
∆U = Q - m × g × (y - y 0) The change in the internal energy of gas formula derives from the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics concerned with heat and temperature and their relation to energy and work. It defines macroscopic variables, such as internal energy, entropy, and pressure, that partly describe a body of matter or radiation.
What is the formula for change in internal energy?
Formula: ΔU=q+w. Where ΔU is the total change in internal energy of a system. q is the exchange of heat between a system and its surroundings. w is the work done by or on the system. The internal energy of a system would decrease when the system gives off heat or does work. Therefore, the interior energy of a system increases when the warmth ...
How do you convert potential energy into internal energy?
This experiment demonstrates that when we hit a mat with a mallet, the temperature of the mat increases. During the impact, the kinetic energy of the mallet is converted partly into energy of inelastic deformation of the mat and partly into the internal energy of the mallet and the mat.
What is internal energy of an ideal gas?
The internal energy of an ideal gas is therefore the sum of the kinetic energies of the particles in the gas. The kinetic molecular theory assumes that the temperature of a gas is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of its particles, as shown in the figure below.
Does internal gas affect your weight?
Those with a food intolerance often experience gas, cramps, and bloating, making it feel like they're gaining weight. Depending on how severe the food intolerance is, they might also experience diarrhea. The fix: While you might feel super bloated and uncomfortable throughout the day because of your diet, you might not actually be gaining weight.
What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
The internal energy of ideal gas is U = cV T. The change in internal energy for ideal gas is therefore ∆U = cV ∆T, where cV is specific heat (at constant volume), and ∆T is change in tem- perature.
What is the formula for change in internal energy?
Thus, in the equation ΔU=q+w w=0 and ΔU=q. The internal energy is equal to the heat of the system. The surrounding heat increases, so the heat of the system decreases because heat is not created nor destroyed.
What is the change in the internal energy of the gas at constant pressure?
At constant pressure, the change in the enthalpy of a system is equal to the heat flow: ΔH=qp.
Why is the internal energy of an ideal gas 0?
An ideal gas by definition has no interactions between particles, no intermolecular forces, so pressre change at constant temperature does not change internal energy.
What is the change in internal energy of a gas which is compressed isothermally?
1 Answer. Zero is the change in the internal energy of a gas, which is compressed isothermally.
What is internal energy of air?
The internal energy of the room is given by the molecular motion and is called as the kinetic internal energy given by 2fnRT. Using the gas law we have PV=nRT and as the gas is mainly comprised of nitrogen and oxygen both being diatomic we take the degree of freedom as 5. Thus we calculate internal energy as 25PV=25×1.
How do you find the internal energy of a gas?
Now heat Q is transferred at constant volume to the gas until it reaches a temperature T. All the heat that was necessary to heat the gas is finally present as internal energy U. Thus, at a temperature T the gas has the following internal energy U: U=cv⋅m⋅T applies in general to perfect gases!
Is the change in internal energy at constant?
Internal energy change is the heat change at constant volume whereas the enthalpy change is the heat change at constant pressure.
How does the internal energy of a closed system change when a gas expands?
The internal energy of the system decreases as the gas expands.
What is the change in internal energy in an isothermal process?
In an Isothermal process the temperature is constant. Hence, the internal energy is constant, and the net change in internal energy is ZERO. ... An ideal gas by definition has no interactions between particles, no intermolecular forces, so pressure change at constant temperature does not change internal energy.
What is the value of internal energy of a perfect gas?
completely kinetic. completely potential.
What is the change in internal energy in an adiabatic process?
Solution : In an adiabatic process ,
Q = constant i.e., dQ = 0 `therefore dU = - dW ne0`
So , in an adiabatic process , the change in internal energy is equal to the amount of work done .
What is the relationship between the temperature and the kinetic energy of a gas?
As already mentioned, the kinetic theory of gases shows a direct relationship between the mean kinetic energy of the molecules in a gas and its temperature. So if you know the temperature of a gas (and the number of particles), then a certain internal energy is directly connected with it. This is independent of the pressure or volume of the gas. ...
How is kinetic energy related to gas temperature?
