How to calculate boiling point elevation?
How to calculate the boiling point
- Check the altitude at Machu Picchu (before your departure to Peru). ...
- Input this altitude (in imperial unit) to the formula for pressure: pressure = 29.921 * (1 - 0.0000068753 * 7970)^ 5.2559 = 22.25 inHg
- Now, input this pressure into the boiling point equation: boiling point = 49.161 * ln (22.25) + 44.932 = 197.44°F
- Congratulations! ...
Why is boiling point elevation important in the real world?
Colligative properties such as freezing point depression or boiling point elevation can be used to calculate the molecular weight of a soluble solid. To complete this calculation, the mass of solute and solvent must be known as well as the freezing points/boiling points of the pure solvent and the solution.
What is the formula for boiling point?
The Formula for Boiling Point
- R is that the universal gas constant
- Tb is that the boiling temperature of the pure solvent [in K]
- M is that the molar mass of the solvent
- ΔHv is that the heat of vaporization per mole of the solvent.
How does elevation affect boiling point of water?
The key factor is declining air pressure at higher altitudes. Falling air pressure lowers the boiling point of water by just under 1 degree Fahrenheit for each 500 feet of increased elevation. The lower boiling point means water will cook off more quickly, and at a lower temperature.

How do you find the boiling point elevation constant?
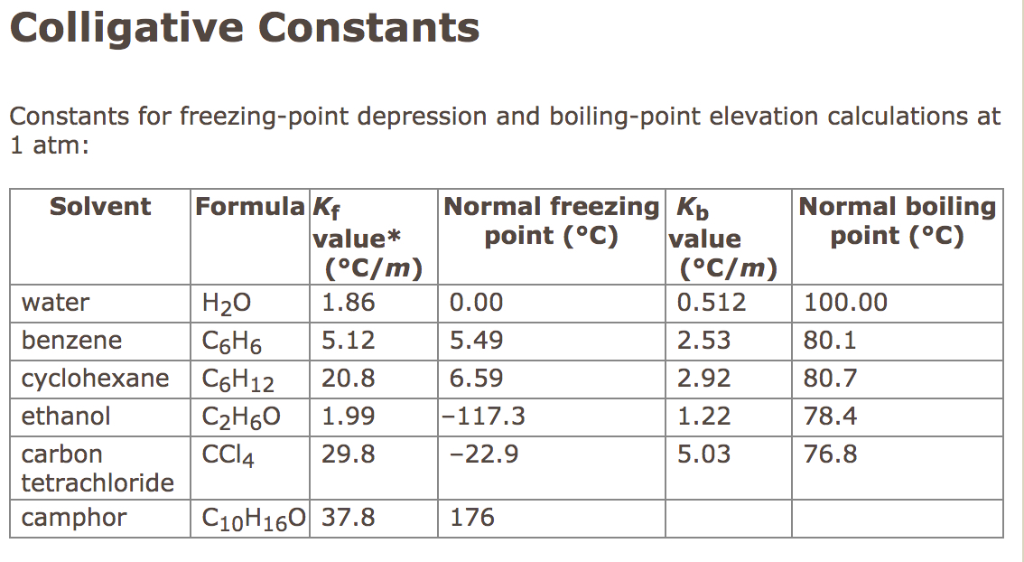
Insert the ebullioscopic constant or boiling point elevation constant, Kb = 0.512 °C⋅kg/mol . Fill in the molality of the solution, m = 3 . Using the boiling point elevation equation: ΔT = i * Kb * m = 1 * 0.512 * 3 = 1.536 °C …and boiling point of the solution is: Tsolution = Tsolvent + ΔT = 100 + 1.536 = 101.536 °C.
What is the boiling point elevation constant of water?
0.51°C/m.1, the molal boiling point elevation constant for water is 0.51°C/m. Thus a 1.00 m aqueous solution of a nonvolatile molecular solute such as glucose or sucrose will have an increase in boiling point of 0.51°C, to give a boiling point of 100.51°C at 1.00 atm.
