How often does the Earth's magnetic pole reversal occur?
What do sediment cores tell us about the Earth's polarity?
Why is the N-S compass 180 degrees wrong?
How many times has the Earth's magnetic field flipped its polarity?
Why does the Earth have a magnetic field?
How fast is the North Pole moving?
How often do dinosaurs revert back?
See 4 more
About this website

How often does magnetic reversal occur on Earth?
They can happen as often as every 10 thousand years or so and as infrequently as every 50 million years or more. The last reversal was about 780,000 years ago.
How long ago did earth experience its last magnetic reversal?
They came up with the most accurate date yet of Earth's last magnetic field reversal called the Laschamp event, which they estimate occurred between 41,560 and 41,050 years ago and lasted less than 1000 years.
How many times has the magnetic field reversed in the past 5 million years?
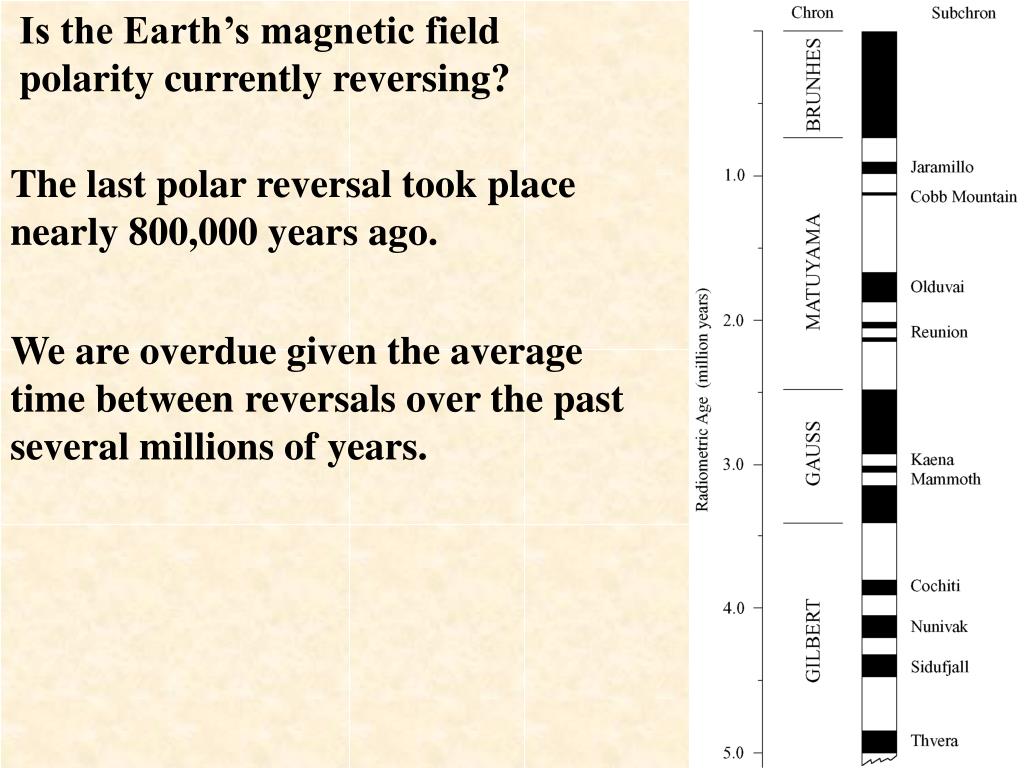
Over the last 5 million years, the Earth's magnetic field reversed itself at least 20 times (Figure 7). Over the last 20 million years, the reversal happens about every 200 thousand to 300 thousand years; however, it is very difficult to predict when a reversal will occur.
How many times has the earth reversed its magnetic field in the last 20 million years?
Cosmic rays It has always been a feature of our planet, but it has flipped in polarity repeatedly throughout Earth's history. Each time it flips – up to 100 times in the past 20 million years, while the reversal can take about 1,000 years to complete – it leaves fossilised magnetisation in rocks on Earth.
Is Earth's magnetic field normal or reversed 65 million years ago?
