Symptoms
Noonan syndrome is a genetic condition that can cause differences in facial features and results in short stature. Patients with this syndrome frequently have cardiac issues such as irregular heart rhythms and thickening of the heart muscle, and they may also experience developmental delays.
Causes
Noonan syndrome prognosis. Noonan syndrome can range from being very mild to severe and life-threatening. The majority of patients with Noonan syndrome lead normal lives. Prognosis is largely dependent on the type and severity of cardiac disease, which may occur in 50% to 80% of cases.
Prevention
There's no cure for Noonan syndrome, but medical care can help with almost every symptom. Medicines and surgery can help heart problems. Medicines or blood transfusions can treat bleeding. Growth hormone can help speed up slow growth. Surgery can correct undescended testicles.
Complications
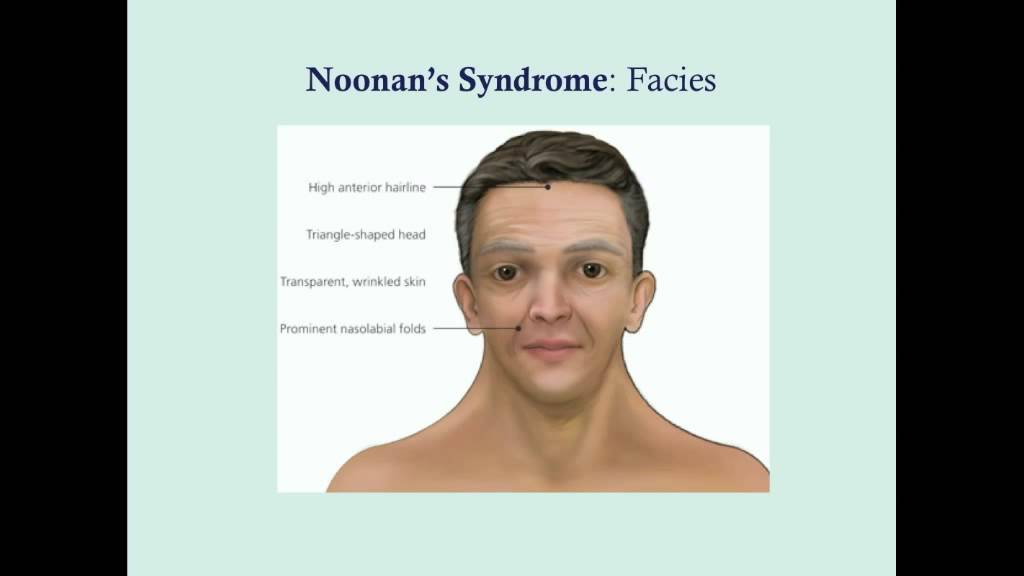
Jacqueline Noonan was practicing as a pediatric cardiologist at the University of Iowa when she noticed that children with a rare type of heart defect, valvular pulmonary stenosis, often had a characteristic physical appearance, with short stature, webbed neck, wide spaced eyes, and low-set ears. Both boys and girls were affected.
How does Noonan syndrome affect the body?
What is the prognosis for Noonan syndrome?
Does Noonan syndrome have a cure?
What famous person has Noonan syndrome?
See more
How does Noonan syndrome occur?
Noonan syndrome is caused by a genetic mutation and is acquired when a child inherits a copy of an affected gene from a parent (dominant inheritance). It can also occur as a spontaneous mutation, meaning there's no family history involved.
Who is at risk for Noonan syndrome?
Noonan syndrome is a condition that some babies are born with. It causes changes in the face and chest, usually includes heart problems, and slightly raises a child's risk of blood cancer (leukemia). Noonan syndrome is a pretty common condition, affecting 1 in 1,000–2,500 babies.
How is Noonan inherited?
Noonan syndrome is inherited in families in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that a person who has Noonan syndrome has one copy of an altered gene that causes the disorder. In about one-third to two-thirds of families one of the parents also has Noonan syndrome.
Is Noonan syndrome diagnosed at birth?
