See more
What kind of climate is Nevada?
Nevada is the driest state in the United States. It is made up of mostly desert and semi-arid climate regions, and, with the exception of the Las Vegas Valley, the average summer diurnal temperature range approaches 40 °F (22 °C) in much of the state.
Does Nevada have 4 seasons?
Any time you visit is sure to be extraordinary. Even in our deserts, there are four seasons in Nevada. Sure, there are some hot, dry desertscapes—and they're stunning.
What is the climate and weather in Nevada?
Nevada is the driest state in the US and is divided into semi-arid and arid climatic regions. The summers in Las Vegas get uncomfortably hot and the winters very cold, making the more mild spring and autumn months the best and most popular times to visit.
What are the average monthly temperatures in Nevada?
Average Temperatures for Las VegasMonthLowHighJan36.8°F57.1°FFeb41.4°F63.0°FMar47.0°F69.5°FApr53.9°F78.1°F8 more rows
Is Nevada a good state to live?
It is considered a great place to raise a family thanks to its slow crime rates, high security, ample recreational activities, and proximity to Las Vegas shopping, food, and entertainment. The area is known for its upscale living.
What part of Nevada has the best climate?
With 292 sunny days, Moapa Valley has some of the best weather in Nevada. Summer temperatures can spike to 108 degrees Fahrenheit. January's winter lows average a cool 37 degrees Fahrenheit....1. ParadiseParadise. ... Henderson. ... Las Vegas. ... Mesquite. ... Sunrise Manor. ... Moapa Valley.
Is Nevada The hottest state?
Texas is absolutely the hottest and most insufferable state in the entire nation. Forget about Death Valley, Arizona, Nevada, Florida—none of them measures up.
What is the weather like in Nevada all year round?
In Nevada, the summers are hot, muggy, and wet; the winters are short, very cold, snowy, and windy; and it is partly cloudy year round. Over the course of the year, the temperature typically varies from 27°F to 90°F and is rarely below 10°F or above 98°F.
Does Nevada get a lot of snow?
Snow is a common feature in Nevada during the winter season, which runs from December through February. Generally, the winter season is long and cold in northern Nevada and often short and overbearing in the southern parts of the state.
What is the hottest state in the US?
Florida is the hottest state in the U.S., with an average annual temperature of 71.5°F (21.9°C) between 1991 and 2020. It is the southernmost contiguous U.S. state with a subtropical climate in its northern and central regions and a tropical climate in its southern regions.
Does Nevada get tornadoes?
Tornadoes in Arizona and Nevada are rare. Arizona averages only five a year across the entire state, and Nevada nets a mean of two.
How cold are winters in Nevada?
Winter Weather in Las Vegas Nevada, United States. Daily high temperatures increase by 6°F, from 61°F to 67°F, rarely falling below 48°F or exceeding 76°F. The lowest daily average high temperature is 56°F on December 24.
What are the seasons in Nevada?
In Nevada, the summers are hot, muggy, and wet; the winters are short, very cold, snowy, and windy; and it is partly cloudy year round. Over the course of the year, the temperature typically varies from 27°F to 90°F and is rarely below 10°F or above 98°F.
Does Nevada get a lot of snow?
Snow is a common feature in Nevada during the winter season, which runs from December through February. Generally, the winter season is long and cold in northern Nevada and often short and overbearing in the southern parts of the state.
How hot is Nevada in winter?
Winter Weather in Las Vegas Nevada, United States. Daily high temperatures increase by 6°F, from 61°F to 67°F, rarely falling below 48°F or exceeding 76°F. The lowest daily average high temperature is 56°F on December 24.
What are winters like in Nevada?
Winters are surprisingly cold and dry. The average daytime high in Las Vegas is 57°F in December and January, but at night it dips down into the 30s°F. Most days in winter are pleasant enough to wear a light sweater, but always bring a warm jacket when you head outside after dark.
What is the climate of Nevada?
