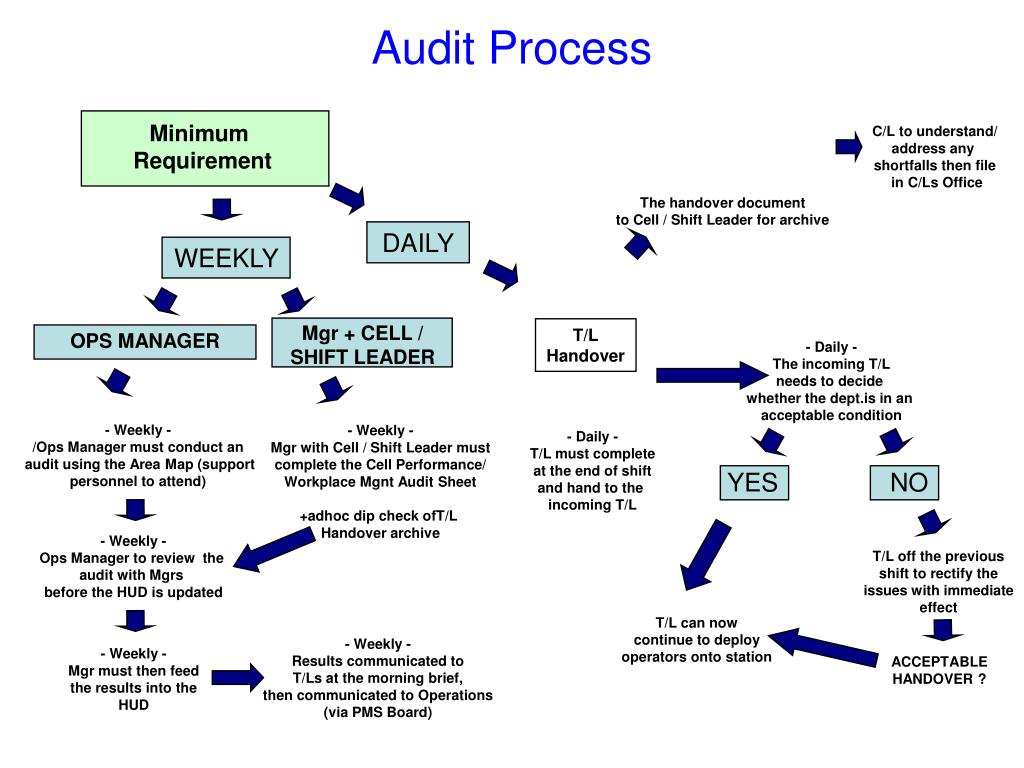
Audit Process
- Planning. The auditor will review prior audits in your area and professional literature. ...
- Notification. The Office of Internal Audit Services will notify the appropriate department or department personnel regarding the upcoming audit and its purpose, at which time an opening meeting ...
- Opening Meeting. ...
- Fieldwork. ...
- Report Drafting. ...
- Management Response. ...
What are the steps in audit planning?
- Determine audit subject.
- Define audit objective.
- Set audit scope.
- Perform pre-audit planning.
- Determine audit procedures and steps for data gathering.
How do you write an audit plan?
The planning process involves three things:
- Design specific objectives for the audit that will confirm the amount shown on Cy's books.
- Consider the risks associated with each objective. What would lead Joan to say that Cy's financial statement items are correct when they aren't?
- Design specific audit procedures that will achieve the objectives and minimize the risks.
What should an auditor do when planning an audit?
Preparation before Audit
- Agreement with the Client. Having accepted an audit engagement, the auditor should enter into an agreement with the client. ...
- Scope of Audit work (Audit Engagement Letter) The scope of audit may be ascertained with reference to relevant statute. ...
- Knowledge of the Client’s Business
- Knowledge of the Accounting System in Use. ...
How do I develop an audit plan?
Preparing for an Audit
- Have all requested materials/records ready when requested
- Organize files so we minimize disruption of your day
- Provide complete files
- Please make yourself available during the time of the audit and communicate any planned absences
- Provide work space for auditors if requested
What are the parts of audit planning?
The 5 Elements of an Effective Internal Audit Preparation and Planning ProcessResearch the Audit Area. ... Maintain Open Communications Throughout the Planning Process. ... Conduct Process Walk-Throughs. ... Map Risks to the Organization, Process, or Function. ... Obtain Data Prior to Fieldwork.
