The Three Stages of Classical Conditioning
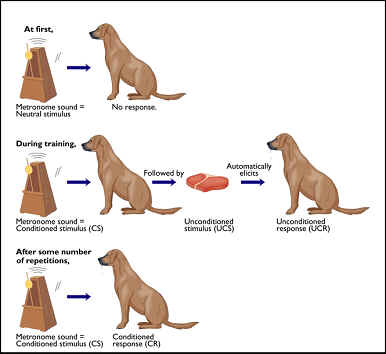
- Before Conditioning. At this stage, the UCS and CS have no relationship. ...
- During Conditioning. During the second stage, the UCS and NS are paired leading the previously neutral stimulus to become a CS.
- After Conditioning. Once the UCS and CS have been associated, the CS will trigger a response without the need to present the UCS with it.
What are the three stages of classical conditioning?
There are some terms associated with classical conditioning, which include:
- Unconditioned stimulus: It refers to things that trigger a naturally occurring response. ...
- Unconditioned response: It is a naturally occurring response that follows the unconditioned stimulus. ...
- Conditioned stimulus: It is also known as the neutral stimulus. ...
- Conditioned response: This is the acquired response to the conditioned stimulus. ...
What are the principles of classical conditioning?
So here are some most important principles of classical conditioning:
- ACQUISITION The process in which a conditioned stimulus has the ability to elicit a conditioned response. ...
- HIGH ORDER CONDITIONING High-order conditioning occurs when a strong conditioned stimulus is paired with a neutral stimulus. ...
- EXTINCTION This is the most important principle of classical conditioning. ...
What is the final phase of classical conditioning?
final phase of classical conditioning in which the conditioned stimulus alone causes a conditioned response when NS becomes CS
What therapy is based on classical conditioning?
With repeated presentations, the two stimuli become associated and the person develops an aversion towards the stimuli which initially caused the deviant behavior. Aversion therapy is based on classical conditioning. According to learning theory, two stimuli become associated when they occur frequently together (pairing).
What is classical conditioning in simple terms?
Classical conditioning is a type of learning that happens unconsciously. When you learn through classical conditioning, an automatic conditioned response is paired with a specific stimulus. This creates a behavior.
What is the process of classical conditioning quizlet?
Classical conditioning. a form of learning based on the repeated association of two (or more) different stimuli; learning is only said to have occurred when a particular stimulus consistently produces a response that it did not previously produce. Conditioning.
What is the process of conditioning in psychology?
Conditioning is a form of learning in which either (1) a given stimulus (or signal) becomes increasingly effective in evoking a response or (2) a response occurs with increasing regularity in a well-specified and stable environment. The type of reinforcement used will determine the outcome.
What does classical conditioning mean in psychology quizlet?
classical conditioning. a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events. unconditioned response (US) in classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (US), such as salivation when food is in the mouth.
What kind of learning is classical conditioning?
Classical conditioning is a learning process focused more on involuntary behaviors, using associations with neutral stimuli to evoke a specific involuntary response.
Who discovered the basic process of classical conditioning?
PavlovClassical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and was discovered by Pavlov, a Russian physiologist. In simple terms, two stimuli are linked together to produce a new learned response in a person or animal.
What are the 3 stages of classical conditioning?
At each stage, stimuli and responses are identified by different terminology. The three stages of classical conditioning are before acquisition, acquisition, and after acquisition.
What is classical conditioning example?
Classical conditioning refers to learned behaviors when a neutral stimulus is associated with a learned response. For example, when a dog sees a leash, it learns that it's time to go for a walk.
What is an unconditioned stimulus?
An unconditioned stimulus is a stimulus that leads to an automatic response. In Pavlov's experiment, the food was the unconditioned stimulus. An unconditioned response is an automatic response to a stimulus. The dogs salivating for food is the unconditioned response in Pavlov's experiment.
How are generalization and discrimination related to classical conditioning?
How are generalization and discrimination related to classical conditioning? When one responds to a stimulus similar to the conditioned stimulus, generalization has occurred. The ability to respond differently to different stimuli is discrimination.
When a conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without an unconditioned stimulus a subject will?
If the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus, the conditioned response will eventually be eliminated.
Which of the following is an example of instinctive drift?
