What is the proper PPE for MRSA?
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Patients colonized or infected with MRSA may be placed in private rooms or cohorted with similar patients to reduce the spread of MRSA. Contact Precautions (gloves and gowns) are used during clinical encounters with patients who are colonized or infected with MRSA.
What is MRSA and how dangerous is it?
What is MRSA? MRSA is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a potentially dangerous type of staph bacteria that is resistant to certain antibiotics and may cause skin and other infections. As with all regular staph infections, recognizing the signs and receiving treatment for MRSA skin infections in the early stages reduces the
What is the portal of exit for MRSA?
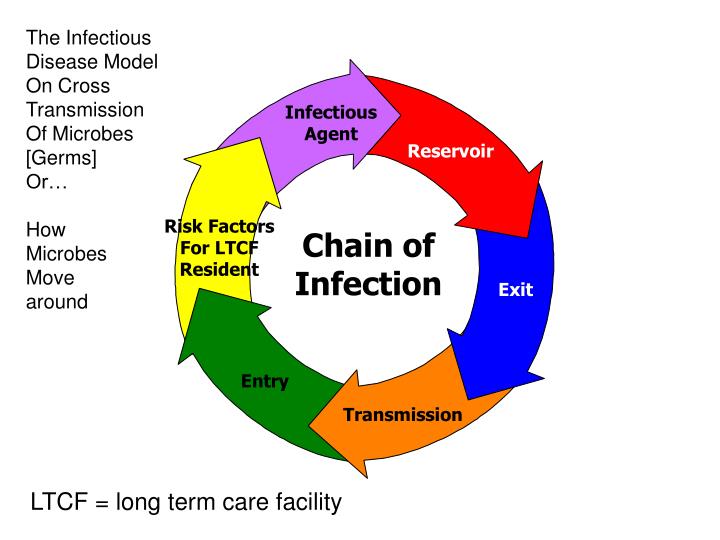
Section 10: Chain of Infection
- Reservoir. The reservoir of an infectious agent is the habitat in which the agent normally lives, grows, and multiplies.
- Portal of exit. Portal of exit is the path by which a pathogen leaves its host. ...
- Modes of transmission. ...
- Portal of entry. ...
- Host. ...
- Implications for public health. ...
How do you contact MRSA?
To prevent MRSA infections, healthcare personnel:
- Clean their hands with soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer before and after caring for every patient.
- Carefully clean hospital rooms and medical equipment.
- Use Contact Precautions when caring for patients with MRSA (colonized, or carrying, and infected). ...
- Test some patients to see if they have MRSA on their skin. ...
What is the most common route of transmission for MRSA?
Transmission Routes of MRSA MRSA is transmitted most frequently by direct skin-to-skin contact. MRSA can also be transmitted by: Contact with drainage from infected scrapes, cuts, or other skin wounds. Contact with personal items contaminated with drainage from infected scrapes, cuts, or other skin wounds.
What is the transmission of MRSA?
MRSA is transmitted most frequently by direct skin-to-skin contact or contact with shared items or surfaces (e.g., towels, used bandages) that have come into contact with someone else's infected site. Animals with MRSA can also transfer the infection to people who frequently handle them.
Is MRSA direct or indirect transmission?
MRSA is usually spread through physical contact - not through the air. It is usually spread by direct contact (e.g., skin-to-skin) or contact with a contaminated object. However, it can be spread in the air if the person has MRSA pneumonia and is coughing.
What is the portal of exit of MRSA?
Portal of exit: drainage from the open wound; Break in the chain: HCW uses proper handwashing techniques, wears protective gloves and handles bed linens properly. Mode of transmission: MRSA transferred on to hands by indirect contact; Break in the chain: HCW performs proper handwashing, gloving and linen handling.
What is the main route to spread infection?
Body fluids – A body fluid e.g. blood, urine, pus, saliva from one person enters the body of another e.g. through cuts or other means such as sexual intercourse (e.g. syphilis, HIV etc.). Through saliva (e.g. glandular fever).
Is MRSA spread by droplets?