What is audit planning and its importance?
Planning your audit ensures that all areas of the process are covered and given appropriate attention. It can also help you identify any potential problems or obstacles with the auditing process, map out activity so that it is carried out in a timely way, and manage your audit workflow for maximum efficiency.
What are the 4 phases of an audit process?
Although every audit process is unique, the audit process is similar for most engagements and normally consists of four stages: Planning (sometimes called Survey or Preliminary Review), Fieldwork, Audit Report and Follow-up Review.
What are the 5 stages of an audit?
Internal audit conducts assurance audits through a five-phase process which includes selection, planning, conducting fieldwork, reporting results, and following up on corrective action plans.
What are the main advantages of audit planning?
Advantages of Audit PlanningIt provides right means to accomplish audit objectives.It ensures that no important area is left out. ... It helps in identifying potential problems.It ensures timely completion of audit work.It facilitates coordination of the audit work done by auditors and other experts.More items...
What is audit plan with example?
An audit plan represents a blueprint for conducting an audit. It addresses why, when, how, where, and by whom questions associated with audit performance. A good audit design identifies all the risks involved in the operations and employs specific audit procedures to minimize them.
What happens during planning stage of audit?
. 05 Planning the audit includes establishing the overall audit strategy for the engagement and developing an audit plan, which includes, in particular, planned risk assessment procedures and planned responses to the risks of material misstatement.
What are the 5 C's of internal audit?
Ensure Every Issue Includes the 5 C's of Observations. Criteria, Condition, Cause, Consequence, and Corrective Action Plans/ Recommendations.
What is audit life cycle?
An audit cycle is the accounting process an auditor uses to ensure a company's financial information is accurate. The audit cycle typically involves several distinct steps, such as the identification process, audit methodology stage, audit fieldwork stage, and management review meeting stages.
What are the 3 phases of audit?
Audit Phases Audit engagements are performed in three general phases: planning, fieldwork & review, and reporting.
What are the 14 steps of auditing?
The 14 Steps of Performing an AuditReceive vague audit assignment.Gather information about audit subject.Determine audit criteria.Break the universe into pieces.Identify inherent risks.Refine audit objective and sub-objectives.Identify controls and assess control risk.Choose methodologies.More items...•
What is ISO audit process?
An ISO 9001 audit is a systematic, independent, objective and documented process for gathering facts. These will help you identify areas for improvement and ensure you have best practice processes in place. Driving continual improvement is a key part of ISO 9001.
What is the importance planning?
Planning helps us see in advance those things that can help us achieve our goal and those things that can prevent us from achieving our goal and work out what to do about them. Planning helps us to be accountable for what we do.
What is the importance of an audit?
An audit is important as it provides credibility to a set of financial statements and gives the shareholders confidence that the accounts are true and fair. It can also help to improve a company's internal controls and systems.
What is audit planning ACCA?
Typically an audit plan will include sections dealing with business understanding, risk assessment procedures, planned audit procedures ie the responses to the risks identified and other mandatory audit procedures. Changes to the audit strategy and audit plan.
What is audit planning?
Planning is fundamental stage of auditing process. The carefully thought-out audit planning process ensures the success of the business project. Auditing Process. Audit Planning Process. "Audit planning is a vital area of the audit primarily conducted at the beginning of audit process to ensure that appropriate attention is devoted ...
What is the audit process?
Audit Process. The audit process is a definite set of steps used in a financial, operational or compliance audit. This set of steps depends of the audit services company. The auditing process usually includes three main steps: planning, fieldwork and reporting.
Why use audit flowchart?
This is the most effective way of preparation and documentation of the audit process. Financial audit process has a clear structure, and therefore audit flowchart is often used to denote an audit process. This is the most effective way of preparation and documentation of the audit process.
Why is chart audit important?
Chart Audit is incredibly convenient for representing important information about audit process and audit planning process. It also helps auditors to define the problem areas and to elaborate the ways of their solving and effectiveness improvement.
Why is auditing important?
It helps the auditor obtain sufficient appropriate evidence for the circumstances, helps keep audit costs at a reasonable level, and helps avoid misunderstandings with the client. It addresses the specifics of what, where, who, when and how:
What are the three types of audit procedures?
There are three types of audit procedures: data selection, reliability validation, relevance confirmation.
How many steps are there in an audit?
