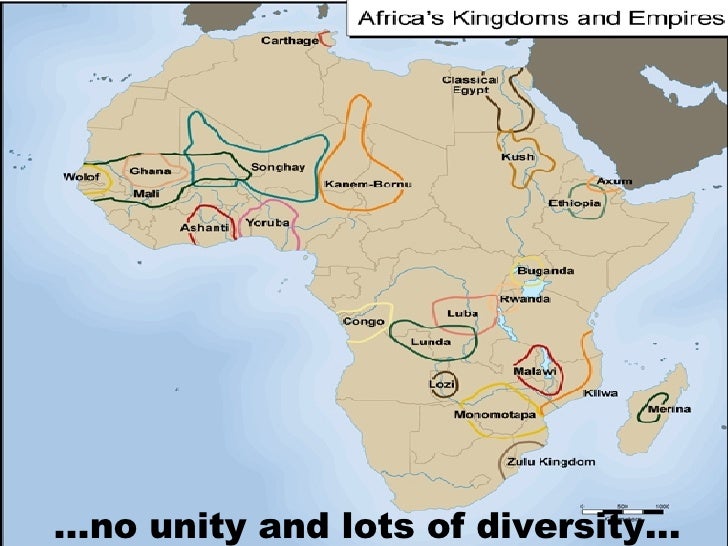
What are the 9 kingdoms in Africa?
9 Ancient African Kingdoms You Should Know About 1 The Aksumite Empire. 2 The Kingdom of Ghana. 3 The Mali Empire. 4 The Songhai Empire. 5 The Kingdom of Zimbabwe. 6 The Kingdom of Mutapa. 7 The Ethiopian Empire. 8 The Kingdom of Kongo. 9 The Benin Empire.
What is the longest lasting African kingdom?
Stretching from the Middle Ages all the way to the Cold War, the Ethiopian Empire (or Abyssinia, as it was also known) is the longest lasting of the African kingdoms on this list. It survived some of the most tumultuous events in modern-day history.
Who was the richest king in Africa?
Of all the African kingdoms on this list, the Malian Empire’s most famous ruler, Mansa Musa, was the richest – even by today’s standards. He is regarded as one of the wealthiest people in world history with records suggesting that Mali was the largest producer of gold on Earth during his reign. 4. The Songhai Empire Where?
What are the top 10 African empires?
1 The Aksumite Empire 2 The Kingdom of Ghana 3 The Mali Empire 4 The Songhai Empire 5 The Kingdom of Zimbabwe 6 The Kingdom of Mutapa 7 The Ethiopian Empire 8 The Kingdom of Kongo 9 The Benin Empire
See more

Which kingdom is the oldest in Africa?
1. The Aksumite Empire. Also known as the Kingdom of Aksum (or Axum), this ancient society is the oldest of the African kingdoms on this list. This kingdom spread across what is today Ethiopia and Eritrea in an area where evidence of farming dates back 10,000 years.
What were the 3 African kingdoms?
A succession of three great kingdoms came to power as their people, gained control of valuable trade routes in West Africa. Ghana was the first of these empires, followed by the kingdoms of Mali and Songhai.
How many kingdoms are in Africa?
threeHowever, only three are currently sovereign, while the remaining are sub-national monarchies.
Who is the powerful king in Africa?
His Majesty King Mohammed VI of Morocco is the wealthiest monarch in Africa. He derives his fortune from his control of Société Nationale d'Investissement (SNI), a large Moroccan investment holding company with assets valued at more than $10 billion.
What was the last African empire?
Mali EmpireMali Empire• c. 17th centuryMahmud IV (last)LegislatureGbaraHistorical eraPostclassical Era to Early Modern Era• Establishedc. 123025 more rows
When did Africa rule the world?
In ancient times, the Oracle of Amon at Siwah was the most celebrated, and Heliopolis, Memphis, and Thebes, were representatives of the best of Egyptian civilization and culture.
Who is king of Africa?
King Mswati, 46, is Africa's last absolute monarch.