The condition is present from before birth, although milder cases may not be diagnosed until a child gets older. The most common features of Noonan syndrome are: unusual facial features, such as a broad forehead, drooping eyelids and a wider-than-usual distance between the eyes. short stature (restricted growth)
Who carries the gene for Noonan syndrome?
Noonan syndrome is caused by a faulty gene, which is usually inherited from one of the child's parents.
Is Noonan syndrome like autism?
Few reports have described the psychiatric co-morbidity of Noonan syndrome. While mental retardation is a common feature of Noonan syndrome, the diagnosis of autism using operational criteria has not been reported. In this paper, the authors describe the association of Noonan syndrome with autism.
Does Noonan syndrome affect males or females?
Noonan syndrome affects both males and females, and there is a normal chromosomal makeup (karyotype). Only females are affected by Turner syndrome, which is characterized by abnormalities affecting the X chromosome.
What gene mutation causes Noonan syndrome?
Expand Section. Mutations in multiple genes can cause Noonan syndrome. Mutations in the PTPN11 gene cause about half of all cases. SOS1 gene mutations cause an additional 10 to 15 percent, and RAF1 and RIT1 genes each account for about 5 percent of cases.
What causes wide set eyes in babies?
In normal development, the eye sockets (orbits) develop laterally and rotate to their normal midline position. In orbital hypertelorism, the eye sockets fail to rotate into their normal position, resulting in wide-set eyes with extra bone between the eyes.
Can you live a normal life with Noonan syndrome?
Life expectancy with Noonan syndrome is generally normal, but there may be health problems that need to be addressed with medical or surgical attention. Bleeding can result in blood loss, which can cause symptoms of fatigue.
How long can you live with Noonan syndrome?
It is one of the most common non-chromosomal disorders in children with congenital heart disease, with an estimated prevalence worldwide of 1 in 1000-2500. The average age at diagnosis is nine years, and life expectancy is likely normal if serious cardiac defects are absent.
Can Noonan syndrome be treated?
There's no single treatment for Noonan syndrome, but it's possible to treat many aspects of the condition. Your child may initially need quite a lot of treatment and support to help manage the various problems they have. However, they'll typically need much less care as they get older.
What causes noonan syndrome?
Noonan syndrome is caused by a faulty gene, which is usually inherited from one of the child's parents. There's no evidence to suggest the genetic fault is caused by environmental factors, such as diet or exposure to radiation.
How is noonan syndrome inherited?
How Noonan syndrome is inherited. In around 30-75% of cases, Noonan syndrome is inherited in what's known as an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that only one parent has to carry a copy of one of the faulty genes to pass it on, and each child they have will have a 50% chance of being born with Noonan syndrome.
What is the risk of having another child with Noonan syndrome?
If one of you does carry a faulty gene or has been diagnosed with Noonan syndrome, there's a 50% risk of each further child you have being born with the condition.
Is noonan syndrome genetic?
In around 1 in 5 cases, no specific genetic fault can be found. The symptoms of Noonan syndrome are generally similar, no matter which gene is affected. However, the faulty PTPN11 gene is commonly associated with pulmonary stenosis (a narrowed heart valve) and the faulty RAF1 gene is more often associated with cardiomyopathy ...
What is noonan syndrome?
Listen. Noonan syndrome is a genetic disorder that causes abnormal development of multiple parts of the body. Features of Noonan syndrome may include a distinctive facial appearance, short stature, a broad or webbed neck, congenital heart defects, bleeding problems, problems with bone structure (skeletal malformations), and developmental delay.
How many chances do children with noonan syndrome have?
Each child of a person with Noonan syndrome has a 50% (1 in 2) chance to inherit the condition. In other cases, the change in one of the genes that can cause Noonan syndrome is new and not found in either parent.
What is the long term outcome of noonan syndrome?
