What is the definition of body fat composition?
The body is composed of water, fat, protein and minerals. The body is divided into fat-free areas which make up your body composition. Body fat is the most varied component of the body, which is made up of essential fat and stored fat.
What exercises improve body composition?
- 1 min: March in place to warm up
- Squats — 20 reps
- Reverse lunges — 12 reps on each leg
- Push ups (on the knees or toes) — 10-12 reps
- Dips — 10-12 reps
- Walking lunge with arms overhead — 10-12 reps
- Lateral leg lift
- Plank
- Glute bridge
- Back extension
Are body composition scales good for calculating body fat?
The short answer is no. Although they're convenient and easy to use, body fat scales unfortunately are not very accurate, according to Cedars-Sinai. At best, they can only give you a very rough estimate of your body fat percentage.
What characterizes healthy body composition?
What characterizes healthy body composition? high proportion of muscle, bone, and water and an acceptably low proportion of fat. The body adapting to a gradual increase in the amount of exercise is the definition of which stage of exercising? progressive overload.

What is the basic composition of fat?
Fats are hydrophobic hydrocarbon molecules consisting of fatty acids and glycerol. Glycerol has three carbons, each of which is attached to a hydroxyl group. Most fats are formed through replacement of the hydrogen of each hydroxyl group by a fatty acid.
What is the composition of a fat cell?
Under a microscope, fat cells look like bulbous little spheres. Like other cells in the body, each has a cell membrane and a nucleus, but their bulk is made up of droplets of stored triglycerides, each of which consists of three fatty-acid molecules attached to a single glycerol molecule.
Why is human fat yellow?
Why? Because humans can't quickly metabolize the yellow carotene found in vegetables and grains. So carotene migrates to our fat cells and settles there.
What is stored in fat?
Adipose (fat) cells are specialized for the storage of energy in the form of triglycerides, but research in the last few decades has shown that fat cells also play a critical role in sensing and responding to changes in systemic energy balance.
What is the structure and function of fat cells?
Adipose tissueDefinitionA type of specialized connective tissue whose main functions are to store the energy, protect the organs and contribute to the endocrine profile of the bodyFunctionEnergy storing, hormone production, thermal isolation (white adipose tissue); thermogenesis (brown adipose tissue)3 more rows
Is there protein in fat cells?
The fat stored is in a semi-liquid state, and is composed primarily of triglycerides, and cholesteryl ester. White fat cells secrete many proteins acting as adipokines such as resistin, adiponectin, leptin and apelin. An average human adult has 30 billion fat cells with a weight of 30 lbs or 13.5 kg.
Which cells are known as fat cells?
Adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue, is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes are energy storing cells that contain large globules of fat known as lipid droplets surrounded by a structural network of fibers.
What organelles do fat cells contain?
However, each type of fat cell is somewhat specialized and has a distinct intracellular distribution of organelles and gene expression profile. All fat cells have Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum, but these organelles make up a more significant portion of pink adipocytes than other adipocyte types.
Where are carbon atoms in fatty acids?
The carbon atoms in fatty acids are arranged in straight chains, and the first site of unsaturation (double bond) in most of the unsaturated acids appears between the ninth and tenth carbon atoms, starting the counting from the terminal carboxyl group ( see table).
How many fatty acids are in butterfat?
Fats vary widely in complexity; some contain only a few component acids, and at the other extreme more than 100 different fatty acids have been identified in butterfat, although many are present in only trace quantities. Most of the oils and fats are based on about a dozen fatty acids ( see table). In considering the composition ...
What are triglycerides made of?
Since the glycerides, which make up 90 to 99 percent of most individual fats or oils of commerce, are esters formed by three fatty-acid molecules combining with one molecule of glycerol, they may differ not only in the fatty acids that they contain but also in the arrangement of the fatty-acid radicals on the glycerol portion. Simple triglycerides are those in which each molecule of glycerol is combined with three molecules of one acid—e.g., tripalmitin, C 3 H 5 (OCOC 15 H 31) 3, the glyceryl ester of palmitic acid, C 15 H 31 COOH. Only a few of the glycerides occurring in nature are of the simple type; most are mixed triglycerides (i.e., one molecule of glycerol is combined with two or three different fatty acids). Thus stearodipalmitin, C 3 H 5 (OCOC 15 H 31) 2 (OCOC 17 H 35 ), contains two palmitic acid radicals and one stearic acid radical. Similarly, oleopalmitostearin, C 3 H 5 (OCOC 15 H 31 ) (OCOC 17 H 33 ) (OCOC 17 H 35 ), contains one radical each of oleic, palmitic, and stearic acids. Each mixed triglyceride containing three different acid radicals may exist in three different isomeric forms, because any of the three can be linked with the centre carbon of the glycerol molecule. A mixed triglyceride containing two radicals of the same acid and one radical of another acid has only two isomeric forms.
