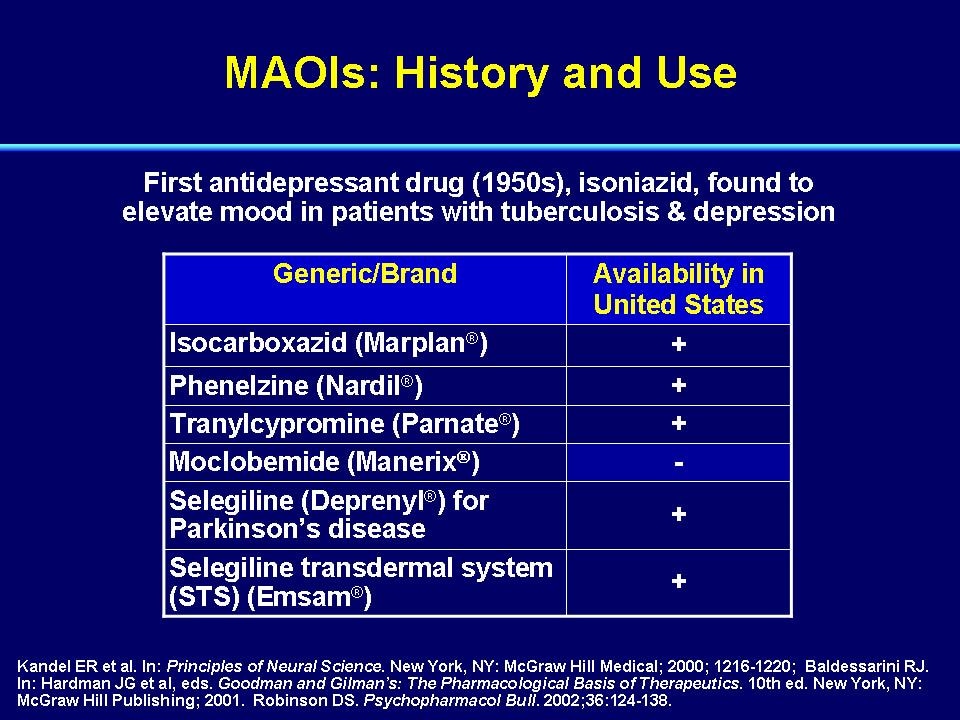
What are biological influences on depression?
The biological factors that might have some effect on depression include: genes, ho rmones, and brain chemicals. Genetic Factors Depression often runs in families, which suggests that individuals may inherit genes that make them vulnerable to developing depression. However, one may inherit an ...
What are the biological effects of depression?
Depression can cause headaches, chronic body aches, and pain that may not respond to medication.
What are the common causes of depression?
Lots of things can increase the chance of depression, including the following:
- Abuse. Physical, sexual, or emotional abuse can make you more vulnerable to depression later in life.
- Age. People who are elderly are at higher risk of depression. ...
- Certain medications. ...
- Conflict. ...
- Death or a loss. ...
- Gender. ...
- Genes. ...
- Major events. ...
- Other personal problems. ...
- Serious illnesses. ...
What is the biological reason for depression?
Other biological causes for depression can include physical illness, the process of ageing and gender. Stress can trigger depression but understanding its particular meaning to the person is important. Certain temperament and personality styles pose risks for developing non-melancholic depression.
What are the causes of depression?
What are the two most important biological factors that influence depression?
Why Are We So Focused on Biology?
How do scientists measure depression?
How does the brain change?
How does depression affect the brain?
Why do people get depressed?
See 2 more
What is the role of genetics in depression?
The inheritance of risk for depression is considered, at best, polygenetic—that is, a number of unknown genes each contributes a tiny risk under ce...
Can genes for depression be modified?
Scientists know that the expression and function of many genes can be altered without doing the near-impossible—making any changes to the gene stru...
What happens in the brain with depression?
