What organelle causes lysosomal storage disease?
The majority of the lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are caused by mutations in the genes encoding a lysosomal enzyme. These monogenic disorders involve forty different acid hydrolases in the lysosomes. Genes with a specific chromosomal locus encode them. Many types of mutations can produce a defective enzyme.
What are lysosomal storage diseases give example?
What Are Lysosomal Storage Diseases and Disorders? Gaucher disease is one of the most common lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs). LSDs are inherited disorders resulting from a lack of specific enzymes that break down certain lipids (fats) or carbohydrates (sugars) in the body cells.
What enzyme causes lysosomal storage disease?
Tay-Sachs disease: This is caused by a lack of the enzyme hexosaminidases A (Hex-A). This enzyme breaks down a fatty substance called GM2 ganglioside in brain cells. Without it, the fat builds up in nerve cells and damages them. Babies with Tay-Sachs grow normally for the first few months of life.
What are the symptoms of lysosomal storage disease?
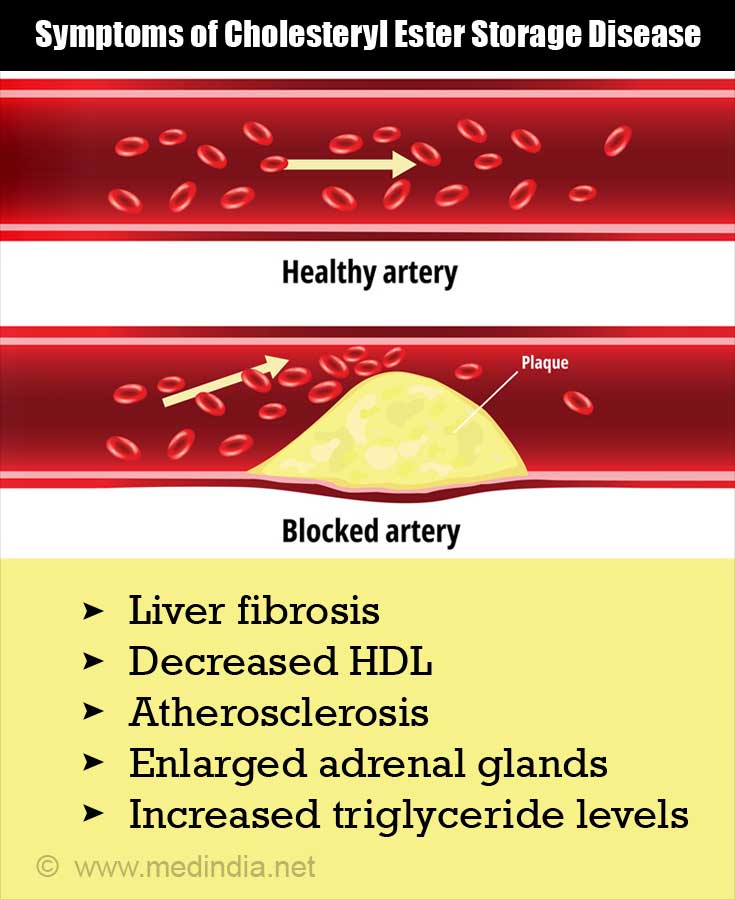
Symptoms of Lysosomal Storage DiseasesDelay in intellectual and physical development.Seizures.Facial and other bone deformities.Joint stiffness and pain.Difficulty breathing.Problems with vision and hearing.Anemia, nosebleeds, and easy bleeding or bruising.Swollen abdomen due to enlarged spleen or liver.More items...
How is lysosomal storage disease diagnosed?
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) cause a toxic buildup that damages your body's cells and organs. Researchers have found more than 70 types of LSDs. Providers usually diagnose LSDs during pregnancy or infancy. Diagnosis includes blood and urine tests.
How is lysosomal storage disease treated?
The main treatment methods include Enzyme replacement therapy, Bone marrow transplantation, Substrate reduction therapy, use of molecular chaperones, and Gene therapy.
How many lysosomal storage disorders are there?
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are a group of over 70 diseases that are characterized by lysosomal dysfunction, most of which are inherited as autosomal recessive traits. These disorders are individually rare but collectively affect 1 in 5,000 live births.
