Why does the Bohr model work perfectly for only hydrogen?
The Bohr model works only for hydrogen because it considers only the interactions between one electron and the nucleus. The Bohr model is based on the energy levels of one electron orbiting a nucleus at various energy levels. Any other electrons in the atom will repel the one electron and change its energy level. 2.9K views
What are some problems with the Bohr model?
Here are the following:
- It was primarily for hydrogen atom
- It couldn’t elaborate spectra of multi-electron atoms
- Wave nature of electron was not justified by the model (inconsistent with the de Broglie’s hypothesis of dual nature of matter)
- It didn’t illustrated molecules making process of chemical reactions
What are true about Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom?
Bohr's model of hydrogen
- Key points. Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus.
- The planetary model of the atom. At the beginning of the 20th century, a new field of study known as quantum mechanics emerged. ...
- Quantization and photons. ...
- Atomic line spectra. ...
- Absorption and emission. ...
What does Bohr model stand for?
Bohr model. In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than ...

How do you draw a Bohr model for hydrogen?
4:069:244 Easy Steps to Draw Bohr Rutherford (aka 'Bohr') Diagram with ExamplesYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe four steps to mastering a bohr rather her diagram we're going to start with the first which isMoreThe four steps to mastering a bohr rather her diagram we're going to start with the first which is draw the nucleus with the element name. Inside. Second is draw in the number of shells.
What is the Bohr model easy explanation?
Bohr's model consists of a small nucleus (positively charged) surrounded by negative electrons moving around the nucleus in orbits. Bohr found that an electron located away from the nucleus has more energy, and the electron which is closer to nucleus has less energy.
What did Bohr discover about hydrogen?
In 1913, Niels Bohr proposed a theory for the hydrogen atom, based on quantum theory that some physical quantities only take discrete values. Electrons move around a nucleus, but only in prescribed orbits, and If electrons jump to a lower-energy orbit, the difference is sent out as radiation.
Why does Bohr model only work for hydrogen?
Because hydrogen and hydrogen-like atoms only have one electron and thus do not experience electron correlation effects.
How would you describe the Bohr model of the atom?
In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, is a system consisting of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons—similar to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces in place of gravity.
What is Bohr's model known and why?
The model was proposed by physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. In this model, the electrons travel around the nucleus of an atom in distinct circular orbits, or shells. The model is also referred to as the planetary model of an atom. The electrons orbit around the nucleus similar to how planets orbit around the sun.
What are the main points of Bohr's model?
Answer: 1) electron revolve around the nucleus in the the circular orbits , which have constant energy. 2) electron revolves in only those circular orbits whose angular momentum is multiple of nhi/2π 3)energy is realised or absorbed in form of photon, only when an electron makes an transition from one orbit to other.
What is the main discovery of Bohr's model?
Atomic model Bohr was the first to discover that electrons travel in separate orbits around the nucleus and that the number of electrons in the outer orbit determines the properties of an element.
What was Bohr's main discovery?
What was Niels Bohr's most important discovery? Niels Bohr proposed a model of the atom in which the electron was able to occupy only certain orbits around the nucleus. This atomic model was the first to use quantum theory, in that the electrons were limited to specific orbits around the nucleus.
How did Bohr explain hydrogen line spectrum?
Niels Bohr explained the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom by assuming that the electron moved in circular orbits and that orbits with only certain radii were allowed.
How can the Bohr model be used to explain the line spectrum for hydrogen?
Explanation: Bohr tells us that the electrons in the Hydrogen atom can only occupy discrete orbits around the nucleus (not at any distance from it but at certain specific, quantized, positions or radial distances each one corresponding to an energetic state of your H atom) where they do not radiate energy.
Why did Bohr use hydrogen for his line spectrum experiments?
Explanation: Bohr based this assumption on the fact that there are only a few lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom and he believed that the lines were the result of light being released or absorbed as an electron moved from one orbit to another in the atom.
How did Bohr explain the spectrum of hydrogen?
Niels Bohr explained the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom by assuming that the electron moved in circular orbits and that orbits with only certain radii were allowed.
What are the two most important ideas in the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom?
Main Points of the Bohr Model Electrons orbit the nucleus in orbits that have a set size and energy. The energy of the orbit is related to its size.
Which model of hydrogen is based on the assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around?
Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus.
How does Bohr describe the process of absorption and emission?
According to Bohr's model, an electron would absorb energy in the form of photons to get excited to a higher energy level as long as the photon's energy was equal to the energy difference between the initial and final energy levels. After jumping to the higher energy level—also called the excited state —the excited electron would be in a less stable position, so it would quickly emit a photon to relax back to a lower, more stable energy level.