Sometimes it flips back and forth several times within a million years. Earth's magnetic field has been "normal" for the past 780,000 years. Scientists call this time period the Brunhes normal.
How do we know earth's magnetic field has reversed in the past?
As a matter of geological record, the Earth's magnetic field has undergone numerous reversals of polarity. We can see this in the magnetic patterns found in volcanic rocks, especially those recovered from the ocean floors. In the last 10 million years, there have been, on average, 4 or 5 reversals per million years.
Can humans survive a magnetic reversal?
You can relax - a pole reversal doesn't directly affect the human body. However, it may indirectly affect humanity - by causing power-grid failure, frequent earthquakes, and floods. It will not be sudden, though. A pole shift may take a long time to complete, and the natural disasters will be spread out in the period.
When north goes south: Is Earth's magnetic field flipping?
Something odd is happening to Earth’s magnetic field. Over the last 200 years, it’s been slowly weakening and shifting its magnetic north pole (where a compass points, not to be confused with ...
Why are polarity reversals important?
Such polarity reversals provide important clues to the nature of the processes that generate the magnetic field, said Clement. Since the time of Albert Einstein, researchers have tried to nail down a firm time-frame during which reversals of Earth's magnetic field occur.
How long does it take for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse polarity?
Arlington, Va.—. The time it takes for Earth's magnetic field to reverse polarity is approximately 7000 years, but the time it takes for the reversal to occur is shorter at low latitudes than at high latitudes, a geologist funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) has concluded.
How much money does the NSF give in 2021?
With a fiscal year 2021 budget of $8.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, ...
How long does polarity transition last?
The reason for this uncertainty? Each published polarity transition reported a slightly different duration, from just under 1,000 years to 28,000 years.
What is the purpose of the National Science Foundation?
[email protected]. The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation.
Is the magnetic field static or dynamic?
Our planet's magnetic field varies with time, indicating it is not a static or fixed feature. Instead, some active process works to maintain the field. That process is most likely a kind of dynamic action in which the flowing and convecting liquid iron in Earth's outer core generates the magnetic field, geologists believe.
Does magnetic field change direction?
The magnetic field has exhibited a frequent but dramatic variation at irregular times in the geologic past: it has completely changed direction. A compass needle, if one existed then, would have pointed not to the north geographic pole, but instead to the opposite direction. Such polarity reversals provide important clues to the nature of the processes that generate the magnetic field, said Clement.
What is the purpose of the computer model?
Based on a set of physics equations that describe what scientists believe are the forces that create and maintain the magnetic field, Glatzmaier and colleague Paul Roberts at the University of California, Los Angeles, created a computer model to simulate the conditions in the Earth's interior. The computer-generated magnetic field even reverses ...
How often does the Earth's magnetic field reverse?
Our planet's magnetic field reverses about once every 200,000 years on average. However, the time between reversals is highly variable. The last time Earth's magnetic field flipped was 780,000 years ago, according to the geologic record of Earth's polarity.
What is the magnetic field on Earth?
Scientists believe Earth's magnetic field is generated deep inside our planet. There, the heat of the Earth's solid inner core churns a liquid outer core composed of iron and nickel. The churning acts like convection, which generates electric currents and, as a result, a magnetic field. This magnetic field shields most of the habited parts ...
How long did the Geodynamo model run?
The equations are continually solved, each solution advancing the clock forward about a week. At its longest stretch, the model ran the equivalent of 500,000 years, Glatzmaier said.
How far can you peer into the Earth's center to observe the magnetic field?
However, there is no way to peer 4,000 miles (6,400 kilometers) into Earth's center to observe the process in action.
When did Glatzmaier and Roberts develop their computer model?
That inability spurred Glatzmaier and Roberts to develop their computer model in 1995. Since then, they have continued to refine and evolve the model using ever more sophisticated and faster computers. The model is essentially a set of equations that describe the physics of the geodynamo.
What are the bits of a pole reversal?
