
Precautions
Similar to any other prescription medication, long term use of atenolol is also associated with side effects. Though in most cases the side effects associated with the use of atenolol are minimal and often well tolerated, in some cases serious side effects may develop and would required to be treated promptly by the healthcare provider.
Is atenolol safe to take long term?
What are the most popular Beta Blockers?
- Propranolol (Inderal) for anxiety. Propranolol is used for short-term relief from performance anxiety symptoms. ...
- Atenolol (Tenormin) for anxiety. Atenolol is another beta-blocker popular among performers. ...
- Metoprolol (Lopressor) for anxiety. ...
What is the best beta blocker for anxiety?
What Is Atenolol and How Does It Work?
- Atenolol belongs to a class of drugs known as beta-blockers. ...
- Atenolol may also be used to treat irregular heartbeat, heart failure, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and to prevent migraine headaches.
- Atenolol is available under the following different brand names: Tenormin.
What type of medication is atenolol?
Side effects requiring immediate medical attention
- Cold arms or legs
- difficult or labored breathing
- shortness of breath
- tightness in chest
- wheezing
What are the side effects of atenolol?
See more
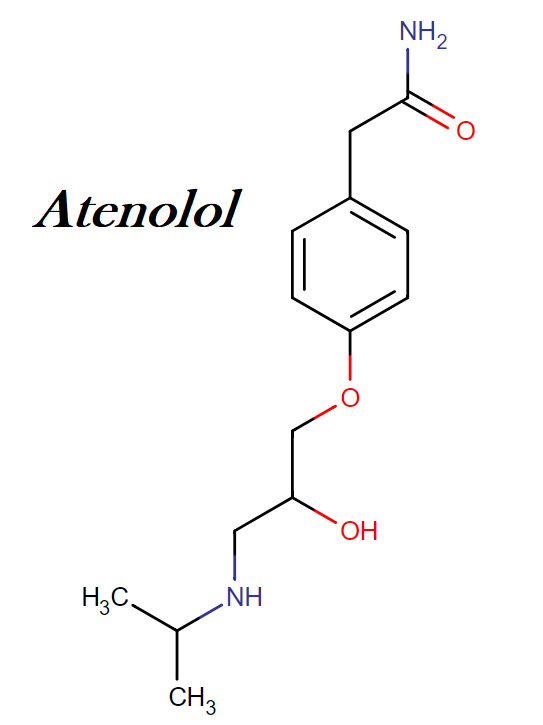
What is the classification of atenolol anti?
Atenolol belongs to a class of drugs known as beta blockers. It works by blocking the action of certain natural chemicals in your body, such as epinephrine, on the heart and blood vessels.
What is the mechanism of action of atenolol?
Cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonists such as atenolol work by selectively binding to the beta-1 adrenergic receptors found in vascular smooth muscle and the heart, blocking the positive inotropic and chronotropic actions of endogenous catecholamines such as isoproterenol, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, ...
What is atenolol also known as?
Brand name: Tenormin. Find out how atenolol treats high blood pressure (hypertension), irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia) and angina, and how to take it.
Is atenolol a antihypertensive?
Atenolol is one of the most widely used β blockers clinically, and has often been used as a reference drug in randomised controlled trials of hypertension. However, questions have been raised about atenolol as the best reference drug for comparisons with other antihypertensives.
Is atenolol a diuretic?
What is this medication? ATENOLOL; CHLORTHALIDONE (a TEN oh lole; klor THAL i done) is a combination of a beta blocker and a diuretic. It is used to treat high blood pressure. This medicine may be used for other purposes; ask your health care provider or pharmacist if you have questions.
Which side effect is most often caused by atenolol?
Commonly reported side effects of atenolol include: cardiac failure, bradycardia, dizziness, fatigue, and cold extremity.
What is a good replacement for atenolol?
Losartan.Hydrochlorothiazide.Metoprolol.Norvasc.Carvedilol.Furosemide.
What does beta blocker mean?