Why are fatty acids important?
Because of their preponderant weight in the glyceride molecules and also because they comprise the reactive portion of the molecules, the fatty acids influence greatly both the physical and chemical character of glycerides. Fats vary widely in complexity; some contain only a few component acids, and at the other extreme more than 100 different ...
What is a simple triglyceride?
Simple triglycerides are those in which each molecule of glycerol is combined with three molecules of one acid —e.g., tripalmitin, C 3 H 5 (OCOC 15 H 31) 3, the glyceryl ester of palmitic acid, C 15 H 31 COOH.
What are monoglycerides and diglycerides?
Monoglycerides and diglycerides are partial esters of glycerol and have one or two fatty-acid radicals, respectively. They are seldom found in natural fats except as the products of partial hydrolysis of triglycerides.
How many double bonds are there in an acid?
Unsaturated acids may contain up to six double bonds, and as unsaturation increases the melting points become lower.
What are the major classes of compounds in the human body?
Most of the elements are found within compounds. Water and minerals are inorganic compounds. Organic compounds include fat, protein, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids. Water: Water is the most abundant chemical compound in living human cells, accounting for 65 percent to 90 percent of each cell.
How many elements are in the human body?
Elements in the Human Body. Six elements account for 99% of the mass of the human body. The acronym CHNOPS may be used to help remember the six key chemical elements that are used in biological molecules. C is carbon, H is hydrogen, N is nitrogen, O is oxygen, P is phosphorus, and S is sulfur.
What is the most important element in the body?
Hydrogen is in water, plus it's an important electron carrier. Nitrogen is about 3.3% of body mass. It's found in proteins and nucleic acids. Calcium accounts for 1.5% of body mass. It's used to build bones and teeth, plus it's important for muscle contraction. Phosphorus is about 1% of body mass.
What are the minerals in the blood?
Common minerals include sodium, chlorine, calcium, potassium, and iron. Carbohydrates: Although humans use the sugar glucose as an energy source, there isn't that much of it free in the bloodstream at any given time. Sugar and other carbohydrates only account for about 1% of body mass.
What are the most important minerals in the human body?
Skin contains a large amount of protein, too. Minerals: Minerals account for about 6 percent of the body. They include salts and metals. Common minerals include sodium, chlorine, calcium, potassium, and iron.
What is the second most abundant element in the body?
In addition to being a component of water, oxygen is essential for cellular respiration. Carbon is contained in all organic compounds, which is why carbon is the second most abundant element in the body, accounting for about 18% of body mass. Carbon is found in proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. It's also found in carbon dioxide.
What is the most abundant element in the human body?
Oxygen is the most abundant element in the human body accounting for approximately 65% of a person's mass. Each water molecule consists of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom, but the mass of each oxygen atom is much higher than the combined mass of the hydrogen. In addition to being a component of water, ...
What Is Body Fat?
Your body is made up of water, protein, fat, and minerals. There are two types of fat in your body.
What is body composition?
Body composition is a term used often by doctors and health professionals. It refers to the percentage of fat, bone, and muscle in your body. Doctors use body composition to see if you’re at a healthy weight for your individual body.
How to find out what your body fat percentage is?
To find out what your body fat percentage is, a health professional might use skin calipers to measure your stored fat. However, there are other more accurate ways of measuring your body composition. . Skin calipers. A health professional will use skin calipers to measure your skinfold thickness.
What is stored fat?
Also known as stored fat, this is found in your adipose tissue. This type of fat is used as energy for your body. It insulates and cushions your body. It surrounds your organs and is just under your skin. Excessive stored fat can be harmful to your health.
Why is body composition important?
This helps them find out your level of health. Body composition is important because someone else can be the same height and weight as you, but they might have more body fat and less muscle.
What does a high BMI mean?
Typically, a high BMI of more than 30 does indicate obesity. If you have a BMI of over 30, you may have a higher body fat percentage. This could put you at risk for health problems like hypertension (high blood pressure), osteoarthritis, stroke, or type 2 diabetes.
Why do doctors use BMI?
Doctors use BMI to measure your height and weight, and to find if you are underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. BMI is associated with body fat percentage but doesn’t give an accurate picture of your body makeup. BMI is more helpful as a global index for nutrition.
What Is Body Composition?
Body composition is the term used in the fitness and health community to refer to the percentage of fat, water, bone, muscle, skin, and other lean tissues that make up the body.
How Is Body Mass Index Different?
Body mass index (BMI) is another popular term used in the medical and health community to describe body measurements.
