
How to find braking distance?
Calculate the total braking distance. This formula is 1/2 the initial velocity in feet per second multiplied by the time required to stop, which is 0.5 x 102.7 x 5.135 = 263.68. The calculated thinking distance is 2 x 102.7 = 205.4. Add the two numbers together. 469.08 feet is the total braking distance. To estimate stopping time, pick a fixed ...
How do you calculate distance formula?
distance = speed × time. time = distance ÷ speed. To calculate one of the variables (speed, distance or time) we need the other two. For example, to find the time taken to make a journey, we ...
What is the braking distance at 50 mph?
The braking distance at 50mph is 38m - almost twice as long as a cricket pitch. The braking distance at 70mph is a huge 75m, which is about 9 London buses. What can affect braking distances?
How to measure stopping distance?
and measure from this point. To physically measure the stopping distance, we use a Bosch Laser rangefinder placed on the starting line. This is aimed at a plate which is then placed on the vehicle mounted laser sensor. As a third method we use our RTK GPS & GLONASS VBOX system and share the same antenna as the primary brake testing VBOX.
How do you calculate braking and stopping distance?
To determine how far the vehicle will travel while braking, use the formula of 1/2 the initial velocity multiplied by the time required to stop.
How do you calculate braking distance GCSE?
0:293:47GCSE Science Revision Physics "Vehicle Stopping Distance"YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipMake a decision and then move their foot to the brake. The braking distance is the distance the carMoreMake a decision and then move their foot to the brake. The braking distance is the distance the car travels from when the driver applies the brakes to when the car stops.
What is braking distance in physics?
The braking distance is the distance taken to stop once the brakes are applied. The braking distance increases if: the car's brakes or tyres are in a poor condition.
What is braking distance in driving?
Braking distance is the distance the vehicle travels from the point at which the driver applies the brake until the vehicle actually comes to a complete stop.
How do you calculate braking force GCSE physics?
Braking forces - HigherK E = 1 2 × m × v 2.This means that:F × d = 1 2 × m × v 2.F × d = 1 2 × m × v 2.
How do u calculate distance?
To solve for distance use the formula for distance d = st, or distance equals speed times time. Rate and speed are similar since they both represent some distance per unit time like miles per hour or kilometers per hour. If rate r is the same as speed s, r = s = d/t.
What is braking distance quizlet?
Braking distance. The approximate distance traveled before coming to a complete stop when the brakes are applied in a vehicle moving at a specific speed.
Does braking distance depend on mass?
So mass does not affect stopping distance in a very simple model like two blocks of different masses. However, in the case of the truck and the car, friction from the ground contributes only a small proportion of the stopping force. Most of it is provided by air resistance, friction within the system, etc.
How do you calculate stopping distance for theory test?
All you need to do is multiply the speed by intervals of 0.5, starting with 2. That'll give you the stopping distance in feet, which is acceptable for the theory test. For example… There are 3.3 feet in a metre – so divide the distance in feet by 3.3 to get the stopping distance in metres.
What is the braking distance at 30mph?
44 feet 45 feetDriver Care - Know Your Stopping DistanceSpeedPerception/Reaction DistanceBraking Distance30 mph44 feet45 feet40 mph59 feet80 feet50 mph73 feet125 feet60 mph88 feet180 feet2 more rows
How do you calculate stopping distance in physics?
Stopping distance = Thinking distance + Braking distance Stopping distance = 30 + 152 = 182 mStopping distance = Thinking distance + Braking distance.Stopping distance = 30 + 152 = 182 m.
How is speed related to braking distance?
Braking distance depends on how fast a vehicle is travelling before the brakes are applied, and is proportional to the square of the initial speed. This means that even small increases in speed mean significantly longer braking distances.
How do you calculate stopping distance for theory test?
The factors are easy to remember - just start at 2 for 20mph and add 0.5 for each 10 mph increase in speed. Example: Question: What is the overall stopping distance at 50mph? Answer: Factor for 50mph is 3.5 and so overall stopping distance at 50mph is 50 x 3.5 = 175 feet.
What is the stopping distance at 70 mph?
103 feet 245 feetDriver Care - Know Your Stopping DistanceSpeedPerception/Reaction DistanceBraking Distance50 mph73 feet125 feet60 mph88 feet180 feet70 mph103 feet245 feet80mph117 feet320 feet2 more rows
How do car brakes work GCSE?
When a force is applied to the brakes of a vehicle, there is work done by the friction between the brakes and the wheel. This reduces the kinetic energy of the vehicle, slowing it down and causing the temperature of the brakes to increase.
How is braking acceleration calculated?
2:585:54Braking Distance - Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFeet per second squared you square that divided by the acceleration. You solve for the acceleration.MoreFeet per second squared you square that divided by the acceleration. You solve for the acceleration.