Overexcitability of the stress response system, shifts in activity of various neurochemicals in the brain, diminished efficiency of nerve circuitry...
How does lack of sleep alter brain function?
Disruption of the sleep-wake cycle is one of the hallmarks of depression and is a major source the mood disturbance in major depression. Lack of...
How does the brain regulate mood?
Emotions are fleeting responses to stimuli; mood is a more sustained state of emotion. Like emotions, mood probably originates with activity of t...
What role does serotonin play in depression?
The neurotransmitter serotonin is one of many signaling chemicals in the brain associated with depressive symptoms. Under normal conditions, seroto...
Does dopamine play a role in depression?
The neurotransmitter dopamine, which mediates motivation and desire, is one of several brain signaling chemicals that are implicated in depression...
How does nerve cell communication go awry in depression?
Where once researchers and clinicians focused on the role of neurotransmitters such as serotonin in depression, they now know that neurotransmitter...
How does stress affect the brain?
Stress can be beneficial to the brain, depending on how intense and long-lasting the stressor is. In brief bursts, stress fosters alertness, learni...
Biological Factors That Contribute to Depression - EzineArticles
Many people are pre-disposed to depression because of their own biological makeup making their risk of suffering from this condition much greater then those who do not share these risk factors. There are four main biological factors that can increase a persons risk for depression and these include (1) genetic factors, (2) biochemical factors, (3) alterations in hormonal regulation and, (4 ...
The Biology of Depression | Psychology Today
Depression makes deep inroads on biology to bring about the many symptoms of depression, from sleep disruption and an inability to experience pleasure to lack of motivation and feelings of guilt.
Biological aspects of depression - PubMed
In most cases, depression involves the interaction of biological and psychosocial factors. The impact of biological factors seems to be more prominent in major depressive syndrome, where typical symptoms and signs such as decrease in weight, changes in libido, dysmenorrhea, and sleeping disorders ca …
Exploring the Biological Perspective on Depression
When we are depressed, physical changes take place within our bodies. The most Important of these changes takes place within the brain. It Is on this basis that depression is considered a physical illness, rather than merely something psychological or something that exists only in the imagination or perception of the 'OFF sufferer (Pretest).
Depression Causes: Your Genes, Environment, and Habits - Psych Central
The causes of depression vary from person to person but may include genetics, significant losses, traumatic experiences, and some personality traits.
Is Depression Hereditary?
The word “hereditary” refers to genetic factors that are passed down to offspring. Our genes impact or DNA and RNA, determining what genetic sequences we are born with.
How does stress affect depression?
One thing we do know is that environmental factors play a huge role in the development of depression. When you’re under constant stress, you feel overwhelmed and oftentimes unfulfilled. Prolonged periods of stress will naturally contribute to our brain chemistry.
What is epigenetics in biology?
Epigenetics takes a slightly different approach to biology and inherited traits. When studying epigenetics, we look at the way that experiences can interact with our biological makeup. Trauma, in particular, can affect our brain development and our DNA.
What happens if you grow up with a depressed caretaker?
If you grew up with a severely depressed caretaker, those symptoms may have become noticeable to you. For example, your caretaker may have stayed in bed or struggled with day-to-day activities when times got tough. As a result, you may have learned to respond to tough situations in a similar way.
How many people have depression?
One study conducted by the National Institute of Mental Health revealed that 16.2 million adults have experienced at least one episode of severe depression.
Can you inherit epigenetic factors?
It is believed that epigenetic factors can be inherited. To put it simply, it is possible that with the DNA you inherit, you could also inherit those patterns of muted genes . This may lead to an increased risk of developing major depressive symptoms if it runs in your family.
Do people with depression come from a family?
The second is that not everyone who notes depression in their family medical history will develop symptoms of depression. On the flip side, 60% of people who have depression do not come from a family where depression was present.
How do neurons work?
