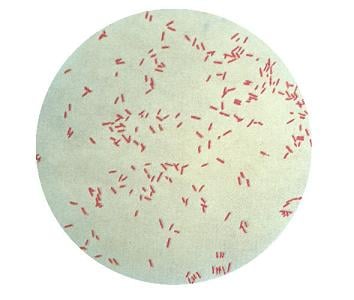
E.coli Morphology and Arrangement
- E.coli is a gram-negative (-ve) bacteria.
- These are straight, rod shaped (bacillus) bacterium.
- They are arranged singly or in pairs.
- Their size is about 1–3 µm × 0.4–0.7 µm (micrometer).
- They are motile due to the presence of peritrichous flagella. ...
- It is a non–sporing bacteria.
- Some of them may be fimbriated. ...
| Names | Escherichia coli APEC O1 |
|---|---|
| Cell arrangement | Pairs, Singles |
| Sporulation | Nonsporulating |
| Metabolism | NA |
| Energy source | NA |
Is E coli true motile?
Escherichia coli is a non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium, usually motile by peritrichous flagella. Escherichia coli is the most common cause of acute urinary tract infections as well as urinary tract sepsis. It has also been known to cause neonatal meningitis and sepsis and also abscesses in a number of organ systems.
What is the measurement of an E coli?
coli bacterium is about 1–2 micrometers long and about 0.25 micrometer in diameter. The E. coli are the same shape as the possible fossils in slide #26, but are 10 to 100 times as big.
What is the treatment for E coli in stool?
E. coli treatment options. E.coli is treated with supportive care. Medications are only rarely used, but hemolytic uremic syndrome due to Shigella poisoning may require hospitalization, intravenous fluid replacement, blood transfusions, or dialysis. Supportive care. The primary goal of supportive care is to maintain hydration and electrolytes.
What is the arrangement of bacteria?
Arrangements of Cocci
- Diplococci : Cocci that remain in pairs after dividing.
- Streptococci : Cocci that remain in chains, like beads on a string.
- Tetrads : The cocci that are arranged in packets of four cells, as the cells divide in two plains.
- Sarcinae : Cocci that divide in three planes and remain in groups cube like groups of eight.
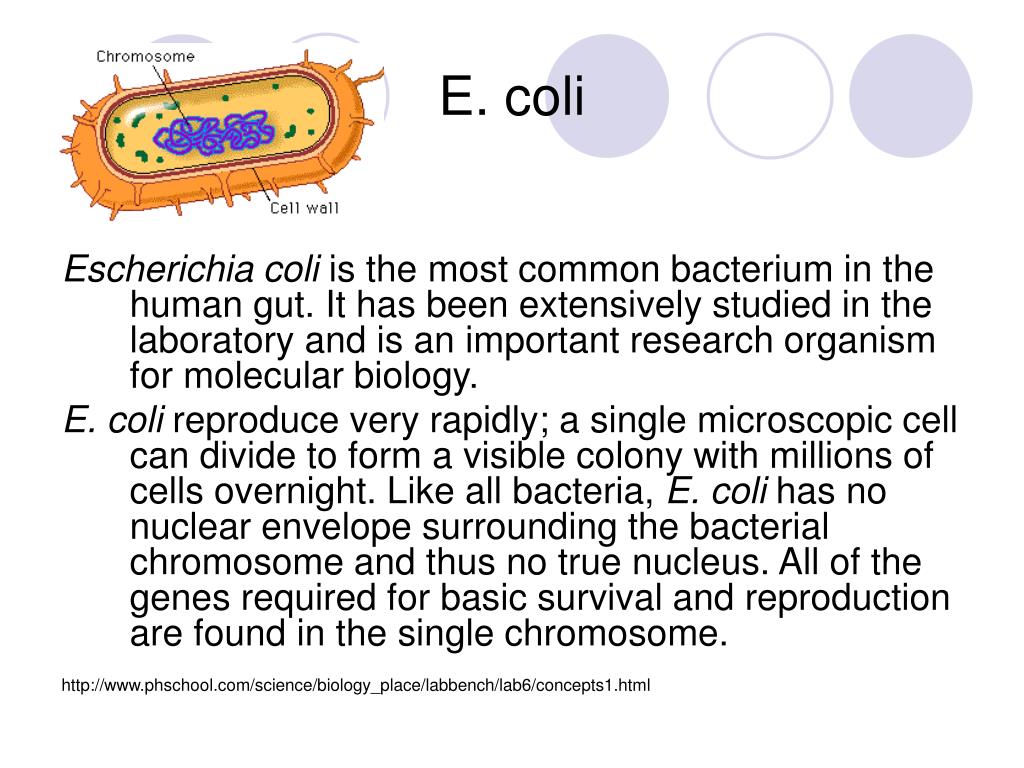
What is the arrangement of E. coli bacteria?