Who named Africa Africa?
One of the most popular suggestions for the origins of the term 'Africa' is that it is derived from the Roman name for a tribe living in the northern reaches of Tunisia, believed to possibly be the Berber people. The Romans variously named these people 'Afri', 'Afer' and 'Ifir'.
Who ruled Africa?
The principal powers involved in the modern colonisation of Africa are Britain, France, Germany, Portugal, Spain and Italy. In nearly all African countries today, the language used in government and media is the one imposed by a recent colonial power, though most people speak their native African languages.
What is Africa real name?
AlkebulanAlkebu-lan “mother of mankind” or “garden of Eden”.” Alkebulan is the oldest and the only word of indigenous origin. It was used by the Moors, Nubians, Numidians, Khart-Haddans (Carthagenians), and Ethiopians.
What is the strongest empire in Africa?
The most powerful of these states was the Songhai Empire, which expanded rapidly beginning with king Sonni Ali in the 1460s. By 1500, it had risen to stretch from Cameroon to the Maghreb, the largest state in African history.
Who is the richest man in Africa?
Aliko DangoteFor the eleventh time in a row, Aliko Dangote (b. 1957) has been named the richest man in Africa in 2022, with an estimated net worth of around $13 billion. 1 He is also the richest black man in the world.
What were the major kingdoms of ancient Africa?
From ancient Sudan to medieval Zimbabwe, get the facts on seven African kingdoms that made their mark on history....7 Influential African EmpiresThe Kingdom of Kush. ... The Land of Punt. ... Carthage. ... The Kingdom of Aksum. ... 5 Myths About Slavery.The Mali Empire. ... The Songhai Empire. ... The Great Zimbabwe.More items...•
What were the African empires?
African empires is an umbrella term used in African studies to refer to a number of pre-colonial African kingdoms in Africa with multinational structures incorporating various populations and polities into a single entity, usually through conquest.
What are the major African civilizations?
Here are eight of Africa's greatest ancient civilizations.Egypt. The Pyramid of Giza in Egypt. ... The Kingdom Of Kush. Historical Meroe pyramids in the Sahara desert in Sudan. ... Punt. ... Carthage. ... Aksum. ... Mali Empire. ... Songhai Empire. ... Zimbabwe.
What were the main kingdoms of West Africa?
Between 700 and 1600 there were three great empires in the centre of West Africa: Ancient Ghana, Mali and Songhai.
How many monarchies are there in Africa?
There are several monarchies in Africa, defined as either actually or nominally self-governing states, territories, or nations on the continent of Africa where supreme power resides with an individual who is recognized as the head of state. All are similar in that the sovereign inherits their office and typically keeps it until their death or until their abdication. However, only three are currently sovereign, while the remaining are sub-national monarchies. Two of these are constitutional monarchies ( Lesotho and Morocco ), in which the sovereign is bound by laws and customs in the exercise of his or her powers, and one is an absolute monarchy ( Eswatini ), in which the sovereign rules without bounds. The sub-national monarchies are not sovereign, and exist within larger political associations. In addition to these, there are also three dependencies of two European monarchies.
How many sub-national states are there in Africa?
A series of sub-national polities exist as constituencies of a number of the 52 remaining sovereign states of Africa. Traditional authority is vested in the monarchs of these constituencies by virtue of customary law as a general rule, although some of them also enjoy either a constitutional or a statutory recognition of their titles in the states that play host to them. Such figures as the Nigerian traditional rulers and the Zulu King of South Africa typify the class.
How did the monarchs in Africa create superiority myths?
To exercise rights as a king or queen in most cases, the monarchs in Africa created superiority myths through rituals and symbolism, practices that were intended to encourage their being seen as mediators between the gods and the people.
Why did the early settlements of West Africa and the largely nomadic community in North Africa form states?
A Queen Mother in Africa. The need for an identity prompted the early settlements of West Africa and the largely nomadic community in North Africa to form states as they had the capacity, due to the trans-Saharan trade, to support formal establishments.
Who was the king of Swaziland in 1902?
