What are the early signs of frozen shoulder?
The most common frozen shoulder symptoms
- Shoulder pain. The most obvious and clear sign of frozen shoulder syndrome is pain, particularly in the musculoskeletal tissues and nerves in the shoulder area.
- Associated neck pain. Because they’re so closely connected, neck pain often comes with shoulder pain. ...
- Stiffness. ...
- Mobility issues. ...
- Increased pain at night. ...
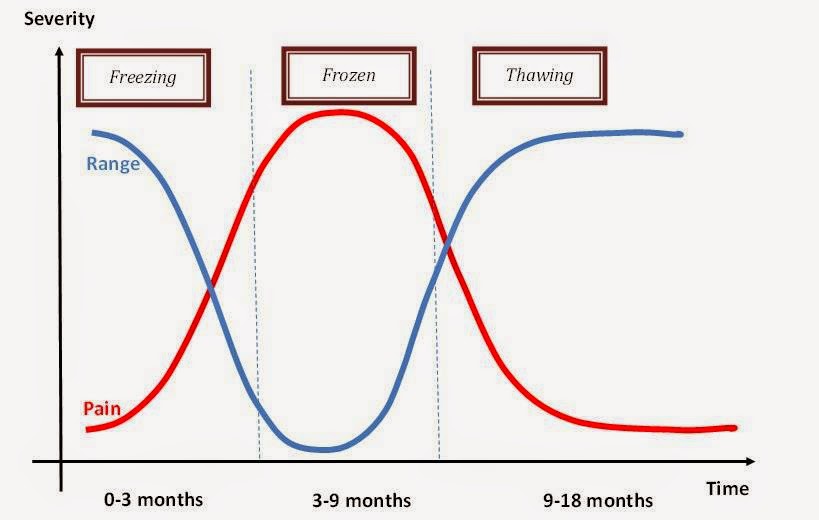
What are the phases of frozen shoulder?
- Freezing (2 to 9 months): Early
- Frozen (4 to 12 months): Developed
- Thawing (12 to 42 months): Developed
What does frozen shoulder feel like?
What Does Frozen Shoulder Feel Like? The first sign of frozen shoulder starts with pain and discomfort in the shoulder joint. Then, you will start to notice the shoulder joint seems stiff and more difficult to move without making the pain and discomfort worse.
What is the treatment for a frozen shoulder joint?
Treatment
- Medications. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others), can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with frozen shoulder.
- Therapy. A physical therapist can teach you range-of-motion exercises to help recover as much mobility in your shoulder as possible.
- Surgical and other procedures. ...
Does frozen shoulder follow capsular pattern?
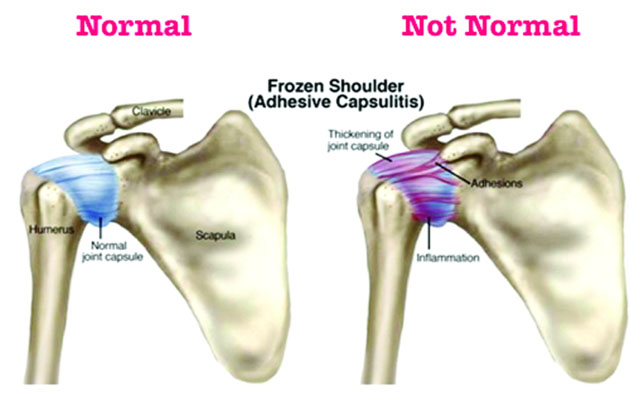
Adhesive Capsulitis, also known as “frozen shoulder”, is a common shoulder condition characterized by pain and decreased range of motion in a capsular pattern (external rotation is more limited than abduction, which is more limited than internal rotation).
Which capsule is involved in frozen shoulder?
What is frozen shoulder? Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, is a painful condition in which the movement of the shoulder becomes limited. Frozen shoulder occurs when the strong connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint (called the shoulder joint capsule) become thick, stiff, and inflamed.
What is a capsular pattern of restriction in the shoulder?
A capsular pattern of restriction is a limitation of pain and movement in a joint specific ratio, which is usually present with arthritis, or following prolonged immobilization.
What happens to the capsule in frozen shoulder?
The shoulder joint is enclosed in a capsule of connective tissue. Frozen shoulder occurs when this capsule thickens and tightens around the shoulder joint, restricting its movement. It's unclear why this happens to some people.
What is the sequence of 3 stages of frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder occurs in three phases: freezing (painful), frozen (adhesive) and thawing, and is often self-limiting.
What is the difference between frozen shoulder and adhesive capsulitis?
Frozen shoulder is also known as adhesive capsulitis. It is characterized by pain and stiffness in the shoulder and sometimes in the upper arm. Symptoms will get progressively worse but with proper treatment can eventually recover.
What does a capsular pattern indicate?