For example, a dog with the nature to bark at visitors thinking they are intruders might have been taught to sit quietly when a guest enters through reward and punishment. Under stress, however, it may have instinctual drift, disregarding the learned behavior and barking at the guest.
Who is the father of classical conditioning?
The best-known example of this is from what some believe to be the father of classical conditioning: Ivan Pavlov. In an experiment on canine digestion, he found that over time dogs were salivating not only when their food was presented to them, but when the people who fed them arrived.
How does operant conditioning work?
In operant conditioning, you learn a behavior by the consequence of that behavior, which in turn affects your future behavior.
What is the term for the unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response that wasn't taught?
Before conditioning. Before conditioning is when the unconditioned stimulus and unconditioned response come into play. This is the natural response that wasn’t taught. For instance, food produces salivating, or a stomach virus produces nausea.
What stimulus is associated with the unconditioned response?
We begin to associate the neutral stimulus with the unconditioned response.
Is classical conditioning exposed?
We’re all exposed to classical conditioning in one way or another throughout our lives.
Is operant conditioning unconscious?
While classical conditioning is considered unconscious learning, operant conditioning is what most people would consider a habit. It’s about reinforcement and is considered more controlled. Classical conditioning is considered more of a reflex.
Who used classical conditioning in the study of human emotion?
John B. Watson used the principles of classical conditioning in the study of human emotion. Watson’s ideas were influenced by Pavlov’s work. According to Watson, human behavior, just like animal behavior, is primarily the result of conditioned responses.
How does classical conditioning help species survival?
This added evidence to the idea that classical conditioning could contribute to species survival by helping organisms learn to avoid stimuli that posed real dangers to health and welfare. Robert Rescorla demonstrated how powerfully an organism can learn to predict the UCS from the CS.
What is the decrease in the conditioned response when the unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented with the conditioned stimulus?
Extinction is the decrease in the conditioned response when the unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented with the conditioned stimulus. When presented with the conditioned stimulus alone, the dog, cat, or other organism would show a weaker and weaker response, and finally no response. In classical conditioning terms, there is ...
What is taste aversion?
Taste aversion is a type of conditioning in which an interval of several hours may pass between the conditioned stimulus (something ingested) and the unconditioned stimulus (nausea or illness). Here’s how it works. Between classes, you and a friend grab a quick lunch from a food cart on campus. You share a dish of chicken curry ...
How long should the interval between stimulus and unconditioned stimulus be?
Typically, there should only be a brief interval between presentation of the conditioned stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus. Depending on what is being conditioned, sometimes this interval is as little as five seconds (Chance, 2009). However, with other types of conditioning, the interval can be up to several hours.
What is the initial period of learning?
In classical conditioning, the initial period of learning is known as acquisition, when an organism learns to connect a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus. During acquisition, the neutral stimulus begins to elicit the conditioned response, and eventually the neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus capable ...
Why did Watson argue that psychology must focus on outward observable behavior?
Watson argued that in order for psychology to become a legitimate science, it must shift its concern away from internal mental processes because mental processes cannot be seen or measured. Instead, he asserted that psychology must focus on outward observable behavior that can be measured. Figure 2.
What are some examples of classical conditioning?
The most famous example of classical conditioning was Pavlov's experiment with dogs, who salivated in response to a bell tone.
Why is classical conditioning important?
Classical conditioning emphasizes the importance of learning from the environment, and supports nurture over nature. However, it is limiting to describe behavior solely in terms of either nature or nurture, and attempts to do this underestimate the complexity of human behavior. It is more likely that behavior is due to an interaction between nature (biology) and nurture (environment).
What is generalization in psychology?
Generalisation. In psychology, generalisation is the tendency to respond in the same way to stimuli that are similar but not identical to the conditioned stimulus. For example, in Pavlov's experiment, if a dog is conditioned to salivated to the sound of a bell, it may later salivate to a higher pitched bell.
What is the term for the gradual weakening of a conditioned response?
In psychology, extinction refers to gradual weakening of a conditioned response by breaking the association between the conditioned and the unconditioned stimuli.
When does conditioned stimulus occur?
For classical conditioning to be effective, the conditioned stimulus should occur before the unconditioned stimulus, rather than after it, or during the same time. Thus, the conditioned stimulus acts as a type of signal or cue for the unconditioned stimulus.