It is a complex process that includes 10 audit steps: Notification, Planning, Opening Meeting, Fieldwork, Communication, Draft Audit, Management Response, Final Meeting, Report Distribution, Feedback.
What Is Audit Planning?
Internal audits and control are vital, but they can be costly and complex without the proper structure. Whether you are auditing for your internal control purposes or complying with external regulations like Sarbanes-Oxley, effective audit planning enables you to bring order to the process and focus on the right risks to drive strategic insight.
Why Is It Important?
Businesses today face numerous and evolving risks. Effective audit planning ensures that you measure the right risks — and as a result, derive the strategic insights you need to manage and mitigate the threats your business faces.
What Is Best Practice in Audit Planning?
So you’ve identified audit planning as the holy grail for a successful audit. What happens next? — you may be wondering how to do it, what the essential steps are and whether you can draw on a best practice example to help you.
Best Practice and Audit Planning Tools
Best practice audit planning will cover the steps above, giving you complete oversight of your risk landscape and the controls that your organization uses to manage its risks. Many businesses are turning to audit planning tools and audit management software to manage this planning process and the broader audit.
How to plan for audit?
Audit planning is a critical part of audit works and performing the correct audit plan could be the factors that lead to the success of audit engagement. The key areas to be included in the plan are: 1 Conducts proper risks assessments including risks of error and fraud 2 Properly assess the resources requirement 3 Properly identified the engagement characteristic 4 Correctly identified report requirement and timeline 5 Properly assess the conflict of interest
Why is it important for an auditor to prepare a strategic audit plan?
Auditors are required to prepare a proper audit plan to ensure that all audit risks are identified and correct audit strategies are deployed to detect all concerning risk areas. It is essential for the auditor to prepare a good strategic audit plan. If the plan is well prepared, all kind of audit risks is identified and detected.
What should an auditor do if audit resources are not sufficient?
If audit resources are not sufficient to conducts audit engagements, then the auditor should negotiate with the client to extend the timeline so that resources could properly manage, or withdraw from the engagement.
What happens if an audit fails to identify this in the audit plan?
If the audit fails to identify this in the audit plan, the audit report that the auditor releases might not the one that the client needs. Also, the different types of audit engagement might have a different level of assurance.
Why is timeline important in audit?
The timeline of the report is also an important part of the audit plan. If the time is not sufficient, auditors should assess the impact of audit quality as the result this. In this planning stage, the auditor should assess if the timeline is sufficient enough for them to perform their works as well as manage their resources.
What is the purpose of pre audit?
Before Audit (Pre-audit activities): Pre-audit activities are also the importance of audit plan and in this stage, as require by standard, the auditor should: Perform client due diligent to make sure that the auditor fully understands the client’s nature of the business, sources of fund, and its major activities.
Why is it important to maintain audit independence?
Maintaining audit independence is very important to ensure the quality of audit opinion. Consider client integrity before accepting the audit engagements. Understand the term and condition of audit engagement before accept to avoid any conflict.
What are the steps in planning an audit?
The steps in planning an audit include ( Planning Procedures ): 1. Basic discussions with the client about the nature of the engagement and the client’s business and industry are performed first, and the auditor meets the key employees, or new employees of a continuing client. The overall audit strategy or the timing of the audit may be discussed, ...
Why should announcements on accounting principles and audit guides be read or reviewed?
Pronouncements on accounting principles and audit guides should be read or reviewed to assist in the development of complete audit programs fitting the unique needs of client’s business and industry.
Why is interim financial statement analyzed?
4. Interim financial statements are analyzed to identify accounts and transactions that differ from expectations (based on factors such as budgets or prior periods). The performance of such analytical procedures is mandatory in the planning of an audit to identify accounts that may be misstated and that deserve special emphasis in the audit program.
What is the purpose of planning for auditing?
During planning process of auditing, we try to understand the entity risks and prioritize these so that we could focus most of our energies to the highest risk areas. Based on the potential work, we also assign resources (human, technical and financial) during planning of auditing process. We also develop our audit program and auditing procedures at this stage.
Why is planning important in auditing?
As you can immediately see that planning is perhaps the most important steps in the auditing process. If you just visit client without proper planning, you cannot expect a great audit report regardless of how hard you work. You will feel pushed and short of time because most audit assignments are time bound.
What information can an entity share before an audit?
