Functions of your skeletal system include:
- Movement. Your skeletal system supports your weight evenly so that you can stand and move with ease. ...
- Blood cells. Your bone contains marrow that produces both red and white blood cells for your body.
- Organs. Your bones are structured in ways that protect your vital organs. ...
- Minerals. Your bones act as storage for some minerals like calcium and vitamin D
What are the most important functions of the skeletal system?
- supports the body
- facilitates movement
- protects internal organs
- produces blood cells
- stores and releases minerals and fat
What are 5 interesting facts about the skeletal system?
What Are 5 Interesting Facts About The Skeletal System?
- There are around 206 bones in the human body – around half of which are in your hands and feet! ...
- The longest bone in your body is the femur, also known as the thigh bone. ...
- You have the same amount of bones in your neck as a giraffe does in theirs – and you know how long giraffes’ necks are!
- The smallest bone in the human body is located in the ear. ...
What are the two purposes of the skeletal system?
- Protection - the cranium and ribs protect the brain and vital organs in the chest.
- Shape - gives shape to the body and makes you tall or short.
- Support - holds your vital organs in place when playing sport. ...
- Movement - muscle are attached to bones, which are jointed. ...
What are the parts and functions of the skeletal system?
Skeletal System Parts
- Bone. Bones serve a variety of functions, but the most important is supporting movement of the limbs and body.
- Joints. Functionally, joints can be divided into three classes based on the range of movement they allow in the associated bones.
- Cellular Composition. Each bone is made of complex sets of cells, tissues and a specialized extracellular matrix. ...

What are the two parts of the skeletal system?
The skeletal system is divided into two parts: the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the skull, spinal column, ribs and sternum. The appendicular skeleton includes all upper and lower extremities, the shoulder girdle and the pelvic girdle. Bones in the human body come in four main shapes, long, short, ...
What are the bones made of?
Bones in the human body come in four main shapes, long, short, flat and irregular and are composed of webs of collagen fibers reinforced with calcium and phosphorous. The collagen provides flexibility while the minerals provide tensile strength. There are 5 functions of the skeletal system in the body, three of which are external and visible to ...
What is the shape of the skull?
The bones of the skull are actually several flat plates joined together by sutures. These sutures allow the skull to pass through the birth canal and expand as the brain continues growing. The sutures fuse together in early childhood, forming the classic shape of the skull.
What is the origin of a skeletal muscle?
All skeletal muscles have an origin and insertion point. The origin is the anchor, the bone that remains immobile while the muscle works. The insertion is the bone that moves as the muscle works, which is one of the main functions of the skeleton. So, for example, in the case of the biceps, the upper arm and shoulder are the origins (anchor) ...
What are the bones that provide protection and flexibility?
The vertebrae are all irregularly shaped bones in the human body that provide both protection and flexibility for movement. There are also fibrous disks between each vertebra, which provide shock absorption.
What are the internal functions of the skeleton?
The internal functions are: blood cell production and storage. 1. Structure. Like the steel framework of a building, the functions of the skeleton and the bones is to provide rigidity, which gives the body shape and supports the weight of the muscles and organs.
Why is vitamin D important for bone health?
When there is a surplus of blood calcium, it’s put back into the bones. This is why dietary calcium and vitamin D are so important. The body uses calcium constantly and, if there isn’t enough calcium in the diet, it will consistently take calcium from the bone to compensate – leading to osteoporosis.
Why do children's skeletons have more bones?
Children’s skeletons actually contain more bones because some of them, including those of the skull, fuse together as they grow up. There are also some differences in the male and female skeleton. The male skeleton is usually longer and has a high bone mass.
How many bones are in the axial skeleton?
The adult axial skeleton consists of 80 bones. It’s made up of the bones that form the vertical axis of the body, such as the bones of the head, neck, chest, and spine.
What are the two parts of the skeletal system?
Regardless of age or sex, the skeletal system can be broken down into two parts, known as the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
What is the thoracic cage made of?