Independence was granted the following year. For most of the colonial period, the Swazi were ruled by Sobhuza II, who became King upon independence.
Where is Morocco located?
Morocco, located in the northwestern corner of Africa, has a long and established history dating back to antiquity. Originally Carthaginian, the territory was controlled by the Roman Empire, the Vandals, and the Byzantine Empire before falling under Arab control in the seventh century.
Who is the 14th Emir of Nigeria?
Sub-national monarchies. Main article: List of current constituent African monarchs. The 14th Emir of Kano, Nigeria, Muhammadu Sanusi II, on his throne before the Durbar, September 2016. The Zulu King, Goodwill Zwelithini, at a tribal event in South Africa.
Which is the biggest country in Africa?
Algeria is the biggest country in Africa and tenth-largest in the world, covering the land area of 2,381,741 sq. km. This was not always the case, with Sudan having held the rank of largest African country until South Sudan separated in 2011, dividing the nation into two countries. 90% of Algeria is desert, and only 12% of it is inhibited by people.
What is the area of Kinshasa?
Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Image credit: Alexandra Tyukavina/Shutterstock. 2. Democratic Republic of the Congo - 2,344,858 sq. km. With the equator crossing much of the African continent, the Democratic Republic of the Congo occupies much of this part of Africa. It is Africa's second-largest country by land area at 2,344,858 sq.
What is the capital of the Democratic Republic of Congo?
Not to be confused with the Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo is often referred to by the acronym DRC, or by its capital and administrative center name, Kinshasa. Situated on the South-east side of the Congo River and the South Western border with the Republic of Congo, Kinshasa serves as the country's main port. The Republic of the Congo is often referred to plainly as Congo, or Brazzaville, which is its capital sitting on the north-west side of the Congo River.
Which country has the most pyramids?
Image credit: Martchan/Shutterstock. 3. Sudan - 1,861,484 sq. km. Although pyramids are often associated with Egypt, Sudan, with over 200 of the ancient structures, is the land with the most pyramids in the world. On July 9, 2011, South Sudan seceded after a vote supported by 98% of the southern Sudanese, which makes South Sudan ...
When did the Congo get its independence?
On June 30, 1960, the Democratic Republic of the Congo proclaimed its independence. The French-claimed Congo received independence soon after, on August 15.
Is Algeria a country?
The Republic of the Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) are two separate countries, occupied initially by the French and Belgians, respectively. Algeria is the largest African country by land area, but only 12% of it is populated. There are many stereotypes associated with Africa, including it being nothing but jungle and tribes, ...
What is the oldest African kingdom?
Also known as the Kingdom of Aksum (or Axum), this ancient society is the oldest of the African kingdoms on this list and is spread across what is today Ethiopia and Eritrea in an area where evidence of farming dates back 10,000 years. The Aksumites were key players in the commercial trading routes which existed between ...
What is the longest lasting African empire?
Stretching from the Middle Ages all the way to the Cold War, the Ethiopian Empire (or Abyssinia, as it was also known) is the longest lasting of the African kingdoms on this list. It survived some of the most tumultuous events in modern-day history. It resisted various enemies attempting to encroach on its territory, from the Ottoman and Italian armies to the Egyptians, and some of its rulers are said to have been descended from King Solomon. During the Scramble for Africa which saw European powers asserting colonial authority across African territories, Ethiopia successfully fought off and defeated Italy in the First Italo-Ethiopian War. The empire’s decline began when they lost the Second Italo-Ethiopian War in 1935 and the monarchy was abolished in 1974 by a military junta.
What is the Mutapa Empire?
The Mutapa Empire encompassed a truly staggering portion of Southern Africa, from the Limpopo and Zambezi Rivers to the Indian Ocean coastline. Its territory was so large that if it were around today, it would stretch across parts of six Southern African nations.
When was the Wagadu kingdom?
When? circa 700 CE – 1240 CE. More commonly known as Wagadu, this kingdom was an important stop along the trans-Saharan trade route which connected African societies in the Sahel to the markets found along the coastlines of the Mediterranean Sea and the trans-Saharan gold trade.
