What is the space between the lungs called?
The space between the lungs is called the (b) mediastinum. The chest cavity is the area surrounded by the thoracic vertebrae, the ribs, the sternum, and the diaphragm. . No air is moving into or out of the lungs during this time.
Where is the heart located between the lungs?
Your heart is located between your lungs in the middle of your chest, behind and slightly to the left of your breastbone (sternum). A double-layered membrane called the pericardium surrounds your heart like a sac.
Where are your lungs located in the human body?
The lungs are located within the chest cavity on either side of the heart. Each lung reaches from the collarbone to the border between the chest and abdominal cavities. The diaphragm, the muscle that helps the lungs take in air, sits below the lungs on top of the abdominal cavity. The human lung is usually between 10 and 12 inches long.
What is located between the ribs and lungs?
The ribs protect the lungs and expand when we inhale. The air in the lungs is expelled by the ribs. What is the tissue between the ribs called? Cartilage is attached to the breast bone by ribs. The ribs have intercostal muscles. The rib cage is usually pulled up by these muscles. The intercostal muscles are pulled between the ribs when you breathe.
See more
What is the middle of the lungs called?
The hilum (root) is a depressed surface at the center of the medial surface of the lung and lies anteriorly to fifth through seventh thoracic vertebrae. It is the point at which various structures enter and exit the lung. The hilum is surrounded by pleura, which extends inferiorly and forms a pulmonary ligament.
Why is there a space in between the lungs?
The pleural cavity is a space between the visceral and parietal pleura. The space contains a tiny amount of serous fluid, which has two key functions. The serous fluid continuously lubricates the pleural surface and makes it easy for them to slide over each other during lung inflation and deflation.
What is between lung and ribs?
The chest cavity is lined by a thin shiny membrane called the pleura, which covers the inside surface of the rib cage and spreads over the lungs as well. Normally, the pleura produces a small amount of fluid which serves as a lubricant to the lungs as they move back and forth against the chest wall during respiration.
What is the space between the lungs and chest wall?
The pleural space is the thin gap between the pleura of the lung and of the inner chest wall. The pleura is a double layer of membranes that surrounds the lungs. Inside the space is a small amount of fluid. The fluid prevents the pleura from rubbing together when you breathe.
Is pleural effusion life threatening?
A pleural effusion can be serious and potentially life-threatening, but it is treatable. If cancer grows in the pleural space, it causes a "malignant pleural effusion." This condition is a sign that the cancer has spread, or metastasized, to other areas of the body.
What causes rib cage pain?
Rib cage pain can be caused by a variety of things, ranging from pulled muscles to a rib fracture. The pain may occur immediately upon injury or develop slowly over time. It can also be a sign of an underlying medical condition. You should report any instance of unexplainable rib cage pain to your doctor immediately.
How painful is pleurisy?
About pleurisy The most common symptom of pleurisy is a sharp chest pain when breathing deeply. Sometimes the pain is also felt in the shoulder. The pain may be worse when you cough, sneeze or move around, and it may be relieved by taking shallow breaths. Other symptoms can include shortness of breath and a dry cough.
What organ is in middle of chest?
The mediastinum is in the center of the chest and contains the heart, thymus, and lymph nodes, along with portions of the aorta, vena cava, trachea, esophagus, and various nerves.
What is pleural space in lungs?
Definition: pleural space. Also called pleural cavity. The cavity that exists between the lungs and underneath the chest wall. It is normally empty, with the lung immediately against the inside of the chest wall.
What does pleural space mean?
(PLOOR-ul KA-vuh-tee) The space enclosed by the pleura, which is a thin layer of tissue that covers the lungs and lines the interior wall of the chest cavity.
What could happen if air gets caught in between the space between the lungs and thoracic cavity?
A pneumothorax occurs when air leaks into the space between your lung and chest wall. This air pushes on the outside of your lung and makes it collapse. A pneumothorax can be a complete lung collapse or a collapse of only a portion of the lung.
Why does left lung have 2 lobes?
The left lung has only two formal lobes because of the space taken up in the left side of the chest cavity by the heart, though it does have the lingula, which is similar to a lobe.
What is the trachea in the lungs?