Studies generally suggest that long-term outcome depends largely on the presence and severity of congenital heart defects. Death in affected people has been frequently associated with the presence of complex left ventricular disease. [7] Studies have indicated that people with Noonan syndrome have a 3-fold higher mortality rate than those in the general population. [8] [9]
What are the conditions that overlap with the RAS pathway?
Other conditions in this group include: [4] neurofibromatosis type 1. LEOPARD syndrome, also called Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines. Costello syndrome.
What is Project OrphanAnesthesia?
Project OrphanAnesthesia is a project whose aim is to create peer-reviewed, readily accessible guidelines for patients with rare diseases and for the anesthesiologists caring for them. The project is a collaborative effort of the German Society of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care, Orphanet, the European Society of Pediatric Anesthesia, anesthetists and rare disease experts with the aim to contribute to patient safety.
Does noonan syndrome need special help?
Some children with Noonan syndrome may need special help in school, including for example, an individualized educational program (IEP). [3] Treatment for bleeding problems depends on the cause. [3] . Growth hormone (GH) therapy can increase the rate at which a child with Noonan syndrome grows in most cases.
Is noonan syndrome inherited?
It is typically inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, but many cases are due to a new mutation and are not inherited from either parent. Treatment depends on the symptoms present in each person. [3] Noonan syndrome belongs to a group of related conditions called the RASopathies.
How is noonan syndrome inherited?
Noonan syndrome is inherited in families in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that a person who has Noonan syndrome has one copy of an altered gene that causes the disorder. In about one-third to two-thirds of families one of the parents also has Noonan syndrome.
What are the genes associated with noonan syndrome?
Individuals who have Noonan syndrome have normal chromosome studies. Four genes - PTPN11, SOS1, RADF1 and KRAS - are the only genes that are known to be associated with Noonan syndrome. Approximately 50 percent of individuals with Noonan syndrome have mutations in the PTPN11 gene.
What percent of people with noonan syndrome have mutations in the RAF1 gene?
Mutations in the RAF1 gene account for between 10 and 15 percent of Noonan syndrome cases. About 5 percent of people with Noonan syndrome have mutations in the KRAS gene and usually have a more severe or atypical form of the disorder.
What are the symptoms of noonan syndrome?
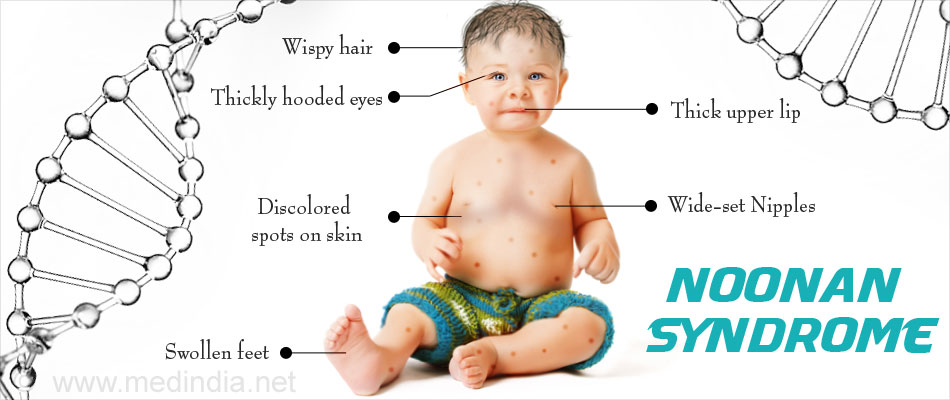
Symptoms of Noonan syndrome may include the following: 1 A characteristic facial appearance. 2 Short stature. 3 Heart defect present at birth (congenital heart defect). 4 A broad or webbed neck. 5 Minor eye problems such as strabismus in up to 95 percent of individuals. 6 Bleeding problems such as a history of abnormal bleeding or bruising. 7 An unusual chest shape with widely-spaced and low set nipples. 8 Developmental delay of varying degrees, but usually mild. 9 In males, undescended testes (cryptorchidism).
How many people have noonan syndrome?