Why Body Composition Is Important
Body composition and body fat percentage may better predict health risks than simple obesity classification based on BMI. 2 A healthier body composition is a higher percentage of lean tissue and a lower percentage of body fat.
How Is Body Composition Measured?
Body composition is measured using tools to estimate your body fat percentage. The ways to measure body composition vary. Some are more accessible but may be less accurate, while others may be harder to access and more accurate. Here are different ways body composition is measured.
How to Improve Body Composition
The best way to improve your body composition is to make healthy changes, like:
Summary
Body composition is a measurement of the amount of body fat and lean tissue in your body. It’s important because having more body fat is associated with an increased risk for some chronic diseases and health problems.
A Word From Verywell
Body composition can give you a better understanding of your current fitness and health level. In addition, repeating the body composition test over time can help you track your progress on your wellness journey.
What are the elements that make up 96% of the human body?
Approximately 96% of body weight consists of only four elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Calcium , phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chlorine, and sulfur, are macronutrients or elements the body needs in a significant amount. 01. of 10.
What are the elements in the human body?
Approximately 96% of body weight consists of only four elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen.
What is the carbon in the air?
All organic molecules ( fats, proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids) contain carbon. Carbon also is found as carbon dioxide or CO 2. You inhale air that contains about 20% oxygen. The air you exhale contains much less oxygen, but is rich in carbon dioxide.
How much potassium is in the human body?
Potassium makes up 0.2% to 0.35% of the adult human body.
What is the second most abundant element in the human body?
All living organisms contain carbon , which forms the basis for all of the organic molecules in the body. Carbon is the second most abundant element in the human body, accounting for 18% of body weight.
How much of the human body is hydrogen?
Hydrogen accounts for 10% of the mass of the human body.
How much of the body is made up of phosphorus?
About 1.2% to 1.5% of your body consists of phosphorus.
What are the different types of body composition?
Body composition can also be expressed in terms of various types of material, such as: 1 Muscle 2 Fat 3 Bone and teeth 4 Nervous tissue ( Brain and nerves) 5 Hormones 6 Connective tissue 7 Body fluids ( blood, lymph, Urine) 8 Contents of digestive tract, including intestinal gas 9 Air in lungs 10 Epithelium
What scale is the composition of the human body?
The composition of the human body can be viewed on an atomic and molecular scale as shown in this article.
What are the molecules in the human body?
The composition of the human body expressed in terms of chemicals: Gases such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, acetaldehyde, formaldehyde, methanethiol. These may be dissolved or present in the gases in the lungs or intestines.
How much water does the human body have?
The adult human body averages ~53% water. This varies substantially by age, sex, and adiposity. In a large sample of adults of all ages and both sexes, the figure for water fraction by weight was found to be 48 ±6% for females and 58 ±8% water for males. Water is ~11% hydrogen by mass but ~67% hydrogen by atomic percent, ...
What are the essential elements for life?
The elements listed below as "Essential in humans" are those listed by the (US) Food and Drug Administration as essential nutrients, as well as six additional elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen (the fundamental building blocks of life on Earth), sulfur (essential to all cells) and cobalt (a necessary component of vitamin B 12 ).
How many elements are in a 70 kg human body?
The average 70 kg (150 lb) adult human body contains approximately 7 × 1027 atoms and contains at least detectable traces of 60 chemical elements. About 29 of these elements are thought to play an active positive role in life and health in humans.
What are the elements that make up the human body?
Almost 99% of the mass of the human body is made up of six elements: oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, and phosphorus. Only about 0.85% is composed of another five elements: potassium, sulfur, so dium, chlorine, and magnesium. All 11 are necessary for life.
What Is Body Fat Percentage?
Many modern scales can estimate your body fat percentage, which is the measurement used to better understand your body composition. Smart scales might not be that accurate but they can be a good indicator along with knowing your BMI (body mass index).
What is body composition?
Our body composition relates to the proportion of varying compounds that we carry in our system. You can divide these into two major categories—fat and non-fat mass.
How to keep fat percentage down?
Exercising is a great way to keep the fat percentage down and improve your overall health and wellbeing. Strength training twice a week helps shed weight and speed metabolism in any age group and is especially known to help older women improve their body image and promote wellness and healthy habits.
What is the ideal body fat percentage for men and women over 50?
The ideal body fat percentage for men and women over 50 is 11–21% for men and 23–33% for women. There are many reasons why this ideal percentage changes with time, though.
What is a healthy body?
A healthy body is one that has a lower proportion of body fat, and you can measure this value against the total body mass.
How much alcohol does an athlete have?
Even athletes have 6–13%, and anything under 2–5% could negatively affect your functioning.
What are the essential fats?
Essential fats, for example, are essential to our survival since they: 1 Protect vital internal organs. 2 Enable the absorption of vitamins. 3 Regulate hormones in our system at the right time.
