Classical Inflation Theory vs. Keynesian Theory
| Classical Inflation Theory | Keynesian Theory |
| • Money supply is the principal cause of ... | • Money supply is not the sole driver of ... |
| • Aggregate demand is relatively elastic ... | • The aggregate supply, in comparison, r ... |
| • Interest rates affect expenditure more ... | • Interest rates affect the demand for m ... |
| • Does not see volatility in the demand ... | • Acknowledges the volatility in the dem ... |
What are the theories of inflation?
What are the theories of inflation in economics? The monetary theory of inflation asserts that money supply growth is the cause of inflation. Faster money supply growth causes faster inflation. In particular, 1% faster money supply growth causes 1% more inflation. With other things constant, the price level is proportional to the money supply.
What is inflation theory explained in simple terms?
Inflation is a general increase in the price level of goods and services in the economy over time. It's caused by demand-pull or cost-push inflation. It can hurt everyday consumers, savers, and fixed-income investors, but it can help borrowers and lenders in certain circumstances. Inflation is the opposite of deflation, which is marked by a ...
What is Keynesian theory of inflation?
What is Keynesian theory of inflation? The Keynesian theory implied that during a recession inflationary pressures are low, but when the level of output is at or even pushing beyond potential gross domestic product, or GDP, the economy is at greater risk for inflation.
Does inflation always lead to more inflation?
The increase in inflation mainly reflects a rapid economic growth rate. An increasing appreciation in demand (AD) in an economy is expected to raise inflation. As a result of the fall in unemployment, there is greater wage pressure, and thus more inflation.

What is the main concept of classical theory?
The classical theory implies that every complex concept has a classical analysis, where a classical analysis of a concept is a proposition giving metaphysically necessary and jointly sufficient conditions for being in the extension across possible worlds for that concept.
What are the theory of inflation?
The monetary theory of inflation asserts that money supply growth is the cause of inflation. Faster money supply growth causes faster inflation. In particular, 1% faster money supply growth causes 1% more inflation. With other things constant, the price level is proportional to the money supply.
What is the classical theory in economics?
The fundamental principle of the classical theory is that the economy is self‐regulating. Classical economists maintain that the economy is always capable of achieving the natural level of real GDP or output, which is the level of real GDP that is obtained when the economy's resources are fully employed.
What does the classical theory of inflation try to explain quizlet?
The Classical Theory of Inflation. Or quantity theory of money. It explains the long-run determinants of the price level and the inflation rate. Inflation rate: the percentage change in the Consumer Price Index, the GDP deflator, or some other index of the overall price level.
What are the 2 theories of inflation?
The economists who have provided the theories of inflation are broadly categorized into two labels, namely, monetarists and structuralists. Monetarists associated inflation to the monetary causes and suggested monetary measures to control it.
What are the three theories of inflation?
There are three main causes of inflation: demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation.
What is the difference between classical theory and Keynesian theory?
Classical economic theory is the belief that a self regulating economy is the most efficient and effective because as needs arise people will adjust to serving each other's requirements. Keynesian economics harbors the thought that government intervention is essential for an economy to succeed.
What is the new classical theory?
New classical macroeconomics, sometimes simply called new classical economics, is a school of thought in macroeconomics that builds its analysis entirely on a neoclassical framework. Specifically, it emphasizes the importance of rigorous foundations based on microeconomics, especially rational expectations.
Who proposed classical theory?
Most consider Scottish economist Adam Smith the progenitor of classical economic theory.
What would a classical economist who sees great merit in the quantity theory of money look for in trying to explain this rise in inflation?
What would a classical economist who sees great merit in the quantity theory of money look for in trying to explain this rise in inflation? A rapid increase in the quantity of money in circulation.
What is the quantity theory of money quizlet?
The quantity theory of money says that the price level times real output is equal to the money supply times the velocity, or the number of times the money supply turns over.
Which country is correctly matched with its 2009 inflation rate?
21. Which country is correctly matched with its 2009 inflation rate? a. 9 percent inflation in the United States.
What are the 4 types of inflation?
Inflation occurs when the prices of goods and services increase. There are four main types of inflation, categorized by their speed. They are "creeping," "walking," "galloping," and "hyperinflation." There are specific types of asset inflation and also wage inflation.
Who discovered the inflation theory?
Physicist Alan GuthPhysicist Alan Guth, the father of cosmic inflation theory, describes emerging ideas about where our universe comes from, what else is out there, and what caused it to exist in the first place.
What are the five causes of inflation?
The Common Causes of InflationGrowing Economy. In a growing or expanding economy, unemployment drops and wages usually rise. ... Expansion of the Money Supply. An expanded money supply can also drive demand-pull inflation. ... Government Regulation. ... Managing the National Debt. ... Exchange Rate Changes.
What causes inflation in Keynesian theory?
Demand-pull inflation is a tenet of Keynesian economics that describes the effects of an imbalance in aggregate supply and demand. When the aggregate demand in an economy strongly outweighs the aggregate supply, prices go up. This is the most common cause of inflation.
What is the classical theory of inflation?
Classical Theory of Inflation says that money is the asset which is utilized by people to purchase goods and services on a regular basis. Money is the mode of exchange in every economy at the present day.
What is inflation in economics?
Inflation is a phenomenon which takes the whole economy into its grasp. It spreads across the whole of the economy. It is such a phenomenon which impacts the whole of the economy and is concerned about the value of the mode of exchange in an economy that is, it concerns itself with money.
How is inflation determined?