Which African kingdoms traded in gold?
While the Ghana Empire traded in gold, the Malian Empire actually mined gold from its mines which, by the end of the 1200s, was the source of approximately 50% of the Old World’s gold supply. Of all the African kingdoms on this list, the Malian Empire’s most famous ruler, Mansa Musa, was the richest – even by today’s standards.
When was Nigeria discovered?
Nigeria. When? circa 1180 CE – 1897 CE. Found in modern-day Nigeria, the Benin Empire was considered one of the oldest and most developed states in West Africa until its annexation by the British Empire. Famous artisans crafted masterpieces from ivory, bronze and iron.
Which two countries were part of the Kingdom of Kongo?
Before European powers divided the African continent during the Scramble for Africa, the modern-day countries of the Democratic Republic of Congo and the Republic of Congo both formed part of the Kingdom of Kongo.

The Aksumite Empire
The Kingdom of Ghana
- This popular empire is spread out across parts of what is today Senegal, Mauritania, and Mali. The empire was in existence between 700 CE – 1240 CE. It was commonly known as Wagadu and was a crucial stop along the trans-Saharan trade route which brought together African communities. The empire was home to about 15,000 to 20,000 people, despite having a limited …
The Mali Empire
- The Kingdom is today spread across parts of Guinea, Ivory Coast, The Gambia, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, Senegal, and Mauritania. The empire existed between 1230 CE – 1670 CE. The people mined gold from their mines, and as a result, their ruler, Mansa Musa, was the richest.
The Songhai Empire
- This popular kingdom is today spread out across parts of Benin, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Burkina Faso, Niger, Nigeria, The Gambia, Senegal, Mali, and Mauritania. The empire existed between 1000 CE and 1591 CE. Being one of the African kingdoms before colonization, it was termed as the largest state in the African continent. One of its most prominent ...
The Kingdom of Zimbabwe
- This kingdom existed between 1220 CE – 1450 CE. It is one of the African kingdoms today and claims its capital as Great Zimbabwe, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The empire was home to about 18,000 people who were spread across an area of about 7km. The empire had a monopoly on the trade of gold and ivory from the Southeastern coast of the continent to its interior. They al…
The Kingdom of Mutapa
- The empire was spread across what is now South Africa, Lesotho, Zambia, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Swaziland. This empire existed between 1430 CE – 1760 CE and is one of the South African kingdoms that existed. It encompassed a vast area of Southern Africa which covered the Limpopo and Zambezi rivers to the Indian Ocean coastline. It is believed that a warr…
The Ethiopian Empire
- It spread across various parts of today Eritrea and Ethiopia, during circa 1137 CE – 1975 CE. The empire lasted from the middle ages to the cold war era in the African kingdoms map. It was strong as it resisted various enemies that tried encroaching its territories. Some of these armies included the Egyptians, Italians, and the Ottoman. It is believed that some of its rulers descended from Ki…
The Kingdom of Kongo
- This empire cut across parts of today's DRC, Angola, Republic of Congo, and Gabon. It existed during circa 1390 CE - 1914 CE, which was before the European powers began their scramble for Africa. It was overseen by a Kikongo warrior named Luken Lua Nimi. His political and military prowess was highly recognized as he dominated central Africa. The empire dealt in ivory, coppe…
The Benin Empire
- This kingdom cut across modern-day Nigeria during 1180 CE and 1897 CE. It was considered one of the oldest and most developed among the various West African kingdoms. It traded in bronze, ivory, and iron, pepper, and palm oil for firearms and manila. It is also one of the African kingdoms that were defeated by the British Empire.
The Kingdom of Kush
- This empire stood as a regional and robust power in Africa for more than a thousand years. It cut across modern-day Sudan and is often overshadowed by its Egyptian neighbours to the north. The empire ruled over a large swath of territory along the Nile River. Most of what is known about it is believed to come from the Egyptian sources. They traded in gold, iron, ivory, and incense. In…