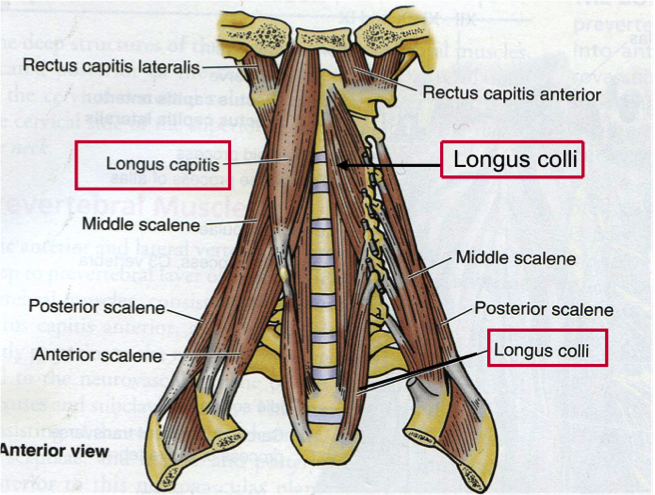
You will find the following muscles under your chin:
- Mylohyoid,
- Lateral Pterygoid, and
- Digastric
What muscles are in your chin?
Other functions of the muscles of your face include:
- Determining what a person looks like.
- Protecting your eyes.
- Keeping food and drink in your mouth (preventing drooling).
- Talking.
- Singing.
- Whistling.
What is the chin muscle called?
- They are attention seeking
- They are fun to be around and they also tend to be humorous
- Flirts of a kind
- Sexually strong
- They have heightened emotions such that they cry when happy, sad, or passionate
- People with a dimple on the chin like to be dominant and express it. The people around them love them b
What are muscles under the chin?
“The anterior digastrics are located directly under the lower jaw right between the chin and neck. “If muscular tension is present in these muscles, tenderness, discomfort or pain will be experienced in this area.
How do you tighten your chin?
You’re likely to get the best results if you:
- Are at a healthy weight and maintain your weight
- Eat a healthy diet
- Quit smoking
- Drink little alcohol
- Protect your skin from the sun and never tan indoors
- Have a small amount of sagging skin
Which muscle raises the skin of the chin?
The mentalis muscle originates from the anterior mandible and inserts onto the chin. The action of the mentalis muscle is to protrude the lower lip, elevate, and wrinkle the skin of the jaw, while the depressor labii inferioris muscle originates from the mandible and inserts onto the lower lip.
Does the chin have a muscle?
The transversus menti, or transverse muscle of the chin, is a facial muscle that is often considered to be the superficial fibers of the depressor anguli oris muscle which cross to the other side of the face.
What is the purpose of the mentalis muscle?
The mentalis muscle (MT) is the only elevator of the lower lip and the chin, and it provides the major vertical support for the lower lip.
What muscles do you use to pout your lips?
MentalisMentalis Sometimes called the 'pouting muscle', contraction of the Mentalis raises and thrusts out the lower lip to make us pout.
Why does the muscle under my chin hurt?
What causes them? TMDs are caused by muscle tension, often triggered by stress. Clenching or grinding your teeth can tire the jaw muscles, leading to muscle spasms, tissue damage, pain, and sore muscles. A TMD can also start with an injury to the jaw joint or a joint disease like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
How do you strengthen your chin muscles?
Step 1: Close your mouth and slowly push your jaw forward. Step 2: Lift up your low lip and push up until you feel the muscles in your chin and jawline stretch. Step 3: Stay in this position for about 10 seconds before repeating the exercise.
What is Caninus muscle?
Description. The canine muscle (M. caninus) is called in Men 'levator anguli oris'. In most Mammals, it acts more on the wing of the nose than on the angle of the mouth or the upper lip. It covers the canine fossa and has, except in Equidae, remarkable relations with it.
What is Procerus muscle?
