What are the basic structures present in a bacteria?
Structure of a typical bacterium. The numbered parts are: (1) pilus, (2) plasmid, (3) ribosome, (4) cytoplasm, (5) cytoplasmic membrane, (6) cell wall, (7) capsule, (8) nucleoid, and (9) flagellum (Source: LadyofHats [Public domain] via Wikimedia Commons).
What are three basic structures of bacteria?
Structurally, there are three architectural regions: appendages (attachments to the cell surface) in the form of flagella and pili (or fimbriae); a cell envelope consisting of a capsule, cell wall and plasma membrane; and a cytoplasmic region that contains the cell chromosome (DNA) and ribosomes and various sorts of ...
What is bacteria and its structure?
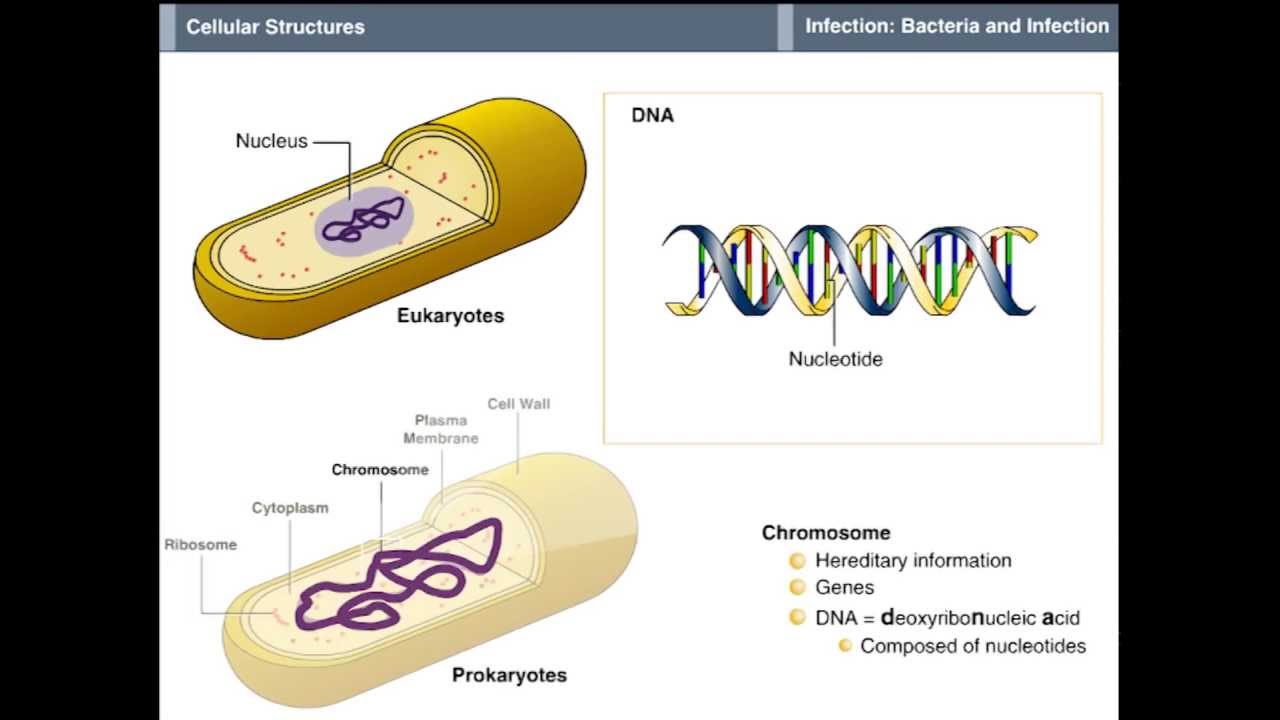
Bacteria are prokaryotic unicellular organisms. They have a relatively simple cell structure compared to eukaryotic cells. They also do not possess any membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus. However, do they possess genetic material (DNA or RNA) in the intracellular space called the nucleoid.
What structures are found in all bacterial cells?
The cytoplasm, plasma membrane, nucleoid, and ribosomes are found in all bacterial cells.
What is structure of cell?
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
What are the 3 main types of bacterial cell walls?
Bacterial Cell wall: Structure, Composition and Typescell wall.glycan backbone.NAG.NAM.peptidoglycan.
What is a bacterial cell?
Bacteria are small single-celled organisms. Bacteria are found almost everywhere on Earth and are vital to the planet's ecosystems. Some species can live under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure. The human body is full of bacteria, and in fact is estimated to contain more bacterial cells than human cells.
