How do chemists make plastics?
Chemists combine various atoms to make molecules, which are simply two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. When making plastics, these molecules generally are called monomers. These monomers then are combined by chemical bonds into a chain or a network—this is called polymerization. And the resulting materials are called polymers.
What is the chemical composition of plastic?
The chemical composition of plastics includes chains of carbon, oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen. In 1284 naturally made plastic compounds from horn and tortoiseshell were identified In 1823, Scottish chemist Charles Macintosh discovered rubber.
What is the chemistry behind the polymerization reaction?
It’s helpful to understand some of the chemistry behind the polymerization reaction to appreciate how the process works and the complexity involved in making plastic. A polymerization reaction starts with a primary ingredient (monomer), such as ethylene or propylene. Ethylene (C 2 H 4) is a stable molecule with two carbon atoms and a double bond.
What is the relationship between plastics and chemicals?
Knowing what these factors mean in the relationship between plastics and chemicals can go a long way toward informing your choice of plastics for different applications. When a plastic and a chemical are not compatible, the chemical essentially attacks the plastic in a reaction that causes the polymer structure to break down.
What are the elements that make plastic?
Why are chemists developing new plastics?
Why are plastics used in everyday products?
What is the process of combining atoms to make a polymer?
What is a polymer that melts when heated?
What is the polymer that joins together like a chain called?
Is plastic science?
See 2 more
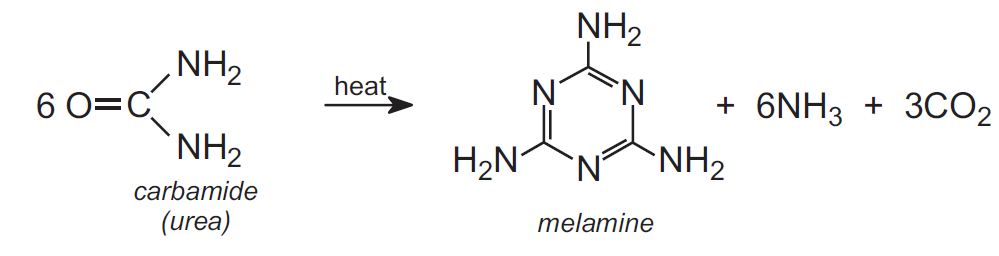
What is the chemical reaction that creates plastic?
polymerisationTypes of polymerisations Synthetic plastic is made by a reaction known as polymerisation, which can be performed in two different ways: Addition polymerisation: Synthesis includes adding together monomers in a long chain.
What process is used to make plastics?
Two main processes are used to produce plastics – polymerisation and polycondensation – and they both require specific catalysts. In a polymerisation reactor, monomers such as ethylene and propylene are linked together to form long polymer chains.
Which chemical is used in plastic manufacturing?
Generally, these additives are: hardeners, catalysts, stabilizers containing phenol or amines, blowing agents, lubricants, dyes, fungicides, bactericides and solvents. The most common plastics manufactured are: polyethylene (PE), Poly Vinyl Chloride, (PVC), Polystyrene (PS), Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE or Teflon®).
What are 3 types of plastic processing?
Manufacturing ProcessMold setup: If the part has inserts, these are added either by hand or robotically. ... Plastic extrusion: Small plastic pellets are melted and extruded through a heated chamber by a screw.Molding: The molten plastic is injected into the mold.More items...
What chemical processes are used to make plastic bags?
Polyethylene, a commonly used plastic found in grocery bags and packaging, is formed by adding together molecules of ethylene in another type of polymerization called an addition reaction. Addition reactions happen between molecules that have double bonds or triple bonds. In this case, ethylene contains double bonds.
What is the main ingredient in plastic?
Structure. Most plastics contain organic polymers. The vast majority of these polymers are formed from chains of carbon atoms, with or without the attachment of oxygen, nitrogen or sulfur atoms.
How was plastic invented by mistake?
Although earlier plastics had relied on organic material, the first fully synthetic plastic was invented in 1907 when Leo Hendrik Baekeland accidentally created Bakelite. His initial quest was to invent a ready replacement for shellac, an expensive product derived from lac beetles.
How many chemicals are in plastics?
More than 10,000 additives, processing aids, and monomers are used to make plastics, with about 2,400 identified as potentially hazardous, according to the results of a comprehensive study cataloging publicly known chemicals used in plastics manufacture (Environ.
How is plastic made step by step?
Plastics are made from raw materials like natural gas, oil or plants, which are refined into ethane and propane. Ethane and propane are then treated with heat in a process called “cracking” which turns them into ethylene and propylene. These materials are combined together to create different polymers.
What is the most common manufacturing process for plastics?
Injection Molding. Injection molding (IM) works by injecting molten thermoplastic into a mold. It is the most widely used process for mass manufacturing of plastic parts.