These bits of a pole reversal are referred to as instabilities. They constantly occur in the fluid flow of the core, tracking through it like little hurricanes, though at a much slower pace—about one degree of latitude per year.
Why does the solid inner core inhibit magnetic reversals?
Our solution shows how convection in the fluid outer core is continually trying to reverse the field but that the solid inner core inhibits magnetic reversals because the field in the inner core can only change on the much longer time scale of diffusion. Only once in many attempts is a reversal successful, which is probably the reason why the times between reversals of the Earth’s field are long and randomly distributed.
How long does it take for a double reversal to happen?
They have been telling us that the process takes hundreds or thousands of years. Recent studies have shown that it can happen in the space of weeks or months, and I suggest it can happen overnight. Perhaps rapid reversals don’t leave much evidence – perhaps rapid reversals are quite common! For example, if it was normal for a double reversal to happen quickly – where the poles return to their original position – we wouldn’t know about any historical instances.
What happens if a geomagnetic field is reversed?
If a reversal involves a dramatic lessening of our geomagnetic field’s strength, then basically our shields are down, and cosmic rays reaching ground-level will greatly increase. Forget about navigational problems – we could be fried.
How long has the magnetic pole been reversed?
The last one occurred 780,000 years ago. The average time period between reversals is 450,000 years, but there isn’t really any pattern, it is random. We are overdue by average only.
What causes a magnetic reversal?
My interpretation is that a massive solar storm could be the straw that breaks the camel’s back and trigger a reversal if the Earth is ready for one. The Electric Universe folk have also suggested that a highly-charged comet passing by could also do the trick. Or perhaps ocean currents, after being affected by climate change, are the trigger? And if climate change is caused by the Sun, then that ties in nicely with the first theory.
Why can't the spacing between successive flows be determined accurately?
the spacing in time between successive flows erupted during a transition cannot be determined accurately because the errors associated with radiometric ages are typically much greater than the duration of a polarity transition. [ The Magnetic Field of the Earth: Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle, page 205]
Where is the lava flow polarity reversal?
Palaeomagnetic results from lava flows recording a geomagnetic polarity reversal at Steens Mountain, Oregon suggest the occurrence of brief episodes of astonishingly rapid field change of six degrees per day. The evidence is large, systematic variations in the direction of remanent magnetization as a function of the temperature of thermal demagnetization and of vertical position within a single flow, which are most simply explained by the hypothesis that the field was changing direction as the flow cooled. [ Nature]
What is the study of the past magnetic field?
The study of the past magnetic field of the Earth is known as paleomagnetism. The polarity of the Earth's magnetic field is recorded in igneous rocks, and reversals of the field are thus detectable as "stripes" centered on mid-ocean ridges where the sea floor is spreading, while the stability of the geomagnetic poles between reversals has allowed paleomagnetism to track the past motion of continents. Reversals also provide the basis for magnetostratigraphy, a way of dating rocks and sediments. The field also magnetizes the crust, and magnetic anomalies can be used to search for deposits of metal ores.
What is secular variation?
