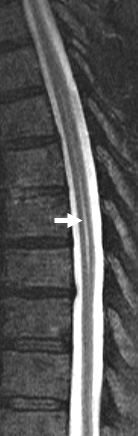
What causes the cervical enlargement of the spinal cord?
The most common causes of spinal cord injuries in the United States are:
- Motor vehicle accidents. Auto and motorcycle accidents are the leading cause of spinal cord injuries, accounting for almost half of new spinal cord injuries each year.
- Falls. A spinal cord injury after age 65 is most often caused by a fall.
- Acts of violence. ...
- Sports and recreation injuries. ...
- Diseases. ...
What is the treatment for cervical?
- Short-term neck immobilization with a hard or soft cervical collar and/or cervical pillow
- Physical therapy with exercise and gradual mobilization
- Avoidance of activities that cause pain
- Cervical traction
How do cervical and lumbar enlargements work?
Cervical Enlargement
- Ascending and Descending Pathways in the Spinal Cord. ...
- Non-Mammalian Vertebrates. ...
- The Biological Basis for Mind Body Interactions. ...
- Radiologic Anatomy of the Spine. ...
- Patient Evaluation and Organ System Examination. ...
- The Somatosensory System. ...
- Cytoarchitecture of the Spinal Cord. ...
- Functional Organization of the Spinal Cord. ...
What is the center of enlargement?
straight lines from each point on the image, through its corresponding point on the object, and continuing for a little further. The point where all the lines cross is the Centre of enlargement. NOTE; The center enlargement of the enlargement can either be between the image and the object or after the object/image.
What is the function of cervical enlargement?
The cervical enlargement of the spinal cord is the source of the spinal nerves that contribute to the brachial plexus and supply the upper limbs.
What is the meaning of cervical enlargement?
cer·vi·cal en·large·ment. [TA] a spindle-shaped swelling of the spinal cord extending from the third cervical to the second thoracic vertebra, with maximum thickness opposite the fifth or sixth cervical vertebra, consequential to the innervation of the upper limb.
Where is the cervical enlargement located?
The cervical enlargement is the more pronounced, and corresponds with the attachments of the large nerves which supply the upper limbs. It extends from about the third cervical to the second thoracic vertebra, its maximum circumference (about 38 mm.)
Why is the cervical enlargement bigger?
The reason behind the enlargement of the cervical region is because of the increased neural input and output to the upper limbs. An analogous region in the lower limbs occurs at the lumbar enlargement.
What are the symptoms of cervical pain?
SymptomsPain in the neck that may travel to your arms or shoulders.Headaches.A grinding feeling when you move your neck.Weakness in your arms and legs.Numbness in your shoulders, arms, or hands.Stiffness in the neck.Trouble keeping your balance.Trouble controlling your bladder or bowels.
What is cervical problem?
Cervical spondylosis is a general term for age-related wear and tear affecting the spinal disks in your neck. As the disks dehydrate and shrink, signs of osteoarthritis develop, including bony projections along the edges of bones (bone spurs). Cervical spondylosis is very common and worsens with age.
Can cervical spondylosis affect the brain?
Key points: • This study suggests that patients with cervical spondylosis may present anatomical and functional adaptive changes in the brain. Cervical spondylosis may lead to white matter damage, gray matter volume loss, and functional adaptive changes in the sensorimotor cortex.
What is the significance of cervical and lumbar enlargements?
The cervical and lumbar regions of the spinal cord show a larger diameter compared to the rest of the regions. The cervical enlargement and lumbar enlargement represent an increased amount of neurons in the gray matter and axons in the white matter that serve the upper limbs and lower limbs, respectively.
What could happen if there is damage to C1 C5?
Without immediate medical attention, C1 spinal cord injuries are typically fatal. The C3-C5 spinal nerves innervate the diaphragm, and because messages from the brain may not be able to get past the C1 level, individuals may not be able to breathe.
What is cervical vertebra?