The bacterium Escherichia coli is rod-shaped, and a unit cell keeps regular dimensions of about 1.5 µm long and 0.5 µm wide. The rod-shaped cell is composed of two parts: a cylinder in the center and caps at both ends. The length of the cylinder corresponds to the length of the rod cell.
What is E. coli shape and arrangement?
E. coli is gram-negative (-ve) rod-shaped bacteria. It is 1-3 x 0.4-0.7 µm in size and 0.6 to 0.7 µm in volume. It is arranged singly or in pairs. It is motile due to peritrichous flagella.
What is the cellular arrangement or a cellular feature of E. coli?
Cell Structure and Metabolism E. coli is a Gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria, which possesses adhesive fimbriae and a cell wall that consists of an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides, a periplasmic space with a peptidoglycan layer, and an inner, cytoplasmic membrane.
What is the arrangement of bacteria?
In fact, structure of bacteria has two aspects, arrangement and shape. So far as the arrangement is concerned, it may Paired (diplo), Grape-like clusters (staphylo) or Chains (strepto). In shape they may principally be Rods (bacilli), Spheres (cocci), and Spirals (spirillum).
Is E. coli a rod or cocci?
E. coli is a Gram negative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacteria of the genus Escherichia, commonly found in the lower intestine of humans and animals.
Is E. coli a cocci?
Escherichia coli are typically Gram-negative, rod shaped (2.0–6.0 μm in length and 1.1–1.5 μm wide bacilli) bacteria with rounded ends. The actual shape of these bacteria does, however, vary from spherical (cocci) cells through to elongated or filamentous rods.
What is cell arrangement?
While arrangement refers to the groupings of individual cells, morphology describes the appearance of groups of bacteria, or colonies. Colony shapes can be round, irregular, filamentous or curled. Colonies might be flat or have a rounded elevation.
What is the structure and function of E. coli?
Escherichia coli cells are surrounded by a complex cell wall composed of two concentric lipid bilayers, the outer membrane and the cytoplasmic membrane with a peri- plasmic space in between. This cell wall plays many functional roles in protection, transport, locomotion, sensing, detoxification, and energy production.
What are two structures of E. coli?
In E. coli, there are two distinct membranes: the OM and the inner membrane (IM) (Fig.
What is the arrangement of staphylococcus?
Structure. Staphylococci are Gram-positive cocci about 0.5 – 1.0 μm in diameter. They grow in clusters, pairs and occasionally in short chains. The clusters arise because staphylococci divide in two planes.
What is the arrangement of staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus USA300_TCH1516NamesStaphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus USA300_TCH1516Cell arrangementClusters, SinglesSporulationNonsporulatingMetabolismNAEnergy sourceNA32 more rows
How do you identify bacterial morphology and arrangement?
6:267:25BIO2020 Episode 017: Bacterial morphology and arrangementYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe common arrangements of coxy are singles diplococci streptococcus. And Staphylococcus ii and theMoreThe common arrangements of coxy are singles diplococci streptococcus. And Staphylococcus ii and the common arrangements of bacilli are singles diplo bacilli and streptobacillus.
What is the shape and arrangement of Bacillus subtilis?
What is the shape and arrangement of Bacillus subtilis? Bacillus subtilis gram stain test reveals them as rod-shaped bacteria cells under a microscope. They may be arranged as clumps, singly, or as chains.
What is the arrangement of Bacillus cereus?
Morphology of Bacillus cereus Bacillus cereus is gram-positive rod-shaped bacilli with square ends. Occasionally may appear gram variable or even gram-negative with age. They are single rod-shaped or appear in short chains. Clear cut junctions between the members of chains are easily visible.