Listen to pronunciation. (BAY-tuh-BLAH-ker) A type of drug that blocks the action of substances, such as adrenaline, on nerve cells and causes blood vessels to relax and dilate (widen). This allows blood to flow more easily and lowers blood pressure and the heart rate.
What is a common side effect of the beta blocker medication atenolol?
Side effects commonly reported by people taking beta blockers include: feeling tired, dizzy or lightheaded (these can be signs of a slow heart rate) cold fingers or toes (beta blockers may affect the blood supply to your hands and feet) difficulties sleeping or nightmares.
What is the best beta blocker for hypertension?
Atenolol was the beta‐blocker most used. Current evidence suggests that initiating treatment of hypertension with beta‐blockers leads to modest CVD reductions and little or no effects on mortality. These beta‐blocker effects are inferior to those of other antihypertensive drugs.
Does atenolol cause insomnia?
Beta blockers such as atenolol are prescribed for hypertension (high blood pressure), a risk factor for heart disease that can precede heart attack, stroke, heart failure, kidney disease, and many other conditions. Some patients complain that sleep disturbances (including insomnia) are an unfortunate side effect.
What is the mechanism of action of beta blockers?
Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure. Beta blockers also help widen veins and arteries to improve blood flow.
Is atenolol a vasodilator or vasoconstrictor?
Vasodilating beta-blockers, e.g. carvedilol, reduce peripheral resistance by binding to alpha-adrenoceptors, causing vasodilation without affecting cardiac output....Non-selective, cardioselective and vasodilating beta-blockers.Beta-blockerAtenololVasodilationNoISA*NoLipid solubilityLowExcretionRenal9 more columns•Jul 21, 2017
Is atenolol a beta 2 blocker?
Atenolol is a "cardioselective" beta-adrenoceptor antagonist. It inhibits selectively beta-1 receptors with a lower affinity for beta-2 receptor subtype.
Is atenolol a vasodilator?
Although there is disagreement regarding the use of β-blockers in arterial hypertension, we have to agree that current evidence is mainly based on studies and meta-analyses of older β-blockers with no vasodilatatory properties, namely atenolol and metoprolol.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use atenolol if you are allergic to it, or if you have: 1. a serious heart condition such as "AV block" (second or third degree); 2....
How Should I Take Atenolol?
Take atenolol exactly as it was prescribed for you. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose...
atenolol Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose of Atenolol for Hypertension:Initial dose: 50 mg orally once a dayMaintenance dose: 50 to 100 mg orally once a dayMaximum dose: 10...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to...
What Happens If I Overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222.Overdose symptoms may include extreme weakness or lack of energy, v...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Atenolol?
Tell your doctor about all your current medicines and any you start or stop using, especially: 1. digoxin, digitalis; 2. indomethacin; 3. any other...
What is the analytical term for atenolol?
Analyte: atenolol; matrix: chemical purity; procedure: liquid chromatography with detection at 226 nm and comparison to standards
Where is atenolol distributed?
In animals, atenolol is well distributed into most tissues and fluids except brain and /cerebrospinal fluid/. Unlike propranolol, only a small portion of atenolol is apparently distributed into the CNS.
What is atenolol used for?
Atenolol is a cardioselective beta-blocker used in a variety of cardiovascular conditions. Sir James Black, a scottish pharmacologist, pioneered the use of beta-blockers for the management of angina pectoris in 1958 for which he received the Nobel Prize. Beta-blockers quickly became popular in clinical use and where subsequently investigated for use in myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, and hypertension during the 1960s. Later they continued to be investigated for use in heart failure throughout the 1970-1980s. Atenolol itself was developed early on in this history by Alvogen Malta under the trade name Tenormin and received FDA approval in September, 1981.
How long does atenolol last?
In patients with normal renal function, atenolol has a plasma half-life (t1/2) of 6-7 hours. Children with normal renal function may exhibit a shorter elimination half-life. In one study in children ages 5-16 (mean: 8.9) with arhythmias and normal renal and hepatic function, the terminal elimination half-life averaged 4.6 hours. Plasma t1/2 of the drug increases to 16-27 hours in patients with creatinine clearances of 15-35 ml/minute per 1.73 sq m and exceeds 27 hours with progressive renal impairment.
