
Explore
What are the 3 parts of a neuron?
- Sensory neurons.
- Motor neurons.
- Interneurons.
- Neurons in the brain.
What are the three main parts of a neuron?
- Dendrites (which contain receptors that interprets signals from other neurons)
- Axons
- Axon terminals
- Soma
What are the parts of neuron and their functions?
The nervous system subdivides into the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of everything else. The central nervous system's responsibilities include receiving, processing, and responding to sensory information.
What is the anatomy and physiology of the nervous system?
What part of neuron is sometimes myelinated? Axon. The axon is the elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal. The larger the diameter of the axon, the faster it transmits information. Some axons are covered with a fatty substance called myelin that acts as an insulator.
What part of the neuron is sometimes myelinated?
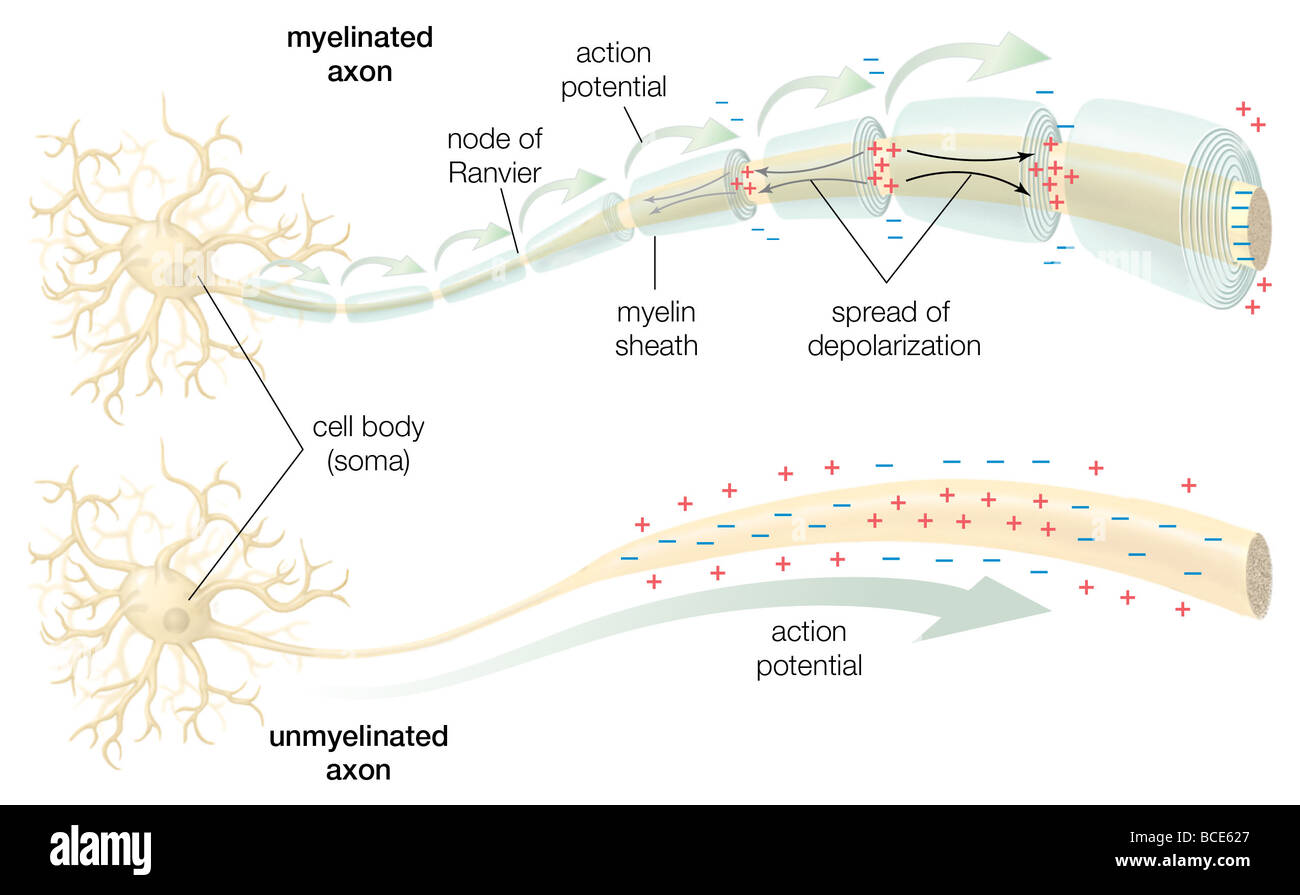
What are the 7 parts of a neuron?