A capsular pattern is a joint-specific pattern of restriction. of passive movements. It indicates the existence of a contraction of the joint capsule.
What does capsular mean?
Definition of capsular 1 : of, relating to, or resembling a capsule. 2 : capsulated.
What is cyriax capsular pattern?
Cyriax (Dr. James Cyriax, 1905–1985, Orthopaedic Surgeon in England) referred to this evolutional sequence of movement pattern typical for the given joint “capsular pattern”. In the shoulder joint it begins with limitation of external rotation, then abduction and ends with limitation of internal rotation.
What is the pathophysiology of frozen shoulder?
The pathology of frozen shoulder includes a chronic inflammatory response with fibroblastic proliferation which may be immunomodulated. Primary frozen shoulder is a common, severely debilitating condition with a prevalence of between 2% and 5%. It is frequently difficult to manage.
Which movements are restricted in frozen shoulder?
People with frozen shoulder have limitations in both active and passive range of motion (picture 1). They also tend to have the most trouble rotating their arm or shoulder outward, away from their body, and putting the affected arm behind their back.
What is shoulder joint capsule?
The joint capsule surrounds the shoulder joint. It is a fluid filled sac that lubricates the joint. The ligaments tighten in certain arm positions, holding the ball in the socket.
Which tablet is best for shoulder pain?
Taking ibuprofen or acetaminophen (such as Tylenol) may help reduce inflammation and pain.
What vitamins are good for frozen shoulder?
What are the Best Supplements for Frozen Shoulder? Some over-the-counter supplements like turmeric, Omega-3 fatty acids, and glucosamine and chondroitin may help relieve joint pain and reduce inflammation.
What is a shoulder capsule release?
What is capsular release for frozen shoulder? Capsular release is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis). This is a condition that develops when the capsule of connective tissues surrounding the shoulder thickens and tightens, causing pain and restricted movement.
What is a frozen shoulder caused by?
Although many shoulder diseases involve pain and loss of motion, frozen shoulder is most often caused by inflammation (swelling, pain and irritation) of the tissues surrounding the joint. The tissue that envelops the joint and holds it together is called the capsule.
What is frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis or shoulder contracture, is a condition where the synovial membrane – a soft tissue that forms a...
What are the symptoms of frozen shoulder?
Early symptoms include unexpected shoulder pain and difficulty raising the arm above the head or across the body. Usually only one shoulder is affe...
What is the main cause of frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder is an inflammatory process that usually appears unexpectedly with no known cause. There are, however, certain factors that put some...
Who is prone to frozen shoulder?
People who have thyroid disease, diabetes, an autoimmune disease, and/or injury, stroke, heart attack, or prolonged immobilization are also at high...
How is frozen shoulder diagnosed?
Your doctor will take your medical history, have you describe your symptoms and conduct a physical exam, including testing your range of motion. Th...
What is the treatment for frozen shoulder?
The goal of treatment is to reduce the underlying inflammation and prevent your shoulder from becoming stiff. Nonsurgical treatment is the first op...
What is the surgery for frozen shoulder?
If nonsurgical treatments are not providing relief for someone with adhesive capsulitis, two surgical options are available: manipulation under ane...
How long is recovery from frozen shoulder surgery?
After surgery, patients are usually in a sling for comfort for a week or two, but aggressive range- of motion physical therapy starts almost immedi...
How successful is surgery for frozen shoulder?
When conservative, nonsurgical treatments fail, surgery can be very successful at restoring full range of motion.
What is frozen shoulder?from members.physio-pedia.com
Frozen shoulder or adhesive capsulitis is a common source of shoulder pain. It occurs in about 2% to 5% of the population and commonly presents in 40 to 60-year-olds. It is more prevalent in women (70%). (Sheridan et al 2006)
What exercises can be used to regain shoulder strength?from physioworks.com.au
Gentle and specific shoulder joint mobilisation and stretches, muscle release techniques, acupuncture, dry needling and exercises to regain your range and strength are used for a prompt return to function. Care must be taken not to introduce any exercises that are too aggressive.
How long does it take for adhesive capsulitis to worsen?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Patients with adhesive capsulitis usually present with progressively worsening shoulder pain over weeks to months, followed by significant limitation in shoulder motion. Disease progression is described in 3 clinical phases:
How long does it take to recover from shoulder surgery?from physioworks.com.au
This combination of treatment can improve your stiffness by up to 80% in most cases. Post-capsular release surgery can see most patients return to work within 6 to 12 weeks.
What is the best treatment for shoulder injury?from physioworks.com.au
Researchers have discovered that managing your shoulder injury with physiotherapy is usually successful. Typically, you have two options: non-operative or a surgical approach. Your condition will dictate which option is best for you at this time. Non-operative care is conservative rehabilitation.