If you trained a high-powered microscope on a slice of brain tissue, you might be able to see a loosely braided network of neurons that send and receive messages. While every cell in the body has the capacity to send and receive signals, neurons are specially designed for this function. Each neuron has a cell body containing the structures that any cell needs to thrive. Stretching out from the cell body are short, branchlike fibers called dendrites and one longer, more prominent fiber called the axon.
How does a PET scan help with depression?
A PET or SPECT scan can map the brain by measuring the distribution and density of neurotransmitter receptors in certain areas. Use of this technology has led to a better understanding of which brain regions regulate mood and how other functions, such as memory, may be affected by depression.
Why is the hippocampus smaller?
The more bouts of depression a woman had, the smaller the hippocampus. Stress, which plays a role in depression, may be a key factor here, since experts believe stress can suppress the production of new neurons (nerve cells) in the hippocampus.
Why is neurotransmitter important in depression?
The ultimate goal in treating the biology of depression is to improve the brain's ability to regulate mood. We now know that neurotransmitters are not the only important part of the machinery. But let's not diminish their importance either. They are deeply involved in how nerve cells communicate with one another.
Why is gene research important?
Another goal of gene research, of course, is to understand how, exactly, biology makes certain people vulnerable to depression. For example, several genes influence the stress response, leaving us more or less likely to become depressed in response to trouble.
What is the brain imaging that affects mood?
Increasingly sophisticated forms of brain imaging — such as positron emission tomography (PET), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) — permit a much closer look at the working brain than was possible in the past.
What are the biology of depression?
They've identified genes that make individuals more vulnerable to low moods and influence how an individual responds to drug therapy. One day, these discoveries should lead to better, more individualized treatment (see "From the lab to your medicine cabinet"), but that is likely to be years away. And while researchers know more now than ever before about how the brain regulates mood, their understanding of the biology of depression is far from complete.
What is the role of genetics in depression?
The inheritance of risk for depression is considered, at best, polygenetic—that is, a number of unknown genes each contributes a tiny risk under certain environmental conditions. None of them makes depression inevitable. The baseline risk of depression in the population is 10 percent; having a first-degree relative (parent or sibling) with depression doubles or triples an individual’s risk, to 20 to 30 percent over the course of a lifetime.
Can genes for depression be modified?
Scientists know that the expression and function of many genes can be altered without doing the near-impossible—making any changes to the gene structure itself. Such changes are known as epigenetic modifications. Some life experiences can create vulnerability to depression through epigenetic changes. For example, in rat pups, lack of maternal care can permanently reset the sensitivity of receptors to stress hormones. If their mothers fail to lick and groom them, they grow up to display an exaggerated response to stress hormones and develop depression-like behavior in response to stress.
What happens in the brain with depression?
Overexcitability of the stress response system, shifts in activity of various neurochemicals in the brain, diminished efficiency of nerve circuitry and nerve generation, disturbances in energy use nerve cells, the intrusion of inflammatory substances in the brain, upsets in the brain’s 24-hour (circadian) clock—all play a role in depression onset or progression and influence the kind and severity of symptoms.
What role does serotonin play in depression?
Under normal conditions, serotonin inhibits pain, influences the processing of various emotions, and mediates many mental capacities important in social life.
Does dopamine play a role in depression?
The neurotransmitter dopamine, which mediates motivation and desire, is one of several brain signaling chemicals that are implicated in depression. It is associated with two of the most prominent features of depression—anhedonia, or the inability to experience pleasure, and appetite alterations.
How does nerve cell communication go awry in depression?
In fact, many experts see depression as a nerve circuit disorder, marked by a power failure in the brain’s wiring, affecting communication between one area of the brain and another.
What areas of the brain play a role in depression?