What are bacterial cell walls made up of?
The cell wall consists mainly of peptidoglycan (PG), a mesh of polysaccharide strands (composed of a poly-[N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc)-N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc)] backbone) cross-linked via short peptide bridges attached to the MurNAc residues (Vollmer et al., 2008a).
Do bacterial cells have a nucleus?
Bacteria, of course, have no nucleus and therefore also nuclear membrane. genetic information- DNA is organized into numerous chromosomes and is packaged in the nucleus. The nucleus is bounded by a membrane mRNA, tRNA and rRNA are made in the nucleus and shipped out into the cytoplasm.
What are characteristics of bacteria?
Five characteristics of bacteria include being unicellular, prokaryotic, microscopic, lacking a nucleus, and having a plasma membrane. These traits are shared by all bacteria.
What are the different types of bacteria?
E. coliHelicobacter pyloriCyanobact...SalmonellaHelicobacterLactobacill...Bacteria/Lower classifications
What are the short hairlike appendages of bacteria?
Bacterial cells possess short, fine, hair like, protein-contributed appendages that extend from the cell surface. These appendages are called fimbriae (ring. fimbria) and pili (sing, pilus), are thinner than flagella, and are not involved in locomotory activities.
How do peritrichous bacteria stop and tumble randomly?
These bacteria stop and tumble randomly by reversing the direction of flagellar rotation. The flagella of peritrichous bacteria rotate counter clockwise, like montrichous and lophotrichous ones, to move forward. The flagella bend at their hooks to form a rotating bundle that propels them forward. Clockwise rotation of the flagella disrupts the bundle and the cell tumbles.
How many spherical molecules are in a chain of bacteria?
Each chain contains approximately 1,000 spherical, smaller flagellin molecules each of 40 Å diameter. In this way, the bacterial flagellum fundamentally differs from the flagellum of an eukaryotic cell, which has 9 + 2 type of arrangement in its filament.
How fast does flagella rotate?
Flagellar rotation can move bacteria through liquid media at speeds of up to 60 cell lengths/sec.
How does slime help bacteria?
Slime layer is more easily deformed, is more difficult to see, and can be very easily removed by washing the bacterial cells. Gliding bacteria often produce slime, which presumably aids in their motility. The slime probably attaches them to the substratum and lubricates the surface for more efficient movement.
What are the structures of bacteria?
They consists of various cell surface structures, cell wall, plasma membrane, many cytoplasmic inclusions, and the bacterial chromosome (nucleoid). Except some, all structures do not occur in every genus. Furthermore, gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria differ, particularly, with respect to their cell walls.
What does the S layer do to bacteria?
By this act, they help retain proteins near the bacterial cell much like the outer membrane does in gram-negative bacteria. ADVERTISEMENTS: (ii) S-layer may protect bacterial cell against ion and pH fluctuations, osmotic stress, enzymes, or the predaceous bacterium Bdellovibrio.
What is lipid A?
Lipid A—a phospholipid responsible for the toxic effects. A core polysaccharide of 5 sugars linked to lipid A. An outer polysaccharide consisting of up to 25 repeating units of 3-5 sugars; the somatic or O antigen of several Gram-negative bacteria used for clinical identification. 10. Teichoic Acid.
What is the endotoxin in the cell wall?
b) is an endotoxin—an integral part of the cell wall (as opposed to exotoxins which are released from bacteria). Endotoxin is directly responsible for many disease symptoms caused by these organisms, including fever (it is pyrogenic whether or not the bacterium is alive!), and shock (especially hypotension).
What is the natural defense against bacteria?
Lysozyme is present in human tears, saliva and mucous and is a natural defense to bacterial infection. Lysozyme treatment will cause bacteria to lose their cell wall, swell and rupture, unless they are in a solution with the same osmotic pressure as inside the bacterial cell.
What drugs interfere with peptidoglycan synthesis?
Penicillins, cephalosporins, and vancomycin interfere with peptidoglycan synthesis by inhibiting the transpeptidase that cross- links the 2 adjacent tetrapeptides. d) Lysozyme cleaves the peptidoglycan backbone by breaking glycosyl bonds.
What is the composition of tetrapeptides?
The composition of the tetrapeptide differs among bacteria. The amino acid, diaminopimelic acid is unique to bacterial cell walls. The amino acid, D-alanine, is involved in the cross-links between tetrapeptides and in the action of penicillin.