What process is used to manufacture a plastic water bottle?
This can be done through one of two processes called polymerisation and polycondensation. delivered to bottle manufacturers in pellet, powder, flake or liquid form – provides the basic plastic for making a plastic bottle.
What is plastic extrusion process?
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.
What are the elements that make plastic?
To make today’s plastics, chemists start with various elements (atoms such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and so on) derived from natural resources. Remember that magnificent, elegant periodic table of chemical elements that lists the building blocks of everything on earth? That’s the list of ingredients.
Why are chemists developing new plastics?
And this is only the beginning, as chemists are constantly developing innovative new plastics—to help make aircraft lighter, hearts pump longer, food stay fresher, homes more energy efficient and so on.
Why are plastics used in everyday products?
That’s why plastics are used in so many helpful everyday products, from spatulas to car bumpers and from medical implants to fabrics for clothing.
What is the process of combining atoms to make a polymer?
Chemists combine various atoms to make molecules, which are simply two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. When making plastics, these molecules generally are called monomers. These monomers then are combined by chemical bonds into a chain or a network—this is called polymerization. And the resulting materials are called polymers.
What is a polymer that melts when heated?
If the monomers join together lined up like a chain (picture a string of pearls), the polymer is called a thermoplastic. This plastic behaves sort of like an ice cube: it melts when heated and solidifies when cooled … like water, over and over again. Polypropylene (the stuff butter tubs often are made of) is an example of a thermoplastic.
What is the polymer that joins together like a chain called?
If the monomers join together lined up like a chain (picture a string of pearls), the polymer is called a thermoplastic. This plastic behaves sort of like an ice cube: it melts when heated and solidifies when cooled … like water, over and over again.
Is plastic science?
Kidding … Actually, it’s science in action. Specifically, chemistry. Plastics are the result of the very real marriage of raw materials, engineering, and energy—all brought together through chemistry.
What is the chemistry of plastic?
The chemistry of making plastic. It’s helpful to understand some of the chemistry behind the polymerization reaction to appreciate how the process works and the complexity involved in making plastic. A polymerization reaction starts with a primary ingredient (monomer), such as ethylene or propylene. Ethylene (C 2 H 4) is a stable molecule ...
What can modify the appearance of a polymer?
Additives and colorings can modify the appearance of the polymer. Polymer plants are semi-continuous processes. Raw material is fed into a reactor continuously at the front end, while polymer powder and pellets are packaged in batches. Most sites operate multiple lines with many bins and silos for storage and blending.
What are the different grades of polyethylene?
The most common polyethylene grades are: 1 high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This polymer has a density greater than or equal to 0.941 g/cm 3. It has a low degree of branching, with mostly linear molecules, has high tensile strength, is resistant to many chemicals, and is used in such products as bottles, jugs, water pipes, and toys. 2 medium-density polyethylene (MDPE). With a density range between 0.925 and 0.940 g/cm 3, MDPE has better shock and stress crack resistance than HDPE and is commonly used for gas pipes, plastic bags, and packaging films. 3 low-density polyethylene (LDPE). This grade has a density range of...
What are the two most common plastics?
This article explains the chemistry and production processes behind two of the most popular plastics — polyethylene and polypropylene. Plastics are some of the world’s most diverse and useful manufacturing materials. While plastics encompass a large number of materials, polyethylene and polypropylene are two of the major plastic types found in many ...
What determines the quality of polyethylene?
In general, polyethylene is categorized based on its density, the linearity of the molecules ( i.e., degree of branching), and its molecular weight (length of the chains). Other polymer qualities, including the molten flowing property, known as the melt-flow index, are a function of the crystalline structure and are also primarily determined by the polymerization reaction. The melt-flow index determines the polymer’s behavior in downstream operations, such as extrusion, blow molding, or film production.
How is polypropylene made?
Similarly, polypropylene (PP) is made by breaking the double bond in a propylene (C 3 H 6) molecule, in the presence of a catalyst, to form long chains of three-carbon-atom molecules ( Figure 2 ). The third carbon atom adds a complexity: On which side of the chain will the methyl (CH 3) groups fall? They could all be on one side of the chain’s centerline, or backbone (isotactic), they could appear alternately on opposite sides of the backbone (syndiotactic), or their positions could be random (atactic). These arrangements have different physical properties.
What is the reaction that consumes hydrogen?
Polymerization reactions will also consume hydrogen, which is required to quench the reaction ( i.e., end the chains), and some will involve a secondary ingredient (known as a comonomer). Since the concentrations of these components in the reactor affect the probabilities that specific reactions will take place, the composition in the reactor effectively sets the amount of branching and the length of the chain.
Who invented the plastic compound?
In 1862, Londoner Alexander Parkes unveiled the first man-made Parkesine plastic compound
When were plastic compounds discovered?