Many areas of the brain contribute to the symptoms of depression, such as the hippocampus, which is the seat of memory and learning , and the superchiasmatic nucleus, which is the “body clock” that paces all physiologic activity, notably the sleep-wake cycle. But brain imaging studies suggest that there is a primary “depression circuit,” consisting of the amygdala, which flags emotion-related stimuli; the prefrontal cortex, which analyzes and interprets experience, modulates emotional reactivity, and controls attention; and the two-way network of nerve fibers that connect them.
What are the biological aspects of depression?
Biological aspects of depression. In most cases, depression involves the interaction of biological and psychosocial factors. The impact of biological factors seems to be more prominent in major depressive syndrome, where typical symptoms and signs such as decrease in weight, changes in libido, dysmenorrhea, and sleeping disorders ca …. ...
What are the effects of biological factors on depressive symptoms?
The impact of biological factors seems to be more prominent in major depressive syndrome, where typical symptoms and signs such as decrease in weight, changes in libido, dysmenorrhea, and sleeping disorders cannot be explained on psychodynamic grounds alone.
Why is the hippocampus smaller in depression?
Some researchers have found that the stress hormone cortisol is produced in excess in depressed people. These investigators believe that cortisol has a toxic or "shrinking" effect on the development of the hippocampus. Some experts think depressed people may be simply born with a smaller hippocampus and are thus inclined to have depression. There are many other brain regions, and pathways between specific regions, thought to be involved with depression, and likely, no single brain structure or pathway fully accounts for clinical depression.
Why is the hippocampus smaller?
A smaller hippocampus has fewer serotonin receptors. Serotonin is one of many brain chemicals known as neurotransmitters that allow communication across circuits that connect the brain regions involved in processing emotions. Scientists do not know why the hippocampus may be smaller in some people with depression.
What makes you more vulnerable to depression later in life?
Abuse. Physical, sexual, or emotional abuse can make you more vulnerable to depression later in life.
What is the normal response to loss?
Grief is a common, normal response to loss. Losses that may lead to grief include the death or separation of a loved one, loss of a job, death or loss of a beloved pet, or any number of other changes in life, such as divorce, becoming an "empty nester," or retirement.
Why do people get clinical depression?
Problems such as social isolation due to other mental illnesses or being cast out of a family or social group can contribute to the risk of developing clinical depression. Serious illnesses. Sometimes, depression happens along with a major illness or may be triggered by another medical condition. Substance misuse.
What is the best treatment for chronic pain?
There is help for chronic pain and depression. A multifaceted program of medicine, psychotherapy, support groups, and more can help you manage your pain, ease your depression, and get your life back on track.
What is chronic pain?
When pain lingers for weeks to months, it's called "chronic." Not only does chronic pain hurt, it disturbs your sleep, your ability to exercise and be active, your relationships, and your productivity at work. Can you see how chronic pain may also leave you feeling sad, isolated, and depressed?
What are the factors that cause depression?
Factors that may interact to cause depression include: certain gene sets. personality traits. significant life events. stress and trauma. seasonal changes.
What medical conditions can cause depression?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) reports that the following medical conditions can cause depression: stroke.
What causes depression in teens?
Depression causes. If you have a depressive disorder, a combination of genetic, psychological, and environmental factors are likely involved. One popular theory suggests that different sets of genes interact with your environment to cause depression. It’s common for depression to begin in your teen years.
What is the biopsychosocial model?
The biopsychosocial model is one popular theory for what causes depression. In this model, depression is thought to be caused by a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. Major depressive disorder (MDD) is the official term for depression. In this article, we’ll refer to MDD as “depression.”.
What is seasonal depression?
This kind of depression is called major depressive disorder (MDD) with seasonal pattern, former ly known as seasonal affective disorder . If you live with this condition, your depression symptoms are triggered by seasonal changes.
How does stress affect depression?
For example, stress has been shown to contribute to depression by altering the expression of certain genes.
Why is depression a medical condition?
hormonal disorders. Depression as a medical symptom may increase feelings of apathy, making it harder to care for yourself through your medical condition. Other research points to the overlooked importance of the gut’s microbiome — the types and amounts of important bacteria that live in your digestive system.