The thoracic cage is made up of the sternum (breastbone) and 12 pairs of ribs. These bones form a protective cage around the organs of the upper torso, including the heart and lungs. Some of the ribs attach directly to the sternum, while others are linked to the sternum via cartilage.
What is the term for a disease that affects bone strength?
Metabolic bone diseases. Metabolic bone diseases refer to a group of conditions that affect bone strength or integrity. They can be due to things such as a deficiency in vitamin D, loss of bone mass, and use of certain medications, such as steroids or chemotherapy.
How many cranial bones are there in the human body?
Cranial bones. The eight cranial bones form the bulk of your skull. They help to protect your brain.
How many vertebrae are there?
The 24 vertebrae can be further divided into the:
What are the other types of bone loss?
Osteopenia, osteitis deformans, and osteomalacia (Similar to the osteoporosis, these are other types of the bone loss), Scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis (They are the abnormalities of the spinal curve). Bones function, types & structure, The skeleton & Curvature of Spine in Adults.
What is the skeletal system?
The skeletal system. The skeletal system consist s of the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton consists of the skull, the backbone and the rib-cage, The skeletal system gives the shape to the body, and without it, the body will look like a paper kite without a rigid frame.
What are the two types of tissues in the bones?
There are two types of tissues inside the bones which are Compact bone and Spongy bone. Compact bone is dense & hard tissue that makes up the outer layer of most bones and the main shaft of long bones, such as those in the arms and legs, Nerves and the blood vessels live inside this tissue. Spongy bone is made up of smaller plates filled ...
How many bones are there in the human body?
The human skeleton system is the internal framework of the body, It contains around 300 bones at birth and decreases to 206 bones by the adulthood after some bones have fused together, Bone mass in the skeleton system reaches maximum density around age 30.
What is the importance of the skeletal system?
The importance and structure of the skeletal system in the human body. The movement is the ability of the organism to change its position from a place to another, it is from the characteristics that distinguish between the living organisms & non-living things, The human movement occurs with the participation and integration ...
What is the difference between a male and female pelvis?
The skeletons of the adult males and females have some variation, primarily to accommodate the childbirth, The female pelvis is more rounded, proportionally larger and flatter, The male’s pelvis is nearly 90 degrees or less of angle, while the female’s pelvis is 100 degrees or more.
How many ribs are in a rib cage?
The rib-cage consists of 12 pair s of ribs, The first 10 pairs are connected to the sternum (the breast bone) anteriorly, The rib-cage protects the lungs and the heart, It helps in the inhalation and exhalation processes (the breathing).
What are movable joints?
Movable joints: Movable joints allow a wide range of motion. Your elbow, shoulder, and knee are movable joints. Ligaments: Bands of strong connective tissue called ligaments hold bones together. Tendons: Tendons are bands of tissue that connect the ends of a muscle to your bone.
How to keep your skeletal system healthy?
How can I keep my skeletal system healthy? To keep your skeletal system strong and healthy, you should: Get plenty of vitamin D and calcium in your diet (try milk, yogurt or almonds) to keep bones strong. Drink plenty of water to help keep tissues healthy. Exercise regularly to strengthen bones and joints.
How many bones are there in the skeletal system?
The main part of your skeletal system consists of your bones, hard structures that create your body’s framework — the skeleton. There are 206 bones in an adult human skeleton.
What is the skeletal system?
The skeletal system works as a support structure for your body. It gives the body its shape, allows movement, makes blood cells, provides protection for organs and stores minerals. The skeletal system is also called the musculoskeletal system.
What causes bones to break?
Fracture: Disease, a tumor, or trauma can put stress on a bone, causing it to break. Osteosarcoma: Cancer that forms in the bones can cause tumors that may weaken and break bones. Osteoporosis: Bone loss caused by not getting enough calcium can lead to fragile and brittle bones, known as osteoporosis.