In 1284 naturally made plastic compounds from horn and tortoiseshell were identified
How is emulsion polymerization done?
In emulsion polymerization, the mono mers are emulsified in water with a suitable soap and a water-soluble free-radical catalyst is added to induce polymerization. After polymerization has reached the desired level, the reaction is stopped by adding a radical inhibitor. About 10 percent of synthetic elastomer produced through emulsion technique. The rest is coagulated with acidified brine, washed, dried, and pressed into 35-kg bales.
How does polyisoprene stick together?
This long chain of strands is called as polyisoprene polymer. As the drying continues, the polyisoprene strands stick together by forming electrostatic bonds. The attraction between these strands holds the rubber fibers together and allows them to stretch and to recover.
What happens when rubber is vulcanized?
Vulcanization of rubber creates disulfide bonds between chains. The result is that the chains tighten more quickly for a given strain, thereby increasing the elastic force constant and making rubber harder and less extensible.
What causes a rubber band to relax?
Relaxation of a stretched rubber band is thus driven by a decrease in entropy and temperature, and the force experienced is a result of the cooling of the material being converted to potential energy . The material undergoes adiabatic cooling during contraction.
What are the physical properties of rubber?
Physical properties. In a relaxed state, rubber is in the form of long, coiled-up chains. By stretching of rubber all chains will come very close as result, the kinetic energy exerted in the form of heat. In chain elongation process entropy and temperatures required during this process are increased.
What are the raw materials used to make plastic?
To make plastics, chemists and chemical engineers must do the following on an industrial scale: First, they must start with various raw materials that make up the monomers. Ethylene and propylene, for example, come from crude oil, which contains the hydrocarbons that make up the monomers.
Who wrote How Plastics Work?
Craig Freudenrich, Ph.D. "How Plastics Work" 14 December 2007.
How is resin pellets made?
The resin pellets are heated and compressed into a liquid tube, like toothpaste. The resin goes into the chilled mold, and compressed air gets blown into the resin tube. The air expands the resin against the walls of the mold. This process is used to make plastic bottles.
What is the process of polymer resin?
The final polymer resins are usually in the forms of pellets or beads. Finally, the polymer resins are processed into final plastic products. Generally, they are heated, molded and allowed to cool.
How are hydrocarbons obtained?
The hydrocarbon raw materials are obtained from the "cracking process" used in refining oil and natural gas (see How Oil Refining Works ). Once various hydrocarbons are obtained from cracking, they are chemically processed to make hydrocarbon monomers and other carbon monomers (like styrene, vinyl chloride, acrylonitrile) used in plastics.
What is rotational molding?
Rotational molding: The resin pellets are heated and cooled in a mold that can be rotated in three dimensions. The rotation evenly distributes the plastic along the walls of the mold. This technique is used to make large, hollow plastic items (toys, furniture, sporting equipment, septic tanks, garbage cans and kayaks).
What happens when a chemical reaction causes molecules to react together to form polymer chains?
Polymerization occurs when a chemical reaction causes molecules to react together to form polymer chains. These polymer chains can be engineered to control the specific physical properties of the resulting plastic resin, thus allowing the product to be designed for many different uses.
Where does plastic come from?
We see it all around, in everything from food packaging, medical equipment, furniture, and vehicles, to toys, computers, and clothing. But most people don't realize that natural gas is where a lot of plastic production starts.
How is ethane formed?
Ethane is formed the same way other hydrocarbons (e.g. oil and gas) are generated. Hundreds of millions of years ago, organic material such as plankton fell to the bottom of a seabed. Over time, it was trapped in sediment in an anoxic environment (lacking oxygen to break these organic materials down completely).
What is the first stop in the processing of plastic from natural gas?
The first stop in the processing of plastic from natural gas is the cracker plant. Crackers turn either naphtha, a crude oil-based product, or ethane, a natural gas liquid, into ethylene, a starting point for a variety of chemical products. In parts of the wet gas-rich Marcellus and Utica shales, ethane is significantly cheaper than naphtha, ...
How is polyethylene resin transported?
Polyethylene resin can be transported by truck, barge, or train to a manufacturing facility to make end products. Cracker plants, therefore, usually have access to a lot of transportation options and warehouse facilities to store and ship resins and liquid products.
Why is it called cracking?
This process is called cracking, because heat energy is used to break apart or crack molecules to form new molecules. At that temperature ethane (C2H6) molecules lose two hydrogen molecules, which split off to form a separate, stable hydrogen molecule (H2), leaving molecules which are about 80 percent ethylene (C2H4).
What are the components of natural gas?