What are the polysaccharides in a cell wall?
Polysaccharide and protein constituents of bacterial cell walls are often antigens used in lab identification. The cell walls of some Gram-negative bacteria contain porin proteins in the outer membrane which are involved in regulating the passage of small hydrophilic molecules into the cell, including essential nutrients and antimicrobial drugs.
What is the outermost structure of a bacterial cell?
Outermost structure common to all bacteria, except Mycoplasma species which do not have a cell wall. Multi-layered, located just outside of cytoplasmic membrane. In Gram-negative bacteria, the cell wall is composed of inner layer of peptidoglycan and an outer membrane. Polysaccharide and protein constituents of bacterial cell walls are often ...
What is the function of pili?
Function: Attachment: pili helps the bacteria to attach the host cell surface. Most of the human pathogens of respiratory tract, urinary tract are attached with the help of pili. Pili (fimbrae) possess antigenic property. Specialized function: some pili are modified for specialized function.
What is the function of a mesosome?
Mesosome: Mesosome is a spherical or round sac like structure found commonly in gram positive bacteria. Function: It is the site for respiration in bacterial cell. 12. Cytoplasm: It is colorless, viscus fluid present inside cell membrane. All the cell organelles and inclusions are found floating in cytoplasmic fluid.
What is the function of prosthecae?
Prosthecae increase surface area for nutrition absorption. It is usually formed in bacteria living in very dilute environment where concentration of nutrition is low.
What is the thickness of a spore?
Spore. 1. Capsule: Capsule is 0.2µm thick viscus layer outer layer to the cell wall. Capsule is 98% water and 2% polysaccharide or glycoprotein/ polypeptide or both. There are two types of capsule. i. Macro-capsule: thickness of 0.2µm or more, visible under light microscope.
What is the function of the cell wall?
Function: Helps in attachment to solid surface. 7. Cell wall: It is an important structure of a bacteria. It give shape to the organism. On the basis of cell wall composition, bacteria are classified into two major group ie. Gram Positive and gram negative.
What is the hollow tube that holds the chain of bacteria?
Some bacteria forming chain or trichome are enclosed by a hollow tube like structure known as Sheath.
Which layer of the cell wall is present in both Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria?
Peptidoglycan layer is present in cell wall of both gram positive as well as gram negative bacteria. However, gram positive have thick layer of peptidoglycan.
Why are ribosomes useful?
These ribosomes are useful in protein synthesis. But, humans, are the target of an antibiotic attack in the treatment of bacterial infections.
What are the rings of DNA that are exchanged between bacteria during sexual reproduction?
Additional rings of DNA called plasmid are present in the cytoplasm. These plasmids are exchanged in between bacteria duringsexual reproduction. Flagella: These are the organs of locomotion present in motile bacteria. This is a hair or whip-like structure arising out of basal granule.
What type of cell can be single, double or multiple flagella?
A bacteria cell can consist of single, double or multiple flagella.
What is the wall of Gram positive bacteria made of?
The gram positive bacteria have a thick wall made of single layers of mucopeptide.
Why is the cell membrane important?
So, the cell membrane is useful for the transport of substances and also respiration.
What are the layers of bacteria?
Bacteria is a prokaryotic cell. It is enveloped by three layers like the capsule, cell wall, and cell membrane.
How are bacterial cells helpful in attachment to another bacterial cell during sexual reproduction?
They are helpful in attachment to another bacterial cell during sexual reproduction by conjugation.
What is the name of the hairlike constructions that give a method for movement to those bacteria that have them?
Flagella (solitary, flagellum) are hairlike constructions that give a method for movement to those bacteria that have them.
What are pili in bacteria?
Many types of bacteria have pili (solitary, pilus), little hairlike projections arising out of the external cell surface.
Why are bacteria important to the environment?
Most eminently, various researchers all throughout the planet made commitments to the field of microbial biology, showing that bacteria were vital for food networks and for the general soundness of the Earth’s environments.
What happens if you don't have pili?
Without pili, numerous illness causing bacteria lose their capacity to taint since they’re not able to append to have tissue .
What is the cell envelope?
The cell envelope is comprised of a few layers: the inside cytoplasmic film, the cell divider, and – in certain types of bacteria – an external capsule.
What color is a Gram positive stain?
When presented to a gram stain, gram-positive bacteria hold the purple shade of the stain.
What are somewhat a couple of bacteria?
Somewhat a couple of bacteria are parasites or microorganisms that cause infection in creatures and plants.