What is the function of the skeleton?
Besides giving us our human shape and features, it: Allows movement: Your skeleton supports your body weight to help you stand and move. Joints, connective tissue and muscles work together to make your body parts mobile. Produces blood cells: Bones contain bone marrow.
What are the conditions that affect the skeletal system?
Others develop due to wear and tear as you get older.Conditions that may affect the skeletal system can include: Arthritis: Age, injury, and medical conditions such as Lyme disease can lead to arthritis, a painful wearing down of joints. Fracture: Disease, a tumor, or trauma can put stress on a bone, causing it to break.
What are the two types of bone marrow?
The unique connective tissue that fills the interior of most bones is referred to as bone marrow. There are two types of bone marrow: yellow bone marrow ...
What is the body system composed of?
The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones, cartilages, ligaments and other tissues that perform essential functions for the human body. Bone tissue, or osseous tissue, is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton, the internal support structure of the body. In the areas of the skeleton where whole bones move against each other (for example, joints like the shoulder or between the bones of the spine), cartilages, a semi-rigid form of connective tissue, provide flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement. Additionally, ligaments composed of dense connective tissue surround these joints, tying skeletal elements together (a ligament is the dense connective tissue that connect bones to other bones). Together, they perform the following functions:
What is the difference between red and yellow bone marrow?
Yellow bone marrow contains adipose tissue , and the triglycerides stored in the adipocytes of this tissue can be released to serve as a source of energy for other tissues of the body. Red bone marrow is where the production of blood cells (named hematopoiesis, hemato- = “blood”, -poiesis = “to make”) takes place.
What is the condition where the spine is humped?
Orthopedists commonly treat bone and joint injuries but they also treat other bone conditions including curvature of the spine. Lateral curvatures (scoliosis) can be severe enough to slip under the shoulder blade (scapula) forcing it up as a hump.
What is the function of bone tissue?
For one, the bone tissue acts as a reservoir for a number of minerals important to the functioning of the body, especially calcium, and phosphorus. These minerals, incorporated into bone tissue, can be released back into the bloodstream to maintain levels needed ...
What is cartilage in the skeleton?
In the areas of the skeleton where whole bones move against each other (for example, joints like the shoulder or between the bones of the spine), cartilages, a semi-rigid form of connective tissue, provide flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement. Additionally, ligaments composed of dense connective tissue surround these joints, ...
What is the function of red bone marrow?
The red bone marrow is responsible for forming red and white blood cells as well as platelets. Red blood cells transport oxygen to tissues, and remove carbon dioxide. Without red blood cells, your tissues would not be able to produce ATP using oxygen.
How are immovable joints formed?
Immovable joints are formed when two bones are held together by fibrous connective tissue with no synovial fluid. These kinds of joints hold the bones of the cranium together.
What is the appendicular skeleton?
It protects the brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs, esophagus and major sense organs like the eyes, ears, nose, and tongue. The appendicular skeleton is related to the limbs and consists of the bones of the arms and legs, as well as the shoulder and hip girdles.
How many bones are there in the skeletal system?
The anatomy of the skeletal system is complex, and it includes hundreds of bones in the human body. The anatomy of the system varies widely between organisms, as evolution has selected for various adaptations in certain species which change the structure and function of their bones.
Why does bone marrow revert to a higher proportion of red blood cells?
Bone marrow will revert to a higher proportion of red marrow if the body suffers an injury and needs to create more red blood cells . The bone marrow composition also changes during pregnancy and lactation in mammals. Over the course of gestation, blood volume increases by about 1.5 liters, and even the concentration of red blood cells and white blood cells increase.
What is the skeletal system?
Definition. The skeletal system provides support and protection for the body’s internal organs and gives the muscles a point of attachment. Humans have an endoskeleton, where our bones lie underneath our skin and muscles. In other animals, such as insects, there is an exoskeleton on the outside of the body.