What is the pathophysiology of adhesive capsulitis?from ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
The most commonly accepted hypothesis states that inflammation initially occurs within the joint capsule and synovial fluid. The inflammation is followed by reactive fibrosis and adhesions of the synovial lining of the joint. The initial inflammation of the capsule leads to pain, and the capsular fibrosis and adhesions lead to a decreased range of motion.
How long does frozen shoulder last?from physioworks.com.au
Frozen shoulder is a condition that resolves over an 18 to 24 month period in most cases. 60% to 80% of frozen shoulder patients will respond favourably to non-surgical treatment.
What is frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis or shoulder contracture, is a condition where the synovial membrane – a soft tissue that forms a protective capsule around the shoulder joint – swells, thickens and contracts. Scar tissue forms, leaving less room for the upper arm to move around. This causes pain and restricts movement in the shoulder. The cause of this condition is unknown, but it often occurs in people who have other inflammatory disorders. Other people develop frozen shoulder after an injury or period of immobilization, such as after a traumatic fall or surgery.
What is the treatment for frozen shoulder?
The goal of treatment is to reduce the underlying inflammation and prevent your shoulder from becoming stiff. Nonsurgical treatment is the first option and works well with an early diagnosis. Surgical treatment is a second option that is appropriate for severe cases or where nonsurgical treatment is unsuccessful.
What is the main cause of frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder is an inflammatory process that usually appears unexpectedly with no known cause. There are, however, certain factors that put some people at greater risk for getting frozen shoulder.
How long is recovery from frozen shoulder surgery?
After surgery, patients are usually in a sling for comfort for a week or two, but aggressive range- of motion physical therapy starts almost immediately so that the scar tissue doesn’t reform. During the first six weeks after surgery, there is a strong focus on regaining range of motion. Therapy will then progress to strengthening with a gradual return to sport by about three months after surgery, assuming range of motion and strength are near normal.
How successful is surgery for frozen shoulder?
When conservative, nonsurgical treatments fail, surgery can be very successful at restoring full range of motion.
What is the procedure for adhesive capsulitis?
If nonsurgical treatments are not providing relief for someone with adhesive capsulitis, two surgical options are available: manipulation under anesthesia or a shoulder arthroscopy procedure called arthroscopic capsular release.
How to tell if you have a shoulder injury?
Usually only one shoulder is affected, but about one-third of patients experience symptoms in both. Early symptoms include: 1 Pain in the shoulder, especially unexpected pain, when no known injury is present. 2 Difficulty lifting one’s arm above the head. 3 Difficulty extending one’s arm across the body or reaching behind the back.
What is the capsular pattern of the spine?
A capsular pattern is the reproducible limitation of joint movements when the joint capsule is the limiting structure.
What is capsular pattern of elbow?
The capsular pattern is flexion more limited than extension, and the close packed position is extension with the forearm in supination.
What is the capsular pattern of the subtalar joint?
The closed packed position of the subtalar joint is supination. The capsular pattern has a limited ROM defined in varus and valgus.
How do you diagnose frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder is a “clinical diagnosis” which means that your physiotherapist can diagnose it during your initial assessment.
What is capsular pattern?
A capsular pattern is when your joint is restricted into lateral rotation (when your elbow is tucked into your side and you move your hand away from you), abduction (moving your arm out to the side), and medial rotation ( putting your hand behind your back). Most patients suffering from frozen shoulder have difficulty putting on a bra, ...
How to contact a physiotherapist for frozen shoulder?
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, have been diagnosed with frozen shoulder and would like to see one of our expert physiotherapists you can call 0207 482 3875 or email [email protected]. If you would like to speak to a specialist before booking, then please send us an email with your details and we will call you back.
How long does a frozen shoulder last?
Your pain will gradually increase, particularly at night and your shoulder becomes restricted. This stage can last 6 weeks to 9 months. Stage 2: ‘Frozen or stiff stage’.
What age does a frozen shoulder hurt?
It is a common cause of shoulder pain particularly in those aged between 40 and 60 and is more common in women and those with diabetes.
How long does shoulder pain last?
Your pain begins to improve but you notice your shoulder is stiff. It often lasts between 6 and 9 months. Stage 3: ‘Unfreezing or thawing stage’. Your shoulder movement becomes easier, the pain is significantly reduced, and you are able to return to normal activities. This stage can last between 6 months and 2 years.
Why does my shoulder freeze?
The exact cause of frozen shoulder is unknown. Sometimes you can develop the condition following a fall, a stroke or after a shoulder operation. However, most of the time it develops for no apparent reason.
How to examine a capsular pattern?
How to examine Capsular Pattern? With passive movement, a full ROM must be carried out in all possible directions. A mid-range movement will not elicit potential findings. While evaluating the end feel, the examiner must look at the pattern of limitation or restriction.
What is capsular pattern of restriction?
