
What is the space between the iris and the cilliary body?
Feb 28, 2022 · The ciliary body is an inner eye structure, located at the border between the choroid and the iris. It is composed of several unique structures that give the ciliary body its unique shape and function. These structures include the ciliary muscle, ciliary processes, ciliary vessels and ciliary epithelia.
What connects the ciliary body to the lens?
Jan 28, 2022 · The ciliary body is a disk-shaped tissue entirely hidden behind the iris. The inner part is the ciliary muscle, made of smooth muscle. Smooth muscles contract and relax automatically, so you don’t have conscious control over them. Instead, the ciliary body functions in response to natural reflexes based on environmental stimuli.
Where is the ciliary body in relation to the iris?
The ciliary body is a circular structure that is an extension of the iris, the colored part of the eye. The ciliary body produces the fluid in the eye called aqueous humor. It also contains the ciliary muscle, which changes the shape of the lens when your eyes focus on a near object. This process is called accommodation.
What does the cilliary muscles do?
Mar 03, 2021 · The ciliary body is a circular structure in the eye that is connected to the iris and is located directly behind it. It produces the aqueous fluid inside the eye. The ciliary body also includes a muscle that enables the lens of the eye to focus on near objects.
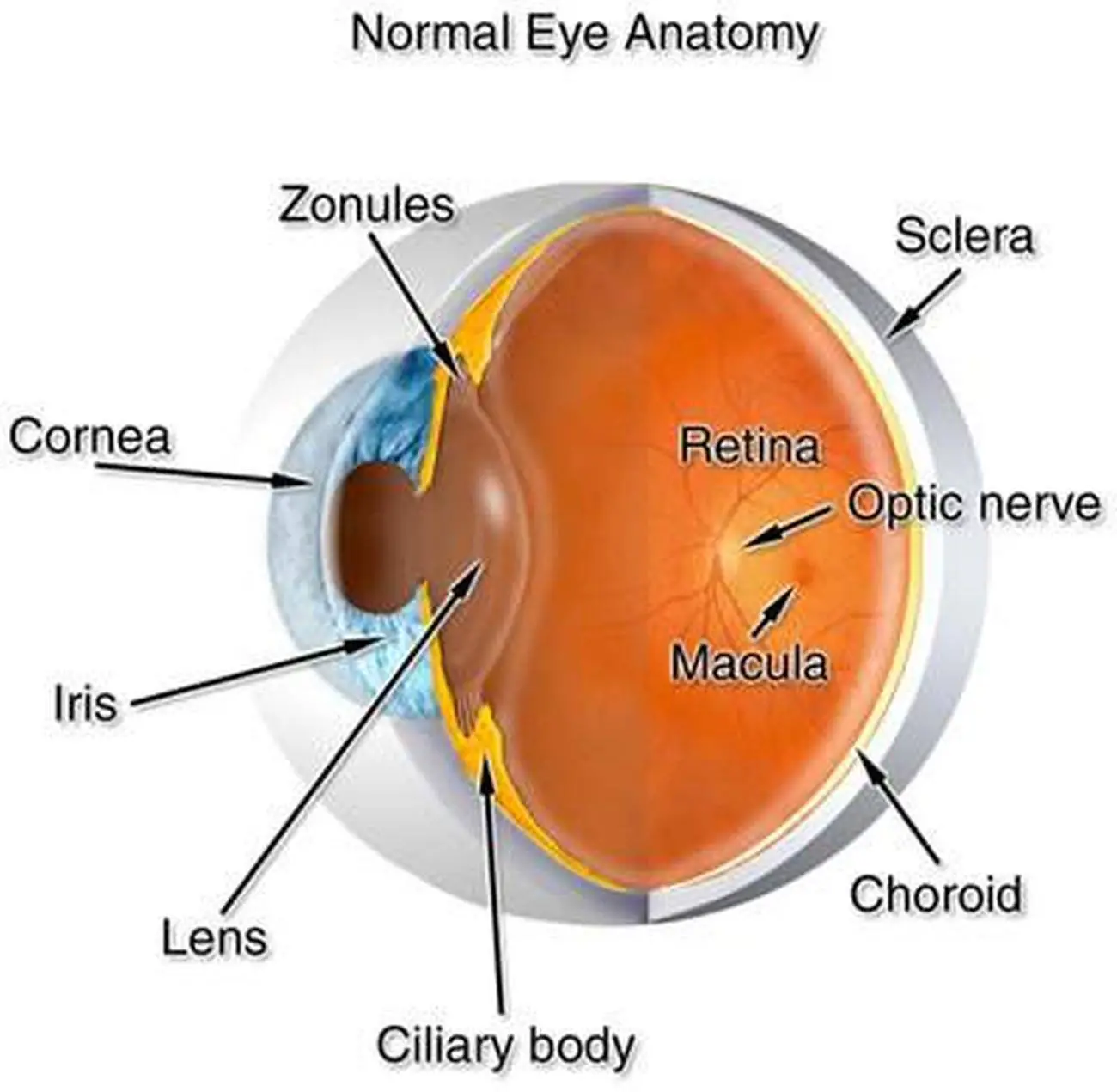
What is the ciliary body function?