Your cervical spine consists of the first seven vertebrae in your spine. It provides support for the weight of your head, surrounds and protects your spinal cord, and allows for a wide range of head motions.
What are the cervical nerves?
The cervical nerves consist of eight paired nerves that are a part of the peripheral nervous system. They emerge from the spinal cord through the seven cervical vertebrae. The cervical vertebrae are the spinal bones located just below the skull.
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
Seven bonesSeven bones in the neck—the cervical spine. 12 bones in the chest—the thoracic spine. Five bones in the lower back—the lumbar spine.
What is the circumference of a cervical enlargement?
It extends from about the fifth cervical to the first thoracic vertebra, its maximum circumference (about 38 mm.) being on a level with the attachment of the sixth pair of cervical nerves . The reason behind the enlargement ...
Why is the cervical region enlarged?
The reason behind the enlargement of the cervical region is because of the increased neural input and output to the upper limbs. An analogous region in the lower limbs occurs at the lumbar enlargement .
Which enlargement occupies the segmental levels C5 to T1?
It is one of two symmetrical enlargements which occupy the segments of the limb plexuses, the other being the lumbosacral enlargement for the lumbar and sacral plexuses. Hence it occupies, in the spinal cord, the segmental levels C5 to T1. As the spinal cord is shorter in length than the vertebral column, it extends from ...
What is the greatest circumference of the spinal cord?
As the spinal cord is shorter in length than the vertebral column, it extends from the C3 to T1/T2 vertebral levels, its greatest circumference (approximately 38 mm ) at the C6 level. The cervical enlargement is a result of the increased volume of motor cells in the ventral horns of the grey matter.
What is the source of the spinal nerves that contribute to the brachial plexus and supply the upper
Cervical enlargement. The cervical enlargement of the spinal cord is the source of the spinal nerves that contribute to the brachial plexus and supply the upper limbs.
Why are spinal canals so large?
The spinal canals are relatively large in order to house the cervical enlargement of the spinal cord. The spinal canal is triangular with the apex of the triangle posterior. The canal decreases in size from vertebra C1 through vertebra C3 and has a fairly uniform dimension from C3 through C7. C7 is a transitional vertebra, whose spinous process is longer and thicker and has a more inferior tilt than the more rostral cervical spinous processes of C3 to C6. On a T1-weighted MR image, the exact size of the subarachnoid space is difficult to assess because of its low signal intensity, and it may be confused with the posterior longitudinal ligament and the cortical bone (Fig. 3-6 ).
What are the effects of C3–C4?
Intraspinal microstimulation at widespread sites in C3–C4 produces robust output effects in stimulus-triggered averages of arm muscle EMG activity. Most output sites in C3–C4 activate muscles at more than one joint. Qualitatively, the effects from C3–C4 are similar to those evoked from the cervical enlargement, although there are differences in the frequency, distribution, and mean latency of effects from the two levels. Most interesting, effects evoked from C3–C4 have amplitudes that are significantly larger in extensor than in flexor muscles, whereas the effects evoked from C6–T1 are larger in flexors. The neural activity patterns and the stimulation-evoked output effects suggest that non-CM components of motor commands for different movements are routed through different premotor pathways in the spinal cord. Flexion movements of the hand, like grasping, may primarily involve activation of circuits in the cervical enlargement, and arm reaching and hand extension may primarily engage those in the upper cervical segments.
What is the linkage between the cervical and lumbar enlargement of the spinal cord?
A linkage between the cervical and lumbar enlargement of the spinal cord by propriospinal neuronal circuits with long axons can also be inferred on the basis of H-reflex studies. For example, during rhythmic movements of one foot, a cyclic H-reflex modulation was observed in the upper limbs. According to recent studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging, the supplementary motor area might be involved in the supraspinal control of this coupling between upper and lower limb movements.
Why are spinal canals so large?