What is the main force behind short stopping distances?
Tyres. The friction of the tyres on the road, as the tyres are being slowed down by the brakes, is the main force behind short stopping distances. If too much force is applied to the brake discs by the brake callipers this will cause the tyres to overcome their limits of friction and the wheels will lock. The type and condition of the road, ...
What is electronic brakeforce distribution?
Other electronic safety aids such as electronic brakeforce distribution ensure that braking power is dynamically assigned to each wheel in varying amounts as the relative grip of the surface changes. This means that a vehicle could have two wheels in gravel on the side of the road and two wheels on the tarmac and still brake in a straight line ...
What is the braking distance?
The braking distance, also called the stopping distance, is the distance a vehicle covers from the time of the full application of its brakes until it has stopped moving. This is often given as a 100-0kph distance, e.g. 56.2m, and is measured on dry pavement. Occasionally the time taken to stop is given, too.
What happens when you have wet tyres?
If the conditions are wet or damp, there will be less grip and the stopping distance will be further. If the tyres are under- or over-inflated this will affect the stopping distance, as will the quality of the brake pads and the brake balance. Prior to anti-lock brakes, a driver would need to be skilled to get the maximum braking potential out ...
How do brakes slow down a car?
Brakes slow a car down using friction. Calculations of stopping distance assume that each wheel’s brakes are strong enough to lock the wheel and won’t suffer any fade over the distance of the braking exercise. Different types of brakes have different levels of efficiency and consistency. Most cars have disc brakes.
What type of brakes do most cars have?
Different types of brakes have different levels of efficiency and consistency. Most cars have disc brakes. This image shows the front discs of an FPV GT with cross-drilled and slotted brake rotors – a sports-oriented brake package.
What causes rolling resistance?
Rolling resistance. Rolling resistance is caused by gravity acting on the tyre which causes it to deform where it meets the road. This uses energy – i.e. some of the forwards energy is translated into the energy required to deform the tyre. This is a minor factor.
How does speed affect stopping distance?
How Speed Effects Braking Distance. The faster you drive the longer it takes to stop. This means speeding increases your stopping distance and force of impact. If you double your speed then your stopping distance and force of impact are 4 times greater. YouTube.
What does speeding up your car do to your stopping distance?
The faster you drive the longer it takes to stop. This means speeding increases your stopping distance and force of impact.
Why is speeding dangerous?
The increases in braking distance and force of impact are one of the reasons that speeding is so dangerous.
How many feet does total stopping distance add?
Perception and Reaction time each add 55 feet (110 feet total) to your total stopping distance.
What are the factors that affect braking distance?
Two factors that effect your braking distance are Perception and Reaction times . Perception is when you see a hazard and recognize that you have to stop and Reaction is how long it takes you to hit the brakes. These two factors each add a delay to the braking process.
What to do if playback doesn't begin?
If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
What is proper braking?
Proper braking is a critical part of being a safe driver. Learning a few things about using your brakes will make you a safer driver and help you pass the Permit Test to get your Florida Learners Permit.
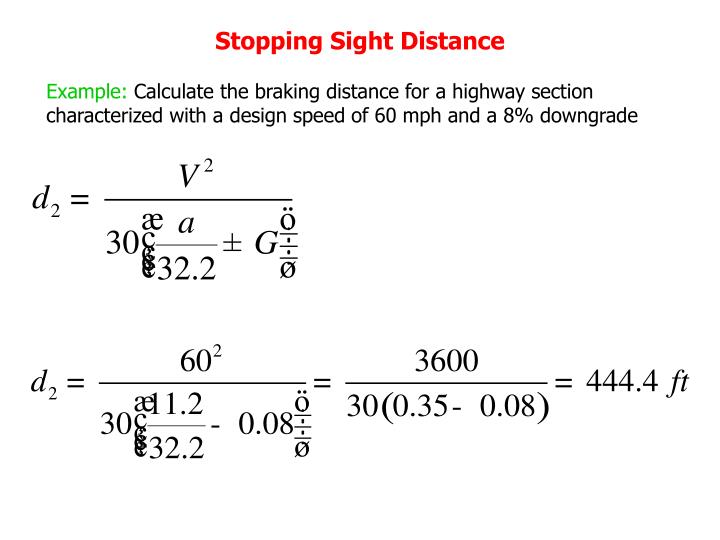
What is stopping sight distance ?
Stopping sight distance (SSD) is the minimum sight distance available on a highway at any spot having sufficient length to enable the driver to stop a vehicle traveling at design speed, safely without collision with any other obstruction.
How to calculate breaking distance?
