
En español. Calcium channel blockers are used to control high blood pressure (hypertension), chest pain (angina), and irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia).
Full Answer
What you should know about calcium channel blockers?
Types, examples, side effects, and all else you need to know
- Types. There are two different types of calcium channel blockers, which are called dihydropyridines and nondihydropyridines.
- Uses. Doctors commonly use calcium channel blockers to treat high blood pressure. ...
- Side effects. Fatigue is a possible side effect of calcium channel blockers. ...
- Summary. ...
What drugs block calcium channels?
examples of calcium channel blockers include amlodipine ( norvasc ), amlodipine and atorvastatin ( caduet ), amlodipine and benazepril ( lotrel ), amlodipine and valsartan ( exforge ), amlodipine and telmisartan (twynsta), amlodipine and olmesartan (azor), amlodipine and olmesartan and hydroclorothiazide (tribenzor), amlodipine and aliskiren and …
What are the most common calcium channel blocker side effects?
Side Effects Of Calcium Channel Blockers
- Heart Palpitations. In rare cases, an individual being treated with calcium channel blockers may experience uncomfortable and abnormal heart palpitations.
- Drowsiness. ...
- Lightheadedness And Dizziness. ...
- Leg And Feet Swelling. ...
- Headaches. ...
- Constipation. ...
- Rash or Flushing. ...
- Increased Appetite. ...
- Tender Or Bleeding Gums. ...
- Nausea. ...
What drugs are channel blockers?
Examples of common calcium channel blockers include:
- amlodipine (Norvasc)
- diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac)
- felodipine
- isradipine
- nicardipine (Cardene SR)
- nifedipine (Procardia)
- nisoldipine (Sular)
- verapamil (Calan, Verelan, Covera-HS)
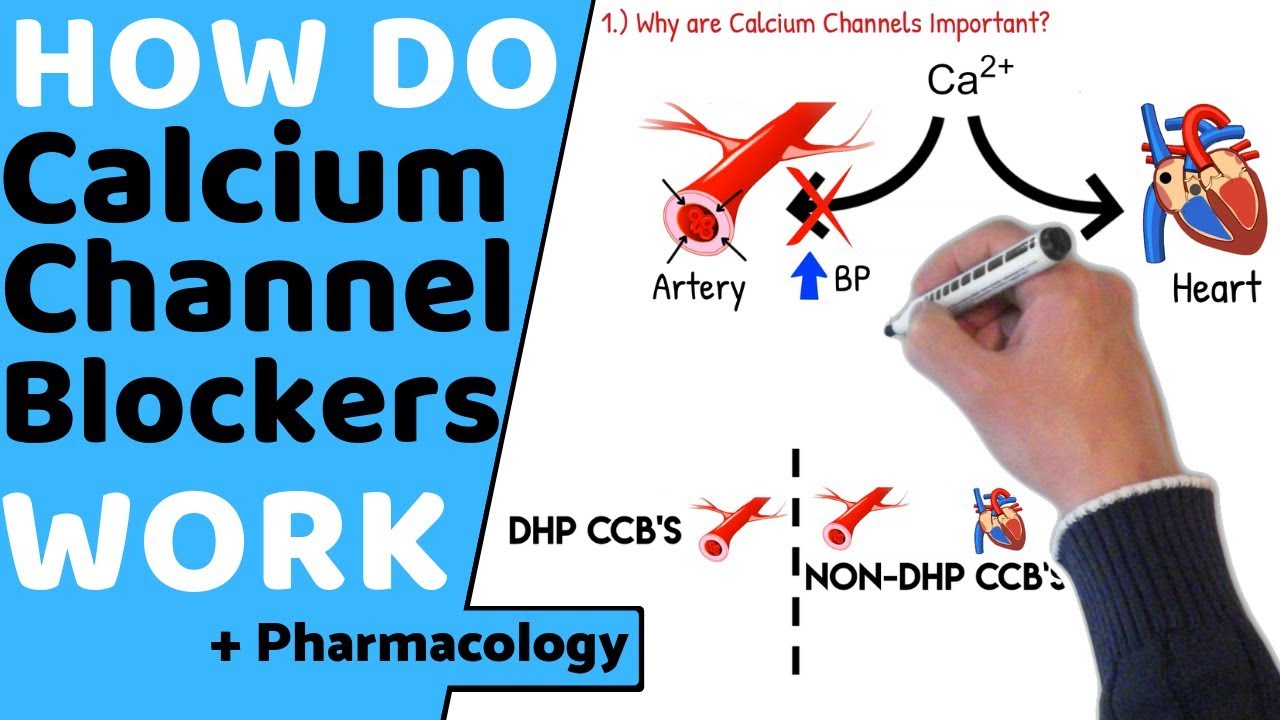
What are Calcium channel blocking agents?
