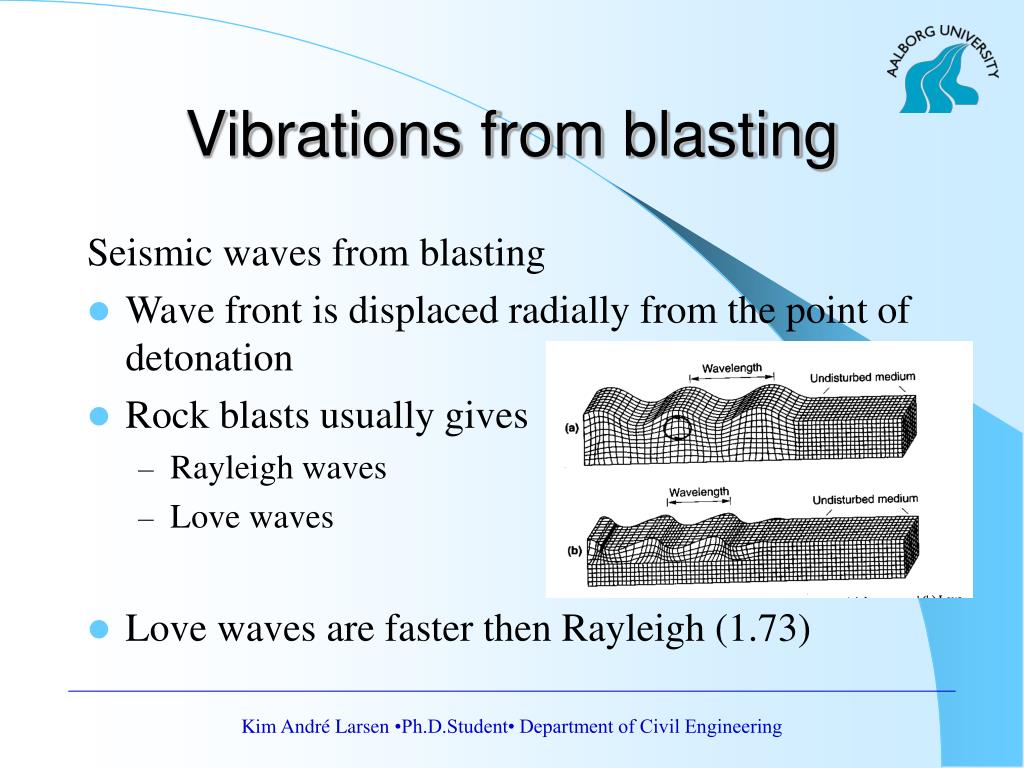
- British physicist Lord Rayleigh demonstrated the Rayleigh Waves mathematically.
- A Rayleigh wave is a seismic surface wave producing the sudden shake in an elliptical motion, with no crosswise or perpendicular motion.
- It moves along the ground just like a wave moves across a lake or an ocean.
- The greater part of the shaking felt from an earthquake is because of the Rayleigh wave, which can be considerably bigger than other waves.
- Because it rolls, it moves the ground up and down and side-to-side in the same direction that the wave is moving.
Full Answer
What is the difference between Rayleigh and Love waves?
· What is the characteristics of Rayleigh waves? Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions.
What waves are slower than primary waves?
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids.Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase …
How do Rayleigh and Love waves travel?
Rayleigh wave is a secondary wave characterized by low frequency and strong energy, propagating mainly along the interface of medium and rapid attenuation of energy with increase in interface distance. The same as reflected wave and refracted wave, Rayleigh wave also contain subsurface geological information.
What are terahertz waves?
The small arrival prior to the large-amplitude pulse is the S wave, and the large pulse itself is a Rayleigh-wave pulse. The Rayleigh wave shows a clear phase shift between the radial (q 0) and vertical (w 0) components and is much larger than the body-wave arrivals. The experimental result shown in part (B) is a recording of a breaking pencil lead point-force source on a piece of …

How do Rayleigh waves form?
Rayleigh waves are formed when the particle motion is a combination of both longitudinal and transverse vibration giving rise to an elliptical retrograde motion in the vertical plane along the direction of travel.
What is a wave that travels near the surface of a rock?
A surface wave traveling near the surface of rock formations has been defined as a Rayleigh wave . The motion of these waves will be longitudinal as well as transverse, and their amplitude decreases as they traverse large distances. These waves are of low velocity and frequency, but amplitude is high and is defined as noise in the seismic data. Such waves are normally present in the seismic record and can be removed from the main seismic data by some filtration method.
What is love wave?
Love waves are a major type of surface wave having a horizontal motion that is shear or transverse to the direction of propagation. The velocity of propagation of any body wave in any homogeneous, isotropic material is determined by the elastic moduli and densities of the material through which it passes.