The procerus muscle is a pyramidal-shaped muscle arising from the fascia of the superior nasal region, near the junction of the nasal bones, and the superolateral nasal cartilage. [1] The procerus muscle fibers run superiorly and merge with the frontalis muscle. Muscle fibers insert into the skin between the eyebrows.
What is the nasalis muscle?
Also known as the compressor naris, the nasalis muscle is located within the nose. It works like a sphincter, or ring-like muscle. The muscle works as its alternative name suggests: to compress nasal cartilage. Also, it depresses the tip of the nose while it elevates the nostril's corners.
What are the 5 muscles of facial expression?
– Lower group- contains depressor anguli oris, depressor labi inferioris and the mentalis. – Upper group- contains risorius, zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, levator labii superioris, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi and levator anguli oris.
What muscle depresses the jaw?
lateral pterygoidAmong all the four muscles of mastication (medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid, masseter, and temporalis), the lateral pterygoid is the only muscle that participates in depressing the mandible.
What muscle closes the jaw?
The masseter muscle is one of the four muscles responsible for the action of mastication (chewing). When the masseter contracts it causes powerful elevation of the mandible causing the mouth to close.
What is a chin muscle look like?
0:040:57What chin muscles look like, after dimple explanation goes viralYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThat's your mentalis muscle it's in your chin. And is very weird you have identified correctly aMoreThat's your mentalis muscle it's in your chin. And is very weird you have identified correctly a weird muscle well done almost every muscle in your body connects a bone to another bone.
Why do chin muscles look weird?
The TikTok star explained how mentalis muscles stick “all of its little muscle fibers into your skin and when it moves, it yanks onto your skin”, and this is what causes the dimpling effect on our chins.
Can you pull a jaw muscle?
Just like any other area of the body, muscle strains or ligament sprains can happen around the jaw. Jaw sprains and strains can begin as a small issue but if left untreated, can become a chronic and longstanding issue. A jaw strain happens when muscle fibres cannot cope with the demandsplaced on them.
What are chins made of?
The alveolar region (upper or superior part of the symphysis) is sculpted by bone resorption, but the chin (lower or inferior part) is depository in its nature. These coordinated bone growth and modeling processes mold the vertical symphysis present at birth into the prominent shape of the chin.
Overview
Your face has almost 20 flat skeletal muscles that attach to different places on your skull. The craniofacial muscles are essential to chewing and making facial expressions. They originate from bone or fascia and insert into your skin. Craniofacial muscles work together to control movements in your:
Anatomy
Facial muscles are located throughout your face. They can be categorized by general location:
Conditions and Disorders
To function, the facial muscles get signals from the brain via the facial nerve. But sometimes, they can’t receive those signals properly.
Frequently Asked Questions
You should seek medical attention right away if you have any facial weakness or facial paralysis.
What muscles are used in chin ups?
The Pectoralis Major, our chest muscle, is activated at the beginning of the exercise. The rhomboids retract (draw in) the scapula as the Teres Major assists the lats. Several “core” muscles are also used in the movement including the erector spinae (support spine and torso rotation), external obliques (largest, superficial core musculature that aids in lateral flexion ‘side bending’ and intra abdominal pressure for core support) and mostly the Rectus Abdominis (the ‘six pack” abs muscle that keep our body from swinging during the chin-up.
What muscles do chin ups work?
Chin-ups are a foundational mass-building exercise. They increase grip strength and core strength as well. They primarily work the Latissimus Dorsi, or lats , as they’re often referred to. This is the broadest muscle of the back extending from under the arms all the way down to the hips. It’s responsible for pulling the arms down and in. In the bodybuilding community, they’re known as “wings”. Along with the lats, the other primary muscle worked by chin-ups are the biceps. This is the “flex” muscle of our arms, or the “guns”. Biceps are responsible for flexing the elbow and supination (turning palms upward) of the forearm.
How to do isometric chin up?
Isometric (constant tension) Chin-up: Use a box to help get yourself to the top of the movement (chin over bar). Hold your bodyweight for as long as possible in that position. This will keep constant tension on the muscles, therefore building strength. Do 3 sets and hold for 5 to 30 seconds.
