
What is the purpose of the One Belt One Road Initiative?
BRI is a transcontinental long-term policy and investment program which aims at infrastructure development and acceleration of the economic integration of countries along the route of the historic Silk Road. The Initiative was unveiled in 2013 by China`s president Xi Jinping and until 2016, was known as OBOR – One Belt One Road.
Is BCIM part of the belt and Road Initiative?
Since the second Belt and Road Forum in 2019, BCIM has been dropped from the list of projects due to India's refusal to participate in the Belt and Road Initiative. For a more comprehensive list, see List of projects of the Belt and Road Initiative. The Belt and Road initiative. China in red.
What is the belt and Road Initiative and why is it controversial?
The Belt and Road Initiative, reminiscent of the Silk Road, is a massive infrastructure project that would stretch from East Asia to Europe. Some analysts see the project as a disturbing expansion of Chinese power, and the United States has struggled to offer a competing vision.
What are some examples of belt and Road Initiative infrastructure investments?
Examples of Belt and Road Initiative infrastructure investments include ports, skyscrapers, railroads, roads, airports, dams, and railroad tunnels . The initiative was incorporated into the Constitution of China in 2017. The Chinese government calls the initiative "a bid to enhance regional connectivity and embrace a brighter future."
What is the belt and road initiative in simple terms?
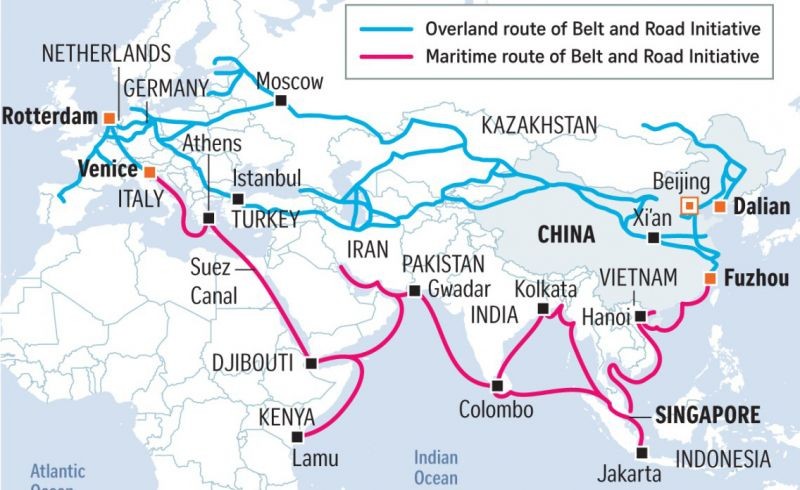
China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) (一带一路) is a strategy initiated by the People's Republic of China that seeks to connect Asia with Africa and Europe via land and maritime networks with the aim of improving regional integration, increasing trade and stimulating economic growth.
What countries are in the Belt and Road Initiative?
The five countries of Central Asia – Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan – are an important part of the land route of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
How does the Chinese belt and road initiative work?
The Belt and Road Initiative debt trap 'Debt trap diplomacy' is the accusation that China uses Belt and Road as part of a manipulative global strategy, funding major infrastructure projects in developing nations with unsustainable loans, then using the debt to gain leverage over those governments.
Who is paying for the belt and road initiative?
Despite all of the attention for the AIIB, it is the Chinese policy banks that are doing the heavy lifting for Belt and Road lending. The two main institutions of this type – the Export-Import Bank of China (ExIm) and China Development Bank (CDB) – are the largest sources of finance for Silk Road loans.
Is Russia a part of BRI?
The land corridors include: The New Eurasian Land Bridge, which runs from Western China to Western Russia through Kazakhstan, and includes the Silk Road Railway through China's Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Kazakhstan, Russia, Belarus, Poland and Germany.
How many countries have one belt on the road?
In March 2022, the number of countries that have joined the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) by signing a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with China is 147*. The countries of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) are spread across all continents: 43 countries are in Sub-Saharan Africa.
What is the disadvantages of BRI?
There are potential environmental, social, and corruption risks associated with any large infrastructure project. These could include, for example, biodiversity loss, environmental degradation, or elite capture.
Who owns all the land in China?
China is a socialist country and all land in China belongs to Chinese citizens as a whole. Article 10 of the 1982 Constitution upholds the Chinese land policy that reflects the traditional view of socialism - land of the country must be owned by the country (State) or its agricultural Collectives.
How much land does China own in the world?
China, home to 20 percent of the world's population but only 8 percent of the world's arable land, has gone abroad in search of farmland.
Is China's Belt and Road Initiative good for the global economy?
Despite potential gains for the United States, BRI poses significant risks to U.S. economic interests. BRI's size and scope give it the potential to boost global gross domestic product (GDP) by as much as $7.1 trillion by 2040 and reduce global trade costs by up to 2.2 percent.