What is the structure of fat cells?
Anatomy of fat. Under a microscope, fat cells look like bulbous little spheres. Like other cells in the body, each has a cell membrane and a nucleus, but their bulk is made up of droplets of stored triglycerides, each of which consists of three fatty-acid molecules attached to a single glycerol molecule.
What type of fat is found in white adipose tissue?
A third type of fat, "beige fat," is found in white adipose tissue, but unlike white-fat cells, these cells contain UCP-1. Beige-fat cells seem to have the flexibility to act like either white fat or brown fat, depending on the situation, according to the Endocrine Connections paper.
What is the main substance used for energy storage?
The stuff we typically think of as fat is "white fat," which is the main substance used for energy storage. When insulin levels go up — say, after a meal — white adipocytes take in more fatty acids, literally swelling in size, Meerman told Live Science. When insulin drops, fat cells release their stores as a source of quick energy for the body.
What are adipocytes used for?
Other clusters of adipocytes are used mostly for support, such as the cushion of fat that surrounds the eyes, according to a 2006 paper in the journal Nature. These fat cells probably don't release a lot of energy into the body unless the organism enters starvation mode.
How do white adipocytes help with glucose?
Beyond playing a role in providing energy storage, white adipocytes help regulate blood sugar levels. They take up sugar, or glucose, in response to insulin secreted by the pancreas, pulling excess sugar out of the bloodstream. That's one of the big problems with excess body fat, according to the 2006 Nature paper: Too much fat throws off the glucose-regulating function of adipocytes (as does too little fat), and blood sugar levels can be thrown out of whack. [ Can You Turn Fat Into Muscle?]
What are fat cells?
On a cellular level, fats make the membranes that surround cells possible and act as messengers that bind to proteins and enable various reactions. With that in mind, the humble fat cell seems a bit miraculous. Adipocytes, as they're properly known, are the cells that store excess lipids, the molecules that include fats and related substances.
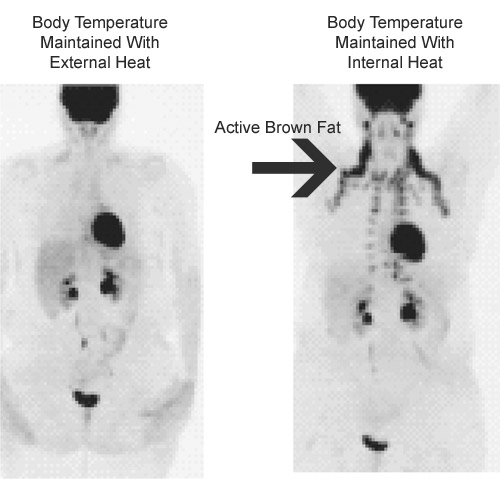
What is the process of brown fat cells?
Specifically, brown-fat cells release something called uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1), which makes the process of fatty-acid oxidation in the cells' powerhouses (the mitochondria) less efficient. That means more of the energy the mitochondria process is "wasted" as heat, thus warming the body, according to a 2017 paper in ...

Major Classes of Compounds in The Human Body
Elements in The Human Body
- Six elements account for 99% of the mass of the human body. The acronym CHNOPS may be used to help remember the six key chemical elements that are used in biological molecules. C is carbon, H is hydrogen, N is nitrogen, O is oxygen, P is phosphorus, and S is sulfur. While the acronym is a good way to remember the identities of the elements, it doesn't reflect their abunda…
Does The Body Contain All The elements?
- The average human body contains tiny amounts of elements that serve no known biological function. These include germanium, antimony, silver, niobium, lanthanum, tellurium, bismuth, thallium, gold, and even radioactive elements like thorium, uranium, and radium. However, not all elements on the periodic table are found in the body. These are primarily the synthetic elements…
Sources
- Anke M. (1986). "Arsenic". In: Mertz W. ed., Trace elements in human and Animal Nutrition, 5th ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press. pp. 347-372.
- Chang, Raymond (2007). Chemistry, Ninth Edition. McGraw-Hill. pp. 52.
- Emsley, John (2011). Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. OUP Oxford. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- Anke M. (1986). "Arsenic". In: Mertz W. ed., Trace elements in human and Animal Nutrition, 5th ed. Orlando, FL: Academic Press. pp. 347-372.
- Chang, Raymond (2007). Chemistry, Ninth Edition. McGraw-Hill. pp. 52.
- Emsley, John (2011). Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements. OUP Oxford. p. 83. ISBN 978-0-19-960563-7.
- Subcommittee on the Tenth Edition of the Recommended Dietary Allowances, Food and Nutrition Board; Commission on Life Sciences, National Research Council (February 1989). Recommended Dietary Allowa...