaerobic glycolysis. [9] Fibromyalgia:Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain condition characterized by diffuse tender points on the body in the absence of abnormal diagnostic testing.
How much ATP does glycolysis produce?
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP per glucose molecule, and thus provides a direct means of producing energy in the absence of oxygen. This process of breaking down glucose in the absence of oxygen is aptly named anaerobic glycolysis. [1]
Anaerobic Glycolysis
As mentioned in The Aerobic System Part 1 blog, before glucose or glycogen can be used to create energy, they must first be converted to a compound known as glucose-6-phosphate. Technically glycolysis starts once this compound has been made.
The Low Down on Lactate
Lactate has been scrutinised and incorrectly accused of many things over the years, but mainly for causing the burning sensation in your muscles that causes you to slow down or stop what you’re doing.
Save your Avocados
This is where the same physiological mechanisms can be used to preserve your food. As we now know from The Aerobic System Part 1, fats go through aerobic metabolism inside the body. They also go through aerobic metabolism outside the body; this is why an avocado will turn brown and rot once cut open and exposed to oxygen.
Lactate Threshold
The lactate threshold, also known as the anaerobic threshold, is essentially the tipping point where the anaerobic processes begin to overwhelm the aerobic system’s ability to produce energy and buffer by-products, and thus lactate begins to accumulate.
What is the energy produced by glycolysis?
Energy is produced from the breakdown of carbohydrates, namely muscle glycogen and blood glucose. The anaerobic release of energy through glycolysis results in the production of lactic acid (lactate and hydrogen irons) this is occurring when a person starts to feel fatigue in their muscles.
What is the lactic acid system?
Also referred to as the lactic acid system, this system is the predominate system for athletes in short duration high intensity events such as the 400M sprint and speed skating. It is able to resynthesize ATP at a fast rate and is rapidly active at the start of intense exercise. It is generally accepted that the lactic acid system will be ...
What is the difference between fast and slow glycolysis?
As its name would suggest the fast glycolytic system can produce energy at a greater rate than slow glycolysis- it has greater power. However, because the end product of fast glycolysis is lactic acid, it can quickly accumulate and is thought to lead to muscular fatigue (1). The contribution of the fast glycolytic system increases rapidly after the initial 10 seconds of exercise. This also coincides with a drop in maximal power output as the immediately available phosphogens, ATP and especially PCr begin to run out. By about 30 seconds of sustained activity the majority of energy comes from fast glycolysis (2). At 45 seconds of sustained activity there is a second decline in power output (the first decline being after about 10 seconds). Activity beyond this point corresponds with a growing reliance on the oxidative energy system.
How many sessions are there in the glycolytic system?
Below the Introduction (technical explanation), we offer 7 sessions (in 3 stages) for training the Glycolytic System.
Does glycolysis cause muscle fatigue?
However, because the end product of fast glycolysis is lactic acid, it can quickly accumulate and is thought to lead to muscular fatigue (1). The contribution of the fast glycolytic system increases rapidly after the initial 10 seconds of exercise.
Is glycolysis anaerobic or aerobic?
Traditionally, if the final product was lactic acid, the process was labelled anaerobic glycolysis and if the final product remained as pyruvate the process was labelled aerobic glycolysis. Oxygen availability only determines the fate of the end product and is not required for the actual process of glycolysis itself.
Does training increase monocarboxylate transporters?
This type of training which creates high levels of intramuscular levels of lactate and pyruvate (monocarboxylates) has also been shown to increase the concentration of monocarboxylate transporters in the muscle.
What is the anaerobic system?
The anaerobic system is creating energy quickly, and then the aerobic system takes over producing energy and clearing lactate. When you are riding, you’ll use the anaerobic system rolling out of the parking lot and resuming your ride from a stop sign.
How to train anaerobic energy?
How to Train the Anaerobic Energy System. Training the anaerobic system for cycling is fairly straightforward—complete high-intensity intervals. However, aerobic fitness levels play an essential role. Aerobic fitness serves as the foundation for the anaerobic system, which is why base training is vital.
How is aerobic capacity measured?
While aerobic capacity is usually measured in terms of VO2 max, anaerobic capacity is measured in power output during a thirty-second sprint test. Alongside capacity, another important metric is repeatability—how many times you can repeat a hard effort. Both are crucial for performance. The good news that you can increase both your power output and repeatability with the right training.
Why is aerobic fitness important?
Aerobic fitness serves as the foundation for the anaerobic system, which is why base training is vital. Not only will your anaerobic power be higher, but so will your glycogen storage , which is the fuel for anaerobic efforts.
What energy system do cyclists use?
Cyclists use the anaerobic energy system quite often in a ride. It is important to remember that all three of your energy systems are active to some degree. However, it can help to think of the anaerobic system with three different applications, starting, sprinting, and threshold.
What is the most important byproduct of the Krebs cycle?
The most important byproduct of this process is lactate . Some of the excess lac tate enters the Krebs cycle for aerobic respiration, and the rest is cleared via the bloodstream. As your effort becomes more intense, the amount of lactate eventually outpaces the body’s ability to use and clear it. This balance point is referred to as Lactate Threshold .
Why is lactate limited in anaerobic energy?
Even though this energy system produces energy rapidly, because of anaerobic byproducts, it is limited due to the excess byproducts. A custom training plan, automatically built for your goals. Try Plan Builder. The most important byproduct of this process is lactate.