Nevada’s climate. The Sierra Nevada wring moisture from winter storms that develop over the Pacific and travel west with the jet stream, while the Rocky Mountains shield the state from any moisture moving up fro the Gulf of Mexico. The dry air over the state contributes to extreme temperatures.
What is the average temperature in Nevada in the winter?
In the southern part of the state, average high temperatures range from the 50s in the winter to nearly 100°F in July and August. Those are monthly averages. Daily high temperatures can be higher, like the state record high temperature of 125°F. In contrast, winter high temperatures in northeast Nevada are barely above freezing and reach only to the mid-80s.
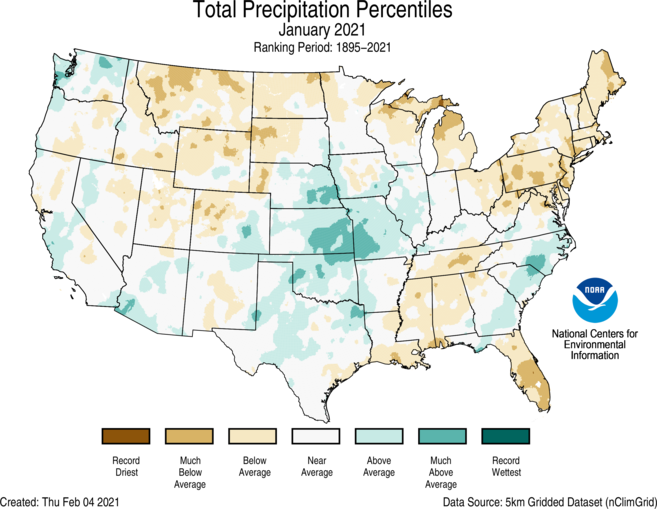
How much precipitation does Nevada get?
Average annual precipitation state-wide may be 10.3″, but it is lower in southern Nevada — only 7.1″ — and higher in northeastern Nevada, averaging 12.85″. Beyond the difference in the amount of rain and snow, there are differences in when, during the year, precipitation arrives. In southern Nevada, the summer is relatively wet, but in northern Nevada, the summer is dry.
When is Nevada nighttime low?
Nightime lows in much of the state are, on average, below freezing from October through April. In the spring and fall, particularly, nighttime lows average near freezing while highs average in the 60s or 70s. For all we think of southern Nevada as a hot desert, average low temperatures are in the 30s from December through February.
Is Nevada hot or cold?
Summers are hot, particularly in the southern part of the state, while winters can be cold. Nevada’s annual average precipitation was 10.3″ between 1901 and 2000. Nevada’s average summer (June – August) high temperature was 84.6°F, and the state’s average low winter temperature was 52.7°F.
How warm is Nevada in summer?
The number of very warm summer (June–August) days when daytime temperatures exceeded 95°F has increased across the state, with the largest increases in southern and northwestern Nevada (Figure 3), consistent with published analyses documenting increasing heat-wave frequency and/or severity across the Southwest (Allen & Sheridan, 2016; Gershunov et al., 2009) using a variety of heat-wave metrics. Increases in very warm nighttime temperatures (> 65°F) were larger in the southern portions of Nevada (Figure 3).
How much has the average temperature increased in Nevada?
Figure 1. Nevada’s annual average temperature has increased about 2°F since the early 20th century. Data from NOAA Climate at a Glance.
What is the role of evaporative demand in drought?
Evaporative demand—the atmospheric thirst driven by temperature, wind, humidity, and solar radiation— plays an important role in droughts and can be particularly impactful in water-limited regions like Nevada ( Hobbins et al., 2017 ).
What are the effects of heat waves?
Extremely high temperatures pose a danger to human life and physical and mental health (Bandala et al., 2019; Zuo et al., 2015 ), to transportation and power infrastructure (Chapman et al., 2013), and to ecosystems. Extreme heat increases fire risk for some vegetation types ( Zuo et al., 2015) and can also negatively impact wildlife (Albright et al., 2017). Extreme heat also impacts air quality, as higher temperatures are associated with increased ozone levels ( Wise & Comrie, 2005 ).