Which scientists thought electrons might orbit the nucleus like the rings around Saturn?
Many scientists, including Rutherford and Bohr, thought electrons might orbit the nucleus like the rings around Saturn. Image credit: Image of Saturn by NASA
Which Bohr model isn't applicable for systems more than one electron?
Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom isn’t applicable for systems more than one electron.
What are the limitations of Bohr's model?
Limitations of the Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom: 1 Bohr’s model doesn’t work well for complex atoms. 2 It couldn’t explain why some spectral lines are more intense than others. 3 It could not explain why some spectral lines split into multiple lines in the presence of a magnetic field. 4 The Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle contradicts Bohr’s idea of electrons existing in specific orbits with a known radius and velocity.
How is the energy of an electron in the shell explained?
According to Bohr’s calculation, the energy for an electron in the shell is given by the expression: The hydrogen spectrum is explained in terms of electrons absorbing and emitting photons to change energy levels , where the photon energy is: Bohr’s Model of the Hydrogen Atom isn’t applicable for systems more than one electron.
What was Bohr's assumption?
The assumption was the quantization of the structure of atoms. Bohr’s proposed that electrons orbited the nucleus in specific orbits or shells with a fixed radius. Only those shells with a radius provided by the equation below were allowed, and it was impossible for electrons to exist between these shells.
Which principle contradicts Bohr's idea of electrons existing in specific orbits with a known radius and?
The Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle contradicts Bohr’s idea of electrons existing in specific orbits with a known radius and velocity. Although the modern quantum mechanical model and the Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom may seem vastly different, the fundamental idea is the same in both.
Which model of atomic theory asserted that electrons revolved around a positively charged nucleus?
But Bohr supported the planetary model, which asserted that electrons revolved around a positively charged nucleus just like the planets around the sun.
Who created the atomic hydrogen model?
Niels Bohr introduced the atomic Hydrogen model in the year 1913. Bohr Model of the hydrogen atom attempts to plug in certain gaps as suggested by Rutherford’s model. It holds a special place in history as it gave rise to quantum mechanics by introducing the quantum theory.
What is the Bohr model of hydrogen?
Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom: To describe the structure of atoms, the first model was proposed by J.J Thomson. According to this, the positively charged particle is distributed throughout the atom, and negatively charged particles are embedded in it like seeds of watermelon. Soon after it failed, Rutherford proposed an atomic model; with the help of the alpha-scattering experiment, he proved that all positively charged particles are present at the centre of the nucleus. He also proposed that the electron revolves around the nucleus in a varying radius. He was not able to explain the stability of atoms and discrete wavelengths in the hydrogen spectrum. Then Bohr gives a model for hydrogen-like atoms and explains the stability and discrete wavelengths in the hydrogen spectrum.
How did Niels Bohr modify the Rutherford model?
Niels Bohr made some modifications to the Rutherford model by adding the ideas of the newly developing quantum hypothesis. To explain the position, motion of the electron, and stability of the atom, he gave three postulates.
Does the spectral line of hydrogen atoms talk about the fine structure?
It does not talk about the fine structure of the spectral lines of hydrogen atoms.
Planetary Model of the Atom
Quantum mechanics first appeared in the mid-1920s. One of the founders of quantum mechanics, Neil Bohr, was interested in a hotly debated topic at the time – the structure of the atom. Numerous atomic models had emerged, including J.J. Thompson’s theory and Ernest Rutherford’s discovery of the nucleus.
Atomic line spectra
Another example of quantization is atomic line spectra. When an element or ion is heated by a flame or excited by an electric current, the excited atoms emit light of a specific color. The emitted light can be refracted by a prism, resulting in spectra with a distinct striped appearance due to the emission of specific wavelengths of light.
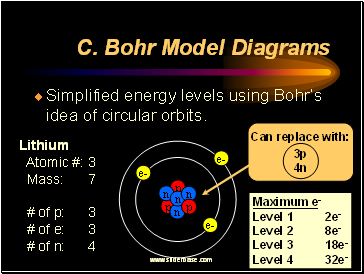
Bohr Model for Heavier Atoms
The nucleus of heavier atoms contains more protons than the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. To cancel out the positive charge of all of these protons, more electrons were necessary. Each electron orbit, according to Bohr, could only hold a certain amount of electrons. When the level was full, extra electrons were moved to the next level.
Sample Questions
Subatomic particles are the particles that make up an atom. Protons, electrons, and neutrons are all included in this category.