What is the ciliary body composed of?
What is the function of ciliary body what helps its realization?
What Innervates ciliary body?
What is ciliary body epithelium?
Does the ciliary body focus the pupil?
What is the function of ciliary muscles Class 10?
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is a ring-shaped thickening of tissue inside the eye that divides the posterior chamber from the vitreous body. It contains the ciliary muscle, vessels, and fibrous connective tissue. Folds on the inner ciliary epithelium are called ciliary processes, and these secrete aqueous humor into the posterior chamber.
What does accommodation mean in a ciliary muscle?
Accommodation essentially means that when the ciliary muscle contracts, the lens becomes more convex, generally improving the focus for closer objects. When it relaxes, it flattens the lens, generally improving the focus for farther objects.
What is the ciliary epithelium responsible for?
The ciliary epithelium of the ciliary processes produces aqueous humor, which is responsible for providing oxygen, nutrients, and metabolic waste removal to the lens and the cornea, which do not have their own blood supply. Eighty percent of aqueous humor production is carried out through active secretion mechanisms (the Na+K+ATPase enzyme creating an osmotic gradient for the passage of water into the posterior chamber) and twenty percent is produced through the ultrafiltration of plasma. Intraocular pressure affects the rate of ultrafiltration, but not secretion.
Where is aqueous humor produced?
The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.
What is intraocular pressure?
Intraocular pressure depends on the levels of production and resorption of aqueous humor. Because the ciliary body produces aqueous humor, it is the main target of many medications against glaucoma. Its inhibition leads to the lowering of aqueous humor production and causes a subsequent drop in the intraocular pressure.
What is the best treatment for glaucoma?
Timolol, Levobunolol, and Betaxolol are common beta blockers prescribed to treat glaucoma. Alpha-adrenergic agonists work by decreasing production of fluid and increasing drainage. Brimonidine and Apraclonidine are two commonly prescribes alpha agonists for glaucoma treatment.
What are the functions of the ciliary body?
Ciliary body functions. There are three main functions of the ciliary body: accommodation, holding the lens in place and producing aqueous fluid. Accommodation refers to the eye’s ability to automatically increase its focusing power to enable the eye to see near objects clearly. This action depends on the ciliary muscle.
What are the two parts of the eye?
The other two parts are the iris (the colored part of the eye), and the choroid (the part of the eye that nourishes the retin a). These two segments are connected together by the ciliary body.
Where does aqueous humor drain?
The aqueous humor — which is constantly produced by the ciliary body — drains through a channel called the trabecular meshwork, located at the angle where the iris and cornea meet.
Can elevated pressure cause blindness?
This elevated pressure can in turn lead to glaucoma — the term used to describe a group of related eye conditions that cause damage to the optic nerve and can lead to blindness if left untreated.
Why does presbyopia occur?
Presbyopia occurs because the lens of the eye thickens over time and loses its natural flexibility. The ciliary body retains its ability to function, but the lens fails to change shape to enable near objects to come into focus. Fortunately, presbyopia is treatable with eyeglasses, contact lenses or vision surgery.
What to do if you have presbyopia?
If you have noticed signs of presbyopia, contact an eye doctor for an eye exam and to discuss the best treatment option moving forward. The ciliary body is not the only part of the vision system that must be cared for.
What are the best medications for glaucoma?
Some of the most common forms of glaucoma medication that affect the ciliary body include: 1 Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as Azopt (brinzolamide) and Trusopt (dorzolamide). 2 Beta blockers such as Betoptic (betaxolol) and Timoptic (timolol). 3 Alpha-adrenergic agonists such as Alphagan P (brimonidine) and Iopidine (apraclonidine).
What is the ciliary body of the eye?
eye anatomy. In human eye: The uvea. The ciliary body is the forward continuation of the choroid. It is a muscular ring, triangular in horizontal section, beginning at the region called the ora serrata and ending, in front, as the root of the iris. The surface is thrown into folds, called ciliary processes,….
What is the anatomy of the eye?
anatomy. A horizontal cross section of the human eye, showing the major parts of the eye, including the protective covering of the cornea over the front of the eye.
What is the cross section of the eye?
cross section of the human eye. A horizontal cross section of the human eye, showing the major parts of the eye, including the protective covering of the cornea over the front of the eye.