What are lysosomal enzymes?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes, such as glycosidases, proteases and sulfatases. Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), are transported to the Golgi apparatus, and are tagged for lysosomes by the addition of mannose-6-phosphate label.
What organelle is responsible for Tay-Sachs disease?
Tay-Sachs is an autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations in both alleles of a gene (HEXA) on chromosome 15. HEXA codes for the alpha subunit of the enzyme β-hexosaminidase A. This enzyme is found in lysosomes, organelles that break down large molecules for recycling by the cell.
What happens if a cell lacks lysosomes?
In the absence of lysosomes or if it goes non-functional, cells tend to accumulate all the wastes, worn out particles within it and become toxic, which otherwise would be eliminated by lysosomes. Consequently, the cell wouldn't function properly and die ultimately.
What are the storage diseases?
Storage diseases are a heterogeneous group of inherited defects in metabolism characterized by accumulation of storage material within the cell (lysosomes). From: Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease (Sixth Edition), 2017.
Is Gaucher disease a lysosomal storage disease?
All three forms of Gaucher disease are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Gaucher disease is categorized as a lysosomal storage disorder (LSD). Lysosomes are the major digestive units in cells. Enzymes within lysosomes break down or “digest” nutrients, including certain complex carbohydrates and fats.
What are lysosomes?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in every eukaryotic cell. They are widely known as terminal catabolic stations that rid cells of waste products and scavenge metabolic building blocks that sustain essential biosynthetic reactions during starvation.
What are the different types of glycogen storage disease?
What are the types of GSD?type 0 (Lewis' disease) – liver.type I (von Gierke's disease) Type Ia – liver, kidneys, intestines; Type Ib – liver, kidneys, intestines, blood cells.type II (Pompe's disease) – muscles, heart, liver, nervous system, blood vessels.More items...
What is lysosomal storage disease?
Lysosomal storage diseases are inherited metabolic diseases that are characterized by an abnormal build-up of various toxic materials in the body’s cells as a result of enzyme deficiencies . There are nearly 50 of these disorders altogether, and they may affect different parts of the body, including the skeleton, brain, skin, heart, ...
Why is it important to detect lysosomal storage disease early?
Early detection of lysosomal storage diseases, whether before birth or as soon as possible afterward, is important because when therapies are available, either for the disease itself or for associated symptoms, they may significantly limit the long-term course and impact of the disease .
What is Batten disease?
Batten Disease: Batten disease is the juvenile form of a group of progressive neurological disorders known as neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCL). It is characterized by the accumulation of a fatty substance (lipopigment) in the brain, as well as in tissue that does not contain nerve cells.
Why are storage diseases called storage diseases?
Each cell has hundreds of lysosomes that degrade complex cellular components such as proteins (substrates) into simpler components. When this process does not take place, the substrate begins to accumulate in the cells. That is why these diseases are called “storage diseases”.
When does Sandhoff disease start?
GM2-Gangliosidosis Type II (Sandhoff Disease): The first symptoms of Sandhoff disease typically begin between the ages of three and six months. The disease is clinically indistinguishable from GM2-Gangliosidosis Type I.
Is lysosomal storage disorder genetic?
The genes associated with many, but not all, lysosomal storage disorders have been identified. To learn more about the genetic locations associated with specific diseases, search the Rare Disease Database for reports on those topics.
Continuing Education Activity
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are inborn errors of metabolism characterized by the accumulation of substrates in excess in various organs' cells due to the defective functioning of lysosomes. They cause dysfunction of those organs where they accumulate and contribute to great morbidity and mortality.
Introduction
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are diseases caused by defects in single-genes. Enzyme defects cause nearly seventy percent of the LSDs, and the rest are defects in enzyme activator or associated proteins. A gene on a particular chromosome locus transcribes a particular enzyme—improper enzyme-coding results in inactive enzymes.
Etiology
The majority of the lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are caused by mutations in the genes encoding a lysosomal enzyme. These monogenic disorders involve forty different acid hydrolases in the lysosomes. Genes with a specific chromosomal locus encode them.
