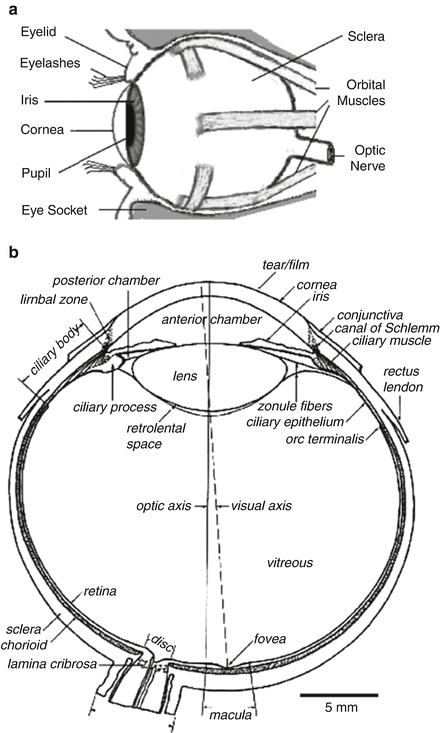
Anatomy of the eye. The eye is surrounded by the orbital bones and is cushioned by pads of fat within the orbital socket. Extraocular muscles help move the eye in different directions. Nerve signals that contain visual information are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain.
What is the normal anatomy of the eye?
- The anterior chamber is the fluid-filled space between the iris and the cornea.
- The anterior chamber angle is the angle between the iris and the cornea where they join the sclera towards the outside of the eye.
- The trabecular meshwork is situated in the apex of the anterior chamber angle and is the main outflow route for aqueous humour.
What to expect in anatomy and physiology?
Upon successful completion of this course, students will:
- Use anatomical terminology to identify and describe locations of major organs of each system covered.
- Explain interrelationships among molecular, cellular, tissue, and organ functions in each system.
- Describe the interdependency and interactions of the systems.
- Explain contributions of organs and systems to the maintenance of homeostasis.
What are the parts and functions of the eye?
The internal components of the eye include:
- Lens
- Retina
- Aqueous humour
- Optic nerve
- Vitreous humour
How do I study for anatomy and physiology?
Study Past Anatomy And Physiology Exams. Past test time, take advantage of the test itself and use it to prep you for the next, regardless of your score. Go back over the entire test paying extra attention to what challenged you most. Use the questions for your future practice sessions and keep an eye on the upcoming material that may trick you ...

What is the biconvex structure of the lens?
Biconvex means that the lens is curved on both sides.
What is the cornea?
The cornea itself is a transparent, dome shaped clear layer that covers the iris and the pupil. It allows light to enter the eye, and its curved shape helps focus light on the retina in the back of the eye.
Which ligaments attach to the lens?
The ciliary processes connect to suspensory ligaments which attach directly to the lens and hold the lens in place behind the iris as well as help it change shape.
What color are melanin eyes?
People with a high concentration of melanin have dark brown eyes, those with medium amounts have green eyes, and people with low concentrations of melanin have blue eyes.
What is the sclera?
The sclera is like a wall that’s built around the eye, that only has a tiny opening at the back to let the optic nerve through.
Which layer of the sclera contains the two structures?
The outer fibrous layer contains two main structures: the sclera and the cornea.
How do eyes help us visualize?
Our eyes allow us to visualize the world around us. They do this by converting light waves into neural signals so that our brains can process them.
What is the membrane that covers the sclera?
The conjunctiva is the membrane covering the sclera (white portion of your eye). The conjunctiva also covers the interior of your eyelids.
What is the white part of the eye?
The sclera is sometimes known as the "whites" of the eye. It covers more than 80% of the eyeball's surface. 2
What is the episclera?
The episclera is a thin layer of tissue that lies on top of the sclera. The episclera has tiny blood vessels that supply the sclera with nutrients.
How many fibers are in the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is a bundle of about 1.2 million nerve fibers that transmit visual information to the central nervous system (brain). 7
How do eyes work?
The eyes work in the same way as cameras. When you focus on an object, light is reflected and enters the eye through the cornea. As the light passes through, the dome-shaped nature of the cornea bends light , enabling the eye to focus on fine details.
Where are light rays focused?
Light rays are focused on the macula lutea when an eye is looking directly at an object.
How many muscles are there in the eye?
The eye has six muscles. These muscles arise from the eye socket (orbit) and work to move the eye up and down, side to side, or in a circular motion.
Why is the cornea important?
Much like a camera lens, the cornea helps to focus light coming into the eye onto the retina. The cornea is also full of nerves that alert us to irritations that could potentially harm our vision and eye health. And the cornea is susceptible to injury.
What is the iris?
The iris is part of the uveal tract—the middle layer of the wall of the eye. The uveal tract includes the ciliary body, the structure in the eye that releases a clear liquid called the aqueous humor. Iris color depends on the amount of melanin pigment in the iris.
What is the structure of the eye that helps to focus light?
Cornea. The cornea is the transparent, dome-like structure on the front part of the eye. It gives the eye two-thirds of its focusing or refracting power. One-third is produced by the internal crystalline lens. Much like a camera lens, the cornea helps to focus light coming into the eye onto the retina.