The Breaking Distance formula is defined as distance travelled by the vehicle after applying the brakes and untill the vehicles stops is calculated using breaking_distance = ( Velocity ^2)/ (2* [g] * Coefficient of Friction). To calculate Breaking Distance, you need Velocity (v) and Coefficient of Friction (μ). With our tool, you need to enter the respective value for Velocity and Coefficient of Friction and hit the calculate button. You can also select the units (if any) for Input (s) and the Output as well.
What is velocity in physics?
Velocity - Velocity, in physics, is a vector quantity (it has both magnitude and direction), and is the time rate of change of position (of an object). (Measured in Meter per Second)
What is stopping distance x?
The stopping distance x is then the sum of the reaction distance and the braking distance:
What happens when the velocity is zero?
Force leads to acceleration, and acceleration changes the velocity. When the velocity is zero, the object has stopped. We can use physics and kinematics equations to find out how fast something comes to a stop, but that time will never be zero. This means that the object still travels between the time the force is applied and it comes to a stop. The distance it covers is that time is called the stopping distance.
How does friction slow an object?
In this free body diagram, friction is slowing the object by working opposite the direction of motion.
What is the only source of friction?
In that case, the only source of friction is between the wheels and the road. Friction can be thought of as a force that acts against the direction of an object's motion, so friction is the outside force that stops the car, according to Newton's First Law. The force of friction ( {eq}F_ {mu} {/eq}) is determined by the coefficient of friction ( {eq}mu {/eq}), which is a value that describes the "roughness" or the amount of friction between two surfaces. The coefficient is multiplied by the Normal Force, which on a flat surface is the same magnitude as the weight of the car.
What is the difference between a and g?
Remember that a and g point in different directions. g points straight down, and a , points in the direction against the vehicle's motion, since the vehicle is braking. Since a applies directly to the motion of the vehicle, it can be inserted directly into a kinematics equation, like this one:
How to relate force to acceleration?
None of the kinematics equations use force as a variable, but we can relate force to acceleration. Start by solving F = ma for acceleration.
What does a mean in physics?
a = acceleration. If the car is slowing down, this will be a negative value.
What is Reaction Distance?
Reaction distance is the distance your vehicle travels while you react. So the time it takes from the moment you see a hazard until you actually start braking. Reaction times vary from driver to driver.
What is stopping distance?
The stopping distance = reaction distance + braking distance. So the distance it takes for your vehicle to come to a complete stop from the moment you spot a hazard.
How to prevent rear end collisions?
An important part of preventing a rear-end collision is knowing your stopping distance and how quickly your vehicle can come to a complete stop. Create a safety margin that gives sufficient distance between the vehicle in front so there is time to react and safely stop. In order to make a complete stop before a collision occurs, you must mentally calculate the stopping distance .
How much does speed increase stopping distance?
Small increases in speed also affect stopping distance. Increasing your speed just 10 mph from 50 mph to 60 mph increases the total stopping distance by up to 40%.
What is reaction distance?
The reaction distance is the distance you travel from the point of detecting a hazard until you begin braking or swerving.
What is stopping distance?
The stopping distance is the reaction distance + braking distance. First we calculate the reaction distance:
Does it matter if you get 10 metres with one method and 12.5 metres with another?
So if the alternatives are 10, 20, 40, 60, it does not matter if you get 10 metres with one method and 12.5 metres with another – both are obviously closest to 10, which is thus the right answer.
What is the distance traveled when you hit the brake?
The distance traveled from the moment you first hit the brake is called the braking distance . The stopping distance, on the other hand, is the total distance traveled during the perception and reaction time summed with the braking distance.
How to calculate the stopping distance?
In the book "A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets", AASHTO gives the formula for calculating the stopping distance. This formula is commonly used in road design for establishing the minimum stopping sight distance required on a given road. With correct parameters, it's a perfect equation for an accurate calculation of the stopping distance of your car.
What is the AASHTO formula?
The AASHTO formula is as follows: G is the grade (slope) of the road, expressed as a decimal. It is positive for an uphill grade and negative for a road going downhill; f is the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road .
How fast can you hit the brakes?
In reality, many drivers are able to hit the brake much faster. You can use the following values as a rule of thumb: 1 second - a keen and alert driver; 1.5 seconds - an average driver; 2 seconds - a driver who is tired, or an elderly person; 2.5 seconds - the worst case scenario.
What is the grade of a road?
G is the grade (slope) of the road, expressed as a decimal. It is positive for an uphill grade and negative for a road going downhill;
How many meters does a car travel before it comes to a stop?
Your car will travel 260 meters before it comes to a stop.
What is the delay between the moment you notice the danger ahead and the instant in which you actually start to decele?
This delay is called the reaction time . The car is still moving with the same speed.