The trachea is a tube that carries the air in and out of your lungs. Each lung has a tube called a bronchus that connects to the trachea. The trachea and bronchi airways form an upside-down “Y” in your chest. This “Y” is often called the bronchial tree. The bronchi branch off into smaller bronchi and even smaller tubes called bronchioles.
How many lobes does the right lung have?
This spongy, pinkish organ looks like two upside-down cones in your chest. The right lung is made up of three lobes. The left lung has only two lobes to make room for your heart.
Why do we need lung function tests?
If you have a respiratory disorder, you may need tests to see how well your lungs are working. They also help to diagnose chronic lung illness. Some of these tests are routine for people with chronic illness such as asthma. Common lung function tests and scans include:
How to keep your lungs healthy?
While your body has a built-in system to keep your lungs healthy, there are several important things you can do every day to help reduce your risk of lung disease or to ease symptoms: Avoid secondhand smoke. Avoid the outdoors when there are high levels of air pollution or pollen.
What is the respiratory system?
The respiratory system. The lungs are the main part of the respiratory system. This system is divided into the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The upper respiratory tract includes the: Mouth and nose. Air enters and leaves the lungs through the mouth and nostrils of the nose. Nasal cavity.
How many alveoli are there in the bronchiole?
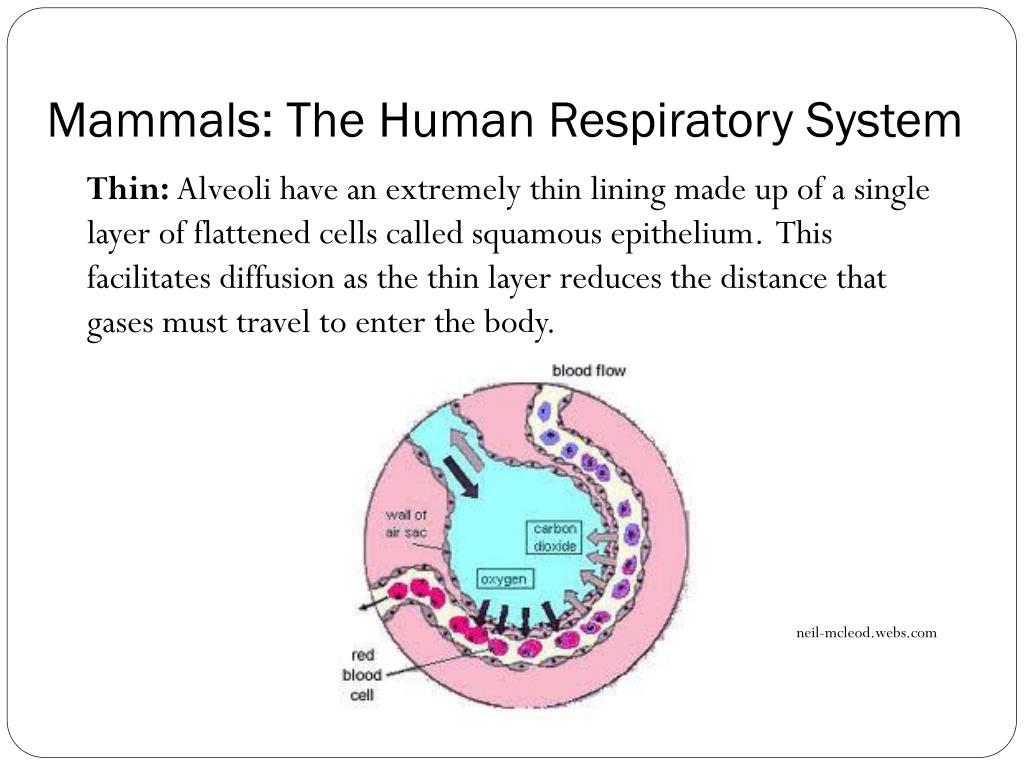
They look like tiny grape bunches or very tiny balloons. There are about 600 million alveoli in your lungs. The small bubble shapes of the alveoli give your lungs a surprising amount of surface area — equivalent to the size of a tennis court. This means there’s plenty of room for vital oxygen to pass into your body.
What is a marker for lung?