Why does my eye look red?
It also keeps the eye in a rounded shape. Scleritis is an inflammation of the sclera. It can cause intense eye pain, redness, and loss of vision for some people. It can also be associated with trauma or infection—more than half of scleritis cases are associated with an underlying systemic disease.
What happens when you pull your eye?
If the force of the pulling becomes strong enough, the vitreous humor may actually separate from the retina. This is called a posterior vitreous detachment, as it normally occurs at the back (posterior) of the eye. If this happens suddenly and with a shower of flashes, it could indicate that it has caused a retinal tear, and it is important to have this evaluated immediately.
What is the jelly-like substance that fills the inside of the eye?
The vitreous humor , which lies against the retina, makes up a large part of the eye. It is a jelly-like substance that fills the inside of the eye. Made mostly of water, the vitreous fluid gives the eye its shape. It is composed of water, collagen, and proteins and contains cells that help to maintain its clarity.
What is the structure of the eye that allows the eye to focus on objects?
The crystalline lens is a transparent structure in the eye—suspended immediately behind the iris—that brings rays of light to a focus on the retina. Small muscles attached to the lens can make it change shape which allows the eye to focus on near or far objects.
How does the retina work?
The retina acts like the film in a camera to create an image. When focused light strikes the retina, chemical reactions occur within specialized layers of cells. These chemical reactions cause electrical signals, which are transmitted through nerve cells into the optic nerve, which carries these signals to the brain, where the electrical signals are converted into recognizable images. Visual association areas of the brain further process the signals to make them understandable within the correct context.
Where is the anterior chamber angle located?
Anterior Chamber Angle and Trabecular Meshwork. The anterior chamber angle and the trabecular meshwork are located where the cornea meets the iris. The trabecular meshwork is important because it is the area where the aqueous humor drains out of the eye.
How many extraocular muscles are there in the eye?
Six extraocular muscles are attached to each eye to move the eye left and right, up and down, and diagonally, or even around in circles when one wishes.
What part of the eye is the white part?
The white part of the eye that one sees when looking at oneself in the mirror is the front part of the sclera. However, the sclera, a tough, leather-like tissue, also extends around the eye. Just like an eggshell surrounds an egg and gives an egg its shape, the sclera surrounds the eye and gives the eye its shape.
What do eyelashes do?
The eyelashes help filter out foreign matter, including dust and debris, and prevent these from getting into the eye.
How much of the information we receive about the world around us is visual?
More than 75% of the information we receive about the world around us consists of visual information. The eye is often compared to a camera. Each gathers light and then transforms that light into a "picture.". Both also have lenses to focus the incoming light. Just as a camera focuses light onto the film to create a picture, ...
What is the orbit of the eye?
The orbit is the bony eye socket of the skull. The orbit is formed by the cheekbone, the forehead, the temple, and the side of the nose. The eye is cushioned within the orbit by pads of fat. In addition to the eyeball itself, the orbit contains the muscles that move the eye, blood vessels, and nerves.
How many times do your eyes move a day?
Image from Human Anatomy Atlas. Did you know that your eyes move over 100,000 times a day? The extraocular muscles are the busiest skeletal muscles in your body. The extraocular muscles are a subgroup of muscles in the head region that act to move the eyes.
Which lobe of the brain is the visual processing center?
The final leg of the visual journey, so to speak, ends on the completely opposite side from where it began. The occipital lobe is the posteriormost lobe of the cerebrum, and within it is the visual cortex. The primary visual processing center is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe.
Which muscle abducts and moves the eye laterally?
Superior oblique. Medially rotates the eye (intorsion) Inferior oblique. Laterally rotates the eye (extorsion) The extraocular muscles , with the exception of the lateral rectus and superior oblique, are innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III).
Which muscle is innervated by the oculomotor nerve?
They are: the superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, superior oblique, and inferior oblique. The extraocular muscles, with the exception of the lateral rectus and superior oblique, are innervated by the oculomotor nerve (CN III). The lateral rectus is innervated by the abducens ...
What are the orbits of the skull?
Orbits (Eyesockets) Like most structures in the body, the orbits of the skull do more than one job. The orbits, or eye sockets as they're more commonly known, give shape to the forehead and eyebrows. They also protect the eyes. The orbits are made up of the frontal, maxilla, lacrimal, zygomatic, palatine, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones.
What is an example of visualization?
You open your eyes and see the world, but are you conscious of the fact that you are doing so? You saw a link, clicked on it, and now you're reading this blog post. Hello, reader. I like your shirt. Your hair looks really good, too. That you've interpreted what you just saw and have taken it as a compliment is an example of visualization, a.k.a. "Hurrah! You can see things."
Which nerve is passing through the posterior of the eyeball and into the brain?
Image from Human Anatomy Atlas. Passing through the posterior of the eyeball and into the brain is the optic nerve (CN II), a sensory nerve, which continues into the optic chiasm. When you visualize the world, the two hemispheres of the brain receive different input: the right side of the brain receives visual information from the left side ...