Epidemiology
When considered singly, lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) are rare, some very rare, with only a few patients reported in the literature. They occur worldwide; the most common among them are Fabry, Gaucher, Metachromatic leucodystrophy, and Pompe. When viewed as a group, the LSDs are much more common.
Pathophysiology
Apart from the recycling of substrates, lysosomes are involved in other crucial functions to cellular homeostasis.
History and Physical
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) invariably affect multiple organs. Even within the same disease, the clinical picture can be heterogeneous. Some LSDs present prenatally or very early after birth. Others present in childhood or adulthood. Infant phenotypes have much more severe disease than adults.
Evaluation
Clinical suspicion for a particular lysosomal storage disease (LSD) precedes the screening tests. Many LSDs have similar features between themselves and, with other non-lysosomal inborn errors of metabolism and diligence is required.
How to diagnose lysosomal storage disorder?
There are a few diagnoses carried out in a specialized laboratory. Tissue biopsies are also used for diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Disorder in the patient by analyzing the sample of tissue or cells collected from the patient’s body for analysis. Skin fibroblasts test, blood test, amniotic fluid test and urine test are also used for testing the presence of this syndrome in a patient’s samples.
What are the symptoms of lysosomal storage disease?
Symptoms Of Lysosomal Storage Diseases 1 Skin Rashes 2 Burning pains in hand and feet 3 Lung dysfunction 4 Damage to Central Nervous System 5 Muscle weakness 6 Heart failure in infants 7 Mental and physical deterioration 8 Respiratory problems 9 Kidney failure 10 Pain and numbness found in hand and feet 11 Anemia 12 Stiff limbs and unable to walk 13 Tiredness 14 Depression 15 Heart failure followed by strokes and death at an early age.
What is a disease caused by the lack of enzymes in the lysosomes of a cell?
A disease which is caused by the lack of enzymes in the Lysosomes of a cell is called as a Lysosomal storage disease . The enzyme present in the lysosomes play an important role in eliminating all unwanted substances present in a cell of the human body.
Why do lysosomes have a lack of enzymes?
The enzymes present in the Lysosomes helps in digesting food particles, dead cells, old cells and engulfing disease-causing microorganisms including protozoa, fungi, bacteria also viruses.
What is the function of lysosomes?
The main function of Lysosomes is to protect the cell from being digested as it surrounds the cell membrane.
Why do macromolecules get piled up?
These macromolecules get piled up because of the lack of enzymes in the Lysosome. These disorders can affect many parts of the body including the circulatory system, the central nervous system, digestive system, skin, liver, eyes, bones, spleen, kidneys, etc. There are more than 50 different types of Lysosomal storage diseases.
How to treat lysosomal storage disease?
In addition, umbilical cord blood transplantation is being performed at specialized centers for a number of these diseases. In addition, substrate reduction therapy , a method used to decrease the production of storage material, is currently being evaluated for some of these diseases. Furthermore, chaperone therapy, a technique used to stabilize the defective enzymes produced by patients, is being examined for certain of these disorders. The experimental technique of gene therapy may offer cures in the future.
How do lysosomal disorders originate?
Although each disorder results from different gene mutations that translate into a deficiency in enzyme activity, they all share a common biochemical characteristic – all lysosomal disorders originate from an abnormal accumulation of substances inside the lysosome.
What is the incidence of lysosomal storage disorder?
Individually, LSDs occur with incidences of less than 1:100,000; however, as a group, the incidence is about 1:5,000 – 1:10,000. Most of these disorders are autosomal recessively inherited such as Niemann–Pick disease, type C, but a few are X-linked recessively inherited, such as Fabry disease and Hunter syndrome (MPS II).
What is the function of lysosomes?
Lysosomes are sacs of enzymes within cells that digest large molecules and pass the fragments on to other parts of the cell for recycling. This process requires several critical enzymes. If one of these enzymes is defective due to a mutation, the large molecules accumulate within the cell, eventually killing it.
What was the first LSD?