How long does it take for atenolol to reach peak concentration?
Peak plasma atenolol concentrations are achieved within 5 minutes following direct IV injection of the drug, and decline rapidly during an initial distribution phase; after the first 7 hours, plasma concentrations reportedly decline with an elimination half-life similar to that of orally administered drug.
How long does it take for atenolol to distribute?
Distribution takes about 3 hrs for the central compartment, 4 hrs for the shallower peripheral compartment, and 5-6 hrs for the deeper peripheral compartment.
What percentage of atenolol is bound to plasma protein?
Approximately 5-15% of atenolol is bound to plasma protein.
How much atenolol is in blood?
Plasma levels are usually less than 3 mg/L during therapeutic administration, but can range from 3–30 mg/L in overdose victims.
What is atenolol used for?
Atenolol is used for a number of conditions including hyperthyroidism, hypertension, angina, long QT syndrome, acute myocardial infarction, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal.
How many prescriptions were written for atenolol in 2012?
In 2012, 33.8 million prescriptions were written to American patients for this drug.
When was atenolol first used?
Atenolol was patented in 1969 and approved for medical use in 1975. It is available as a generic medication. In 2018, it was the 42nd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 18 million prescriptions.
Is atenolol a good antihypertensive?
β-blockers, of which atenolol is mainly studied, provides weaker protection against stroke and mortality in patients over 60 years old compared to other antihypertensive medications. Diuretics may be associated with better cardiovascular and cerebrovascular outcomes than β-blockers in the elderly.
Is atenolol used during pregnancy?
Use is not recommended during pregnancy and alternative drugs are preferred when breastfeeding. It works by blocking β1-adrenergic receptors in the heart, thus decreasing the heart rate and workload. Atenolol was patented in 1969 and approved for medical use in 1975. It is available as a generic medication.
Does atenolol help with heart pain?
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart-associated chest pain. Atenolol, however, does not seem to improve mortality in those with high blood pressure. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain irregular heart beats.
What is atenolol used for?
Other uses for this medicine. Atenolol is also used sometimes to prevent migraine headaches and to treat alcohol withdrawal, heart failure, and irregular heartbeat. Talk to your doctor about the possible risks of using this medication for your condition.
What are the side effects of atenolol?
Atenolol may cause side effects. Tell your doctor if any of these symptoms are severe or do not go away: 1 dizziness 2 lightheadedness 3 tiredness 4 drowsiness 5 depression 6 nausea 7 diarrhea
What to do if you are allergic to atenolol?
tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to atenolol, any other medications, or any of the ingredients in atenolol tablets. Ask your pharmacist for a list of the ingredients. tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription medications, vitamins, nutritional supplements, and herbal products you are taking.
Why is atenolol prescribed?
Why is this medication prescribed? Atenolol is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure. It also is used to prevent angina (chest pain) and improve survival after a heart attack. Atenolol is in a class of medications called beta blockers.
How long does it take to get the full effect of atenolol?
Atenolol controls high blood pressure and angina but does not cure them. It may take 1-2 weeks before you feel the full benefit of atenolol. Continue to take atenolol even if you feel well.
Can you stop taking atenolol without a doctor?
Do not stop taking atenolol without talking to your doctor. Suddenly stopping atenolol may cause chest pain, heart attack, or irregular heartbeat. Your doctor will probably decrease your dose gradually.
Can you get pregnant while taking atenolol?
tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. If you become pregnant while taking atenolol, call your doctor immediately.
What is atenolol used for?
Atenolol is used to treat high blood pressure and chest pain. It can also help prevent heart attack or heart damage after a heart attack.
Why do seniors need a smaller amount of atenolol?
For seniors: Seniors may need a smaller dosage of atenolol at first because they can be more sensitive to the way medications act in their body. Also, as people age, they sometimes have a harder time clearing drugs from their body. After a low initial dosage, their dosage may then increase gradually.
How long can MAOIs be taken after taking atenolol?