Inflation is determined by the quantity theory of money. This theory which is contained in the classical theory of inflation is employed to explain the most important and long run determinants of inflation rate and price level. Inflation is a phenomenon which takes the whole economy into its grasp. It spreads across the whole of the economy.
When does inflation occur?
Inflation occurs in an economy when the overall price level increases and the demand of goods and services increases. There is another aspect of inflation which is coined as hyperinflation. Hyperinflation is another form of inflation which occurs when the price rates increase extraordinarily. The price rates reach an all time high like exceeding ...
When did Germany experience hyperinflation?
A good instance of such an inflation occurred in 1920 in Germany when their economy shot up to an extraordinary height. Germany experienced a hyperinflation during that period.
The Level of Prices and the Value or Money
Suppose we observe over some period of time the price of an ice-cream cone rising from a nickel to a dollar.
Thl Effects of a Monetary Injection
Let's now consider the effects of a change in monetary policy. To do so, imagine that the economy is in equilibrium and then, suddenly, the Fed doubles the supply of money by printing some dollar bills and dropping them around the country from helicopters.
A Brief Look at thf. Adjustment Process
So far, we have compared the old equilibrium and the new equilibrium after an injection of money. How does the economy move from the old to the new equilibrium? A complete answer to this question requires an understanding of short-run fluctuations in the economy, which we examine later in this book.
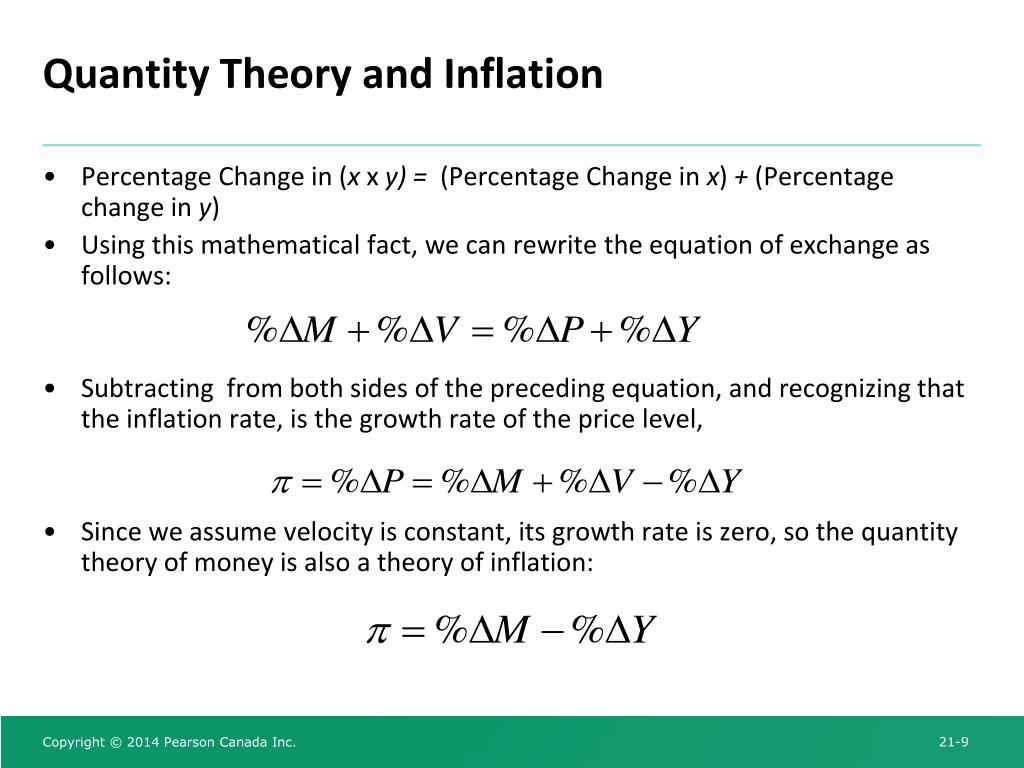
Velocity and the Quantity Equation
We can obtain another perspective on the quantity theory of money by considering the following questknv How many times per year is the typical dollar bill used to pay for a newly produced good or service? The answer to this question is given velocity of money by a variable called the velocity of money.
The Fisher Eppect
According to the principle of monetary neutrality, an increase in the rate of money growth raises the rate of inflation but does not affect any real variable. An important application of this principle concerns the effect of money on interest rales.
What is inflation theory?
According to inflation theory, the universe was created in an unstable energy state, which forced a rapid expansion of the universe in its early moments. One consequence is that the universe is ...
Who developed inflation theory?
Developed in 1980 by particle physicist Alan Guth, inflation theory is today generally considered a widely-accepted component of the big bang theory, even though the central ideas of the big bang theory were well established for years prior to the development of inflation theory.
How did the Big Bang Theory prove its success?
The big bang theory had proven quite successful over the years, especially having been confirmed through the discovery of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation. Despite the great success of the theory to explain most aspects of the universe which we saw, there were three major problems remaining:
What are the different types of inflation?
Inflation Theory goes by several other names, including: 1 cosmological inflation 2 cosmic inflation 3 inflation 4 old inflation (Guth's original 1980 version of the theory) 5 new inflation theory (the name for the version with the bubble problem fixed) 6 slow-roll inflation (the name for the version with the bubble problem fixed)
Is inflation theory a quantum theory?
Some physicists point out that these predictions are present in all versions of inflation theory, so don't really consider them distinct theories. Being a quantum theory, there is a field interpretation of inflation theory. In this approach, the driving mechanism is the inflaton field or inflaton particle .
