What is the brain stem and what does it do?
The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain that is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Each of the three components has its own unique structure and function. Together, they help to regulate breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and several other important functions.
What are three structures make up the brain stem?
Traditionally, the nuclei are divided into three columns:
- Raphe nuclei (medium column)
- Magnocellular red nucleus (medial zone)
- Parvocellular reticular nucleus (lateral zone)
What does the brain stem do in the nervous system?
The brain stem also plays an important role in the regulation of cardiac and respiratory function. It regulates the central nervous system (CNS) and is pivotal in maintaining consciousness and regulating the sleep cycle. Components of the Brainstem. The three components of the brainstem are the medulla oblongata, midbrain, and pons.
What are the main parts of the brain stem?
What are the three main regions of the brain stem quizlet?
- Medulla oblongata.
- Pons.
- Midbrain.
See more

What are the 3 parts of the brainstem and their functions?
AnatomyMidbrain: The top part of the brainstem is crucial for regulating eye movements.Pons: The middle portion of the brainstem coordinates facial movements, hearing and balance.Medulla oblongata: The bottom part of the brainstem helps regulate your breathing, heart rhythms, blood pressure and swallowing.
What cells are in the brain stem?
In the brain, we have neural stem cells. That means that these neural stem cells can give rise to neurons, astrocytes, or oligodendrocytes.
What is the brain stem called?
Medulla AKA Medulla Oblongata (myelencephalon)
What are the 4 parts of the brainstem?
In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata....BrainstemPartsMedulla, Pons, MidbrainIdentifiersLatintruncus encephaliMeSHD0019339 more rows
What are the 5 functions of the brain stem?
The brainstem has many basic functions, including regulation of heart rate, breathing, sleeping, and eating. It also plays a role in conduction. All information relayed from the body to the cerebrum and cerebellum and vice versa must traverse the brainstem.
What structure is not found in the brain stem?
The brainstem is the part of the brain formed by medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain. The choroid plexus is not part of the brainstem.
What is not part of the brain stem?
It contains the midbrain (mesencephalon), the pons and the medulla oblongata. Brainstem does not include cerebellum which is part of the hindbrain.
What is brain stem and its function?
The brainstem (brain stem) is the distal part of the brain that is made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Each of the three components has its own unique structure and function. Together, they help to regulate breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and several other important functions.
What happens if there is damage to the brain stem?
Damage to the brain stem can cause several different kinds of disorders. For example, if the brain stem has suffered a stroke, the patient may expe...
What is the main function of the brain stem?
The main function of the brain stem is to control vital involuntary functions. These include breathing, heart rate, digestion, and reflexive moveme...
What is in the brainstem?
The brain stem consists of three important structures: the midbrain, pons, and medulla. The midbrain is the uppermost segment of the brain stem, th...
Where does the brainstem begin?
The brainstem begins at the level of the cerebral peduncles (anteriorly) and the corpora quadrigemina or quadrigeminal plate (posteriorly) or tectal plate. It continues along a slight posteroinferior course until it ends at the decussation of the pyramids (at the level of the foramen magnum of the skull ).
What are the parts of the brain?
The brainstem is widest at its proximal end and becomes narrower toward the distal end. There are three parts of the brainstem: 1 the medulla oblongata is the narrowest and most distal part 2 the pons lies anteriorly and in the middle segment of the brainstem 3 and the midbrain is the widest and most superior segment.
What is the narrowest part of the brain?
The medulla ob longata or medulla is the narrowest and most caudal part of the brainstem. It is a funnel-like structure that extends from the decussation of the great pyramids, passes through the foramen magnum (which is the largest of all the foramina and fissures of the skull ), to the inferior pontine sulcus ( pontomedullary groove ). As the medulla continues upward in the posterior cranial fossa, it terminates at the inferior pontine sulcus (anteriorly) and the medullary striae of the fourth ventricle (posteriorly).
What is the division of the midbrain?
Most textbooks divide the midbrain into tectum and tegmentum, but the division is actually extended caudally into other brainstem segments. The tectum (Latin word for roof) and tegmentum (Latin word for covering) are used in relation to the developing central cavity of the neural tube .
Where does the medulla end?
As the medulla continues upward in the posterior cranial fossa, it terminates at the inferior pontine sulcus (anteriorly) and the medullary striae of the fourth ventricle (posteriorly). At the upper posterior surface of the medulla, there is the fourth ventricle, the floor of which is called rhomboid fossa.
What part of the brain is connected to the rest of the body?
Similarly, the majority of brain tissue is connected to the rest of the body via the brainstem . The brainstem is a stalk-like projection extending caudally from the base of the cerebrum.