What did Watson believe about the mind?
Watson believed that all individual differences in behavior were due to different experiences of learning. He famously said:
What is the deterministic approach to psychology?
The deterministic approach also has important implications for psychology as a science.
What is Classical Conditioning?
Classical conditioning, sometimes called Pavlovian or respondent conditioning, is a form of associative learning that modifies behavior. It does this by creating associations between two stimuli and thus developing new stimulus-response connections. A neutral stimulus, which formerly elicited no automatic response, is paired with an unconditioned stimulus in order to establish a new conditioned response.
Why is classical conditioning important?
Classical conditioning is important because it is a basic form of learning that shapes the behavior of humans and animals. It also plays a significant role in things like phobias and emotional reactions. Understanding classical conditioning can assist in the treatment of phobias, help promote positive learning environments, and give individuals greater insight into why they respond in the way they do.
What is stimulus generalization?
Stimulus Generalization occurs when something similar but distinct from the conditioned stimulus causes the same conditioned response. If the dogs have learned to associate a certain bell sound with their food, the sound of the doorbell might elicit the same response even though it is not exactly the same sound.
What happens when a dog's conditioned response ceases?
Extinction happens when the learned or conditioned response ceases after a period of time during which the unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented alongside the conditioned stimulus. While the dogs would continue to show the conditioned response to the bell for some time, this behavior would eventually cease if the food is no longer presented after the bell.
What was the conditioned stimulus in Pavlov's experiments?
In both Pavlov's experiments with dogs and Watson's experiments with Albert, neutral stimuli became conditioned stimuli through the process of classical conditioning. By repeatedly presenting the neutral stimulus before the unconditioned stimulus, a new association was created. With Pavlov's dogs, the conditioned stimulus was the sound of a bell; with Albert, the conditioned stimulus was the white rat.
How did Watson prove that humans are conditioned?
Watson built upon Pavlov's experiments with salivation in dogs to show that human emotional responses could also be conditioned or learned in the same way. To prove this, he conducted the "Little Albert" experiments. These experiments, now considered unethical, tested the fear response of a nine-month-old infant named Albert B. In this case, the unconditioned stimulus was the clanging of a metal bar near his head which automatically caused a fear response (unconditioned response). Neutral stimuli, such as a white rat, were then presented right before the loud noise. Eventually, Albert learned to respond with fear (conditioned response) to the white rat (conditioned stimulus) which had not previously evoked this response.
How does classical conditioning affect our daily actions?
Hearing a song (conditioned stimulus) may trigger a happy feeling or increased heart rate (conditioned response) because it reminds us of a significant other. The smell of a certain perfume (conditioned stimulus) might elicit sad tears (conditioned response) because it reminds us of a grandmother who has passed away. Getting off a certain exit on the highway (conditioned stimulus) may produce an anxious response of palms sweating and heart racing (conditioned response) because it is the exit we take to get to a stressful job. Two important examples of how classical conditioning works are a fear response and taste aversion.
What is classical conditioning?
Classical Conditioning Definition: Classical conditioning is a learning process in which a neutral stimulus is paired with another stimulus that nautically produces a response. After repeated pairing, the previously neutral stimulus begins to evoke the response all on its own.
What are the four principles that affect classical conditioning?
Four important principles that can affect the classical conditioning process are stimulus generalization, stimulus discrimination, extinction, and spontaneous recovery .
How do phobias form?
In the cases of phobias, these associations often form after a single pairing of the conditioned stimulus and the unconditioned stimulus. For example, the sight of a needle paired with the sharp pinch of pain caused by injection might cause a child to become afraid of needles.
Why did Pavlov's dog salivate?
To learn more, Pavlov began ringing a bell whenever the dogs were fed. Eventually, an association formed between the sound of the bell and the presentation of food, and the dogs began to salivate whenever they heard the sound of the bell.
How does classical conditioning affect fear?
Classical conditioning can play a role in the development of fear responses. In the Little Albert experiment, for example, researchers repeatedly paired a loud noise with the sight of a white rat. This association caused the little boy in the experiment to become fearful of the rat.
How many steps are there in the conditioning process?
There are three basic steps in the conditioning process:
What is the process of learning?