Why do urban heat islands increase temperatures?
Urban heat Islands occur in developed areas that retain heat, leading to higher temperatures relative to more-rural, non-developed surrounding areas. Heat is released from vehicles, power plants, and other machine and equipment, along with the stored solar energy in buildings and other infrastructure. Together this causes the increased temperatures. This is in part illustrated by the photo below, where the black lizard is recording a higher temperature due to absorbing more solar energy. Urban heat islands often show a stronger nighttime temperature trend compared to rural areas because heat in urban areas does not dissipate due to the infrastructure.
What happened in Nevada in 1997?
The winters of 1997 and 2017 were particularly severe examples of these conditions and caused major flooding and flood damages in Reno and along both the Truckee and Carson Rivers (Figure 15). In southern Nevada, intense summer thunderstorms have unleashed flash floods that have crashed through neighborhoods and the resort corridor along the Las Vegas Strip with devastating effects (Figure 15).
How can Nevada help with heat?
In Nevada’s cities, urban planners and public health officials can work together to help build resilience in the face of more-extreme urban heat and greater flooding potential by managing green spaces and increasing bright reflective surfaces in the built environment (Georgescu et al., 2014) to reduce the urban heat island effect and flooding risks.
How many people in Nevada experience precipitation above or below average?
Population by difference from average precipitation in September 2021
How many people experience extreme temperature and precipitation?
In September 2021, lived in counties where temperature, precipitation, or both temperature and precipitation was different than the 20th century average for September.
What are the two main ways people experience climate?
Temperature and precipitation are two of the main ways people experience climate. Explore where these weather factors are staying average and when the monthly average hit a 20-year anomaly. Use this map to understand where, county by county, monthly averages are significantly below or above historical average.
Where is the average precipitation in Nevada?
In the southern part of those valleys, the average annual precipitation is less than five inches. It increases to 18 inches in Lamoille Canyon on the western side of the Ruby Mountains of northeast Nevada and to about 40 inches in the Sierra Nevada. Variations in precipitation are due mainly to differences in elevation and exposure to precipitation-bearing storms.
What is the elevation of Nevada?
Nevada is predominately a plateau. The eastern part has an average elevation of between 5,000 and 6,000 feet. The western part is between 3,800 and 5,000 feet, the lower limit being in the vicinity of Pyramid Lake and Carson Sink. The southern part is generally between 2,000 and 3,000 feet. From the lower elevations of the western portion there is a fairly rapid rise westward toward the summits of the Sierra Nevada. The southwestern part slopes down toward Death Valley, California; the southern portion slopes toward the channel of the Colorado River, which is less than 1,000 feet above sea level. The northeastern part slopes toward the north, draining into the Snake River and thence into the Columbia River Basin.
What causes flooding in the northern part of the state?
Melting of the mountain snowpack in the spring usually causes some flooding in northern and western streams during April to June, but damaging floods of this type are infrequent; however, extensive flooding from melting of heavy snowpack has occurred in both the southern and northern parts of the state. Flooding can also be caused by a combination of warm rains and melting snow, especially in the western section. Heavy summer thunderstorms occasionally cause flooding of local streams, but they usually occur in sparsely settled mountainous areas and are seldom destructive. These storms, locally termed cloudbursts, may bring to a locality as much rain in a few hours as would normally fall in several months.
How is irrigation maintained in the Sierra Nevada?
Irrigation is maintained in the cultivated areas by impounding the water from melting snow. The Sierra Nevada snowpack provides water for the valleys of Walker, Carson, Truckee and Fallon.
What are the effects of the mountain barrier in Nevada?
As the air descends the eastern slope, it is warmed by compression, and very little precipitation occurs . The effects of this mountain barrier are felt not only in the west but throughout the state, with the result that the lowlands of Nevada are largely desert or steppes.
How long is the Nevada plateau?
The Nevada plateau has several mountain ranges, most of them 50 to 100 miles long, running generally north-south. The only east-west range is in the northeast where it forms the southern limit of the Columbia River Basin.