We may also request the entity for any information they can share before start of audit e.g financial statement, applicable legislation or standards/procedures, basic information about entity systems/applications or network diagrams etc.
What happens after an audit meeting?
After the meeting, we start our audit work according to our audit program. We request for information and review it keeping in view our understanding of standards and other applicable procedures. Any violations are recorded as exception. It is critical that we document reliable evidence to support our observations.
What is the follow up process?
The follow-up process includes agreeing with the management on suitable timelines for recommendations. Sometimes, the management may respond with additional information which might help the auditor understand the exception better, and he may agree with the management’s point of view and settle the audit observation.
What are the steps of auditing?
Primarily this is a four stage process: Planning. Field Work. Reporting. Follow up/Corrective Action. Here are details of activities that you will be doing in each step of auditing process:
Do you have to plan an audit assignment?
As you will expect from a professional, you have to plan your auditing assignment well before you actually start your work. During the planning process, we understand the entity well by looking at the information available to us before actually visiting the entity.
What is the purpose of audit planning if the audit may not ultimately follow the carefully thought out plan?
Often overlooked, the real benefit of audit planning is gained from the process itself. In painstakingly documenting endless client details, auditors achieve more than just compliance with professional standards—they also develop more efficient engagements and help reduce professional liability risk.
What is risk assessment in audit?
Risk assessment (AU-C §315): Gaining an understanding of the client and its environment presents an opportunity for the auditor to view the client's business and the engagement from a perspective other than the debits and credits underlying the financial statements. A holistic view of the various industry, regulatory, internal, and external factors may allow for linkages that might otherwise be lost in the minutiae of performing the engagement. Identifying areas of greatest risk early in an audit can allow for additional testing or analysis, reducing the likelihood of error that may result in a professional liability claim. As exemplified in the claim scenario, accounts affected by the internal control deficiency should have been deemed high - risk, and testing should have been tailored to address the concern.
How to save time in audit?
Invest the time: Proper planning is an investment in time that is intended to pay dividends in later phases of the engagement. Identifying a potential issue or complex audit area at the start of the planning process could save time later in the audit. That additional effort, while it may seem difficult in the moment, could save time as deadlines approach. Errors are more likely to occur when timing is compressed, causing work to be rushed. If planning can alleviate even a portion of the demand for time during the busiest periods of the year, exponential gains in efficiency and reduction of professional liability risk can be realized.
What are the pitfalls of planning?
Many planning pitfalls, including relying too heavily on checklists or compartmentalizing each step of the audit, result from trying to save time in the present without consideration of the rest of the engagement.
Is planning a discrete phase?
Timing (AU-C §§300.02 and 300.A2): Planning can easily be misconstrued as a discrete phase of an audit, taking place only when scheduled. Instead, it should be viewed as a continuous process that begins upon completion of the prior audit and ends with completion of the current engagement. The information learned during planning should be applied throughout the engagement to achieve appropriate conclusions. In our scenario, planning for the current engagement should have started with the control deficiency identified in the prior audit and addressed the issue throughout the audit process.
Is audit planning a process?
Audit planning is not a simple process. It involves consideration of client industry and regulatory factors, client operations and administration, availability and assignment of firm resources, engagement timing, and much more. Fortunately, the hard work of proper planning may not only enable more efficient audit execution, but it also provides auditors with important risk management techniques. Complying with all applicable professional standards when delivering services helps reduce professional liability risk. Consider the professional liability lessons that can be gleaned from these particular sections of the AICPA Statements on Auditing Standards:
What are the phases of audit planning?
The audit planning process can be divided into the following three phases: 1) starting the project, 2) preliminary survey (planning the audit and conducting risk assessment), and 3) developing the audit program. These steps are followed by fieldwork and reporting. Details of each of the steps are noted below:
What is audit program?
Based on the results of the scope review, preliminary survey, and risk assessment, the auditor develops an audit program that consists of the audit objectives, scope, methodology, and related concerns. The audit program includes audit steps, tasks, and procedures to test if the identified controls or procedures the audited entity has in place to prevent, eliminate, or minimize identified threats are working as intended. The Audit Manager reviews the audit program and the City Auditor approves the document.
What does an in charge auditor do?
For requested audits, the in-charge auditor must research the concerns behind the request. This may involve contacting the requesting party or office. Any meetings with the requesting party or office must involve the City Auditor.