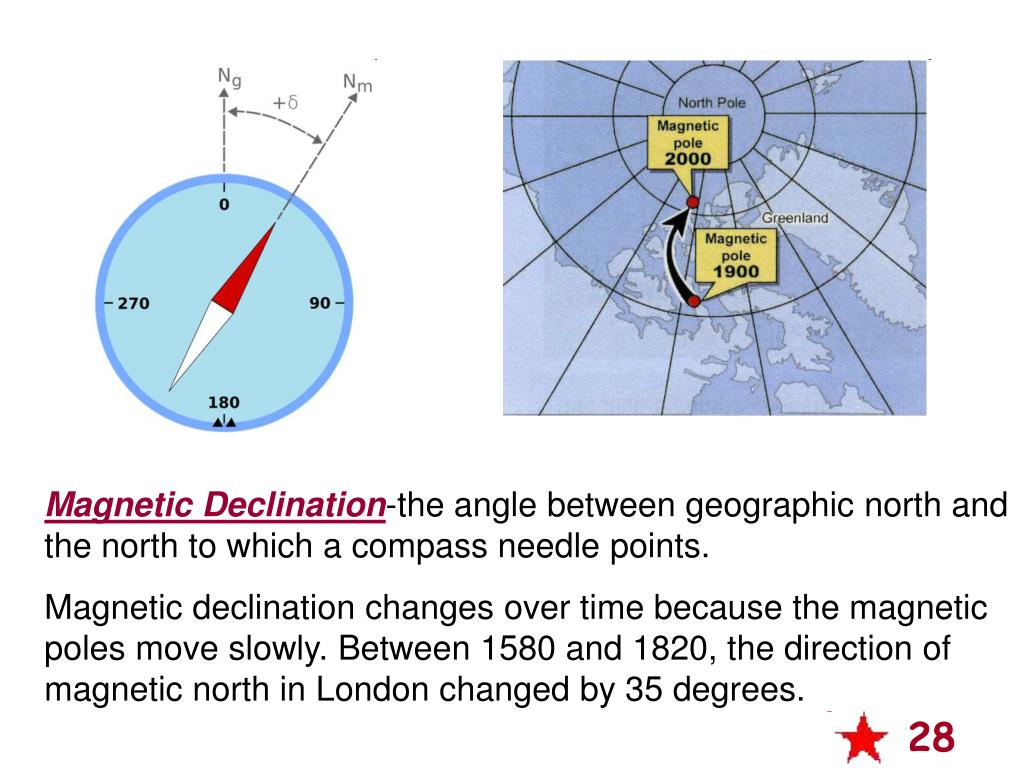
Changes in Earth's magnetic field on a time scale of a year or more are referred to as secular variation. Over hundreds of years, magnetic declination is observed to vary over tens of degrees. The animation shows how global declinations have changed over the last few centuries.
How to find the declination of a magnetic field?
It can be estimated by comparing the magnetic north–south heading on a compass with the direction of a celestial pole. Maps typically include information on the declination as an angle or a small diagram showing the relationship between magnetic north and true north. Information on declination for a region can be represented by a chart with isogonic lines (contour lines with each line representing a fixed declination).
What is the North Pole of a magnet?
A magnet's North pole is defined as the pole that is attracted by the Earth's North Magnetic Pole when the magnet is suspended so it can turn freely. Since opposite poles attract, the North Magnetic Pole of the Earth is really the south pole of its magnetic field (the place where the field is directed downward into the Earth).
How to measure the magnetic field of the Earth?
A typical procedure for measuring its direction is to use a compass to determine the direction of magnetic North. Its angle relative to true North is the declination ( D) or variation. Facing magnetic North, the angle the field makes with the horizontal is the inclination ( I) or magnetic dip. The intensity ( F) of the field is proportional to the force it exerts on a magnet. Another common representation is in X (North), Y (East) and Z (Down) coordinates.
How does the Earth's magnetic field work?
Earth's magnetic field serves to deflect most of the solar wind, whose charged particles would otherwise strip away the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. One stripping mechanism is for gas to be caught in bubbles of magnetic field, which are ripped off by solar winds. Calculations of the loss of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere of Mars, resulting from scavenging of ions by the solar wind, indicate that the dissipation of the magnetic field of Mars caused a near total loss of its atmosphere.
What are the lines on the Earth's rotation axis?
The lines represent magnetic field lines, blue when the field points towards the center and yellow when away. The rotation axis of the Earth is centered and vertical. The dense clusters of lines are within the Earth's core.
How often does the Earth's magnetic pole reversal occur?
Reversals are the rule, not the exception. Earth has settled in the last 20 million years into a pattern of a pole reversal about every 200,000 to 300,000 years, although it has been more than twice ...
What do sediment cores tell us about the Earth's polarity?