According to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, the kinetic energy of the molecules is in turn directly related to the gas temperature. Thus, a change of the internal energy (change of the kinetic energy) inevitably means a change of temperature. This raises the question how a change in internal energy ΔU is related to a change in temperature ΔT.
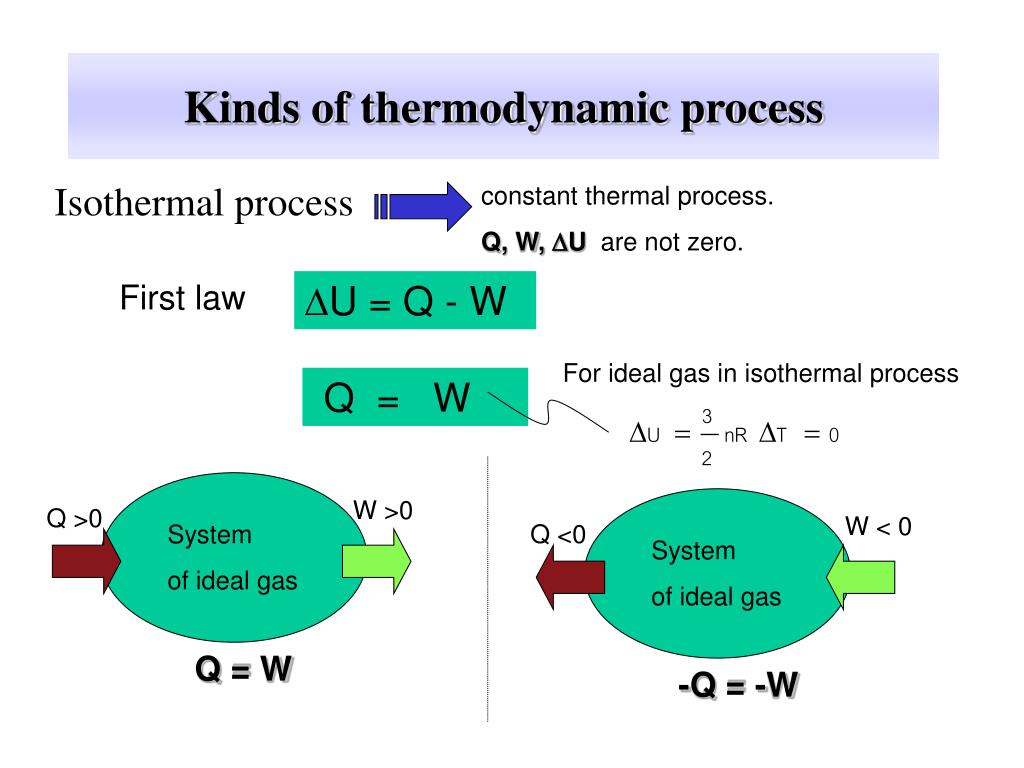
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
In the article Internal e nergy of ideal gases it was explained in detail that in ideal gases only the kinetic energy of the gas molecules exists as internal energy (thermal energy). According to the first law of thermodynamics, this internal energy can be changed by transferring energy as work W or as heat Q:
Is internal energy only dependent on temperature?
Therefore the change of the internal energy is only dependent on the change of the temperature. The change of internal energy during a thermodynamic process is thus clearly determined in ideal gases, if the initial temperature (and thus the initial energy) and the final temperature (and thus the final energy) are known.
Does temperature affect internal energy?
Only the change of temperature determines the change of the internal energy! The fact that the internal energy is only dependent on the state of the gas (in terms of temperature) and not on the type of process, makes the internal energy a state variable.
Change in the internal energy of gas Formula and Calculation
The change in the internal energy of gas formula derives from the mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics Physics Tutorials associated with the Change In The Gas Internal Energy Calculator
The following Physics tutorials are provided within the Thermodynamics section of our Free Physics Tutorials. Each Thermodynamics tutorial includes detailed Thermodynamics formula and example of how to calculate and resolve specific Thermodynamics questions and problems.
What is internal energy?
The internal energy is the total of all the energy associated with the motion of the atoms or molecules in the system. Microscopic forms of energy include those due to the rotation, vibration, translation, and interactions among the molecules of a substance.