The spinal canals are relatively large in order to house the cervical enlargement of the spinal cord. The spinal canal is triangular with the apex of the triangle posterior. The canal decreases in size from vertebra C1 through vertebra C3 and has a fairly uniform dimension from C3 through C7. C7 is a transitional vertebra, whose spinous process is longer and thicker and has a more inferior tilt than the more rostral cervical spinous processes of C3 to C6. On a T1-weighted MR image, the exact size of the subarachnoid space is difficult to assess because of its low signal intensity, and it may be confused with the posterior longitudinal ligament and the cortical bone (Fig. 3-6 ).
What is cervical lymphadenopathy?
Cervical lymphadenopathy refers to the enlargement of cervical lymph nodes, or the lymph nodes in the neck region. It often serves as an important clinical indicator of an underlying condition, most commonly of infectious origin. Localized lymphadenopathy may occur as a result of infection or inflammation of nearby structures such as the throat, ...
Can cervical lymphadenopathy be confused with cervical lymphadenopathy?
Cervical lymphadenopathy can often be confused with cervical lymphadenitis. Although cervical lymphadenitis does usually present with cervical lymphadenopathy, cervical lymphadenitis refers to a direct infection of the cervical lymph nodes, often resulting from bacterial or viral infection.
Can mycobacterium cause cervical lymphadenitis?
Cervical lymphadenitis can occur from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, resulting in tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis, or by other atypical mycobacteria, resulting in non- tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis. Additionally, cat scratch disease, which is caused by the bacterium Bartonella henselae, can result in cervical lymphadenitis.
Is cervical lymphadenopathy a serious condition?
Cervical lymphadenopathy on its own is not a serious condition; however, it may indicate a more serious underlying condition. In many cases, it can be a sign of a mild, benign, self-limiting condition of acute onset. However, it can also be a sign of more serious chronic conditions, such as cancer or autoimmune diseases, ...
What are the symptoms of cervical endometriosis?
The patient may be asymptomatic or report symptoms of discharge, dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, or deep dyspareunia.
Where should I look for cervix?
Search for the cervix should begin in the posterior vagina. Most Nabothian cysts, endocervical polyps, and cases of cervical ectropion may be managed conservatively.
What is the term for the endometrial tissue that is present in the uterus?
Adenomyosis is endometrial tissue present within the myometrium or uterine muscle. It may involve the endocervical canal or form a polypoid mass protruding into the endocervical canal.12Biopsy of cervical lesions shows typical histology of end ometriosis .
What is the transformation zone of the cervix?
The transformation zone of the cervix (where columnar and squamous cells meet) is in a continuous process of repair, and squamous metaplasia and inflammation may block a gland orifice. The endocervical columnar cells continue to secrete but are covered by squamous epithelium, forming a mucinous retention cyst.
Is cervical polyp benign?
Many clinicians encounter cervical lesions that may or may not be associated with cytologic abnormalities. Such abnormalities as ectropion, Nabothian cysts, and small cervical polyps are quite benign and need not generate concern for patient or clinician, whereas others, including those associated with a history of exposure to diethylstilbestrol, ...
What is the name of the condition that causes a discharge in the cervix?
Cervicitis. Cervicitis. With cervicitis, an inflammation of your cervix, your cervix appears red and irritated and may produce a pus-like discharge. Most often, cervicitis causes no signs and symptoms, and you may only learn you have the condition after a pelvic exam performed by your doctor for another reason.
How to prevent cervicitis?
Prevention. To reduce your risk of cervicitis from sexually transmitted infections, use condoms consistently and correctly each time you have sex. Condoms are very effective against the spread of STIs, such as gonorrhea and chlamydia, which can lead to cervicitis.
Can spermicide cause cervicitis?
Allergic reactions. An allergy, either to contraceptive spermicides or to latex in condoms, may lead to cervicitis. A reaction to feminine hygiene products, such as douches or feminine deodorants, also can cause cervicitis. Bacterial overgrowth.
Can you have cervicitis without symptoms?
However, it's also possible to have cervicitis and not experience any signs or symptoms. Often, cervicitis results from a sexually transmitted infection, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea. Cervicitis can develop from noninfectious causes, too.