Full Answer
What are the four phases of cellular respiration?
What are the four processes of respiration quizlet?
- Pulmonary ventilation/breathing. – inspiration (air in) & expiration (air out) in response to changes of O2 & CO2 in blood.
- External respiration. – exchange of O2, CO2 between alveoli/blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
- Transport of respiratory gases. …
- Internal respiration.
What is the overall reaction for cellular respiration?
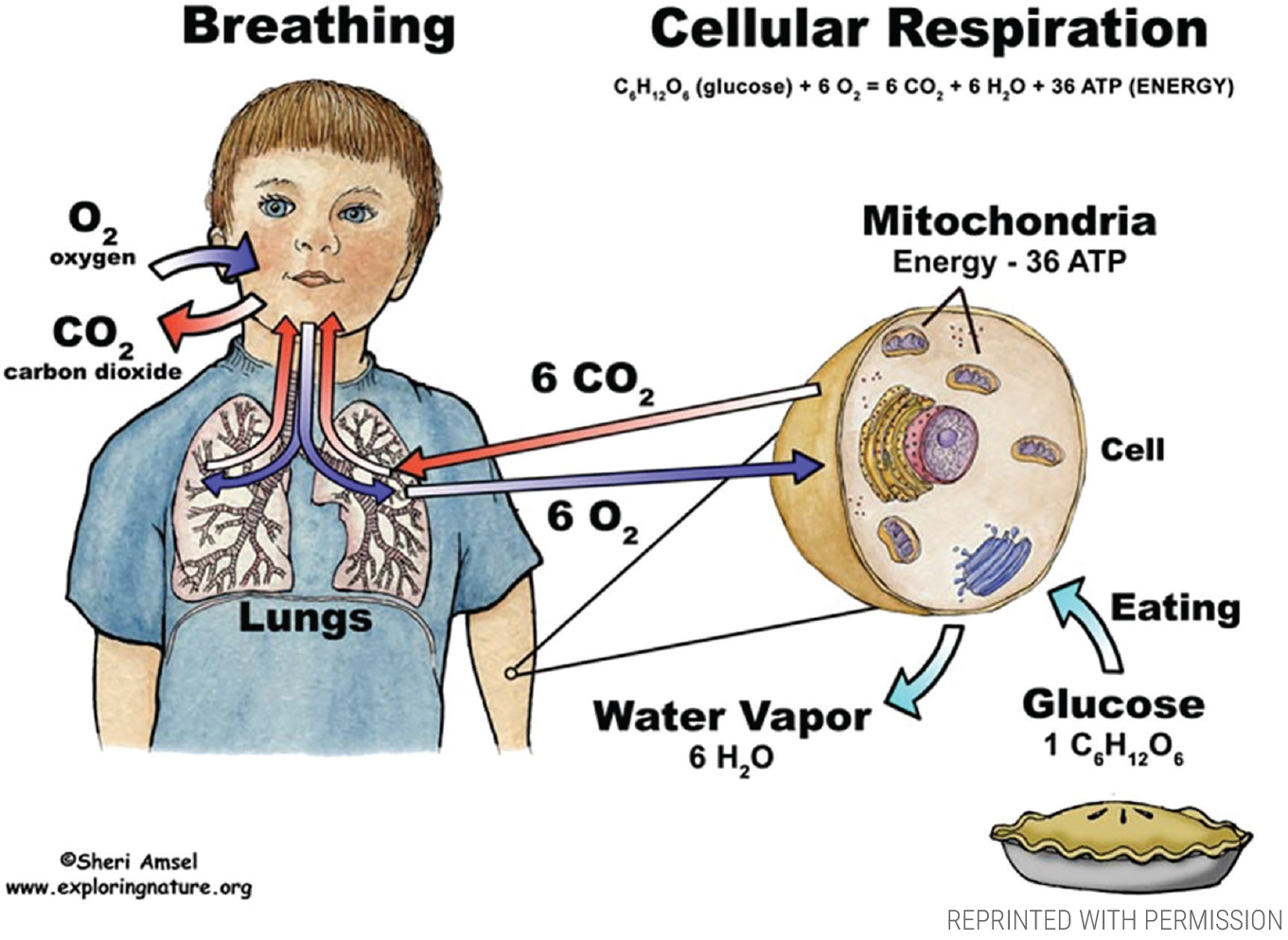
The overall reaction that occurs in cellular respiration is the complete oxidation of glucose by O2 to form CO2, H2O and energy as in normal combustion. What is the formula of cellular respiration? In some cells, cellular respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen and is called anaerobic respiration.