Calcium channel blocking agents restrict the amount of calcium entering cardiac and smooth muscle cells by blocking voltage-gated calcium channels. This causes blood vessels to relax and widen (vasodilate), improves oxygen supply to the heart, and lowers blood pressure. Some calcium channel blockers also slow the heart rate.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What are the different types of calcium channel blockers?
Types of calcium channel blocker drugs. The three main classes of CCB drugs are based on their chemical structure and activity: Dihydropyridines. These work mostly on the arteries. Benzothiazepines. These work on the heart muscle and arteries. Phenylalkylamines. These work mostly on the heart muscle.
How does a calcium channel blocker work?
CCBs reduce blood pressure by limiting the amount of calcium or the rate at which calcium flows into the heart muscle and arterial cell walls. Calcium stimulates the heart to contract more forcefully. When calcium flow is limited, your heart’s contractions aren’t as strong with each beat, ...
What is the best medication for high blood pressure?
The newest guidelines from the American College of Cardiology recommend that ACE inhibitors, diuretics, angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), and CCBs be the first medications to consider when treating high blood pressure. Certain groups of people may especially benefit from CCBs in combination with other medications, including: African-Americans.
What happens when calcium is limited?
When calcium flow is limited, your heart’s contractions aren’t as strong with each beat, and your blood vessels are able to relax. This leads to lower blood pressure. CCBs are available in a number of oral formats, ranging from short-acting dissolving tablets to extended-release capsules.
Can a doctor prescribe a CCB?
Your doctor may prescribe CCBs if you have: high blood pressure. irregular heartbeats called arrhythmias. chest pain related to angina. High blood pressure can also be treated with other forms of medication. Your doctor may prescribe both a CCB and another hypertensive drug at the same time.
Can CCBs interact with other medications?
CCBs may interact with other drugs or supplements you take. Make sure your doctor has an updated list of all of your medications, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Is magnesium good for CCB?
Magnesium is an example of a nutrient that acts as a natural CCB. Research has shown that higher levels of magnesium block the movement of calcium. In animal studies, magnesium supplementation seemed to be most effective in the young with elevated blood pressure, before they developed hypertension. It also seemed slow the progression to hypertension. Magnesium-rich foods include#N#Trusted Source#N#:
What is the purpose of calcium channel blockers?
Calcium channel blockers prevent calcium from entering cells of the heart and blood vessels walls. They are also called calcium antagonists and they relax and widen the blood vessels by affecting the muscle cells in the arterial walls.
How does calcium channel blocker work?
They are drugs used to lower blood pressure and they work by slowing the movement of calcium into the cells of the heart and your blood vessel walls. This makes it easier for the heart to pump and widens blood vessels.
Does Felodipine work for high blood pressure?
So I can suggest this one for your husband but like others already explained, it doesn't necessarily mean that it is going to work for him as good as it worked for me.
Does Verelan help with heart rate?
You also need to know that some calcium channel blockers have the added benefit of slowing your heart rate which can further reduce blood pressure. Also, it can relieve chest pain and control an irregular heartbeat. My friend had experience with verelan and she told me that it is just fine for her.