Natural Gas Liquids (NGLs) include ethane, propane, butane, isobutene, and pentane. They also include a small amount of heavier hydrocarbons, such as hexane, heptane, and octane. Ethane is a major component of NGLs, especially in the Marcellus, Utica and Eagle Ford formations.
What happens when you snap ethylene molecules together?
And when you snap all these ethylene molecules together, you get polyethylene —the ubiquitous plastic found in everything from milk containers to medical devices. But Veser says the cracking process produces a “ whole slew of other side products” in addition to ethylene.
What is the name of the molecule that breaks a molecular bond?
In particular, ethane’s two carbon atoms form a double bond with one another, resulting in a new molecule: ethylene. Veser says it’s this double bond which makes ethylene so useful.
Is the coming chemical boom funded?
This story is part of our series “The Coming Chemical Boom,” which is funded in part by the Fund for Investigative Journalism. Want to read more about how ethane crackers work? Check out our FAQ.
What happens when plastic is not compatible with a chemical?
When a plastic and a chemical are not compatible, the chemical essentially attacks the plastic in a reaction that causes the polymer structure to break down. This occurs at a molecular level and causes the chains that bind the structure together to weaken, become more susceptible to impact and even fail. Part failure can be disastrous for any facility, so be sure to only choose plastics that are up for the job and monitor parts as instructed to ensure they get replaced or repaired when needed.
What is the chemical resistance chart for plastics?
Chemical Resistance Chart for Plastics. One of the most important resources for determining which plastic should be used in a chemical environment is a chemical resistance chart for plastics. These charts show how compatible different plastics are with a variety of chemicals and other fluids that fall on all points of the pH scale, ...
What are the factors that affect plastic compatibility?
Factors Accounted for in Chemical Compatibility Charts. While chemical attack, environmental stress cracking and physical absorption are all serious and important factors covered by a chemical compatibility chart, plastics can be affected by a variety of other factors as well.
How to maintain plastic parts?
As such, it's important to maintain plastic parts by wiping away any spills and splatters that may occur. If fluids and chemicals will be sitting inside of a plastic tank or another part for extended periods of time, you should always "over-engineer," or choose a plastic that can more than handle your specifications.
What is chemical cracking?
Chemical attacks are sometimes considered ESC (environmental stress cracking) when related to vulnerabilities in the plastic's structure. ESC occurs in conjunction with internal and external stresses on a plastic. Internal stresses are placed on a plastic part during fabrication and processing, while external stresses occur from the mechanical load on the part. So, when a chemical weakens the plastic's structure, the forces already at work on a plastic cause thin, spiderweb-like cracking that could seriously affect a part's performance.
What is A&C plastic?
On top of our chemical resistance guide for plastics, we have a treasure trove of other resources on all the chemically resistant plastics we offer and the qualities that make them great for an amazing variety of tasks and applications. If you want to learn more about any of our products, or about who we are as a company , contact A&C Plastics today .
Can plastic stand up to chemicals?
A chemical in its pure form is very different from one that's been watered down. As such, it's crucial that you choose a plastic that can stand up to a chemical at whatever concentration specification you require. In some chemical compatibility charts, multiple entries will be shown detailing how well a polymer resists chemicals at different concentrations. If this is not the case, it would be best to consult with your parts supplier about what a specific plastic can handle.
What are the elements that make plastic?
To make today’s plastics, chemists start with various elements (atoms such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and so on) derived from natural resources. Remember that magnificent, elegant periodic table of chemical elements that lists the building blocks of everything on earth? That’s the list of ingredients.
Why are chemists developing new plastics?
And this is only the beginning, as chemists are constantly developing innovative new plastics—to help make aircraft lighter, hearts pump longer, food stay fresher, homes more energy efficient and so on.
Why are plastics used in everyday products?
That’s why plastics are used in so many helpful everyday products, from spatulas to car bumpers and from medical implants to fabrics for clothing.
What is the process of combining atoms to make a polymer?
Chemists combine various atoms to make molecules, which are simply two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. When making plastics, these molecules generally are called monomers. These monomers then are combined by chemical bonds into a chain or a network—this is called polymerization. And the resulting materials are called polymers.
What is a polymer that melts when heated?
If the monomers join together lined up like a chain (picture a string of pearls), the polymer is called a thermoplastic. This plastic behaves sort of like an ice cube: it melts when heated and solidifies when cooled … like water, over and over again. Polypropylene (the stuff butter tubs often are made of) is an example of a thermoplastic.
What is the polymer that joins together like a chain called?
If the monomers join together lined up like a chain (picture a string of pearls), the polymer is called a thermoplastic. This plastic behaves sort of like an ice cube: it melts when heated and solidifies when cooled … like water, over and over again.
Is plastic science?
Kidding … Actually, it’s science in action. Specifically, chemistry. Plastics are the result of the very real marriage of raw materials, engineering, and energy—all brought together through chemistry.