What is the overall process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.
What molecules does cellular respiration produce?
During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. Energy released during the reaction is captured by the energy-carrying molecule ATP (adenosine triphosphate).

What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
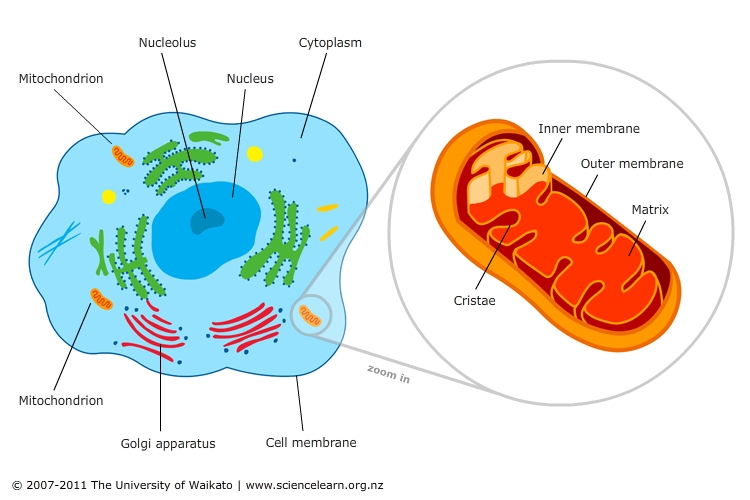
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
How many carbons are in a pyruvate?
Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol.
What is the name of the molecule that is converted to a two carbon molecule?
Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to coenzyme A, called acetyl CoA. Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the cycle of carbon dioxide and NADH?
Carbon dioxide is released and NADH is made. Citric acid cycle. The acetyl CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule and goes through a cycle of reactions, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule. ATP (or, in some cases, GTP), NADH, and FADH_2 are made, and carbon dioxide is released.
How do protons flow back into the matrix?
The protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase, making ATP. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water. During cellular respiration, a glucose molecule is gradually broken down into carbon dioxide and water.
How is ATP produced?
Oxidative phosphorylation is powered by the movement of electrons through the electron transport chain , a series of proteins embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
What is the process of converting glucose into pyruvate?
Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. In the end, it gets converted into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon organic molecule. In these reactions, ATP is made, and is converted to . Pyruvate oxidation.
How does cellular respiration work?
Discover how cellular respiration transforms your food into energy usable by your cells. Cellular respiration releases stored energy in glucose molecules and converts it into a form of energy that can be used by cells. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen ...
How many NAD molecules are in the TCA cycle?
The products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. These molecules go on to fuel the third stage of cellular respiration, ...
What is the process of cellular respiration in which glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
(For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration, see tricarboxylic acid cycle and metabolism .) During the process of glycolysis in cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
What is the process of glycolysis?
Glycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions taking place in most cells that breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules. Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ). Pyruvate molecules produced during glycolysis then enter the mitochondria, where they are each converted into a compound known as acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the TCA cycle. (Some sources consider the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl coenzyme A as a distinct step, called pyruvate oxidation or the transition reaction, in the process of cellular respiration.)
What is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical?
algae: Cellular respiration. Cellular respiration in algae, as in all organisms, is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical...
What are the three main metabolic processes?
The overall process, however, can be distilled into three main metabolic stages or steps: glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation ...
What is the energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during?
Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ).
What is the chemical reaction that turns glucose and oxygen into water, carbon dioxide, and energy?
Cellular respiration is the chemical reaction in which glucose and oxygen are turned into water, carbon dioxide, and energy (ATP). In this reaction, glucose and oxygen are reactants, while water, carbon dioxide, and energy (ATP) are products. Reactions can be represented as chemical equations where chemical formulas are used as shorthand ...
Why do we add 6 to the equation of cellular respiration?
The reason the 6 is put in front of carbon dioxide is to balance out the 6 carbon atoms in the glucose molecule. Likewise, there are 12 hydrogen atoms in glucose, which means a 6 must also be put in front of water, which will turn its 2 hydrogen atoms into 12. Lastly, oxygen now needs a 6 in front to balance out the 12 oxygen atoms in carbon dioxide. The rest of the 6 oxygen atoms in the glucose are balanced by the 6 oxygen atoms from the water.
