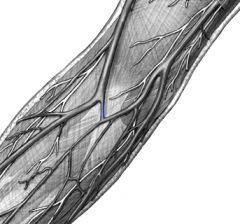
It is used most often for taking blood, or venipuncture, and is the connection for the basilic and cephalic veins. The cephalic vein is another vein located in the upper limb and is also referred to as the antecubital vein. It communicates through the elbow with the median basilic vein to the basilic vein.
What are the four major veins in the antecubital space?
What are the four major veins in the antecubital space? One of the most common sites for venipuncture is the superficial veins in the cubital fossa of upper limbs which include the cephalic, basilic, median cubital, and antebrachial veins and their tributaries.
Where is the antecubital area?
The elbow is the entire joint between the (upper) arm and forearm. The term “antecubital” refers to the 'front' (ventral side) of the elbow. The little depression in the front of the elbow is the antecubital fossa. The pointy process on the back (dorsal side) of the elbow is from the olecranon process of the ulna.
Where is the antecubital located?
The antecubital fossa, also known as the cubital fossa, is located in the depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. The antecubital fossa of the right arm can be classified as right antecubital, and the antecubital fossa of the left arm can be classified as left antecubital.
What are the most common intravenous sites?
and Catheter Sites
- Peripheral Vein Catheter (PVC)
- Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
- Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC)
Where is the antecubital vein found?
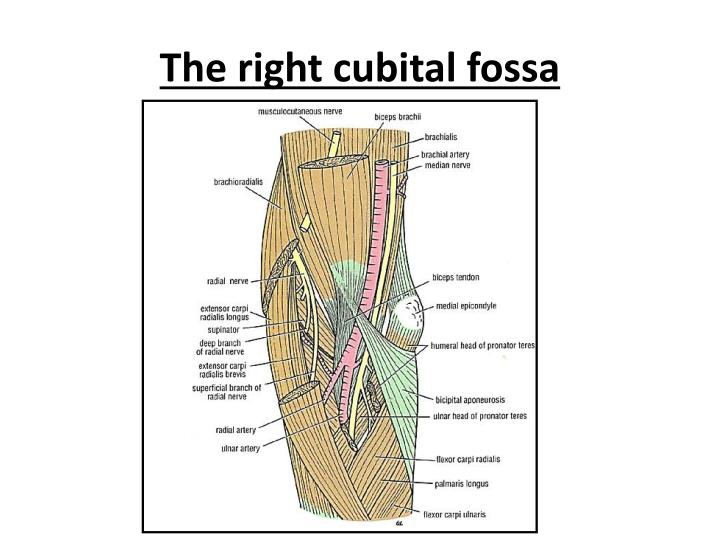
elbowThe Cubital Fossa is a triangular-shaped depression, located between the forearm and the arm on the anterior surface of the elbow, with the apex of the triangle pointing distally. It is also known as the “antecubital” because it lies anteriorly to the elbow.
Why do we use the antecubital vein?
The median cubital vein is not critical to life, but it does help facilitate venous return from the arms back to the pulmonary system. The significance of this vein is its use in venipuncture, the procedure that collects blood for laboratory testing.
What is the main vein used for antecubital injection?
In human anatomy, the median cubital vein (or median basilic vein) is a superficial vein of the upper limb. It lies in the cubital fossa superficial to the bicipital aponeurosis. It connects the cephalic vein and the basilic vein.
What are the 3 main arm veins?
They are the cephalic, median cubital, and basilic veins. These three veins are found in the antecubital area. The cephalic vein is found on the lateral, or outside, of the arm.
What vein should be avoided?
While hand veins may be utilized for blood draws and intravenous infusions, veins in the feet and legs should be avoided for adults. Drawing from these sites can cause blood clotting and hemostasis.
Which vein is used for blood collection?
Of these, the median cubital vein is usually the vein of choice for phlebotomy: It is typically more stable (less likely to roll), it lies more superficially, and the skin overlying it is less sensitive than the skin overlying the other veins. Antecubital veins, right arm.
Why is the antecubital the first site to collect blood?
The collection of blood specimens typically occurs at venous sites on the body, with the median cubital vein in the antecubital fossa being the typical collection site because this vein is relatively large and easily accessible [12].
How do you draw blood from antecubital vein?
Grab the patient's lower arm (below site of puncture) firmly to draw the skin taut and anchor the vein from rolling. Insert the needle at a 15 to 30-degree angle into the vessel. If properly inserted, blood should flash into the catheter.
What two antecubital veins should be drawn for venipuncture?
The antecubital area of the arm is usually the first choice for routine venipuncture. This area contains the three vessels primarily used by the phlebotomist to obtain venous blood specimens: the median cubital, the cephalic and the basilic veins.
Where is the biggest vein in your arm?
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel supplying blood to your upper arm, elbow, forearm and hand. It starts in your upper arm, just below your shoulder, and runs down through the crease in front of your elbow. It separates into several branches along its route.
What vein is not an antecubital vein?
CardsTerm An individual's ABO blood group is determined by the presence or absence of a certain type ofDefinition antigen present on the red blood cellsTerm Which of the following veins is NOT an antecubital vein?Definition FemoralTerm Which of these terms means "muscle pain"?Definition Myalgia67 more rows•Jan 9, 2021
Which vein is the last choice for venipuncture?