How much has China spent on the belt and road?
Total financing and investment stood at $28.4 billion over the period, down from $29.6 billion a year earlier, bringing total cumulative Belt and Road spending to $932 billion since 2013, GFDC said.
How much money has China dedicated to the belt and road?
China Belt And Road Projects Value Now Exceeds US$4 Trillion.
How many countries are involved in the Silk Road project?
Today there are over 40 countries along the historic land and maritime Silk Roads, all still bearing witness to the impact of these routes on their culture, traditions and customs.
Is Japan part of Belt and Road Initiative?
Japan moves into Belt and Road sphere Given the original QI-ESG programme was due to be spent in three years perhaps the US Exim report has underestimated JBIC's activity. Still the JBIC growth US Exim discovered from 2019 to 2020 speaks for itself.
How many countries are in China?
It is the world's most populous country, with a population of more than 1.4 billion people. China spans five geographical time zones and borders 14 countries, the second most of any country in the world after Russia....China.People's Republic of China 中华人民共和国 (Chinese) Zhōnghuá Rénmín Gònghéguó (Pinyin)ISO 3166 codeCN50 more rows
How many BRI projects are there?
Currently, the Refinitiv BRI database has captured 2,631 projects with a combined value of $3.7 trillion, with the number of enterprises involved in the signature project standing at nearly 2,600. Of these, more than 55 percent are non-Chinese companies.
Why did China start the Belt and Road Initiative?
China proposed the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in 2013 to improve connectivity and cooperation on a transcontinental scale. Quantifying the impacts of the BRI is a major challenge, which is why the World Bank Group has produced empirical research and economic models that assess the opportunities and risks of BRI projects. ...
How much would BRI reduce travel times?
If completed, BRI transport projects could reduce travel times along economic corridors by 12%, increase trade between 2.7% and 9.7%, increase income by up to 3.4% and lift 7.6 million people from extreme poverty.
Is China a BRI?
China has presented the BRI as an open arrangement in which all countries are welcome to participat e. However, an official list of participating countries does not yet exist. In our research we have focused on 71 economies geographically located along BRI transport corridors, including China.
What is the Belt and Road Initiative?
Beijing’s multibillion dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has been called a Chinese Marshall Plan, a state-backed campaign for global dominance, a stimulus package for a slowing economy, and a massive marketing campaign for something that was already happening – Chinese investment around the world. Over the five years since President Xi Jinping ...
What is Belt and Road?
Belt and Road also means that Chinese firms are engaging in construction work across the globe on an unparalleled scale. According to one estimate, China has invested more than $200 bn into Belt and Road projects abroad. Source: American Enterprise Institute.
Why is the initiative sparking global concern?
As Belt and Road expands in scope so do concerns it is a form of economic imperialism that gives China too much leverage over other countries, often those that are smaller and poorer .
How many countries are in Belt and Road?
From South-east Asia to Eastern Europe and Africa, Belt and Road includes 71 countries that account for half the world’s population and a quarter of global GDP. Everything from a Trump-affiliated theme park in Indonesia to a jazz camp in Chongqing have been branded Belt and Road. Countries from Panama to Madagascar, South Africa to New Zealand, ...
How much money has China secured for Belt and Road?
To date, Chinese companies have secured more than $340bn in construction contracts along the Belt and Road. However, China’s dominance in the construction sector comes at the expense of local contractors in partner countries. The vast sums raked in by Chinese firms are at odds with the official rhetoric that Belt and Road is open ...
Which countries are affected by the B and R?
The affected nations – Djibouti, Kyrgyzstan, Laos, the Maldives, Mongolia, Montenegro, Pakistan and Tajikistan – are among the poorest in their respective regions and will owe more than half of all their foreign debt to China.
What is the Belt and Road Initiative?
The official Belt and Road Initiative outline promotes the joint formulation of development plans and measures for advancing cross-national or regional cooperation between countries involved in BRI. This includes intergovernmental cooperation and multi-level macro policy exchange, communication mechanisms and policy support for the implementation of large-scale projects and the coordination in monetary policy.
When was the Belt and Road Initiative launched?
The Initiative was unveiled in 2013 by China`s president Xi Jinping and until 2016, was known as OBOR – One Belt One Road. On March 28, 2015, the official outline for the Belt and Road Initiative was issued by the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) and the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) ...
What is BRI in China?
BRI is a transcontinental long-term policy and investment program which aims at infrastructure development and acceleration of the economic integration of countries along the route of the historic Silk Road. The Initiative was unveiled in 2013 by China`s president Xi Jinping and until 2016, was known as OBOR – One Belt One Road.
What are the five priorities of the Belt and Road Initiative?