Unwashed hands, if having been in contact with MRSA, can spread the bacteria. MRSA also can be spread by the use of contaminated equipment/environment. Droplets (coughing, spitting, etc.) can spread MRSA and may occur when a person sneezes (uncovered) or has a productive cough.
What is the chain of infection?
The six links include: the infectious agent, reservoir, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portal of entry, and susceptible host. The way to stop germs from spreading is by interrupting this chain at any link.
Which of the following is the first chain in the chain of infection?
1. The pathogen. The first link in the chain of infection is the infectious agent or pathogen which can take the form of: Viruses – such as Influenza A, shingles and Hepatitis.
What are the 5 modes of transmission?
Modes of transmissionDirect. Direct contact. Droplet spread.Indirect. Airborne. Vehicleborne. Vectorborne (mechanical or biologic)
What is the chain of infection quizlet?
Transmission occurs when the agent leaves its reservoir or host through a portal of exit, is conveyed by some mode of transmission, and enters through an appropriate portal of entry to infect a susceptible host.
What Does An MRSA Infection Look like?
An MRSA skin infection looks like a boil, pimple or spider bite that may be: 1. Red 2. Swollen 3. Painful 4. Pus-filled and oozing These infections...
What Can Schools Do to Prevent MRSA Infections?
Athletic equipment and locker rooms should be regularly cleaned and disinfected. There's no evidence that spraying or fogging rooms or surfaces wit...
What Can Athletes Do to Prevent MRSA Infections?
To help prevent the spread of MRSA infections: 1. Wash your hands. Use soap and water or an alcohol-based sanitizer. Clean your hands before and af...
If You Suspect An MRSA Infection, What Should You do?
Don't try to treat the infection yourself. Go to your doctor. Minor MRSA skin infections usually heal after being drained. If the infection doesn't...
When Can The Athlete Return to Play?
The National Athletic Trainers' Association recommends that suspicious lesions be tested for MRSA and that the athlete not be allowed to return to...
Mode of Transmission
Physical skin –to- skin contact with an infected person or with a ‘carrier’ individual.
Reference
The evolutionary history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) - Mark C. Enright D. Ashley Robinson, Gaynor Randle, Edward J. Feil, Hajo Grundmann, and Brian G. Spratt.
Recommended Reading
Diabetes and hypertension (high blood pressure) are significant health problems worldwide, but like cardiac disease and fatty liver disease, people of Indian origin are disproportionately affected.
How does MRSA spread?
The main mode of transmission of MRSA infections is through direct contact with wounds, discharge and soiled areas. Other risk factors include close contact, breaks in the skin due to wounds or indwelling catheters, poor personal hygiene and living in crowded conditions.
What is the cause of MRSA?
MRSA usually causes skin and soft tissue infections such as pimples, boils, abscesses or wound infections. The infected area may be red, swollen and painful or it may produce pus. Sometimes, more serious sequelae such as bloodstream infections, lung infections or necrotising fasciitis may occur.
What is the name of the strain of S. aureus that is resistant to antibiotics?
However, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a strain of S. aureus that is resistant to antibiotics including methicillin and other commonly used antibiotics such as oxacillin, penicillin, amoxicillin and cephalosporins.
Where is Staphylococcus aureus found?
Staphylococcus aureus ( S. aureus) is a bacterium that can be found in the nasal cavity and on the skin of some healthy people. These healthy individuals carry the bacteria without signs or symptoms of infection. Yet, the bacteria may sometimes cause diseases such as infection of skin, wound, urinary tract, lung, bloodstream and food poisoning.
How is MRSA spread?
MRSA is spread by: Skin-to-skin contact. MRSA can be transmitted from one person to another through skin-to-skin contact. While MRSA skin infections can occur in participants of many types of sports, they're much more likely to occur in contact sports — such as football, wrestling and rugby. Touching contaminated objects.
How to prevent spreading MRSA?
While your skin infection is healing, keep it covered with a clean, dry bandage at all times. To avoid spreading MRSA to others, wash your hands often, especially after changing your bandage or touching the infection. Don't share clothing, towels or hygiene products with anyone else.
How to prevent MRSA infection?