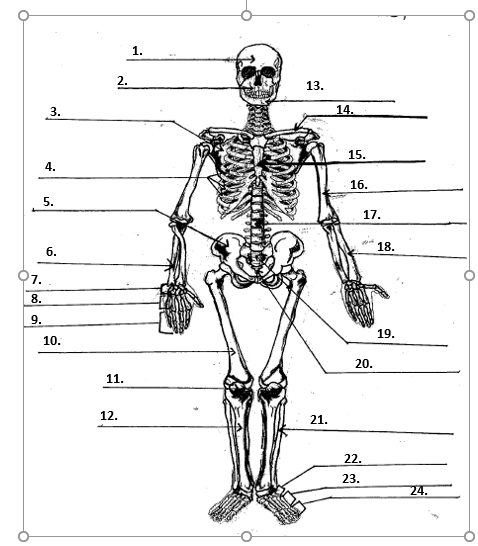
How many bones are there in the human body?
An adult human has 206 bones in their body and variety of different joints. Image shows a human skeleton with the major bones labeled. The human skeleton can be divided into two components: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
Why does my spine tilt?
When the spine has a sideways tilt, or a lateral bend, it is called scoliosis and could be associated with both hyperkyphosis and hyperlordosis.
What is the softer connective tissue that fills the interior of most bones called?
The softer connective tissue that fills the interior of most bone is referred to as bone marrow ( [link] ). There are two types of bone marrow: yellow marrow and red marrow. Yellow marrow contains adipose tissue; the triglycerides stored in the adipocytes of the tissue can serve as a source of energy.
How do you see how bones support movement?
Simply by looking at a person, you can see how the bones support, facilitate movement, and protect the human body. Just as the steel beams of a building provide a scaffold to support its weight, the bones and cartilage of your skeletal system compose the scaffold that supports the rest of your body.
What is the body system composed of bones and cartilage?
The skeletal system is the body system composed of bones and cartilage and performs the following critical functions for the human body: supports the body.
What does orthopedics mean?
While the origin of the word “orthopedics” (ortho- = “straight”; paed- = “child”), literally means “straightening of the child,” orthopedists can have patients who range from pediatric to geriatric. In recent years, orthopedists have even performed prenatal surgery to correct spina bifida, a congenital defect in which the neural canal in the spine of the fetus fails to close completely during embryologic development.
What is the red marrow?
Red marrow is where hematopoiesis —the production of blood cells—takes place. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are all produced in the red marrow. Head of Femur Showing Red and Yellow Marrow. The head of the femur contains both yellow and red marrow. Yellow marrow stores fat.
What is bone in anatomy?
Learning Objectives. Bone, or osseous tissue, is a hard, dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton, the support structure of the body. In the areas of the skeleton where bones move (for example, the ribcage and joints), cartilage, a semi-rigid form of connective tissue, provides flexibility and smooth surfaces for movement. ...
What is the career of an orthopedist?
Career Connection. Orthopedist. An orthopedist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders and injuries related to the musculoskeletal system. Some orthopedic problems can be treated with medications, exercises, braces, and other devices, but others may be best treated with surgery ( [link] ).
What happens when synovial fluid is increased?
Increased synovial fluid production increases mobility within the joint, this is often experience after periods of inactivity. The joints feel a little bit stiffer and they lose some of their range of motion and they lose the ability to move fully freely.
What is the substance that keeps bones healthy?
Bones have little to no blood supply, therefore to keep them nourished and healthy, your body produces an oil-like substance called synovial fluid. This is produced by synovial membranes and it provides joint protection and keeps it healthy, nourished and lubricated.
What are the benefits of physical activity?
A result of a regular longtime routine is stronger ligaments, more stability, and less risk of misalignment of your joint. These are the four main benefits of physical exercise on the skeletal system and bone health.
Does exercise help ligaments?
These have very little to no blood supply. Therefore, any difference or benefit from the exercise will take a longer period of time to take effect. A result of a regular longtime routine is stronger ligaments, more stability, and less risk of misalignment of your joint. These are the four main benefits of physical exercise on ...