According to the outline, the Belt and Road Initiative is based on five cooperation priorities: 1. Policy coordination (Promotion of intergovernmental cooperation, multi-level intergovernmental macro policy exchange and communication mechanism) 2.
What is the Polar Silk Road?
The Polar Silk Road. On January 26, 2018, the State Council Information Office of the People`s Republic of China published a white paper, titled “China`s Arctic Policy”, vowing to actively participating in Arctic affairs.
How many countries are participating in Belt and Road?
According to the Belt and Road Portal, currently 71 countries are taking part in the Initiative, together representing more than a third of the world`s GDP and two thirds of the world`s population.
Where is BRI located?
BRI is a global initiative but by its nature of building on the historic Silk Road puts a major focus on countries in Asia, Eastern Africa, Eastern Europe and the Middle East, a region mainly composed of emerging markets. According to the Belt and Road Portal, currently 71 countries are taking part in the Initiative, ...
When was the Belt and Road Initiative announced?
China's planned Belt and Road Initiative. (SOURCE: Chinese Government) First announced by President Xi Jinping shortly after his election in 2013, the project will cost trillions of dollars in investment and is expected to be completed later this century. It is widely considered to be Xi’s pet project. “China will actively promote international ...
How will the BRI recreate the Silk Road?
The BRI will recreate the Silk Road, an old network of trading routes between the East and the West, by investing large sums of money into other countries to build such infrastructure projects.
What is the BRI in China?
Michael Waltz explains his proposed legislation to stop U.S. retirement funds from investing $50 billion into China's stock exchange and state owned companies. China’ s "Belt and Road Initiative" (BRI) is a planned multitrillion-dollar infrastructure program that is intended to link China with more than 100 countries through railroad, ...
What is the belt of land?
The “belt” will consist of land routes connecting economies in Asia, Europe, Africa and Europe. The “road” -- while not actually a road -- will connect various ocean routes through these areas.
What is Xi's pet project?
It is widely considered to be Xi’s pet project. “China will actively promote international cooperation through the Belt and Road Initiative,” Xi said in 2017. “In doing so, we hope to achieve policy, infrastructure, trade, financial and people-to-people connectivity and thus build a new platform for international cooperation to create new drivers ...
What is the Belt and Road Forum?
The Belt and Road Forum (with its unfortunate acronym, BARF) is the second set-piece event this year at which Mr Xi will lay out China’s claim to global leadership. (The first was a speech against protectionism made at the World Economic Forum in Davos in January).
Why does China need Belt and Road?
China needs it because it provides an answer of sorts to some of its economic problems . And Asia needs it because of an unslakeable thirst for infrastructure. The belt and road initiative has plenty of problems but Mr Xi is determined to push ahead with it. Reuse this content The Trust Project.
What is Xi Jinping's foreign policy?
OVER the weekend Xi Jinping welcomed 28 heads of state and government to Beijing for a coming-out party, which continues today, to celebrate the “belt and road” initiative, his most ambitious foreign policy. Launched in 2013 as “one belt, one road”, it involves China underwriting billions ...
What is the summit called in Beijing?
The summit meeting (called a forum) has attracted the largest number of foreign dignitaries to Beijing since the Olympic Games in 2008. Yet few European leaders are showing up. For the most part they have ignored the implications of China’s initiative.
Is China finding it hard to identify profitable projects in many belt-and-road countries?
To make matters worse, China is finding it hard to identify profitable projects in many belt-and-road countries (Chinese businessmen in central Asia call it “One Road, One Trap”).
What are the implications of China's Belt and Road?
China’s Belt and Road: Implications for the United States. The Belt and Road Initiative poses a significant challenge to U.S. economic, political, climate change, security, and global health interests. The Belt and Road Initiative poses a significant challenge to U.S. economic, political, climate change, security, and global health interests.
What is the Belt and Road Tracker?
Mar 23, 2021. Belt and Road Tracker. This tracker shows how the Belt and Road Initiative has changed countries' bilateral economic relationships with China over time.
Is the Build Back Better World initiative a win?
Regardless of its strategic intent, the Build Back Better World initiative could be a huge win for global welfare, sustainable development, and multilateralism.
Is Europe responding to China's Belt and Road Initiative?
Europe is responding to China's Belt and Road Initiative, but it is unclear whether its alternative can succeed.
What is the Belt and Road Initiative?
When President Xi first announced the framework for what would become the BRI in 2013, his plan was to set up land and sea routes connecting countries across Eurasia — a modern update to the ancient Silk Road. Today, the policy has come to encompass most of China’s overseas investments, from ports and gas pipelines to indoor ski slopes in Australia.
Why is the BRI important?