Parts of a NeuronDendrites. Dendrites are the tree-root-shaped part of the neuron which are usually shorter and more numerous than axons. ... Soma (Cell Body) The soma, or cell body, is essentially the core of the neuron. ... Axon. ... Myelin Sheath. ... Axon Terminals.
What is neuron structure and function?
Nervous system cells are called neurons. They have three distinct parts, including a cell body, axon, and dendrites. These parts help them to send and receive chemical and electrical signals.
What are the major 4 parts of the neuron?
A neuron has 4 basic parts: the dendrites, the cell body (also called the "soma"), the axon and the axon terminal.
What are the 3 parts of the neuron?
Each neuron has three basic parts: cell body (soma), one or more dendrites, and a single axon.Cell Body. In many ways, the cell body is similar to other types of cells. ... Dendrites. Dendrites and axons are cytoplasmic extensions, or processes, that project from the cell body. ... Axon.
What are the 3 major functions of a neuron?
The basic functions of a neuron These are to: Receive signals (or information). Integrate incoming signals (to determine whether or not the information should be passed along). Communicate signals to target cells (other neurons or muscles or glands).
What are the 5 function of neuron?
Conduction of Nerve Impulses 2. Ion Gradients across the Membrane 3. Initiation of the Action Potential 4. Conduction of the Action Potential 5.
What are the 5 structures of a neuron?
Following are the different parts of a neuron:Dendrites. These are branch-like structures that receive messages from other neurons and allow the transmission of messages to the cell body.Cell Body. ... Axon. ... Synapse.
What are the 8 parts of neuron?
Structure of a neuronNucleus. It is the central part of the neuron. ... Dendrites. Dendrites are the “arms of the neuron”, they form branch extensions that come out of different parts of the neuron. ... Cell body. This is the part of the neuron that includes the nucleus. ... Glial cells. ... Myelin. ... Axon terminal. ... Node of Ranvier. ... Axon.
What are the six parts of the neuron?
Terms in this set (6)Soma. body of neuron; responsible for health of neuron and speed of signal.Dendrites. input of neurons; receive electric signals.Axon. Longest part of the neuron; carrier; highway for signal.myelin sheath. layer of fat that wraps axon; protects and speeds up signal.neural impulse. ... terminal branches.
What are types of neurons?
For the spinal cord though, we can say that there are three types of neurons: sensory, motor, and interneurons.Sensory neurons. ... Motor neurons. ... Interneurons. ... Neurons in the brain.
What are the four main parts of a neuron quizlet?
Terms in this set (4)input zone. receives info from other cells through dendrites.intergration zone. cell body (soma) region where inputs are combine and transformed.conduction zone. single axon leads away from the cell body and transmit the electrical impulse.out zone.
What are the 4 structural regions of a neuron and how do they correspond to the four major functions of a neuron?
The four structural regions of a neuron are the dendrites, cell body, axon, and axon terminal. Functionally, the dendrites receive signals from other neurons. The cell body, also called the soma, stores genetic information and provides energy for neural processes.
How many parts are in a neuron?
Neurons have three basic parts: a cell body and two extensions called an axon (5) and a dendrite (3). Within the cell body is a nucleus (2), which controls the cell's activities and contains the cell's genetic material.
What are V4 neurons?
Neurons in area V4 are known to respond selectively to shape-related features, such as curvature and convexity (38), and this alone could account for differences in firing between the illusion-promoting and control stimuli.
What are the two major parts of a neuron?
A neuron consists of two major parts: a cell body and nerve processes.
Which neuron sends information to the central nervous system?
Motor neurons carry information from the central nervous system to organs, glands, and muscles . Sensory neurons send information to the central nervous system from internal organs or from external stimuli. Interneurons relay signals between motor and sensory neurons. Cite this Article. Format.
What happens at the synapse?