Which law states that the energy of a gas depends on its temperature?
This rule was originally found in 1843 by Joule experimentally for real gases and is known as Joule’s second law : The internal energy of a fixed mass of an ideal gas depends only on its temperature (not pressure or volume). The specific enthalpy of a gas described by pV = nRT also depends on temperature only.
What is ideal gas?
An ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces. An ideal gas can be visualized as a collection of perfectly hard spheres which collide but which otherwise do not interact with each other. In reality, no real gases are like an ideal ...
What is the kinetic theory of gases?
The behavior of the system is well described by kinetic theory of gases. Kinetic theory is based on the fact that during an elastic collision between a molecule with high kinetic energy and one with low kinetic energy, part of energy will transfer to the molecule of lower kinetic energy.
How many translation directions does a gas have?
If the gas molecules contain more than one atom, there are three translation directions, and rotational kinetic energy also contributes, but only for rotations about two of the three perpendicular axes. The five contributions to the energy (five degrees of freedom) give:
Why is the ideal gas law used?
The ideal gas law is utilized by engineers working with gases because it is simple to use and approximates real gas behavior. In an ideal gas, molecules have no volume and do not interact. According to the ideal gas law, pressure varies linearly with temperature and quantity, and inversely with volume. pV = nRT.
What is the symbol for the gas constant?
R is the ideal, or universal, gas constant, equal to the product of the Boltzmann constant and the Avogadro constant, In this equation the symbol R is a constant called the universal gas constant that has the same value for all gases—namely, R=8.31 J/mol K.
Change in Internal Energy
A gas sample in a cylinder is supplied with 524 kJ of energy as heat. At the same time, a piston compresses the gas, doing 340 kJ of work. What is the change in internal energy of the gas during this process?
Re: Change in Internal Energy
The gas sample in the cylinder is supplied with 524 kJ of energy, so this is added energy. A piston compressing the gas is also added energy to the system. Therefore you must add both the energy changes given, resulting with an internal energy change of 864 kJ.
Re: Change in Internal Energy
will we ever need to do any conversions for units? do these problems always need to be in kJ?
Re: Change in Internal Energy
Because q and w are both in kilojoules, you don't need to do anything with the units!
Re: Change in Internal Energy
005384106 wrote: will we ever need to do any conversions for units? do these problems always need to be in kJ?
First Law of Thermodynamics
Preliminary Considerations For Determining The Change in Internal Energy
- As already mentioned, the kinetic theory of gases shows a direct relationship between the mean kinetic energy of the molecules in a gas and its temperature. So if you know the temperature of a gas (and the number of particles), then a certain internal energy is directly connected with it. This is independent of the pressure or volume of the gas. Th...
Derivation of The Relationship Using The Example of An Isochoric Process
- To determine the relationship between a change in internal energy and the change in temperature the following experiment is performed. A gas of mass m is confined to a vessel of constant volume. By transferring heat, the temperature of the gas increases and with it the internal energy. Since the volume of the gas cannot change during such an isochoric process, energy cannot be …
Remark on The Formula
- At this point, one should not be misled by the term “specific isochoric heat capacity” cv, which appears in formula (8). In context with the change of internal energy, the quantity cvshould only be considered as a proportionality constant between the change of internal energy and the change of temperature. This proportionality constant is called specific isochoric heat capacity only becaus…
Internal Energy of Ideal Gases
- Even though in thermodynamics often only the change of internal energy ΔU is relevant, for ideal gases the absolute internal energy U can also be determined. To do this, imagine a gas confined to a cylinder with constant volume that is cooled down to absolute zero. In this state, all molecules are at rest and the gas therefore has no internal energy. Now heat Q is transferred at …
Analogy Between Internal Energy and Gravitational Potential Energy
- Internal energy of ideal gases can very clearly be compared in analogy to gravitational potential energyof an object. While the gravitational potential energy represents the energetic (gravitational) state of an object at a given height h, the internal energy represents the energetic (kinetic) state of an ideal gas at a given temperature T. A given height h can be assigned a certai…