Can calcium channel blockers cause high blood pressure?
These calcium channel blockers aren't only used for high blood pressure, they are also used for chest pain or angina, brain aneurysm complications, irregular heartbeats or arrhythmia, migraine, some circulatory conditions such as Raynaud's disease and high blood pressure that affects the arteries in your lungs.
What are the indications for calcium channel blockers?
These agents are often classified into two major categories, either non-dihydropyridines or dihydropyridines. Cardiovascular indications include hypertension, coronary spasm, angina pectoris, supraventricular dysrhythmias, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and pulmonary hypertension. In addition to these, they are also prescribed for Raynaud phenomenon, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and migraine headaches. This activity reviews the mechanism of action, adverse event profile, toxicity, dosing, pharmacodynamics, and monitoring of calcium channel blockade, pertinent for clinicians and other members of the interprofessional team for recognizing and being able to utilize these agents for their intended therapeutic purpose.
How to treat hypotension with calcium chloride?
In the case of hypotension, initial treatment with intravenous fluids requires caution in those who have congestive heart failure , pulmonary edema , or kidney disease. Intravenous calcium administration may reverse the decreased cardiac contractility. Calcium chloride 10% (10 ml for 0.1 to 0.2 ml/kg) or calcium gluconate 10% (20 to 30 ml 0.3 to 0.4 ml/kg) may be administered intravenously and may be repeated every 5 to 10 minutes. Caution must be used with calcium chloride as it may cause skin necrosis when given through a peripheral line. Atropine is a reasonable initial treatment option, but it typically does not reverse the effects of calcium channel antagonist poisoning. Give glucagon as a bolus of 5 to 10 mg intravenously with caution for nausea and vomiting, and patients may be pre-medicated with antiemetics to help avoid this. If the patient is refractory to these interventions, initiate vasopressor therapy using intravenous norepinephrine or push-dose phenylephrine while preparing hyperinsulinemia/euglycemia (HIE) therapy. HIE increases cardiac contractility by enhancing the transport of glucose into the myocardial cells, which corrects they hypo-insulinemia. Administer a bolus of insulin 1 unit/kg, followed by an infusion of 1 to 10 units/kg per hour. Monitor the patient’s glucose for hypoglycemia initially every 10 minutes and then every 30 to 60 minutes to maintain glucose between 100 to 200 mg/dL. Use a concomitant dextrose infusion to maintain these levels. If the initial glucose is less than 200 mg/dL, administer a bolus dose of glucose. Monitor glucose levels and potassium levels closely. Intravenous lipid emulsion therapy lacks clear evidence for efficacy but is a consideration if all else fails. Administer a bolus of intravenous lipid emulsion 20% 1.5 ml/kg, repeat if needed, and then start an infusion of 0.25 to 0.5 ml/kg per minute for an hour. Reports suggest that the use of methylene blue, especially in those with amlodipine overdose resulting in vasodilatory shock, may be effective. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors are also an option in calcium channel antagonist therapy. They increase cardiac output by inhibiting the breakdown of cAMP. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has proven successful in cases refractory to all of the above interventions since it maintains perfusion to vital organs and continues hepatic metabolism.
What is the mechanism of action of calcium channel antagonists?
Calcium channel antagonists block the inward movement of calcium by binding to the L-type “long-acting” voltage-gated calcium channels in the heart, vascular smooth muscle, and pancreas. There are two major categories of calcium channel antagonists based on their primary physiologic effects.
How are calcium channel antagonists absorbed?
Absorption:Calcium channel antagonists are absorbed well orally, however many have low bioavailability due to hepatic first-pass metabolism, primarily by CYP3A4. Distribution:Calcium channel antagonists are highly protein-bound, and many have high volumes of distribution.
Is calcium channel antagonist a contraindication?
Calcium channel antagonists are also contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug or its components. Other contraindications include sick sinus syndrome (except in patients with an artificial pacemaker), severe hypotension, acute myocardial infarction, and pulmonary congestion.