MAOIs can continue to interact with atenolol for up to 14 days after taking them. Examples of MAOIs include:
What happens if you don't take atenolol?
If you don’t take It: If you have high blood pressure or chest pain and don’t take your atenolol, you risk: increasing your blood pressure, damaging your blood vessels or main organs, such as your lungs, heart, or liver, and increasing your risk of a heart attack.
Is atenolol a prescription drug?
Atenolol is a prescription drug. It comes as a tablet you take by mouth.
Can atenolol cause allergies?
Atenolol can cause a severe allergic reaction. Symptoms can include:
Can atenolol interact with other medications?
Atenolol oral tablet can interact with other medications, vitamins, or herbs you may be taking. An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well.
How many mg of atenolol is in a tablet?
Atenolol is available in 25 mg, 50 mg, and 100 mg tablets for oral administration or 0.5 mg/mL for intravenous injection. The dosage and route of administration vary depending on the indication.
How long does atenolol last?
The beta-blocking effects manifest within an hour of ingesting a single oral dose and last for 24 hours. With an intravenous dose, effects are evident within 5 minutes but dissipate after 12 hours.
What are the symptoms of atenolol toxicity?
Symptoms of atenolol toxicity may include bradycardia, lethargy, hypotension, respiratory drive disorders, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, and/or seizures. Treatment of beta-blocker toxicity is primarily supportive. Any unabsorbed drug (if administered orally) is removable by gastric lavage or activated charcoal (within 1 to 2 hours), while hemodialysis can remove atenolol from general systemic circulation. [17]
Does atenolol block beta-1?
Cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonists such as atenolol work by selectively binding to the beta-1 adrenergic receptors found in vascular smooth muscle and the heart, blocking the positive inotropic and chronotropic actions of endogenous catecholamines such as isoproterenol, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, thereby inhibiting sympathetic stimulation.[2] This activity results in a reduction in heart rate, blood pressure and decreases myocardial contractility. However, in heart failure patients, atenolol can increase the end-diastolic pressure and left ventricular fiber lengths - conversely resulting in increased oxygen demand.
Is atenolol hepatic or renal?
Unlike its other beta-1-blocking counterparts, there is little hepatic metabolism of atenolol - it is primarily renally excreted. Therefore, while no hepatic dosage adjustment is needed, it is imperative to assess renal function before starting treatment, with regular monitoring throughout the duration of treatment. In addition, impaired glomerular function results in a significant accumulation of the drug in the body; therefore, patients with creatinine clearance under 35 mL/min should receive much lower doses. [7]
Is atenolol contraindicated for heart failure?
Contraindications to atenolol include sinus bradycardia, second or third-degree heart block, cardiogenic shock, heart failure, severe peripheral arterial disease, metabolic acidosis, and pheochromocytoma. It should also be avoided in patients with a history of asthma, bronchospasm, or other obstructive airway diseases unless there is no alternative, in which case it may be given alongside a bronchodilator. [13][14]
Does atenolol have a membrane stabilizing effect?
In higher doses, it also exerts its effects by competitively blocking beta-2-adrenoreceptors, primarily located in the bronchial and vascular musculature. It has no membrane stabilizing or intrinsic sympathomimetic activity. Atenolol has low lipid solubility, resulting in reduced brain penetrance, resulting in fewer CNS side effects. [3]
What is atenolol used for?
Atenolol is used with or without other medications to treat high blood pressure ( hypertension ). Lowering high blood pressure helps prevent strokes, heart attacks, and kidney problems. This medication is also used to treat chest pain ( angina) and to improve survival after a heart attack .Atenolol belongs to a class of drugs known as beta blockers. It works by blocking the action of certain natural chemicals in your body, such as epinephrine, on the heart and blood vessels. This effect lowers the heart rate, blood pressure, and strain on the heart.
How to report side effects of atenolol in Canada?
In Canada - Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects . You may report side effects to Health Canada at 1-866-234-2345. Precautions. Before taking atenolol, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to it; or if you have any other allergies.
Can nitroglycerin be used for chest pain?