The basilic veinThe basilic vein is responsible for taking blood that doesn't have oxygen from the arms back to the heart and lungs, where it's given oxygen again. While you can usually see it clearly, it's considered a last resort in medical procedures.
Where is the intermediate basilica vein?
Also called the intermediate basilica vein. Located in the medial aspect of the antecubital area, it is the last choice for venipuncture in the M-Shaped pattern because it is more painful and located near the median nerve. THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH... Oxygen/Airway Management/Chest tube/specimen colle…. 154 terms.
Where is the large vein located?
Large vein located on the medial aspect (inner side) of the antecubital area. , it is the last choice vein for venipuncture. Median vein. Also called the intermediate ante-brachial vein. Located near the center of the antecubital area, it is the choice for venipuncture in the M-shapes pattern.
Which vein is preferred for venipuncture?
Median cubital vein. Located near the center of the antecubital area, it is preferred, and thus first choice,vein for venipuncture in the H-shaped pattern. Cephalic vein. Located in the lateral aspect of the aspect of the antecubital area, it is second choice vein for venipuncture in the H-shaped pattern. Basilic vein.
Which vein is not close to nerves?
Well anchored tends to be less painful to puncture and is not close to any major nerves or arteries as others. Median cephalic vein. Also called the intermediate cephalic vein. Located in the lateral aspect of the antecubital area, it is the second choice for venipuncture in the M-shaped pattern, because it is accessible, ...
What is the Antecubital Fossa?
The antecubital fossa is one of the primary locations on the body where doctors and nurses insert an IV. The antecubital fossa is a small triangular space where the arm and forearm meet. This is also the area on the opposite side of the elbow joint.
Why use the Antecubital Fossa?
The antecubital fossa or the area where your forearm and arm meet is often the preferred location for running IVs. You might be wondering why this is?
What Do you Need to Start an IV Insertion?
IV insertions are one of the most fundamental duties of being a nurse and doctor. To properly and effectively insert an IV you will need to medial supplies which include:
How To Start An IV Insertion? Step by Step walkthrough
If you never have inserter IV or you are looking to refresh your memory, then you’re in luck.
How far is the oblique incision?
An approximately 4 cm oblique incision was made from proximal medial to distal lateral, centered over the palpated biceps tendon, beginning approximately 2 cm distal to the antecubital flexion crease.
Can propofol be given in large veins?
Creacion de la fistula arteriovenosa. It is recommended that propofol be given in a large antecubital vein to prevent pain on injection. The injection of a thinner in the antecubital region has been shown to cause electrophysiological axonal loss of the radial, ulnar, and median nerves (4).
The Antecubital Fossa
An anatomical term, antecubital means "of or related to the crook of the elbow." The word fossa means "a shallow anatomical depression or hollow." The antecubital fossa is thus the transitional area between the forearm and the anatomical arm. This is the most common site for blood draws.
Where Is the Antecubital Fossa?
The antecubital fossa, also known as the cubital fossa, is located in the depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint. The antecubital fossa of the right arm can be classified as right antecubital, and the antecubital fossa of the left arm can be classified as left antecubital.
What Is in the Antecubital Fossa?
The structures inside the antecubital fossa, or cubital fossa, traverse the lateral and medial regions. These structures include the radial nerve, the biceps tendon, the brachial artery, and the median nerve.
Why is the median cubital vein used?
The median cubital vein is used the most for its accessibility. It is large and near the skin’s surface, making it easier for phlebotomists to see before anchoring the vein. The median cubital creates less bruising and pain than other draw sites.
Where is the antecubital fossa?
The antecubital fossa is a collection of veins located within the arm’s inner area, opposite of the elbow, where the arm folds in. In this elbow pit, phlebotomists have easy access to the top three vein sites used in phlebotomy: Median cubital vein. Cephalic vein. Basilic vein.
What veins do phlebotomists use?
If none of these veins work, then the phlebotomists use the hand veins. Other draw sites, particularly below the waist, are rarely used.
What is the most common vein for phlebotomy?
Median Cubital Vein. The median cubital vein , also known as the antecubital vein, is the most common vein for phlebotomy. Located in the antecubital fossa, the median cubital vein is a well anchored, stable vein that rarely rolls during venipuncture.
What veins are used for intravenous infusion?
The dorsal venous network is the next most common vein site for phlebotomists. Dorsal hand veins are often utilized for intravenous infusions but are viable options for blood draw sites. However, drawing blood from the hand is affiliated with higher levels of pain and less control.
What is a phlebotomy vein?
Phlebotomy is the practice of drawing blood from patients to gather data about their health. As a phlebotomist, it is critical to know which vein sites offer stable flows for blood draws. There are three phlebotomy vein sites located in the arm most utilized by medical professionals and three additional draw sites that are last resorts.
Where is the basilic vein located?
Also found in the antecubital fossa, the basilic vein serves as a last resort for blood draws. It is not as close to the skin surface as the median cubital and cephalic veins, which poses a greater risk of damage to the median nerve and brachial artery. While the median cubital, cephalic, and basilic veins are the most popular draw sites ...