It is at the synapse where chemical or electrical impulses must cross a gap and be carried to the dendrites of adjacent cells. At electrical synapses, ions and other molecules pass through gap junctions allowing for the passive transmission of electrical signals from one cell to the other. At chemical synapses, chemical signals called neurotransmitters are released which cross the gap junction to stimulate the next neuron. This process is accomplished by exocytosis of the neurotransmitters. After crossing the gap, neurotransmitters bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron and stimulate an action potential in the neuron.
How is information transmitted between the brain and the body?
Information is communicated among nervous system structures through nerve signals. Axons and dendrites are bundled together into what are called nerves. These nerves send signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other body organs via nerve impulses. Nerve impulses, or action potentials, are electrochemical impulses that cause neurons to release electrical or chemical signals that initiate an action potential in another neuron. Nerve impulses are received at neuronal dendrites, passed through the cell body, and are carried along the axon to the terminal branches. Since axons can have numerous branches, nerve impulses can be transmitted to numerous cells. These branches end at junctions called synapses.
What are the junctions between axons and dendrites?
Axons end at junctions known as synapses. Dendrites typically carry signals toward the cell body. Dendrites are usually more numerous, shorter, and more branched than axons. They have many synapses in order to receive signal messages from nearby neurons.
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
Updated July 10, 2019. Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system and nervous tissue. All cells of the nervous system are comprised of neurons. The nervous system helps us to sense and respond to our environment and can be divided into two parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system .
What is the central nervous system?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system consists of sensory and motor nerve cells that run throughout the rest of the body. Neurons are responsible for sending, receiving, and interpreting information from all parts of the body.
What are the parts of a neuron?
Neurons (or nerve cells) are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body. Neurons are composed of three main parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Signals are received through the dendrites, travel to the cell body, and continue down the axon until they reach the synapse ...
Why are neurons important?
Neurons are very important to the body but as it is a cell it will have to die or get injured. The to much of death of neurons results fatal diseases like Alzheimer's,dementia mental retardation etc. the remaking of neurones is known of neurogenesis which doesn't take place in humans .
Why do neurons not proliferate?
This is because neurons do not proliferate, a factor that is necessary for a genetic mutation to accumulate in neoplastic tissue through clonal selection. Primary brain tumors represent only 2% of all cancers and the incidence is peaking at age 85 years.
How does auditory information work?
Auditory information is sensed by movement of liquid in the cochlea, which makes little hairs move and trigger nerves. Some stimuli don't get relayed to the brain but instead respond with instinctive motions in a reflex arc, but that is usually not the case.
What is action potential?
more. An action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. You will see this often in physiology, particularly is neurons because this is how signals travel through our bodies.
What is the branch of a neuron?
A dendrite (tree branch) is where a neuron receives input from other cells. Dendrites branch as they move towards their tips, just like tree branches do, and they even have leaf-like structures on them called spines.
What is the function of neuron?
What is a neuron? Neurons (also called neurones or nerve cells) are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, the cells responsible for receiving sensory input from the external world, for sending motor commands to our muscles, and for transforming and relaying the electrical signals at every step in between.
What does a neuron look like?
A useful analogy is to think of a neuron as a tree. A neuron has three main parts: dendrites, an axon, and a cell body or soma (see image below), which can be represented as the branches, roots and trunk of a tree, respectively. A dendrite (tree branch) is where a neuron receives input from other cells. Dendrites branch as they move towards their tips, just like tree branches do, and they even have leaf-like structures on them called spines.
Which structure is responsible for releasing neurotransmitters?
Axon – The long, thin structure in which action potentials are generated; the transmitting part of the neuron. After initiation, action potentials travel down axons to cause release of neurotransmitter. Dendrite – The receiving part of the neuron.
How many neurons are there in the brain?
Having said that, our roughly 100 billion neurons do interact closely with other cell types, broadly classified as glia (these may actually outnumber neurons, although it’s not really known). The creation of new neurons in the brain is called neurogenesis, and this can happen even in adults.
Which structure is the small protrusions found on dendrites that are, for many synapses?
Spine – The small protrusions found on dendrites that are, for many synapses, the postsynaptic contact site.
What is a dendritic spine?