Noonan syndrome is present in about 1 in 1,000 to 1 in 2,500 people. What is Noonan Syndrome? Noonan syndrome is a disorder that involves unusual facial characteristics, short stature, heart defects present at birth, bleeding problems, developmental delays, and malformations of the bones of the rib cage. Noonan syndrome is caused by changes in one ...
How many chances do you have to pass on the Noonan gene?
The parent who has Noonan syndrome has a 1 in 2 (50 percent) chance to pass on the altered gene to a child who will be affected; and a 1 in 2 (50 percent) chance to pass on the normal version of the gene to a child who will not have Noonan syndrome.
What genes are involved in noonan syndrome?
The cause of Noonan syndrome in 15 to 20 percent of people with this disorder is unknown. The PTPN11, SOS1, RAF1, and RIT1 genes all provide instructions for making proteins that are important in the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway, which is needed for cell division and growth (proliferation), the process by which cells mature to carry out specific ...
What are the symptoms of noonan syndrome?
It is characterized by mildly unusual facial features, short stature, heart defects, bleeding problems, skeletal malformations, and many other signs and symptoms. People with Noonan syndrome have distinctive facial features such as a deep groove in the area between the nose and mouth ( philtrum ), widely spaced eyes that are usually pale blue ...
What percentage of cases are caused by mutations in the PTPN11 gene?
Mutations in the PTPN11 gene cause about half of all cases. SOS1 gene mutations cause an additional 10 to 15 percent, and RAF1 and RIT1 genes each account for about 5 percent of cases. Mutations in other genes each account for a small number of cases.
What is the condition that causes a narrowing of the valve that controls blood flow from the heart to the lungs
Some affected people may also have an abnormal side-to-side curvature of the spine ( scoliosis ). Most people with Noonan syndrome have some form of critical congenital heart disease. The most common heart defect in these individuals is a narrowing of the valve that controls blood flow from the heart to the lungs (pulmonary valve stenosis).
Why is the protein in Noonan syndrome active longer than normal?
Many of the mutations in the genes associated with Noonan syndrome cause the resulting protein to be turned on (active) longer than normal, rather than promptly switching on and off in response to cell signals.
What is the name of the condition where the neck is short?
Many children with Noonan syndrome have a short neck, and both children and adults may have excess neck skin (also called webbing) and a low hairline at the back of the neck. Between 50 and 70 percent of individuals with Noonan syndrome have short stature. At birth, they are usually a normal length and weight, but growth slows over time.
Why do babies have puffy hands?
Infants with Noonan syndrome may be born with puffy hands and feet caused by a buildup of fluid ( lymphedema ), which can go away on its own. Older individuals can also develop lymphedema, usually in the ankles and lower legs.
Overview
Noonan syndrome is a genetic (inherited) condition that causes symptoms and problems in several parts of the body, including the head, heart and limbs (hands and feet).
Symptoms and Causes
Noonan syndrome occurs because of certain mutations (changes) on specific genes inherited from a person’s parents, including the genes PTPN11, SOS1, RAF1, RIT1, and KRAS. Approximately 50 percent of people with Noonan syndrome have a parent who also has the condition.
Diagnosis and Tests
A doctor can diagnose Noonan syndrome with a physical examination and a review of the symptoms. In some newborn babies, Noonan syndrome is often suspected by the baby’s appearance.
Management and Treatment
Doctors treat patients according to their specific symptoms and their causes. For instance, many people living with Noonan syndrome receive medications, surgery and supportive therapies like compression garments for lymphedema. Treatment may involve healthcare providers from several specialties working together to manage the symptoms.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent Noonan syndrome. Genetic mutations, either inherited from parents or occurring spontaneously, cause Noonan syndrome.
Living With
If you or your child is diagnosed with Noonan syndrome, you may have many questions, including:
What causes noonan syndrome?
Causes. Noonan syndrome is caused by alterations (also known as mutations) at specific areas within a person's genetic information. Each of us has a large amount of genetic information that is organized into smaller segments known as genes. Genes provide the necessary instructions that our cells need to perform different functions within our bodies.