Tay–Sachs disease was the first of these disorders to be described, in 1881, followed by Gaucher disease in 1882. In the late 1950s and early 1960s, de Duve and colleagues, using cell fractionation techniques, cytological studies, and biochemical analyses, identified and characterized the lysosome as a cellular organelle responsible for intracellular digestion and recycling of macromolecules. This was the scientific breakthrough that would lead to the understanding of the physiological basis of the LSDs. Pompe disease was the first disease to be identified as an LSD in 1963, with L. Hers reporting the cause as a deficiency of α-glucosidase. Hers also suggested that other diseases, such as the mucopolysaccharidosis, might be due to enzyme deficiencies.
What Are Lysosomal Storage Diseases and Disorders?
Gaucher disease is one of the most common lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs). LSDs are inherited disorders resulting from a lack of specific enzymes that break down certain lipids (fats) or carbohydrates (sugars) in the body cells.
How many types of lysosomal storage diseases are there?
The scientific community has identified more than 40 types of lysosomal storage diseases, and that number keeps growing. Although the different types of LSDs are rare individually, taken together they affect roughly 1 in 7,700 births, making them a relatively common health problem.
What happens if you don't have enough enzymes?
If a person does not have enough of one of these enzymes, the body cannot break down the fat or carbohydrate targeted by enzymes for recycling. These fats or sugars accumulate in cell lysosomes where enzymes are active, disrupting normal function and causing lysosomal storage disorders.
What is Tay-Sachs disease?
Tay-Sachs disease: This disorder causes severe and fatal mental and physical deterioration, with both an early-onset and a late-onset form.
What is Pompe disease?
Glycogen storage disease II (Pompe disease): Depending on the specific subtype, Pompe disease may cause heart enlargement and heart failure in infants. It may also cause respiratory problems and severe muscle weakness in adults.
What is a Lysosomal Storage Disease?
Lysosomes are sacs inside cells, containing enzymes that metabolize (break down) excess sugars and lipids (fats) into substances that cells can use. When lysosomes don’t work properly, these sugars and fats build up in the cell instead of being used or excreted.
Can lysosomal storage cause death?
Lysosomal storage diseases are rare, but can lead to death if untreated. The excess substances built up in your child’s cells can cause a wide range of problems throughout the body, affecting organs including the: Brain. Spleen. Liver.
What is lysosomal storage disorder?
Lysosomal storage disorders are inherited inborn errors of metabolism caused by defects in the genes that encode lysosomal enzymes, leading to enzyme deficiency. 1 These enzymes break down and help to recycle macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins, and are pivotal for cellular communication, response to infection and homeostasis.1,2 Lysosomal storage disorders affect the chemical composition of the lysosomal storage material and can be divided into three broad groups: sphingolipidoses, mucopolysaccharidoses and glycoproteinoses.3
What is Fabry disease?
Fabry disease is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by variants in the GLA gene and is a progressive, life-threatening, multisystemic condition.
What are Lysosomal Storage Diseases?
LSDs are caused by an accumulation of certain substances (called substrates) in a part of the cell called the lysosome. Lysosomes use proteins called enzymes to help break down or recycle many different substrates in the human body. If one of these enzymes does not work properly or is missing altogether, substrates are not broken down and accumulate in the lysosome. Over time, the excess storage of substrates damages the affected organ or body part, and LSD symptoms will occur.
How to diagnose LSD?
It's our mission to: 1 Make the correct diagnosis with minimal delay. 2 Start treatment (if available) as soon as possible. 3 Provide comprehensive care under one roof. 4 Provide genetic counseling and testing to people at risk to be a carrier for an LSD and patients affected with one. 5 Communicate well with our patients and each other. 6 Optimize care and make it easier for patients to manage their disease and to navigate the healthcare system, 7 Provide access to ongoing research in the LSD field.

Symptoms
Classification
Signs and symptoms
Prognosis
Clinical significance
Cause
- In each case, lysosomal storage diseases are caused by an inborn error of metabolism that results in the absence or deficiency of an enzyme, leading to the inappropriate storage of material in various cells of the body. Most lysosomal storage disorders are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. Recessive genetic disorders occur when an individ...
Genetics
Epidemiology
Diagnosis
Treatment
Synthesis
Medical uses
Pathophysiology
Resources