Psychologists define learning as a process in which new knowledge, attitudes, behaviors, or ideas or acquired. It can occur in a variety of ways, including unconsciously and unconsciously. Classical conditioning is an unconscious form of learning.
How did classical conditioning get its name?
Classical conditioning gets its name from the fact that it is the kind of learning situation that existed in the early “Classical” experiments of Ivan Pavlov (1849- 1936). In the late 1890s, the famous Russian physiologist began to establish many of the basic principles of this form of conditioning. Classical conditioning is also sometimes called ...
What is the acquisition stage of conditioning?
Acquisition: Each paired presentation of the CS and US is called a trial and the period during which the organism is learning the association between the CS and US is the acquisition stage of conditioning. The time interval between the CS and US may be varied.
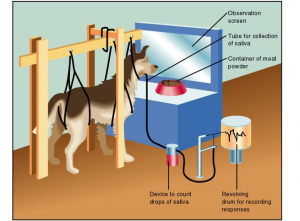
Why is meat powder considered an unconditioned stimulus?
The meat powder is considered as unconditioned stimulus or UCS, because food placed in a dog’s mouth automatically causes salivation to occur. The response that the meat powder elicits (salivation) is called an unconditioned response or UCR, a response that is not associated with previous learning.
What is the goal of tuning fork?
Just before presentation of the meat powder, the goal of conditioning is for the tuning fork to become associated with the unconditioned stimulus (meat powder), and therefore, to bring about the same sort of response as the unconditioned stimulus.
How long does it take for a stimulus to become conditioned?
Research has shown that conditioning is most effective if the neutral stimulus (which will become a conditioned stimulus) precedes the unconditioned stimulus by between a half second and several seconds, depending on what kind of response is being conditioned.
How did Pavlov analyze classical conditioning?
To demonstrate and analyze classical conditioning, Pavlov conducted a series of experiments. In one, he attached a tube to the salivary gland of a dog. He then sounded a tuning fork and just a few seconds later, presented the dog with meat powder.
Why is the tuning fork called the neutral stimulus?
Prior to sound of a tuning fork and meat powder, we know that the sound of tuning fork leads not only to salivation but also to some irrelevant response such as pricking of the ears, the sound in this case is therefore called the neutral stimulus because it has no effect on the response or interest.

Classical Conditioning Definitions
Key Principles
- Behaviorists have described a number of different phenomena associated with classical conditioning. Some of these elements involve the initial establishment of the response while others describe the disappearance of a response. Here is a closer look at five key principles of classical conditioning.
Classical Conditioning Examples
- It can be helpful to look at a few examples of how the classical conditioning process operates both in experimental and real-world settings.
A Word from Verywell
- In reality, people do not respond exactly like Pavlov's dogs. There are, however, numerous real-world applications for classical conditioning. For example, many dog trainers use classical conditioning techniques to help people train their pets. These techniques are also useful for helping people cope with phobias or anxiety problems. Therapists might, for example, repeatedl…
How Classical Conditioning Works
- Stage 1: Before Conditioning:
In this stage, the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) produces an unconditioned response (UCR) in an organism. In basic terms, this means that a stimulus in the environment has produced a behavior / response which is unlearned (i.e., unconditioned) and therefore is a natural response which has … - Stage 2: During Conditioning:
During this stage, a stimulus which produces no response (i.e., neutral) is associated with the unconditioned stimulus at which point it now becomes known as the conditioned stimulus (CS). For classical conditioning to be effective, the conditioned stimulus should occur before the unco…
Classical Conditioning Examples
- Pavlov's Dogs
The most famous example of classical conditioning was Ivan Pavlov's experiment with dogs, who salivated in response to a bell tone. Pavlov showed that when a bell was sounded each time the dog was fed, the dog learned to associate the sound with the presentation of the food. He first p… - Fear Response
Watson & Rayner (1920) were the first psychologists to apply the principles of classical conditioning to human behavior by looking at how this learning process may explain the development of phobias. They did this in what is now considered to be one of the most ethically …
Critical Evaluation
- Classical conditioning emphasizes the importance of learning from the environment, and supports nurture over nature. However, it is limiting to describe behavior solely in terms of either nature or nurture, and attempts to do this underestimate the complexity of human behavior. It is more likely that behavior is due to an interaction between nature (biology) and nurture (environm…