Overview
- What is the skeletal system?
The human skeletal system consists of all of the bones, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments in the body. Altogether, the skeleton makes up about 20 percent of a person’s body weight. - An adult’s skeleton contains 206 bones. Children’s skeletons actually contain more bones becau…
There are also some differences in the male and female skeleton. The male skeleton is usually longer and has a high bone mass. The female skeleton, on the other hand, has a broader pelvis to accommodate for pregnancy and child birth.
Skull bones
- The adult skull comprises 22 bones. These bones can be further classified by location:
Cranial bones. The eight cranial bones form the bulk of your skull. They help to protect your brain.
Auditory ossicles
- The auditory ossicles are six small bones found within the inner ear canal in the skull. There are …
They work together to transmit sound waves from the surrounding environment to the structures of the inner ear.
Hyoid
- The hyoid is a U-shaped bone found at the base of the jaw. It serves as a point of attachment for muscles and ligaments in the neck.
Vertebral column
- The vertebral column is made up 26 bones. The first 24 are all vertebrae, followed by the sacru…
The 24 vertebrae can be further divided into the: - Cervical vertebrae. These seven bones are found in the head and neck.
Thoracic vertebrae. These 12 bones are found in the upper back.
Thoracic cage
- The thoracic cage is made up of the sternum (breastbone) and 12 pairs of ribs. These bones for…
Some of the ribs attach directly to the sternum, while others are linked to the sternum via cartilage. Some have no attachment point and are referred to as “floating ribs.” - Explore the interactive 3-D diagram below to learn more about the skeletal system.
There are a total of 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton. It consists of the bones that make up the arms and legs, as well as the bones that attach them to the axial skeleton.
Pectoral girdle
- The pectoral girdle is where the arms attach to the axial skeleton. It’s made up of the clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade). There are two of each of these — one for each arm.
Upper limbs
- Each arm contains 30 bones, known as the:
Humerus. The humerus is the long bone of the upper arm. - Radius. The radius is one of two long bones of the forearm, found on the thumb side.
Ulna. The ulna is the second long bone of the forearm, found on the pinky finger side.
Pelvic girdle
- The pelvic girdle, commonly known as the hips, is where the legs attach to the axial skeleton. It’…
Each hip bone consists of three parts, known as the: - Ilium. The ilium is the top portion of each hip bone.
Ischium. The ischium is a curved bone that makes up the base of each hip bone.
Lower limbs
- Each leg is composed of 30 bones, known as the:
Femur. The femur is the large bone of the upper leg. - Tibia. The tibia is the main bone of the lower leg. It forms the shin.
Fibula. The fibula is the second bone in the lower leg, found in the outer leg.
Fractures
- A fracture can also be referred to as a broken bone. Fractures typically occur due to an injury or trauma, such as a car accident or a fall. There are many different types of fractures, but they’re generally categorized by the nature and location of the break.
Metabolic bone diseases
- Metabolic bone diseases refer to a group of conditions that affect bone strength or integrity. They can be due to things such as a deficiency in vitamin D, loss of bone mass, and use of certain medications, such as steroids or chemotherapy.
Arthritis
- Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints. This can cause pain and a limited range of movement. Several things can cause arthritis, including the breakdown of cartilage that’s found in joints, autoimmune conditions, or infection.
Cancer
- Cancer can develop in the tissues of the bone or in the cells produced by bones. Cancer that forms in the primary bone tissue is actually quite rare. Cancers of the blood cells produced by bone, such as myeloma or lymphoma, are more common.
Spinal curvatures
- A spinal curvature is when the spine doesn’t curve in its usual shape. Typically, the spine follow…
There are three main types of spinal curvature: - Kyphosis. Kyphosis creates a rounding in the upper back.
Lordosis. Lordosis causes the lower back to curve inward.