Dendritic spines are small structures that receive inputs from the axons of other neurons. Bottom-right image: a segment of dendrite from which spines branch off, like leaves off a tree branch. Note the very small size (~0.001mm). (Image: Alan Woodruff ; De Roo et al / CC BY-SA 3.0 via Commons)
What is the cell body of a neuron?
Neurons are cells within the nervous system that transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, or gland cells. Most neurons have a cell body, an axon, and dendrites. The cell body contains the nucleus and cytoplasm. The axon extends from the cell body and often gives rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals.
What are the cells of a mammalian neuron?
Each mammalian neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon . The cell body contains the nucleus and cytoplasm. The axon extends from the cell body and often gives rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. Dendrites extend from the neuron cell body and receive messages from other neurons.
What are dendrites and synapses?
Dendrites extend from the neuron cell body and receive messages from other neurons. Synapses are the contact points where one neuron communicates with another. The dendrites are covered with synapses formed by the end s of axons from other neurons. Neurons are cells within the nervous system that transmit information to other nerve cells, muscle, ...
How do neurons transmit electrical signals?
When neurons receive or send messages, they transmit electrical impulses along their axons, which can range in length from a tiny fraction of an inch (or centimeter) to three feet (about one meter) or more. Many axons are covered with a layered myelin sheath, which accelerates the transmission of electrical signals along the axon. This sheath is made by specialized cells called glia. In the brain, the glia that make the sheath are called oligodendrocytes, and in the peripheral nervous system, they are known as Schwann cells.
Why are dendrites covered with synapses?
The dendrites are covered with synapses formed by the ends of axons from other neurons. The brain is what it is because of the structural and functional properties of interconnected neurons. The mammalian brain contains between 100 million and 100 billion neurons, depending on the species.
What is the axon sheath?
Many axons are covered with a layered myelin sheath, which accelerates the transmission of electrical signals along the axon. This sheath is made by specialized cells called glia. In the brain, the glia that make the sheath are called oligodendrocytes, and in the peripheral nervous system, they are known as Schwann cells.
How many times more glia are there than neurons?
The brain contains at least ten times more glia than neurons. Glia perform many jobs. Researchers have known for a while that glia transport nutrients to neurons, clean up brain debris, digest parts of dead neurons, and help hold neurons in place.
What are the three parts of a neuron?
Neurons vary in size, shape, and structure depending on their role and location. However, nearly all neurons have three essential parts: a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.
Where do neurons originate?
For instance, until recently, researchers believed that neuron creation occurred in adults in a region of the brain called the hippocampus. The hippocampus is involved in memory and learning.
How do action potentials affect other neurons?
In a chemical synapse, action potentials affect other neurons via a gap between neurons called a synapse. Synapses consist of a presynaptic ending, a synaptic cleft, and a postsynaptic ending. When an action potential is generated, it’s carried along the axon to a presynaptic ending.
What is the name of the structure that connects the cell body to the cell body?
Axon. An axon is a long, tail-like structure which joins the cell body at a specialized junction called the axon hillock. Many axons are insulated with a fatty substance called myelin. Myelin helps axons to conduct an electrical signal. Neurons generally have one main axon .
How many dendrites can a neuron have?
Neurons can have more than one set of dendrites, known as dendritic trees. How many they have generally depends on their role. For instance, Purkinje cells are a special type of neuron found in the cerebellum. These cells have highly developed dendritic trees which allow them to receive thousands of signals.
How many types of neurons are there?
Given the sheer number of neurons, there are thousands of different types, much like there are thousands of species of living organisms on Earth. In terms of function, scientists classify neurons into three broad types: sensory, motor, and interneurons.
How do neuronal signals work?
Neurons send signals using action potentials. An action potential is a shift in the neuron’s electric potential caused by the flow of ions in and out of the neural membrane. Action potentials can trigger both chemical and electrical synapses.
What is the network of neurons in the body?
The network formed by the billions of neurons in your body is responsible for all five senses, controls movement and consciousness. This article explores the various substructures of the neuron to prepare the reader for a lesson on connectomics.
Which extension of the neuron receives most of the signals from other cells?
Dendrites are the extensions of the neuron which receive most of the signals from other cells. In general, dendrites do not extend very far away from the cell body, although some of the neurons in the brain have very long dendrites to receive signals from cells that are far away.
How do axons work?