What does the boiling point elevation constant depend on?
The boiling point elevation is a colligative property, which means that it is dependent on the presence of dissolved particles and their number, but not their identity. It is an effect of the dilution of the solvent in the presence of a solute.
What is the elevation constant?
Molal elevation constant can be defined as the elevation in boiling point produced when one mole of non-volatile solute is dissolved in 1 kg i.e. 1000 g of the solvent. It is also known as the ebullioscopic constant.
What is the KF value of water?
For water, the value of Kf is −1.86oC/m. So, the freezing temperature of a 1-molal aqueous solution of any nonvolatile molecular solute is −1.86oC. Every solvent has a unique molal freezing-point depression constant.
How do you solve boiling point elevation problems?
Solution. To find the temperature change elevation of a solvent by a solute, use the equation: ΔT = iKbm. ... Calculate the Molality of the NaCl. molality (m) of NaCl = moles of NaCl/kg water. From the periodic table: ... Find ΔT. ΔT = iKbm. ... Answer. Adding 31.65 g of NaCl to 220.0 mL of water will raise the boiling point by 2.53 °C.
Why is boiling point elevation important?
By raising the boiling point, it helps to protect against boil-overs. Many brands of antifreeze will list both the amount of boil-over protection and the freeze-up protection offered.
Why elevation of boiling point is a colligative property?
Elevation in boiling point and depression in freezing point are colligative properties because both depend only on the number of particles (ions or molecules) of the solute in a definite amount of the solvent but not on the nature of the solute.
What affects boiling point?
The boiling point of a liquid depends on temperature, atmospheric pressure, and the vapor pressure of the liquid. When the atmospheric pressure is equal to the vapor pressure of the liquid, boiling will begin.
What are the unit of molar elevation of boiling point constant?
K.kg mol-1The molal elevation constant of the solvent is defined as the elevation in its boiling point when one mole of non-volatile solute is dissolved per kilogram (1000g) of solvent. Its unit is K.kg mol-1.
What is model elevation constant write its formula and unit?
The molal elevation constant is the elevation in the boiling point of a solvent when one mole of a non-volatile solute is dissolved in it per kilogram of solvent. The unit of molal elevation constant is given as Kkgmol−1.
What is the formula of molar elevation constant?
i) Molal elevation constant is defined as the elevation in boiling point produced when 1 mole of solute is dissolved in one kg (1000 g) of the solvent. It is also known as the ebullioscopic constant. (Kf). ... ATf = Kf × m, where m is the number of moles of solute per kilograms of solvent.
What is KF in TF KFM?
∆ Tf α m. ∆ Tf = Kf m. Kf is a constant for a given solvent. Kf is called the molal freezing point depression constant and represents how many degrees the freezing point of the solvent will change when 1.00 mole of a nonvolatile nonionizing (nondissociating) solute dissolves in one kilogram of solvent.
What is elevation in boiling point Class 12?
Boiling point elevation refers to the increase in the boiling point of a solvent upon the addition of a solute. When a non-volatile solute is added to a solvent, the resulting solution has a higher boiling point than that of the pure solvent.
What is meant by Cryoscopic constant KF?
A cryoscopic constant is described as the freezing point depression when a mole of non-volatile solute is dissolved in one kg of solvent. The cryoscopic constant is denoted by kf. Freezing point depression refers to the lowering of the freezing point of solvents upon the addition of solutes.
How do you calculate KB of water?
It is given that latent heat of vaporization of water is 9.72kcal/mol at 373.15K. A) Kb=0.515Kkg/mol,Tb=373.20K.
Why does boiling point elevation occur?
The change in chemical potential of a solvent when a solute is added explains why boiling point elevation takes place. The boiling point elevation is a colligative property, which means that it is dependent on the presence of dissolved particles and their number, but not their identity. It is an effect of the dilution of the solvent in ...
What is the boiling point of a solution?