What is a calcium channel blocker?
Calcium channel blocker drugs are designed to block the channel where the calcium is leaking into the cell. These drugs slowly close off these crucial regulatory channels, but over time, the calcium channel essentially stops functioning at all.
What are the layers of calcium channels?
What are calcium channels? Each body cell has an outer membrane with a sandwich of fats called lipids. The layers in the sandwich contain a wonderful host of protective nutrients, including EPA (eico-sapentaenoic acid), phosphatidyl choline, vitamin E and others.
What is the best medicine for high blood pressure?
Among the top 10 drugs prescribed in the U.S. are blood pressure drugs called calcium channel blockers. Calcium channel blockers are prescribed for hypertension (high blood pressure), heart arrhythmias (irregular heart beats), and angina (chest pain.) Unfortunately, research shows that these drugs make one far more susceptible to dying ...
How does calcium flow out of a cell?
Calcium can passively flow out of the cell, but for calcium to re-enter, the cell requires the use of the calcium channel pump. Pumping calcium through the calcium channel requires: a) energy and b) depends upon the cell’s membrane sandwich to have the exact types of layers in the membrane. The channel partly runs on an electric current that is generated by the polarized side arms that protrude from the cell’s sandwich. If the right layers are not in the sandwich, the electric current cannot flow properly to open the calcium channel. Hence, the calcium pump will not work correctly. In effect, it is broken.
Where does calcium pass through the cell?
In normal daily operation, calcium ions pass back and forth through the calcium channels in the cell’ s membrane, repeatedly, many thousands of times per day. Inside the cell, calcium is needed in the mitochondria (where energy is made) and in the endoplasmic reticulum (where drugs, toxins, hormones, etc. are detoxified).
Do calcium channel blockers reduce blood pressure?
In August, 2000, a report from the “Meeting of the European Society of Cardiology in Amsterdam (Netherlands)” showed that despite lowering blood pressure, calcium channel blockers did not reduce the death rate. The real goal of a therapy should not be only to reduce blood pressure or to control any other bodily parameter.
Can you discontinue calcium channel blockers?
Since the use of calcium channel drugs is potentially dangerous and even life-threatening, the time for you to act is now. However, do not try to discontinue these drugs on your own. You need to be under the supervision of a medical doctor.
What is a calcium channel blocker?
Calcium channel blockers ( CCBs) dilate the arteries, reducing pressure within and making it easier for the heart to pump blood, and, as a result, the heart needs less oxygen. By reducing the heart's need for oxygen, calcium channel blockers relieve or prevent angina (chest pain ). Calcium channel blockers also are used for treating high blood ...
What are beta blockers and calcium channel blockers?
Beta blockers, also called beta adrenergic blocking agents, block the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine (adrenaline) from binding to beta receptors on nerves, which can reduce the heart rate and reduce blood pressure by dilating blood vessels.
What is the difference between beta blockers and calcium channel blockers?
Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers are used to treat angina ( chest pain ), high blood pressure, and abnormal heart rhythms, and to prevent migraine headaches.
What is the best medicine for angina?
Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers are used to treat angina (chest pain), high blood pressure, and abnormal heart rhythms, and to prevent migraine headaches. Beta blockers and Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) both dilate the blood vessels through different mechanisms, reducing pressure within and making it easier for the heart to pump blood.
What are the side effects of beta blockers?
Side effects of beta blockers and calcium channel blockers that are similar include nausea, rash, and sexual dysfunction.
What is a beta blocker?
Beta blockers, also called beta adrenergic blocking agents, block the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine (adrenaline) from binding to beta receptors on nerves, which can reduce the heart rate and reduce blood pressure by dilating blood vessels. Beta blockers are used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, angina (chest pain ), ...
Can beta blockers cause hypoglycemia?
Beta blockers may prolong hypoglycemia ( low blood sugar) and mask symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetics who are taking insulin or other diabetic medications.