While dendrites are the primary means by which a cell receives a signal, the cell’s axon is how the neuron sends a signal to another neuron. Axons can be extremely long, some reaching up to 1 meter in full-grown humans. Rather than transmitting signals by a constant change of the voltage difference across the cell membrane, axons instead carry action potentials. Action potentials almost always have the same amplitude (voltage difference) for a given cell. Instead of transmitting the intensity of a signal through the amplitude, cells change the frequency at which action potentials are generated.
What happens to the synapse after the neurotransmitter is released?
After the neurotransmitters have bound to the receptors, they must be removed from the space between the cells to allow for further use of the synapse. This usually occurs in one of three ways: the neurotransmitters may diffuse away, to be broken down at another location; enzymes may be released to break them down; or they may be reabsorbed into the presynaptic terminal for later use.
How do electrical synapses work?
Instead of sending a chemical signal from one cell to another, electrical synapses work by directly transmitting the electrical signal through a gap junction, which is a connection between the cytoplasm of the two cells.
Which is more common, chemical or electrical synapses?
Chemical synapses are more common than electrical synapses. When the action potential in the presynaptic cell reaches the location of the synapse, neurotransmitters are released into the small space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic terminals. The neurotransmitters then bind to neurotransmitter receptors on the postsynaptic cell, which either causes or prevents the postsynaptic cell from firing.
What is the cell body?
The cell body is the large, round part of the neuron. It holds the nucleus and most of the other organelles in a cell. Because it contains most of the organelles, most of the proteins are synthesized in the cell body.
What is a Neuron?
Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. They receive and transmit signals to different parts of the body. This is carried out in both physical and electrical forms. There are several different types of neurons that facilitate the transmission of information.
What are the three parts of a neuron?
A neuron varies in shape and size depending upon their function and location. All neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body and axon.
What are sensory neurons?
Sensory Neurons. The sensory neurons convert signals from the external environment into corresponding internal stimuli. The sensory inputs activate the sensory neurons and carry sensory information to the brain and spinal cord. They are pseudounipolar in structure.
What happens when two neurons are connected by a gap junction?
When two neurons are connected by a gap junction, it results in an electrical synapse. These gaps include ion channels that help in the direct transmission of a positive electrical signal. These are much faster than chemical synapses.
Where are motor neurons located?
Motor Neurons. These are multipolar and are located in the central nervous system extending their axons outside the central nervous system. This is the most common type of neuron and transmits information from the brain to the muscles of the body.
Which structure carries electrical impulses from the cell body to the axon terminals?
Axon is a tube-like structure that carries electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminals that passes the impulse to another neuron.
How does action potential affect other neurons?
In chemical synapses, the action potential affects other neurons through a gap present between two neurons known as the synapse. The action potential is carried along the axon to a postsynaptic ending that initiates the release of chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters.
Which type of neuron receives information from other neurons?
Interneurons. Interneurons, which are found only in the CNS, connect one neuron to another. They receive information from other neurons (either sensory neurons or interneurons) and transmit information to other neurons (either motor neurons or interneurons).
How many basic functions do neurons have?
If you think about the roles of the three classes of neurons, you can make the generalization that all neurons have three basic functions. These are to:
What are the parts of the nervous system?
The human nervous system 1 The central nervous system ( CNS) consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It is in the CNS that all of the analysis of information takes place. 2 The peripheral nervous system ( PNS ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS.
How do motor neurons get information?
Motor neurons get information from other neurons and convey commands to your muscles, organs and glands. For instance, if you picked up a hot coal, it motor neurons innervating the muscles in your fingers would cause your hand to let go.
How many input signals do neurons receive?
Most neurons receive many input signals throughout their dendritic trees. A single neuron may have more than one set of dendrites, and may receive many thousands of input signals. Whether or not a neuron is excited into firing an impulse depends on the sum of all of the excitatory and inhibitory signals it receives.
What are the cells that make up the nervous system?
Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ).
Where does the signal from the sensory neurons in your fingertips travel?
For instance, if you picked up a hot coal, the signal from the sensory neurons in your fingertips would travel to interneurons in your spinal cord. Some of these interneurons would signal to the motor neurons controlling your finger muscles (causing you to let go), while others would transmit the signal up the spinal cord to neurons in the brain, where it would be perceived as pain.