Why do hormones cause depression?
Hormones. Changes in the body's balance of hormones may be involved in causing or triggering depression. Hormone changes can result with pregnancy and during the weeks or months after delivery (postpartum) and from thyroid problems, menopause or a number of other conditions.
What is the mood of depression?
Depression is a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Also called major depressive disorder or clinical depression, it affects how you feel, think and behave and can lead to a variety of emotional and physical problems. You may have trouble doing normal day-to-day activities, and sometimes you may feel as if life isn't worth living.
Why do people with depression have physical changes?
People with depression appear to have physical changes in their brains. The significance of these changes is still uncertain, but may eventually help pinpoint causes. Brain chemistry. Neurotransmitters are naturally occurring brain chemicals that likely play a role in depression.
What are the symptoms of depression in children?
In younger children, symptoms of depression may include sadness, irritability, clinginess, worry, aches and pains, refusing to go to school, or being underweight.
How often do you experience depression?
Symptoms. Although depression may occur only once during your life, people typically have multiple episodes. During these episodes, symptoms occur most of the day, nearly every day and may include: Loss of interest or pleasure in most or all normal activities, such as sex, hobbies or sports.
When does depression start?
Depression often begins in the teens, 20s or 30s, but it can happen at any age. More women than men are diagnosed with depression, but this may be due in part because women are more likely to seek treatment.
When to see a doctor for depression?
When to see a doctor. If you feel depressed, make an appointment to see your doctor or mental health professional as soon as you can. If you're reluctant to seek treatment, talk to a friend or loved one, any health care professional, a faith leader, or someone else you trust.
What are the causes of depression?
The two primary biological causes of depression are genetics and neuroplasticity . People with the 5-HTT gene are vulnerable to depression, while neuroplasticity describes the changes that occur in your brain when depression is triggered by psychological and social factors. Biology helps explain depression that cannot be attributed to unfavorable environmental factors.
What are the two most important biological factors that influence depression?
The two most important biological factors that influence depression are neuroplasticity and genetics .
Why Are We So Focused on Biology?
If biology only accounts for a small portion of depression causes, why are we so interested in the biological causes of depression? There are four reasons for this.
How do scientists measure depression?
Scientists can use large data sets of fraternal and identical twins and measure how frequently both twins experience depression. If genetics had no influence on depression, then the identical twins would be no more likely to both be depressed than the fraternal twins. But if there are more sets of identical twins with depression than sets of fraternal twins, that points to at least some genetic component to the disease. By measuring the difference between depression rates in both types of twins, scientists can calculate just how big a role genetics play in depression. This isn’t a perfect method (since even twins can have different life events that can trigger depression differently in each person), but it gives a reliable best estimate for how much your genes contribute to depression.
How does the brain change?
It does this by adding and subtracting synapses, which are connections between brain cells. When you learn new information or practice a skill, new synapses form; if you don’t use that skill for decades afterward, the brain prunes those synapses to save energy to power the skills you do use.
How does depression affect the brain?
Social, psychological, and environmental disconnections deprive the emotion centers of the brain of the happy experiences they need in order to stay in good working order. If those disconnections persist, that unhappiness grows into depression, which makes it even more difficult to establish those connections and ultimately results in further changes in the emotion centers of the brain.
Why do people get depressed?
The most important of the two biological causes of depression is genetics. There is no single “depression gene,” but there is a particular variant of a gene called 5-HTT that significantly increases your vulnerability to depression. However, just having that gene alone is not enough to make you depressed—it has to be switched on by the environment. A baby born and raised in a perfect environment (with no trauma and all the right connections) wouldn’t spontaneously become depressed, no matter what their genetic makeup. But if a baby with the 5-HTT gene variant and a baby without it are exposed to the same trauma, the former is much more likely to develop depression as a result.