A marker or computer shows the how fast air is flowing and approximate lung volume. Sputum (spit) or mucus sample. Your doctor may take a swab of your mouth or throat. The sample is sent to a lab to check to see if you have a bacterial or viral infection in the throat or lungs.
What is the respiratory area of the lungs?
Respiratory Area of the Lungs (Lung Parenchyma) The structures in the lungs directly responsible for the function of respiration collectively form the lung parenchyma. It includes the bronchial tubes, blood vessels, alveoli, and alveolar ducts [31, 32].
What is the base of the lung?
The base is the concave lower surface of the lung that rests over the diaphragm [9]. Structures including the bronchus, bronchial veins and arteries, pulmonary artery, two of the pulmonary veins, pulmonary plexus of nerves (anterior and posterior), and lymphatic vessels bundle together to form the root of the lungs [9, 10].
What is the mediastinal surface of the lungs?
Mediastinal Surface: The surface between the left and right lungs, it houses the hilum. It also covers the part of the lungs next to the heart [28]. The left lung has a deep indentation, referred to as the cardiac notch, along its mediastinal surface to make space for the apex of the heart [7].
How many alveoli are there in the human body?
A healthy person has 300 to 700 million alveoli (480 million in average) [35], meaning there are around 150 to 350 million alveoli in each lung.
Where does the root of the lung enter and leave?
The structures of the root enter/leave the lung via the hilum [10]. It is the wide depressed area located just a little higher than the center of the medial surface of the lungs [11].
How many pulmonary arteries are there in the human body?
Each lung has one pulmonary artery and two pulmonary veins. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs where it receives oxygen and then is carried back into the heart by the pulmonary veins [38].
What does a healthy lung look like?
A healthy lung has a pinkish appearance , and if you could see it outside the body, it would look like a squishy, rubbery structure [4].
Which lung is smaller, the left or the right?
The right lung is shorter and wider than the left lung, and the left lung occupies a smaller volume than the right. The cardiac notch is an indentation on the surface of the left lung, and it allows space for the heart (Figure 1).
Which layer of the lung is superficial to the lungs?
The visceral pleura is the layer that is superficial to the lungs, and extends into and lines the lung fissures (Figure 2). In contrast, the parietal pleura is the outer layer that connects to the thoracic wall, the mediastinum, and the diaphragm. The visceral and parietal pleurae connect to each other at the hilum.
How to describe the lungs?
By the end of this section, you will be able to: 1 Describe the overall function of the lung 2 Summarize the blood flow pattern associated with the lungs 3 Outline the anatomy of the blood supply to the lungs 4 Describe the pleura of the lungs and their function
What is the pleura of the lung?
Each lung is enclosed within a cavity that is surrounded by the pleura. The pleura (plural = pleurae) is a serous membrane that surrounds the lung. The right and left pleurae, which enclose the right and left lungs, respectively, are separated by the mediastinum. The pleurae consist of two layers.
Why are the right and left lung different?
The right and left lungs differ in size and shape to accommodate other organs that encroach on the thoracic region. The right lung consists of three lobes and is shorter than the left lung, due to the position of the liver underneath it. The left lung consist of two lobes and is longer and narrower than the right lung. The left lung has a concave region on the mediastinal surface called the cardiac notch that allows space for the heart.
What are the lungs?
The lungs are pyramid-shaped, paired organs that are connected to the trachea by the right and left bronchi; on the inferior surface, the lungs are bordered by the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the flat, dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the lungs and thoracic cavity. The lungs are enclosed by the pleurae, which are attached to the mediastinum. The right lung is shorter and wider than the left lung, and the left lung occupies a smaller volume than the right. The cardiac notch is an indentation on the surface of the left lung, and it allows space for the heart (Figure 1). The apex of the lung is the superior region, whereas the base is the opposite region near the diaphragm. The costal surface of the lung borders the ribs. The mediastinal surface faces the midline.
How many lobes are there in the right lung?
Fissures separate these lobes from each other. The right lung consists of three lobes: the superior, middle, and inferior lobes. The left lung consists of two lobes: the superior and inferior lobes. A bronchopulmonary segment is a division of a lobe, and each lobe houses multiple bronchopulmonary segments.