Boiling-point elevation describes the phenomenon that the boiling point of a liquid (a solvent) will be higher when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a higher boiling point than a pure solvent. This happens whenever a non-volatile solute, such as a salt, is added to a pure solvent, such as water. The boiling point can be measured accurately using an ebullioscope .
What is the ebullioscopic constant of a solvent?
Kb, the ebullioscopic constant, which is dependent on the properties of the solvent. It can be calculated as Kb = RTb2M / ΔHv, where R is the gas constant, and Tb is the boiling temperature of the pure solvent [in K], M is the molar mass of the solvent, and ΔHv is the heat of vaporization per mole of the solvent.
How does a liquid boil at a higher temperature?
Put in vapor pressure terms, a liquid boils at the temperature when its vapor pressure equals the surrounding pressure. For the solvent, the presence of the solute decreases its vapor pressure by dilution. A nonvolatile solute has a vapor pressure of zero, so the vapor pressure of the solution is less than the vapor pressure of the solvent. Thus, a higher temperature is needed for the vapor pressure to reach the surrounding pressure, and the boiling point is elevated.
What happens to the chemical potential of a nonvolatile solute?
This means that when a nonvolatile solute is added, the chemical potential of the solvent in the liquid phase is decreased by dilution, but the chemical potential of the solvent in the gas phase is not affected. This means in turn that the equilibrium between the liquid and gas phase is established at another temperature for a solution ...
Why is the above formula less precise?
At high concentrations, the above formula is less precise due to nonideality of the solution. If the solute is also volatile, one of the key assumptions used in deriving the formula is not true, since it derived for solutions of non-volatile solutes in a volatile solvent.
What is the chemical potential of a gas?
Put in chemical potential terms, at the boiling point, the liquid phase and the gas (or vapor) phase have the same chemical potential (or vapor pressure) meaning that they are energetically equivalent. The chemical potential is dependent on the temperature, and at other temperatures either the liquid or the gas phase has a lower chemical potential ...
What does it mean when the boiling point of water is increased?
Boiling point elevation, like freezing point depression, is a colligative property of matter. This means it depends on the number of particles present in a solution and not on the type of particles or their mass.
Why does boiling point increase?
In a nutshell, boiling point increases because most of the solute particles remain in the liquid phase rather than enter the gas phase. In order for a liquid to boil, its vapor pressure needs to exceed ambient pressure, which is harder to achieve once you add a nonvolatile component.
What happens to the temperature of a solution when the concentration of particles increases?
In other words, increasing the concentration of the particles increases the temperature at which the solution boils.
Does salt increase boiling point?
What Boiling Point Elevation Is and How It Works. Adding salt to water increases its boiling point, but you'd have to add a lot of salt to make a difference when cooking. Liam Norris / Getty Images. Dr. Helmenstine holds a Ph.D. in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant.
What is the boiling point of a solution?
A solution is prepared when 1.20 g of a compound is dissolved in 20.0 g of benzene. The boiling point of the solution is 80.94 o C.
Is the boiling point of a solution higher than the boiling point of a solution?
The boiling points of solutions are all higher than that of the pure solvent. Difference between the boiling points of the pure solvent and the solution is proportional to the concentration of the solute particles:
What is the boiling point of a liquid?
By definition, the boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the surrounding pressure and liquid turns into vapor. The phenomenon of boiling is pressure dependent and hence the boiling point of a liquid may change depending upon the surrounding pressure. For example, due to the change in atmospheric pressure ...
What is the ebullioscopic constant for benzene?
Calculate the molecular weight of the compound. Ebullioscopic constant for benzene: 2.53 °C/m and boiling point of pure benzene: 80.1°C
Does adding a nonvolatile solute to a liquid increase the boiling point?
It has been experimentally proven that adding any form of non-volatile solute to a liquid increases its boiling point. The amount by which the boiling point changes is directly proportional to the amount of solute added.
What happens to the boiling point of a solvent?