How many carbon atoms are in a reaction?
Remember from earlier that nothing is created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the atoms on the left side must equal the atoms on the right side. So if there are 6 carbon atoms in the reactants, there must also be 6 carbon atoms in the products. In order to balance the equation for cellular respiration, ...
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down molecules for energy. In order to do this, the cells use that oxygen that you breathe in and produce that carbon dioxide that you breathe out.
How many hydrogen atoms are in glucose?
Likewise, there are 12 hydrogen atoms in glucose, which means a 6 must also be put in front of water, which will turn its 2 hydrogen atoms into 12. Lastly, oxygen now needs a 6 in front to balance out the 12 oxygen atoms in carbon dioxide.
Why do cells feel lethargic?
Think about when you are hungry and feel lethargic. You feel this way because your body does not have food to turn into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate, or ATP.
How are reactions represented?
Reactions can be represented as chemical equations where chemical formulas are used as shorthand to show the reaction. When using chemical formulas, it is important to make sure the atoms on the left and right are balanced as nothing is created or destroyed in the process.
What is Fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation is a type of fermentation (anaerobic respiration) in which complex organic compounds like glucose are converted into lactic acid while releasing some amount of cellular energy.
Why is aerobic respiration more efficient than anaerobic respiration?
The efficiency of aerobic respiration is higher than the anaerobic one because the double bond in oxygen molecule assists the process of ATP production.
What is the basis of life?
Cellular respiration is a basis of life that occurs in all living forms. In most multicellular organisms, cellular respiration occurs in the form of aerobic respiration. The process of cellular respiration involves the breakdown of high energy bonds, which release energy in the form of ATP.
Which type of respiration is the most efficient?
Aerobic respiration is the most efficient type of cellular respiration which occurs in most eukaryotes and some prokaryotes.
Which pathway of cellular respiration produces the largest number of ATPs?
Aerobic respiration equation. In aerobic respiration, one glucose molecule combines with an oxygen molecule and ADP to form carbon dioxide, water, and energy. Aerobic respiration is the most efficient pathway of cellular respiration that produces the largest number of ATPs.
How is cellular respiration determined?
The efficiency of cellular respiration is determined by the number of ATP molecules produced at the end of the process.
What is the process of converting sugar into ATP?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy (sugar) into a usable form of energy (ATP) in the cell.
How Much ATP Is Made?
However, preparation for glycolysis also consumes a bit of ATP, meaning that in actuality the total yield for the process is likely to be around 30 units of ATP.
What is the process of releasing carbon dioxide?
This new structure is known as “acetyl CoA”. This process generates NADH and releases carbon dioxide. The citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle) is where the acetyl CoA that was produced in the last step is combined with a molecule of oxaloacetic acid.
What is the ability of cells to create energy?
In the liver, it is converted back in pyruvate to be handled normally by cellular respiration. The ability of cells to respirate and create energy is what allows them to carry out complex tasks. Thanks to this ability, cells can form a wide variety of organisms we see in the world.
What is the function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert nutrients into the energy that is used to power a variety of functions like transportation, locomotion, and the synthesization of macromolecules. The job of cellular respiration is to form adenosine triphosphate, a molecule used for energy. How does this transition between nutrients ...
How many carbons are in glucose?
Glucose is a sugar with six carbons, and in aerobic respiration, glucose is converted into two pyruvate molecules. When the molecules of pyruvate are oxidized they produce two NADH, which helps carry electrons to other reactions, as well as two molecules of ATP.
Which is more efficient, aerobic or anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration is vastly more efficient than anaerobic respiration, producing around 18 times the amount of energy than fermentation does. By contrast, the process of fermentation will only produce a little ATP (2 units) and sometimes lactic acid.
How does the body use oxygen?
Your body is utilizing the oxygen you breathe in as well as the food you eat to produce energy. The oxygen you breathe in breaks down the sugars from your food and produces heat energy, similar to burning wood to release energy.
Answer
The process of using the chemical energy from food and oxygen molecules to power life processes
New questions in Biology
Help please, I will gibe brainly for the correct answer! Chloe, age 5 is going to the store to buy her father a birthday present. She picks out a stuf …