What is a CT scan of the chest?
CT scan: A CT scan takes a detailed image of the chest so a doctor can check for air in the mediastinum. The scan can show the extent of the pneumomediastinum or confirm cases when a chest X-ray is inconclusive.
Why does air get stuck in my chest?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Newborns. Takeaway. Pneumomediastinum is the abnormal presence of air or another gas in the mediastinum. The mediastinum is the center of the chest and is located between the lungs. Air can get stuck in this area because of trauma or leakage from the lungs or windpipe.
How to diagnose pneumomediastinum?
A doctor will take a medical history and perform a physical examination to diagnose pneumomediastinum. They will probably listen to the chest with a stethoscope.

Other animals
Symptoms
- A healthy lung has a pinkish appearance, and if you could see it outside the body, it would look like a squishy, rubbery structure [4].
Location
- The lungs are located a little toward the posterior part of the human body, just below the collarbone, extending down to the diaphragm, the muscular partition that separates the chest and abdominal cavities. The left and right lungs are situated on the two sides of the body with the heart, another vital organ in the thoracic cavity, located a little in front of, and at the middle of th…
Structure
- Each lung has an apex, base, root, and hilum or hilus of the lung, as well as three surfaces, keeping the lung connected to the sides of the thorax [7]. The apex is the superior part of the lungs, with its highest point located above the first rib, extending through the superior opening of the thoracic cavity, into the inferior floor of where the n...
Function
- Structures including the bronchus, bronchial veins and arteries, pulmonary artery, two of the pulmonary veins, pulmonary plexus of nerves (anterior and posterior), and lymphatic vessels bundle together to form the root of the lungs [9, 10]. This root not only connects the two lungs with each other but also keeps them suspended in the thoracic cavity. It is the convex or dome-s…
Description
- In adults, each lung is 25cm to 30cm long, with the right lung being a little larger than the left lung as the former has three lobes while the latter only has two.
Variations
- Both the left and right lungs have an oblique fissure separating the superior lobes from the inferior lobes [17], while in the right lung there is a horizontal fissure to keep the middle and superior lobes apart [18].
Mechanism
- As the windpipe reaches the lungs, it divides into the left and right primary bronchus, which then enters the left and right lung respectively [33]. Once inside the lungs, the bronchi divide into narrower tubes called bronchioles, while this again branch into terminal bronchioles, the smallest respiratory tubes in human lungs. This intricate structure in each lung is called the bronchial tree…
Definition
- TLC refers to the maximum volume of air the lungs of an adult person can hold. It is the sum of the air released by the lung after a maximum exhalation (vital capacity or VC) and the volume of air left behind within the lungs after a deepest exhalation (residual volume or RV) [46]. The TLC of human lungs is 6 liters [47]. Lung compliance is the measurement of the lungs capacity to expa…
Diagnosis
- Both TLC and lung compliance are measured for the diagnosis and treatment of various lung disorders.
Types
- Lung Cancer: There are three types of this lung cancer, non-small cell, small cell, and lung carcinoid tumor. These three vary in their rate of growth of the cancerous cells, requiring different treatment options. The non-small cell type is the most commonly occurring lung cancer, with subtypes including squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma [56]. Excessive smoking i…
Side effects
- Pulmonary Embolism: A life-threatening disorder characterized by blood clot formation within the lungs. It might occur after a major surgery, as a complication of conditions like a heart attack or cancer or due to smoking too much [64]. Symptoms include shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, discoloration of the skin, coughing up blood, chest pain, and fainting. Anticoagulant drugs are us…
Overview
- Pulmonary Nodules (benign growth on the lungs): Sometimes, there is a small nodule or growth in your lung that shows up as a small spot on CT scan and chest x-ray reports [66]. Such growths can be both malignant and benign, but over 90% of those smaller than 2cm in diameter remain harmless [67].
Classification
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans (Popcorn Lung): A serious lung condition characterized by scarring, inflammation, and narrowing of bronchioles, the smallest of the airways. The name popcorn lungs come from the fact that it may result from inhaling a chemical often used in flavoring microwave popcorn [68]. Wheezing, shortness of breath, dry cough, and fatigue are the common symptoms…