What are the characteristics of Rayleigh waves?
characteristics. …principal surface waves are called Rayleigh waves after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh, who first mathematically demonstrated their existence. Rayleigh waves travel along the free surface of an elastic solid such as the Earth. Their motion is a combination of longitudinal compression and dilation that results in an elliptical ...
What is Rayleigh wave?
history of solid mechanics. In mechanics of solids: Waves. …surface wave, now called a Rayleigh wa ve, propagates typically at slightly more than 90 percent of the shear wave speed and involves an elliptical path of particle motion that lies in planes parallel to that defined by the normal to the surface and the propagation direction.
What is the name of the wave that travels along the surface of an elastic solid?
…principal surface waves are called Rayleigh waves after the British physicist Lord Rayleigh, who first mathematically demonstrated their existence. Rayleigh waves travel along the free surface of an elastic solid such as the Earth. Their motion is a combination of longitudinal compression and dilation that results in an elliptical motion…
What type of wave is a surface wave?
…of surface wave is the Rayleigh wave, in which a particle moves in an elliptical path in the vertical plane from the source. The horizontal component of Rayleigh waves is probably the principal cause of damage from earthquakes. Love waves are another type of surface wave; they involve shear motion.…
What is surface wave?
…surface wave, now called a Rayleigh wave, propagates typically at slightly more than 90 percent of the shear wave speed and involves an elliptical path of particle motion that lies in planes parallel to that defined by the normal to the surface and the propagation direction. Another type of surface…
What are Rayleigh waves?
Rayleigh Waves. At a free surface of an elastic solid, waves can propagate that are confined primarily to that surface. These surface waves are called Rayleigh waves. At the stress-free plane surface (y = 0) of a semi-infinite elastic solid occupying the region y≥0, for example, harmonic Rayleigh waves of the form:
What are the properties of Rayleigh waves?
In an anisotropic elastic structure, the properties of a Rayleigh wave depend on anisotropy and the direction of wave propagation. These waves can propagate not only in a plane but in the curved free surface of a solid as well.
What are the waves that propagate on a stress free surface of an elastic solid?
At a free surface of an elastic solid, waves can propagate that are confined primarily to that surface. These surface waves are called Rayleigh waves. At the stress-free plane surface (y = 0) of a semi-infinite elastic solid occupying the region y≥0, for example, harmonic Rayleigh waves of the form:
What type of wave is transmitted through the surface of a solid?
In addition to the longitudinal and transverse waves that can propagate through the body of an elastic solid, various types of surface waves can also be transmitted across the surface of a solid. Among these are what we call Rayleigh waves. The amplitude of a Rayleigh wave diminishes with depth below the surface, and is ignorably small at depths of more than a few wavelengths. The disturbance is therefore confined to the surface layers of a solid. The surface layers experience both transverse and longitudinal components of motion. In this respect, Rayleigh waves are similar to water waves.
What is Rayleigh wave?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects.
How are Rayleigh waves used?
Low frequency Rayleigh waves generated during earthquakes are used in seismology to characterise the Earth 's interior. In intermediate ranges, Rayleigh waves are used in geophysics and geotechnical engineering for the characterisation of oil deposits. These applications are based on the geometric dispersion of Rayleigh waves and on the solution of an inverse problem on the basis of seismic data collected on the ground surface using active sources (falling weights, hammers or small explosions, for example) or by recording microtremors. Rayleigh ground waves are important also for environmental noise and vibration control since they make a major contribution to traffic-induced ground vibrations and the associated structure-borne noise in buildings.
What type of wave is a Rayleigh wave?
Rayleigh wave. Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects. Rayleigh waves are part of the seismic waves ...
How do Rayleigh waves affect earthquakes?
Because Rayleigh waves are surface waves , the amplitude of such waves generated by an earthquake generally decreases exponentially with the depth of the hypocenter (focus). However, large earthquakes may generate Rayleigh waves that travel around the Earth several times before dissipating.
How fast do Rayleigh waves travel?
Rayleigh waves emanating outward from the epicenter of an earthquake travel along the surface of the earth at about 10 times the speed of sound in air (0.340 km/s), that is ~3 km/s. Due to their higher speed, the P- and S-waves generated by an earthquake arrive before the surface waves.
What type of wave travels near the surface of solids?
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions. The existence of Rayleigh waves was predicted in 1885 by Lord ...
Answer
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. ... At greater depths the particle motion becomes prograde.
New questions in Science
Kuva Kim is reporting about super typhoon Yolanda, internationallyknown as Super Typhoon Haiyan, which hit the Philippines on November 8,2013. with a …