Why is the brainstem important?
All of these brainstem functions are enabled because of its unique anatomy ; since the brainstem houses cranial nerve nuclei and is a passageway for many important neural pathways.
What is the brain stem?
Thus, the brain stem is the base of the whole brain. It consists of three essential components: the midbrain, pons, and medulla (also known as the medulla oblongata). The brain stem is responsible for several vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, sleep, and even consciousness.
What are the three structures that make up the brain stem?
There are three structures that make up the brain stem. They include the midbrain, pons, and medulla. Each of these structures have distinct and essential functions to maintain survival, such as breathing, heart rate, and other non-voluntary functions. Below are detailed descriptions of the aforementioned components.
What is the upper part of the brain?
The midbrain is the upper-most structure of the brain stem, and it is also the widest component. Cerebral peduncles make up the anterior part of the midbrain , connecting the brainstem to the thalamus and other important brain regions. The brain stem is further sectioned into the tectum, Latin for "roof" and the tegmentum, Latin for "covering". Four major bumps can be seen on the tectum, and they represent the superior and inferior colliculi, responsible for visual and auditory processing, respectively.
What is the medulla?
The medulla, also known as the medulla oblongata, is the narrowest and lowest structure within the brain stem. It contains two key divisions: the basilar portion, which contains the pyramids and olives, and the medullary tegmentum, which contains four cranial nerve nuclei and other important structures. The medulla is also where the spinal cord connects to the brain stem, and so it has important roles in transmitting signals between the two structures pertaining to heartbeat, respiration, and other vital functions.
Which nerve is responsible for sensation and movements associated with the head and neck?
Housing the cranial nerve nuclei, which are responsible for sensation and movements associated with the head and neck. Examples are listed above, whereby eight cranial nerves are divided between the pons and medulla.
Which part of the brain controls reflexes?
Several important reflexes are controlled by the medulla, such as vomiting, coughing, swallowing, and sneezing. For the aforementioned reasons, the medulla is also considered the most important segment of the brain stem due to it being necessary for vital functions.
Is a brain stem seizure rare?
Seizures: Brain stem seizures have been reported, although they are rare. These seizures typically follow strokes of the brain stem.
What is the brainstem?
Brainstem, area at the base of the brain that lies between the deep structures of the cerebral hemispheres and the cervical spinal cord and that serves a critical role in regulating certain involuntary actions of the body , including heartbeat and breathing. The brainstem is divided into three sections in humans: the midbrain (mesencephalon), ...
What are the three parts of the brain?
The brainstem is divided into three sections in humans: the midbrain (mesencephalon), the pons (metencephalon), and the medulla oblongata (myelencephalon). The brainstem houses many of the control centres for vital body functions, such as swallowing, breathing, and vasomotor control.
What are the causes of brainstem disorders?
Such disorders can be caused by trauma, tumours, strokes, infections, and demyelination ( multiple sclerosis ).
What are the unpaired structures that connect the cerebrum with the spinal cord?
The brainstemis made up of all the unpaired structures that connect the cerebrum with the spinal cord. Most rostral in the brainstemare structures often collectively referred to as the diencephalon. These structures are the epithalamus, the thalamus, the hypothalamus, and the subthalamus.…
Which part of the brain controls the senses?
The brainstem houses many of the control centres for vital body functions, such as swallowing, breathing, and vasomotor control. All of the cranial nervenuclei, except those associated with olfaction and vision, are located in the brainstem, providing motor and sensory function to structures of the cranium, including the facial muscles, tongue, pharynx, and larynx, as well as supplying the senses of taste, equilibrium, and hearing. The brainstem also has nuclei important for sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic functions. All efferent and afferent pathways between the cerebrumand cerebellumcourse through the brainstem , and many of them decussate, or cross, within this structure.
Which part of the brain is most rostral?
Most rostral in the brainstem are... Because of the important neural structures concentrated in this small portion of the nervous system, even very small lesions of the brainstem may have profound effects.
Where are the cranial nerves located?
All of the cranial nerve nuclei, except those associated with olfaction and vision, are located in the brainstem, providing motor and sensory function to structures of the cranium, including the facial muscles, tongue, pharynx, and larynx, as well as supplying the senses of taste, equilibrium, and hearing.
What is the structure of the brain stem?
Underneath them is the spinal cord, which can be observed as the root. It consists of three major divisions: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain.
Where Is The Location Of The Brain Stem?
Located just above the spinal cord, the brain stem connects the spinal cord to the cerebellum part of the brain. Its connection is made up of three pairs of nerve bundles known as cerebellar peduncles.