Sediment cores taken from deep ocean floors can tell scientists about magnetic polarity shifts, providing a direct link between magnetic field activity and the fossil record. The Earth's magnetic field determines the magnetization of lava as it is laid down on the ocean floor on either side of the Mid-Atlantic Rift where the North American and European continental plates are spreading apart. As the lava solidifies, it creates a record of the orientation of past magnetic fields much like a tape recorder records sound. The last time that Earth's poles flipped in a major reversal was about 780,000 years ago, in what scientists call the Brunhes-Matuyama reversal. The fossil record shows no drastic changes in plant or animal life. Deep ocean sediment cores from this period also indicate no changes in glacial activity, based on the amount of oxygen isotopes in the cores. This is also proof that a polarity reversal would not affect the rotation axis of Earth, as the planet's rotation axis tilt has a significant effect on climate and glaciation and any change would be evident in the glacial record.
Why is the N-S compass 180 degrees wrong?
The N-S markings of a compass would be 180 degrees wrong if the polarity of today's magnetic field were reversed. Many doomsday theorists have tried to take this natural geological occurrence and suggest it could lead to Earth's destruction.
How many times has the Earth's magnetic field flipped its polarity?
Scientists understand that Earth's magnetic field has flipped its polarity many times over the millennia. In other words, if you were alive about 800,000 years ago, and facing what we call north with a magnetic compass in your hand, the needle would point to 'south.'.
Why does the Earth have a magnetic field?
Geophysicists are pretty sure that the reason Earth has a magnetic field is because its solid iron core is surrounded by a fluid ocean of hot, liquid metal. This process can also be modeled with supercomputers. Ours is, without hyperbole, a dynamic planet.
How fast is the North Pole moving?
It is moving faster now, actually, as scientists estimate the pole is migrating northward about 40 miles per year , as opposed to about 10 miles per year in the early 20th century.
How often do dinosaurs revert back?
And while reversals have happened more frequently in "recent" years, when dinosaurs walked Earth a reversal was more likely to happen only about every one million years.
Overview
Time dependence
The geomagnetic field changes on time scales from milliseconds to millions of years. Shorter time scales mostly arise from currents in the ionosphere (ionospheric dynamo region) and magnetosphere, and some changes can be traced to geomagnetic storms or daily variations in currents. Changes over time scales of a year or more mostly reflect changes in the Earth's interior, particula…
Significance
Earth's magnetic field deflects most of the solar wind, whose charged particles would otherwise strip away the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. One stripping mechanism is for gas to be caught in bubbles of magnetic field, which are ripped off by solar winds. Calculations of the loss of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere of Mars, resulting from scavenging of ions by the solar wind, indicate that the dissipation of the magnetic field of Mars …
Characteristics
At any location, the Earth's magnetic field can be represented by a three-dimensional vector. A typical procedure for measuring its direction is to use a compass to determine the direction of magnetic North. Its angle relative to true North is the declination (D) or variation. Facing magnetic North, the angle the field makes with the horizontal is the inclination (I) or magnetic dip. The intensi…
Magnetosphere
Earth's magnetic field, predominantly dipolar at its surface, is distorted further out by the solar wind. This is a stream of charged particles leaving the Sun's corona and accelerating to a speed of 200 to 1000 kilometres per second. They carry with them a magnetic field, the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF).
The solar wind exerts a pressure, and if it could reach Earth's atmosphere it wo…
Physical origin
The Earth's magnetic field is believed to be generated by electric currents in the conductive iron alloys of its core, created by convection currents due to heat escaping from the core.
The Earth and most of the planets in the Solar System, as well as the Sun and other stars, all generate magnetic fields through the motion of electrically cond…
Measurement and analysis
The Earth's magnetic field strength was measured by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1832 and has been repeatedly measured since then, showing a relative decay of about 10% over the last 150 years. The Magsat satellite and later satellites have used 3-axis vector magnetometers to probe the 3-D structure of the Earth's magnetic field. The later Ørsted satellite allowed a comparison indicating a dyn…
Biomagnetism
Animals, including birds and turtles, can detect the Earth's magnetic field, and use the field to navigate during migration. Some researchers have found that cows and wild deer tend to align their bodies north–south while relaxing, but not when the animals are under high-voltage power lines, suggesting that magnetism is responsible. Other researchers reported in 2011 that they could not replicate those findings using different Google Earth images.