What is cell morphology and arrangement?
In microbiology, cell morphology is the branch of science dealing with the cell's structure, shape, size, and arrangement of prokaryotes. Prokaryotes are the basic form of living organisms that are devoid of a well-defined nucleus, instead have a nucleoid, plus have no specialized organelles as eukaryotes.
What is the shape and arrangement of Staphylococcus aureus?
S. aureus cells are Gram-positive and appear in spherical shape. They are often in clusters resembling bunch of grapes when observed under light microscope after Gram staining.
Why does E. coli have a green sheen?
In Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB) medium, the colonies of Escherichia coli grow with a green metallic sheen which is due to the Metachromatic property of dyes (Eosin & Methylene blue) and the lactose fermenting property of E. coli which changes the pH of the medium to Acidic.
What media is used to grow E. coli?
⇒ Special requirements – Escherichia coli or E. coli have no complex nutritional requirements and readily grow in an ordinary media like Nutrient Agar medium (NAM). Commonly the NAM & MacConkey Agar medium is used for the cultivation of Escherichia coli in the Laboratory.
What is the Eosin Methylene Blue Agar?
⇒ The Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB Agar) medium which is a Selective medium for Escherichia coli contains Eosin dye and Methylene Blue dye which inhibits the growth of many gram-positive bacteria, inhibits the growth of Shigella and Salmonella species and supports the growth ...
Why is E. coli pink?
In MacConkey Agar medium, the colonies of Escherichia coli are pink colored due to the lactose fermentation which is of great importance in differentiating E. coli from other Bacteria present in the specimen, especially from Gram-positive bacteria and Salmonella species which are non–lactose fermentors and gives colorless colonies on MacConkey agar medium.
What was the first solid differential medium for the growth of bacteria on the globe?
The first ever developed solid differential medium for the growth of bacteria on the globe was MacConkey Agar Medium (MAC medium), was formulated by and is named after a British bacteriologist, … Continue reading
What is the growth of a bacterium in a broth?
In liquid culture media like Trypticase soy broth or Nutrient broth, the growth of the bacterium occurs as a turbidity in the broth medium with a heavy deposits that disperses in the medium on shaking, which is further analyzed for the morphology (under the microscope), gram reaction, biochemical tests, and Escherichia coli specific tests.
Does blood agar show beta hemolysis?
In Blood Agar medium, some of the strains show beta hemolysis, especially which are isolated from the pathologic conditions whereas those which are isolated from normal persons may or may not show hemolysis on blood agar.
Where is E. coli in the body?
E. coli is in our intestines. How can it be dangerous?
What is the outer membrane of E. coli made of?
The outer membrane, as I mentioned, is asymmetric - the outward facing side of it is made of lipopolysaccharide, which will again vary based on which strain of E. coli we're talking about. The capsule and the lipopolysaccharide can both be important antigenic determinants, as they are so surface-exposed an
What is the abbreviation for E. coli?
Saad Zulfiqar. , studied at University of Lahore. Answered 4 years ago. Escherichia coli, often abbreviated E. coli, are rod-shaped bacteria that tend to occur individually and in large clumps. E. coli bacteria have a single cell arrangement, according to Schenectady County Community College.
How many cells are in a 64x100 incubation?
Therefore, 64*100 = 6400 cells of E. coli at the end of 2hours incubation time.
What happens during the stationary phase of spore formation?
It is during the stationary phase that spore-forming bacteria have to induce or unmask the activity of dozens of genes that may be involved in sporulation process. 4. Death Phase. If incubation continues after the population reaches stationary phase, a death phase follows, in which the viable cell population declines.
How long does it take for a bacteria to grow?
Generation times for bacteria vary from about 12 minutes to 24 hours or more.
What happens during the lag phase?
1. Lag Phase. Immediately after inoculation of the cells into fresh medium, the population remains temporarily unchanged. Although there is no apparent cell division occurring, the cells may be growing in volume or mass, synthesizing enzymes, proteins, RNA, etc., and increasing in metabolic activity.
How is E. coli subdivided?