What is the oldest part of the brain?
The brain stem is the oldest, most primitive part of the human brain. This tube-shaped region is about three inches long and made up entirely out of nervous tissue. The brain stem forms a bridge between the brain and the spinal cord and plays the most vital role of all.
How many functions does the brain stem have?
To summarize, you can say that all the individual roles of the brain stem can be summed up into three main functions. These include:
Why is the brain stem important?
Why? The brain stem is a vital part for your brain and body to function. It controls your body’s breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. In addition, It also controls your consciousness and autonomic functions, which are absolute requirements to sustain life.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the movement of the eye?
This part of the brain stem is home to many vital nerves. These include the abducens nerve (eye movement), the facial nerve (facial expressions), and the trigeminal nerve (feeling in the face).
What are the three divisions of the medulla oblongata?
It consists of three major divisions: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
How many nerves are in the cranium?
Inside the cranium (the dome of the skull), there are 12 nerves, called cranial nerves:
Where is the spinal cord located?
The spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull. Supported by the vertebrae, the spinal cord carries messages to and from the brain and the rest of the body.
What is gray matter made of?
Gray matter is primarily composed of neuron somas (the round central cell bodies), and white matter is mostly made of axons (the long stems that connects neurons together) wrapped in myelin (a protective coating). The different composition of neuron parts is why the two appear as separate shades on certain scans.
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back.
Why are the two different shades of gray on a neuron scan?
Gray matter is primarily responsible for processing and interpreting information, while white matter transmits that information to other parts of the nervous system.
What Are the Main Parts of the Brain Stem?
The brain stem is made up of three parts: the midbrain, the pons and the medulla.
What are the parts of the brain?
There are three main parts of the brain: the cerebrum, cerebellum and the brain stem.
What Is the Brain and Why Does It Matter?
The brain is a three-pound organ that serves as headquarters for our bodies. Without it, we wouldn't be able to process information, move our limbs, or even breathe. Together with the spinal cord, brain structure and function helps control the central nervous system—the main part of two that make up the human nervous system. (The other part, the peripheral nervous system, is made up of nerves and neurons that connect the central nervous system to the body's limbs and organs.) The human nervous system is responsible for helping us think, breathe, move, react and feel.
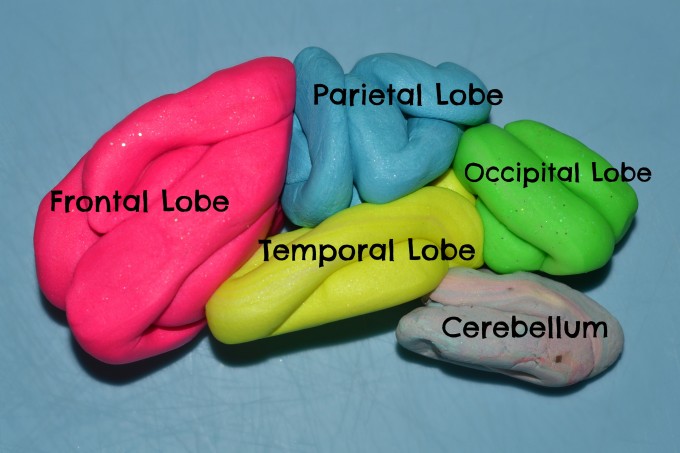
What Are the 4 Lobes of the Brain?
The cerebrum's left and right hemispheres are each divided into four lobes: the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes . The lobes generally handle different functions, but much like the hemispheres, the lobes don't function alone. The lobes are separated from each other by depressions in the cortex known as sulcus (or sulci) and are protected by the skull with bones named after their corresponding lobes.
What Are the Regions of the Brain and How Do They Fit Into the Brain Structure?
The three main parts of the brain are split amongst three regions developed during the embryonic period: the forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain. Together, these regions act as a useful map to understanding the various parts of the brain's structure and functions.
What Is the Cerebellum?
The cerebellum stands for "little brain" in Latin. It looks like a separate mini-brain behind and underneath the cerebrum (beneath the temporal and occipital lobes) and above the brain stem. The cerebellum (along with the brain stem) is considered evolutionarily to be the oldest part of the brain.
How many nuclei are there in the cerebellum?
Earlier, we learned how four nuclei are responsible for connecting the cerebellum to the body. To connect the cerebellum to the brain stem, the brain depends on nerve tracts called cerebellar peduncles. The cerebellar peduncles help process and analyze motor and sensory information, such as the position of our joints and limbs. There are six cerebellar peduncles (three for each hemisphere) with both white and gray matter. The six cerebellar peduncles are: superior (2), middle (2) and inferior (2).