To help prevent the spread of MRSA infections: Wash your hands. Use soap and water or an alcohol-based sanitizer. Clean your hands before and after playing sports, using shared weight training equipment, and changing a bandage on a wound. Take showers.
What is MRSA in sports?
MRSA: Protecting student athletes. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus — or MRSA — is a type of highly drug-resistant bacteria that has been a problem in hospital and health care settings for decades. More recently, MRSA has become a problem among otherwise healthy student athletes. Is your child at risk?
Where did MRSA originate?
MRSA first surfaced in hospitals, where it often caused serious bloodstream infections in people who were sick with other diseases and conditions. Now there are varieties of MRSA that occur in nonhospital settings. These infections typically affect the skin of otherwise healthy individuals — such as student athletes.
What is the name of the infection that starts as small red bumps that turn into a painful abscess
Open pop-up dialog box. Close. Staph infection. Staph infection. MRSA infections start out as small red bumps that can quickly turn into deep, painful abscesses. MRSA is a type of staph bacteria that has become resistant to the effects of many common antibiotics.
What happens if you touch a towel with MRSA?
If drainage from an MRSA skin infection comes into contact with an object — such as a towel, weight training equipment or a shared jar of ointment — the next person who touches that object may become infected with MRSA bacteria.
How does MRSA spread?
Hospital spread of MRSA can include the above methods in addition to spread by blood, saliva, and/or droplets in the air that can land on people's skin or other surface if the person has pneumonia.
How to prevent MRSA?
Prevention of MRSA infections may be accomplished by good hand washing and body cleaning hygiene practices, especially after playing contact sports or if people live in crowded areas (dorms, camps, or barracks, for example).
What is the short form of MRSA?
MRSA is the short form of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and refers to strains of gram-positive coccal-shaped (round) bacteria that are resistant to several antibiotics. MRSA causes mainly skin infections in nonhospitalized people; in hospitalized patients, it can cause sepsis, surgical site infections, and pneumonia.
What is MRSA and staph?
MRSA Slideshow. MRSA and staph infections are caused by a 'super bug' resistant to antibiotics. Learn causes, symptoms, and treatment options of the highly contagious infection, MSRA.
How long does it take for staph to infect?
However, the incubation period for MRSA often ranges from one to 10 days if it enters broken skin or damaged mucous membranes.
How to diagnose MRSA?
However, the definitive way to diagnose MRSA is to have a doctor culture the MRSA bacteria (skin lesion, biopsy, or nasal swab) and then show the organisms are resistant to several different antibiotics.
Can you transfer MRSA to another person?
However, many activities such as kissing, saliva exchange, and sexual contact, although somewhat less likely to transfer MRSA to another, can cause infection if the skin or mucosa is damaged. Hospitalized patients, if they have MRSA pneumonia, may transfer the organisms to others through the air by contaminated droplets.
When we're looking to break the chain of transmission of infectious pathogens, we need all hands on deck to
“When we're looking to break the chain of transmission of infectious pathogens, we need all hands on deck to combat this issue because it’s a public health concern across the spectrum of care. From EMS providers, to a hospital or a physician’s office; to disrupt the MRSA lifecycle, it takes collaboration among all medical providers to create that disruption.” Said Lyles.
Where is S. aureus found?
S. aureus bacteria are commonly found in the nose or on the skin of even healthy individuals and most people who carry it will not develop an infection. The infections that do result in sepsis are often of the intact skin, wounds, lungs, or urinary tract. Often the signs are not visible or are so common they could apply to many conditions.
How to disinfect ambulance equipment?
1. Implement/Follow infection control guidelines. While there are no universal protocols for disinfecting or decontaminating an ambulance, medical equipment and supplies, agencies should strive to develop one. Although there is pressure to move from one call to the next, there are relatively simple and common-sense infection control guidelines that EMS personnel can follow to reduce the risk of transmission of MRSA or other pathogens in the ambulance. These include: 1 Maintaining optimal hand hygiene. 2 Wearing personal protective equipment like gloves, gowns, masks, respirators and eye protection while decontaminating. 3 Changing cot linens after every patient. 4 Using CDC-recommended decontamination supplies daily.