Each E. coli has been primarily subdivided into a number of O groups which have been subdivided into subgroups with different K antigens. Each subgroup includes strains with different H antigens; separate numbers were previously allotted for B antigens, but afterwards these numbers have been included in the same consecutive series as the rest of K antigens.
How to detect E. coli?
After overnight incubation, E. coli colonies are emulsified in saline on a slide and tested by agglutination with polyvalent and monovalent O antiserum against entero-pathogenic serotypes and further identified by biochemical tests.
How many antigens does E. coli have?
E. coli has Three Antigens: O Somatic, Greek Ohne Hauch—without flagella; H—flagella; Greek Hauch—flagella and K (Kapsular) antigens. K antigen is an envelope antigen, which encloses the O antigen, renders the strain inagglutinable by the O antiserum and contributes to virulence by inhibiting phagocytosis.
What is the medical significance of E. coli?
1. Meaning of Escherichia Coli: ADVERTISEMENTS: E. coli is an intestinal pathogen or commensal of the human or animal intestine and is voided in the faeces remaining viable in the environment only for some days.
What are the four biochemical tests widely used for enterobacteriaceae classification?
The four biochemical tests widely used for entero-bacteriaceae classification are Indole (I), Methyl Red (MR), Voges Proskauer (VP) and Citrate (C) utilisation which are referred to by the mnemonic IMV (1) C.E. coli is Indole and MR positive VP and citrate negative (IMV (1) C++ —), H 2 S is not formed and urea is not hydrolysed.
What is the color of salmonella in DCA?
On selective media (Desoxycholate citrate agar-DCA; salmonella shigella-SS medium) used for the isolation of salmonella, their growth is inhibited, however their colonies are pink on DCA as it contains lactose and neutral red. In broth, there is generalized turbidity and deposit which disperses on shaking.
What temperature do nutrient agar colonies grow?
It is an aerobe and a facultative anaerobe. The optimum growth temperature is 37°C. On Nutrient agar, colonies are large, thick, greyish white, moist, smooth, opaque or translucent discs. The smooth (s) form seen in fresh isolation is easily emulsified in saline, whereas the rough (R) form often auto agglutinates in saline.
How big is E. coli?
Most strains of E . coli are rod-shaped and measure about 2.0 μm long and 0.2-1.0 μm in diameter. They typically have a cell volume of 0.6-0.7 μm, most of which is filled by the cytoplasm. Since it is a prokaryote , E.
What are the cell walls of E. coli made of?
E. coli has cell walls made out of two thing peptidoglycan layers, an inner and outer membrane. The Gram-negative outer membrane explains why many strains of E. coli are resistant to penicillin; the mechanism of action is disrupted by the thin cell walls.
Why are E. coli Gram negative?
Their status as Gram-negative bacteria is due to their thin cell walls. E. coli has cell walls made out of two thing peptidoglycan layers, an inner and outer membrane. The Gram-negative outer membrane explains why many strains of E. coli are resistant to penicillin; the mechanism of action is disrupted by the thin cell walls. Many serotypes also have an external, flagella extending from the cell wall that is used to motility. In the mammalian gut, E. coli use their flagella to cling to the microvilli of the intestines.
How does E. coli benefit its host?
E. coli benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K and preventing the colonization of other pathogenic bacteria. E. coli, along with 1,000 other species of bacteria, constitute the normal microbiota of the mammalian gut. These bacteria are harmless to their hosts and are a part of the normal functioning of the human body.
What happens to E. coli when oxygen is not present?
Specifically, when oxygen is not present, E. coli derives its nutrients from the process of fermentation. During fermentation, E. coli breaks down carbohydrates into pyruvate in the absence of oxygen. This process produces ethanol and carbon dioxide. ADVERTISEMENT.
Why is E. coli so useful?
The dense coding and fast growth rates of E. coli make them extremely useful in the lab for bioengineering applications. Recent trends in research have sought to engineer strains of E. coli to produce materials that have a high carbon footprint.
What is the function of E. coli in gene transfer?
E. coli are known to engage in horizontal gene transfer, a process in which one bacterium inserts a section of its genetic code directly into the DNA of another. Horizontal gene transfer in bacteria serves an analogous function to sexual reproduction in eukaryotes in that it provides a source of genetic diversity.