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is the tissue which covers the inner part of the anterior segment of the eye coating. It is composed of the ciliary muscle and processes. On the surface of the ciliary body is the black ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humour.
Where does the ciliary body receive blood?
The ciliary body receives blood vessels from the long posterior ciliary arteries and the major iris circle (see Ch. 1, p. 28 ). Blood flow through the ciliary body is about 7% of total ocular flow. The vessels are highly fenestrated, leaking most of their plasma components into the stroma. Blood flow in the iris and ciliary body is autoregulated like that of the retina (i.e. it does not alter significantly with changes in perfusion pressure), but it is also under autonomic control and can be modified by a variety of adrenergic and muscarinic inputs. Under normal circumstances, aqueous production is independent of ciliary body blood flow until the latter declines to <75% of normal.
What is the color of a tumor?
They are generally brown, corresponding to the color of the overlying pigmented epithelium, unless this has been invaded by the tumor, in which case the true color of the tumor is visible.
What happens when the ciliary body is thicker?
In addition to glaucoma, ciliary body melanoma, as it becomes thicker, gradually compresses the lens equator, causing sectoral opacities and subsequent loss of visual acuity. At more advanced stages, lens subluxation or dislocation may occur.
Is iris melanomas asymptomatic?
has a nodular shape and at the time of diagnosis are generally larger than iris melanomas. In the early stages these tumors are confined to the ciliary body and are consequently asymptomatic. They are generally brown, corresponding to the color of the overlying pigmented epithelium, unless this has been invaded by the tumor, ...
What is the ciliary body?
The ciliary body is a 5–6 mm wide ring of tissue extending from the scleral spur anteriorly to the ora serrata posteriorly and is the anterior continuation of the choroid. It can be further divided into the pars plicata and pars plana. It consists of the ciliary muscle and a tissue, which secretes the aqueous humor.
What are the three parts of the eye?
It is pigmented and has three components: the iris, ciliary body, and choroid . The majority of the vascular layer is made up of the choroid. This layer has many blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and the eye's smooth muscles, which are known as the intrinsic muscles.
What is the anterior segment of the eye?
The anterior segment of the eye is composed of the cornea, lens, ciliary body, and the iridocorneal angle. Its main function is to focus the incoming light onto the light sensing retina at the back of the eye (reviewed in Gestri et al., 2012 ).
What is the function of a zebrafish?
Its main function is to focus the incoming light onto the light sensing retina at the back of the eye (reviewed in Gestri et al., 2012 ). In contrast to terrestrial animals, the zebrafish possess a high refractive spherical lens that accounts for essentially all the refractive power of the eye.
Is the retina part of the nervous system?
In contrast to the anterior segment, the retina is a direct outpocketing of the diencephalon and therefore a part of the central nervous system. At larval stages, the retina is disproportionately large, containing about half of the total number of neurons of the central nervous system.
How many layers are there in a zebrafish retina?
Like all canonical vertebrate retinas, the zebrafish retina is composed of three nuclear layers, separated by two plexiform (synaptic) layers. The outer retina is in close contact with the retinal pigment epithelium and contains one type of rod photoreceptors and four cone photoreceptor types.
Where does uveal melanoma come from?
Uveal melanoma arises mostly from the choroid, although it can be found also in the ciliary body and iris. This tumor can be pigmented, amelanic, or mixed, usually uniform and firm, but sometimes with hemorrhagic or necrotic areas. Orange pigment overlying the inner surface of the tumor is a common feature.

Overview
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora s…
Structure
The ciliary body is a ring-shaped thickening of tissue inside the eye that divides the posterior chamber from the vitreous body. It contains the ciliary muscle, vessels, and fibrous connective tissue. Folds on the inner ciliary epithelium are called ciliary processes, and these secrete aqueous humor into the posterior chamber. The aqueous humor then flows through the pupil into the anterior ch…
Function
The ciliary body has three functions: accommodation, aqueous humor production and resorption, and maintenance of the lens zonules for the purpose of anchoring the lens in place.
Accommodation essentially means that when the ciliary muscle contracts, the lens becomes more convex, generally improving the focus for closer objects. When it relaxes, it flattens the lens, generally improving the focus for farther objects.
Clinical significance
Glaucoma is a group of ocular disorders characterized by high intraocular pressure-associated neuropathies. Intraocular pressure depends on the levels of production and resorption of aqueous humor. Because the ciliary body produces aqueous humor, it is the main target of many medications against glaucoma. Its inhibition leads to the lowering of aqueous humor production and causes a subsequent drop in the intraocular pressure. There 3 main types of medication aff…
See also
• Intraocular pressure
• Iridodialysis
• Glaucoma
• Cyclodestruction
External links
• Histology image: 08011loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
• Atlas image: eye_1 at the University of Michigan Health System - "Sagittal Section Through the Eyeball"