Where is the greatest contrast in precipitation found within a short distance in the United States?
One of the greatest contrasts in precipitation found within a short distance in the United States occurs between the western slopes of the Sierras in California and the valleys just to the east of this range.
What is the climate of Nevada?
Nevada climate is mainly of arid and semi-arid types (Köppen climate classification BWh/BWk, BSh/ BSk), with hot summers and cold winters. Nevada lies in the Western United States and is the driest state in the union. California in the west, Oregon in the northwest, Idaho in the northeast, Utah in the east, and Arizona in the southeast, share borders with the state. The Pacific Ocean and the desert regions in the south influence the dry climate of the state.#N#Nevada, the Silver State, is mostly arid, with an average elevation of 1608 meters and highest of 4401 meters at Boundary Peak. The geography consists of desert lands and semi-arid regions of the Great Basin. The Mojave Desert is in the south, while the Sierra Nevada and Lake Tahoe lie in on the western boundary. The southern portion has flat terrain and receives less rain. Mountain ranges above the desert plains consist of lush forests. The Snake River's tributaries drain the north, while the Colorado River drains the southern portion of the state. The Sierra Nevada is home to several rivers, including the Carson, Truckee, and Walker rivers. The vegetation is of alpine and sub-alpine types in the high mountains.#N#Summers are severely hot and dry in Nevada, with the difference between day and night temperatures, often exceeding 40°F (4.4°C). Day highs frequently stay above the 100°F (37.8°C) mark from June to September and even top 120°F (48.9°C). Winters are long and cold in the north but short and mild in the south. Daytime highs average a comfortable 57°F (13.9°C) in Las Vegas at the peak of winter, while the nights are above freezing at 38°F (3.3°C). Spring is warm, while the autumn has pleasant conditions. Winter minimum temperatures register in the 15°F (-9.4°C) to 20°F (-6.7°C) range in the plains, and temperatures below 0°F (-17.8°C) seldom last for more than a few days.#N#The annual rainfall is scarce and hardly averages 7" (177.8mm) in Nevada, with the majority of the precipitation on the leeward side of the Sierra Nevada. The average precipitation ranges from 5" (127mm) in the south to 12" (304.8mm) in the north. Western and south-central portions record maximum precipitation in the winter, central, and northeast in the spring and eastern during the summer. Snowfall is heavy between 20" (508mm) in the central and 30" (762mm) in the northern regions, while the south receives occasional light outbursts. Humidity rarely exceeds 60% throughout the year. The freeze-free season ranges from 70 days in the extreme north to 225 days in the south. Nevada receives ample sunshine of 3300 hours over the year.#N#Laughlin recorded the highest ever temperature of 125°F (51.7°C) on June 29, 1994, in Nevada, while San Jacinto recorded the coldest temperature of -52°F (-46.7°C) in the winter of 1972.
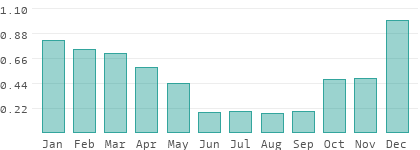
What is the snowiest month in Nevada?
January is the snowiest month of the year in Nevada with 3" (76.2mm) to 12" (304.8mm) of snow. The northern and central regions contribute most of the snowfall, while the south hardly sees any.#N#The average high temperatures are between 36°F (2.2°C) to 65°F (18.3°C), while the average low temperatures are in the 9°F (-12.8°C) to 43°F (6.1°C) range. Carson City, the capital in the Reno area averages between 22°F (-5.6°C) to 45°F (7.2°C), Spring Valley State Park in central Nevada is cold between 9°F (-12.8°C) to 43°F (6.1°C). The diurnal temperature difference is more than 30°F (-1.1°C) during most of the month.#N#Most of the scarce precipitation occurs in the western and southern portions of the state. The 8 hours of sunshine keeps the days warm, but conditions become rapidly chilly after sunset. Skiing enthusiasts find joy in the mountains where the snow accumulates in large quantities. All-wheel drives are preferable on slushy roads and parking areas to stop vehicles from doing donuts. Overall, January is an off-season for tourism in Nevada.