What is the name of the condition that is related to noonan syndrome?
One condition related to Noonan syndrome is known as LEOPARD syndrome (Lentigines, ECG abnormalities, Ocular hypertelorism, Pulmonary stenosis, Abnormalities of genitalia, Retardation of growth, Deafness). LEOPARD syndrome shows clinical overlap with Noonan syndrome, but patients also have findings on the skin, such as café au lait patches and lentigines (small colored spots on the skin with clearly-defined edges) and over time some develop hearing loss. Mutations in PTPN11 and RAF1 are identified in approximately 93 percent of individuals with LEOPARD syndrome .
What is CFC syndrome?
CFC syndrome is caused by gene mutations that are similar to those observed in Noonan syndrome, including alterations in the KRAS, BRAF, and MEK1 genes. People with CFC syndrome have similar facial, skeletal, and cardiac features as people with Noonan syndrome. However, people with CFC syndrome tend to have:
What genes are involved in noonan syndrome?
The cause of Noonan syndrome in the remaining 25-30 percent of people with the disorder is unknown. The PTPN11, SOS1, KRAS, NRAS, RAF1 , BRAF, or MEK1 genes produce proteins that regulate key signaling pathways within cells required for the proper formation of tissues during development.
How to confirm Noonan syndrome?
To confirm — on a molecular level — that an individual has Noonan syndrome, he or she can undergo the process of genetic testing. Genetic testing usually involves the collection of a sample of blood, from which the white blood cells are isolated and used as a source of DNA.
Is noonan syndrome a tumor?
The exact magnitude of the tumor risk in individuals with Noonan syndrome is not well described, and may vary depending on the specific gene mutation. However, the overall cancer risk for individuals with Noonan syndrome or LEOPARD syndrome appears to be relatively low.
Does noonan syndrome change with age?
The facial features of Noonan syndrome may change considerably with age. The characteristic appearance is often most evident in the newborn period and childhood and more subtle in adults. In addition to these clinical findings, coagulation (blood clotting) defects may be present in patients with Noonan syndrome.
What is noonan syndrome?
General Discussion. Noonan syndrome is a genetic disorder that is typically evident at birth (congenital). The disorder is characterized by a wide spectrum of symptoms and physical features that vary greatly in range and severity. In many affected individuals, associated abnormalities include a distinctive facial appearance; a broad or webbed neck;
How many people are affected by noonan syndrome?
Affected Populations. Noonan syndrome appears to affect more males than females and is thought to affect approximately one in 1,000 to one in 2,500 people. However, other reports indicate that the disorder may affect more than one in 1,000 newborns in the general population.
How tall is a person with Noonan syndrome?
Average adult height is approximately five feet, four inches (162.5 cm) in males with Noonan syndrome and approximately five feet (152.7 cm) in females with the disorder. Individuals with the disorder typically reach their adult height by the end of the second decade of life. Growth patterns are influenced by the molecular genetic cause of NS.
What are the abnormalities of the nose?
Affected infants may also have a small jaw (micrognathia); crowding of the lower teeth, low-set, posteriorly rotated external ears (pinnae); and/or distinctive abnormalities of the nose including a depressed nasal root, a wide base, and a rounded (bulbous) tip.
When is noonan surgery performed?
Such surgery is typically performed between 12 and 24 months of age to help prevent the risk of associated infertility. In addition, appropriate supportive measures may be used in affected individuals with lymphedema. Early intervention may be important in helping children with Noonan syndrome reach their potential.
When is noonan syndrome diagnosed?
However, in many cases, Noonan syndrome is diagnosed at birth or early infancy based upon a thorough clinical evaluation, identification of characteristic physical findings, and a variety of specialized tests.
Does noonan syndrome cause weight gain?
Some infants with Noonan syndrome may experience feeding problems and fail to grow and gain weight at the expected rate (failure to thrive). In addition, children with the disorder tend to be short for their age, and approximately 20 percent experience delayed bone maturation.