Though the BRI has been pitched as an antidote to slowing economic growth at home, it is also grounded in a desire to course correct from centuries of Chinese prosperity interrupted by wars, famines and rebellions and to further the country’s stunning economic resurgence that began in the 1970s .
Why did Malaysia promise to invest in Chinese projects?
In January, the Wall Street Journal reported that Malaysia had promised shares in railroad and pipeline projects to Chinese officials in exchange for bailing them out of an embezzlement scandal engulfing then-prime minister Najib Razak.
What happened to China in 2008?
As most of the rest of the world faced financial crisis in 2008, China weathered the worldwide recession with the help of a massive stimulus package. That fortune, however, led to domestic overcapacity, and China found itself dealing with issues like millions and millions of tons of extra steel.
What did President Xi promise in his remarks?
In remarks opening the forum, President Xi promised future projects would address both environmental and ethical concerns.
How has the United States responded to China-led regional integration?
goal that intensified after the start of the U.S.-led war in Afghanistan and President Barack Obama’s pivot to Asia. The Obama administration frequently referenced the need for the Afghan economy to move past foreign assistance, and in 2014 then-Deputy Secretary of State William Burns committed the United States to returning Central and South Asia “to its historic role as a vital hub of global commerce, ideas, and culture.” In this spirit, the Obama administration supported a $10 billion gas pipeline through Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India. It also spent billions of dollars on roads and energy projects in Afghanistan and used its diplomatic muscle to help craft new regional cooperation frameworks to foster Central Asian economic links.
What is the BRI in China?
Experts see the BRI as one of the main planks of a bolder Chinese statecraft under Xi, alongside the Made in China 2025 economic development strategy. For Xi, the BRI serves as pushback against the much-touted U.S. “ pivot to Asia ,” as well as a way for China to develop new investment opportunities, cultivate export markets, and boost Chinese incomes and domestic consumption. “Under Xi, China now actively seeks to shape international norms and institutions and forcefully asserts its presence on the global stage,” writes CFR’s Elizabeth C. Economy.
What was the original Silk Road?
The original Silk Road arose during the westward expansion of China’s Han Dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE), which forged trade networks throughout what are today the Central Asian countries of Afghanistan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, as well as modern-day India and Pakistan to the south. Those routes extended more than four thousand miles to Europe.
Why is China using BRI funds?
Others claim that China is using BRI funds to gain influence in Balkan countries that are on track to become EU members, thereby providing Chinese access to the heart of the European Union’s common market. Russia.
What deal did Trump try to counter the BRI?
The Trump administration has instead tried to counter the BRI with the BUILD Act. This consolidated the Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC), a U.S. government agency for development finance, with components of the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) into a separate agency with a $60 billion investment portfolio. Although this pales in comparison to the more than $1 trillion China is expected to spend on the BRI, advocates say it seeks to crowd in a larger pool of private investment by underwriting risk.
Which countries have accepted BRI financing?
Europe. Several countries in Central and Eastern Europe have accepted BRI financing, and Western European states such as Italy, Luxembourg, and Portugal have signed provisional agreements to cooperate on BRI projects. Their leaders frame cooperation as a way to invite Chinese investment and potentially improve the quality of competitive construction bids from European and U.S. firms.
What is the priority of Xinjiang?
Promoting economic development in the western province of Xinjiang, where separatist violence has been on the upswing, is a major priority, as is securing long-term energy supplies from Central Asia and the Middle East, especially via routes the U.S. military cannot disrupt.

How Much Money Is Being Spent?
What Are The Risks For Countries Involved?
- More recently, governments from Malaysia to Pakistan are starting to rethink the costs of these projects. Sri Lanka, where the government leased a port to a Chinese company for 99 years after struggling to make repayments, is a cautionary tale. Earlier this year, the Center for Global Development found eight more Belt and Road countries at serious risk of not being able to repa…
Why Is The Initiative Sparking Global Concern?
- As Belt and Road expands in scope so do concerns it is a form of economic imperialism that gives China too much leverage over other countries, often those that are smaller and poorer. Jane Golley, an associate professor at Australian National University, describes it as an attempt to win friends and influence people. “They’ve presented this very grand initiative which has frightened p…
Where Does It End?
- Belt and Road is likely to continue, not least because these projects signal loyalty to Xi. The initiative has been enshrined in the Chinese communist party’s constitution, which also eliminated term limits, leaving Xi room to continue Belt and Road for as long as he wants. It also gives disparate Chinese projects overseas the veneer of being part ...
What’s Next?
- Not all of the most ambitious Belt and Road projects are about hard infrastructure. China plans to set up international courts, in Shenzhen and Xi’an, the former hub of the original Silk Road, to resolve commercial disputes related to Belt and Road. “It’s a reminder BRI is about more than roads, railways, and other hard infrastructure,” said Jonathan Hillman, director of the Reconnecti…