What is the weather like in Nevada in February?
February is chilly in the winter season in Nevada with a moderate amount of snowfall. Great Basin National Park in central Nevada receives substantial snowfall over 23" (584.2mm). Day temperatures are between 41°F (5°C) to 69°F (20.6°C), but nights are bitterly cold in the 12°F (-11.1°C) to 46°F (7.8°C) zone. The mountains of Sierra Nevada gather loads of snow and are a sight to watch in the winter.#N#Sunny days occasionally occur in February, but the temperatures rescind quickly after sunset. Wind speeds are high in the plains due to a lack of natural barriers. Winter nights have clear skies that are ideal for stargazing. Snowshoeing, tubing, and ice-skating are popular besides skiing in cold conditions. Daylight hours are sufficient to enjoy the adventures on the white landscape, although the Sierra Nevada has a vibrant nightlife. Pack warm coats even though the days seem to be mild to warm. February is a month for budget travelers to take advantage of discounted rates in Nevada.
What is the temperature in March in Nevada?
March has cold nights in Nevada at the beginning of the spring season. Day highs are usually in the 48°F (8.9°C) to 77°F (25°C) range, while nightly lows are between 20°F (-6.7°C) to 50°F (10°C). Early spring often sees cold temperatures in the range of 20°F (-6.7°C) to 48°F (8.9°C) in Mountain City in the north. Weather in March »
What is the average temperature in Nevada in April?
A few areas in the north and central zones receive 2" (50.8mm) to 4" (101.6mm) of snow.#N#The average high temperatures are in the warm 55°F (12.8°C) to 86°F (30°C), while nights are between a cold 36°F (2.2°C) to mild 56°F (13.3°C) statewide. April sees an average of 1" (25.4mm) to 2" (50.8mm) of rainfall, with 9 to 10 hours of bright sunshine. Caliente in the central region registers a wide temperature range between 36°F (2.2°C) to 68°F (20°C), while Boulder City in the south is warm between 56°F (13.3°C) to 75°F (23.9°C).#N#The icecaps remain intact in the Sierra Nevada, but the lower plains are free from snow in spring. The alpine and sub-alpine zones witness blossoming flowers, and the highlands offer unbridled natural beauty. Hiking in the mountains is a popular activity during the day, and even camping is desirable where the night temperatures are mild. April is one of the best times to visit Nevada.
What is the temperature in Las Vegas in March?
Early spring often sees cold temperatures in the range of 20°F (-6.7°C) to 48°F (8.9°C) in Mountain City in the north. Hawthorne, in the Reno area, begins to experience warmth by the second half of March with temperatures in 34°F (1.1°C) to 61°F (16.1°C) range . Las Vegas has comfortable conditions in the spring season.#N#The central and northern regions receive between 5" (127mm) to 7" (177.8mm) of snow, but the precipitation is negligible. The daily sunshine lasts for at least 8 hours and rapidly melts the snow. March begins the spring turkey hunting season in Nevada. The end of the cold season is the beginning of an increase in pollen levels, and by mid-March, they are significantly high. Keep warm clothes within reach as the conditions tend to be cold in March in Nevada.
What are the dangers of Nevada?
Nevada is vulnerable to thunderstorms, droughts, floods, wildfires, earthquakes, and tornadoes in late spring and summer. The plains witness flooding in spring and summer due to the melting of snow and rain from thunderstorms, with the Nevada Floods of 2013 as a notable example. Cloudbursts may bring more rain in a few hours than the entire season. The dry conditions and scanty rainfall are responsible for severe wildfires at the peak of the summer in much of the state. Nevada also experiences frequent earthquakes of low intensity below 3.5 on the Richter scale. Wind speeds are high across the vast plains with the lack of high mountain ranges to provide natural barriers. Pacific storms occasionally bring heavy snow in the winter.