The boiling point of the solvent above a solution changes as the concentration of the solute in the solution changes (but it does not depend on the identity of either the solvent or the solute(s) particles (kind, size or charge) in the solution). Non-Volatile Solutes.
Why is the boiling point of a solution greater than the boiling point of the solution?
The boiling point of a solution, then, will be greater than the boiling point of the pure solvent because the solution (which has a lowervapor pressure) will need to be heated to a highertemperature in order for the vapor pressure to become equal to the external pressure (i.e., the boiling point). The boiling point of the solvent ...
What is the nonvolatile solute that affects vapor pressure?
The figures below illustrate how the vapor pressure of water is affected by the addition of the non-volatile solute, NaCl.
Is the boiling point of a solution directly proportional to the concentration of the solute?
Experimentally, we know that the change in boiling point of the solvent above a solution from that of the pure solvent is directly proportional to the molal concentration of the solute:
Is the boiling point of NaCl greater than the boiling point of pure water?
the boiling point of the NaCl solution will be greater than the boiling point of pure water.

Why Does Boiling Point Elevation occur?
- The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its vapour pressure is equal to the pressure of its surrounding environment. Non-volatile substances do not readily undergo evaporation and have very low vapour pressures (assumed to be zero). When a non-volatile solu…
Boiling Point Elevation Formula
- The boiling point of a solution containing a non-volatile solute can be expressed as follows: Boiling point of solution = boiling point of pure solvent + boiling point elevation (ΔTb) The elevation in boiling point (ΔTb) is proportional to the concentration of the solute in the solution. It can be calculated via the following equation. ΔTb = i×Kb×m Where, 1. 1.1. 1.1.1. 1.1.1.1. i is the …
Solved Examples
- Example 1
Calculate the boiling point of a 3.5% solution (by weight) of sodium chloride in water. 1 kg of the given solution contains 0.035kg of NaCl and 0.965kg of H2O. Since the molar mass of NaCl is 58.5, the number of moles of NaCl in 1 kg of the solution is: (35g)/(58.5g.mol-1) = 0.598 moles T… - Example 2
10 grams of a non-volatile and non-dissociating solute is dissolved in 200 grams of benzene. The resulting solution boils at a temperature of 81.2oC. Find the molar mass of the solute. Let x = number of moles of solute. The boiling point of pure benzene is 80.1oC and it’s ebullioscopic co…
Overview
Boiling-point elevation describes the phenomenon that the boiling point of a liquid (a solvent) will be higher when another compound is added, meaning that a solution has a higher boiling point than a pure solvent. This happens whenever a non-volatile solute, such as a salt, is added to a pure solvent, such as water. The boiling point can be measured accurately using an ebullioscope.
The equation for calculations at dilute concentration
The extent of boiling-point elevation can be calculated by applying Clausius–Clapeyron relation and Raoult's law together with the assumption of the non-volatility of the solute. The result is that in dilute ideal solutions, the extent of boiling-point elevation is directly proportional to the molal concentration (amount of substance per mass) of the solution according to the equation:
ΔTb = Kb · bc
Explanation
The boiling point elevation is a colligative property, which means that it is dependent on the presence of dissolved particles and their number, but not their identity. It is an effect of the dilution of the solvent in the presence of a solute. It is a phenomenon that happens for all solutes in all solutions, even in ideal solutions, and does not depend on any specific solute–solvent interactions. T…
Uses
Together with the formula above, the boiling-point elevation can in principle be used to measure the degree of dissociation or the molar mass of the solute. This kind of measurement is called ebullioscopy (Latin-Greek "boiling-viewing"). However, since superheating is difficult to avoid, precise ΔTb measurements are difficult to carry out, which was partly overcome by the invention of the Beckmann thermometer. Furthermore, the cryoscopic constant that determines freezing-p…
See also
• Colligative properties
• Freezing point depression
• Dühring's rule
• List of boiling and freezing information of solvents