A capsular pattern of restriction is a limitation of pain and movement in a joint specific ratio, which is usually present with arthritis, or following prolonged immobilization.
How does frozen shoulder happen?
Frozen Shoulder – also called Adhesive Capsulitis and Periarthritis – is fairly common. In fact, it happens to about 5% of the population. ( 5)
How to prevent frozen shoulder?
Keys to preventing frozen shoulder include exercise and maintaining an appropriate sugar level.
How long does frozen shoulder pain last?
Also, a noticeable progressive loss of shoulder range of motion is evident. May last from 4 – 12 months.
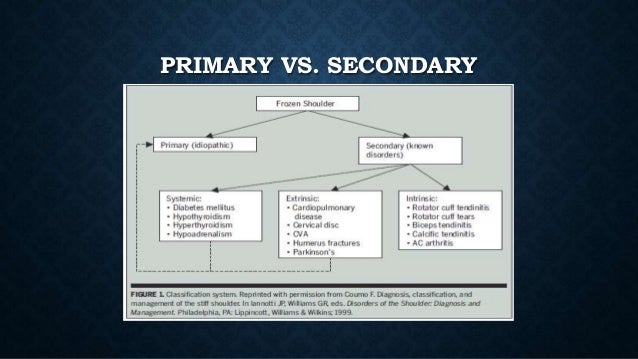
What is primary shoulder pain?
Primary (Idiopathic). This refers to the spontaneous onset of shoulder pain with no known origin. Symptoms worsen and progress to stiffness and limitation of function.
What happens if your shoulder is frozen?
With Frozen Shoulder, synovial inflammation damages the lining of the joint capsule. This results in a thick fibrotic band of tissues.
What is the best way to improve shoulder range of motion?
Joint mobilization and stretching to improve shoulder range of motion
What tests are done to check for shoulder pain?
Your doctor may also request imaging tests for a more detailed look inside your shoulder. These include X-rays, MRI, or Arthrography.
What is frozen shoulder?
Adhesive Capsulitis, also known as “frozen shoulder”, is a common shoulder condition characterized by pain and decreased range of motion in a capsular pattern ( external rotation is more limited than abduction, which is more limited than internal rotation ). 1 Adhesive capsulitis is predominantly an idiopathic condition and has an increased prevalence in patients with diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism. 2,3 Traditionally, adhesive capsulitis goes through three stages: freezing, frozen, and thawing and can last anywhere between 1-2 years. 4 It has been found that the most effective treatment depends on t he specificity of the treatment based on the phase to optimize outcome and avoid adverse effects. 5,6,7 The purposes of this case report were (1) to examine the effects of glenohumeral mobilizations on adhesive capsulitis and (2) to identify the stages of frozen shoulder in order to apply the most effective treatment option and understand which techniques to avoid.
What is appropriate treatment for frozen shoulder?
12 Palliative care includes patient education, decreasing sympathetic output via myofascial and TENS, and gentle shoulder stretching. In the frozen stage, a suprascapular nerve block, distention hydroplasty, and gentle stretching of the shoulder are appropriate interventions. 13,14 And in the thawing stage, a manipulation under anesthesia, arthroscopic release and surgical release are all appropriate interventions. 15
What age is adhesive capsulitis most common?
Adhesive capsulitis is most common in females (70%) between the ages of 40 and 60. It is more commonly observed in the dominant versus nondominant limb and is more prevalent in diabetic patients. 8 The self-limiting affliction of unknown etiology transitions through three distinct stages: freezing, frozen and thawing. 8
What are the positive results of adhesive capsulitis?
If the stage is identified correctly and the appropriate interventions are used, positive results can occur, which include decreased pain, improved mobility and function.
How to restore glenohumeral joint mobility?
To restore glenohumeral joint mobility, a variety of manual techniques were used. Elevation through flexion was one of the first movements to improve throughout treatment, which was done through an inferior glide with emphasis on the coracohumeral ligament (Figure 1) and a posterior glide with emphasis on the anterior-superior capsule (Figure 2) . The restoration of abduction was completed with inferior glides with emphasis on the anterior-inferior (Figure 3) and posterior-inferior (Figure 4) joint capsules. 10
Who is the author of The Natural History of the Frozen Shoulder Syndrome?
Reeves B. The natural history of the frozen shoulder syndrome. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology. 1975;14:193-6.
What is freezing stage?
During the freezing stage, the patient experiences gradually increasing painful limitations in glenohumeral motion. With the examination of passive motion during this stage, the examiner provokes the patient’s symptoms before the end-range motion is reached, suggesting a painful, empty end-feel. The patient demonstrates a large limitation of elevation through flexion and displays a capsular pattern of motion restriction. The capsular pattern of the glenohumeral joint is external rotation most limited followed by abduction and internal rotation. 1