If this product is used for chest pain, it must be taken regularly to be effective. It should not be used to treat chest pain when it occurs. Use other medications(such as nitroglycerinplaced under the tongue) to relieve chest pain as directed by your doctor.
Can you drink orange juice with atenolol?
Apple juice and orange juice may prevent your body from fully absorbing atenolol. It is best to avoid drinking apple/ orange juice within 4 hours of taking atenolol, unless your doctor or pharmacist tells you otherwise. The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
Can you get pregnant with atenolol?
You should not become pregnant while you are using this medication. Atenolol may harm an unborn baby. If you become pregnant while using this medication, talk to your doctor right away about its risks and benefits. This medication passes into breast milk and may have undesirable effects on a nursing infant.
What is atenolol used for?
Atenolol is a medication that is used to treat certain heart conditions.
Why is atenolol called a selective beta blocker?
It is called a selective beta blocker because at low dosages it only works on beta1 receptors and has a low affinity for beta2 receptors located in the airways (breathing tubes). 2. Upsides. Atenolol may be used in the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension).
How long does it take for atenolol to work?
Usual starting dosage is 25-50 mg/day. Takes one to two weeks for the full hypotensive effect to be seen. No dosage adjustment is needed in liver disease. Atenolol has a selective action on beta1 receptors located in the heart; however, this selectivity is only apparent at low dosages.
What medications interact with Atenolol?
Common medications that may interact with atenolol include: alpha-blockers such as doxazosin or terazosin. indigestion and heartburn medications, such as cimetidine and ranitidine. insulin. methylphenidate.
Does atenolol cause liver problems?
May cause changes in liver enzymes, headache, hallucinations, and impotence. Cardioselectivity of atenolol is not absolute, and at dosages higher than 50mg/day atenolol is more likely to inhibit beta2 receptors, mostly located in the bronchial and vascular musculature.
Can you share Atenolol with children?
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use atenolol only for the indication prescribed.
Does atenolol cause low blood sugar?
If you have diabetes, atenolol may mask some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
What is the purpose of atenolol?
Atenolol is used to treat angina (chest pain) and hypertension (high blood pressure). Atenolol is also used to lower the risk of death after a heart attack. Atenolol Classification. Therapeutic:antianginals, antihypertensives. Pharmacologic: beta blockers.
Why is atenolol used for heart attacks?
Atenolol is also used to lower the risk of death after a heart attack.
What drugs can cause an unopposed alpha-adrenergic response?
or nitrates. Concurrent use with amphetamine, cocaine, ephedrine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine, or pseudoephedrine may result in unopposed alpha-adrenergic stimulation (excessive hypertension, bradycardia). Concurrent thyroid administration maypeffectiveness. May alter the effectiveness of
Can atenolol cause dizziness?
Atenolol can cause side effects that may impair your thinking or reactions. Be careful if you drive or do anything that requires you to be awake and alert. Avoid drinking alcohol, which could increase drowsiness and dizziness while you are taking atenolol.
Can you take atenolol with heart failure?
You should not use this atenolol if you have a serious heart condition such as "AV block," very slow heartbeats, or heart failure.
Is atenolol a part of a diet?
Atenolol is only part of a complete program of treatment for hypertension that may also include diet, exercise, and weight control. Follow your diet, medication, and exercise routines very closely if you are being treated for hypertension.
What are the side effects of atenolol?
Commonly reported side effects of atenolol include: cardiac failure, bradycardia, dizziness, fatigue, and cold extremity. See below for a comprehensive list of adverse effects.
What is the clinical significance of elevated ANA levels?
The clinical significance of elevated ANA levels is unknown. [ Ref]
Does atenolol cause blurred vision?
Along with its needed effects, atenolol may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention. Check with your doctor immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking atenolol: More common. Blurred vision.
Does atenolol need medical attention?
Side effects not requiring immediate medical attention. Some side effects of atenolol may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine.

Overview
Atenolol is used with or without other medications to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
May Treat: Hypertension · Acute myocardial infarction · Acute coronary syndrome · Anginal pain in coronary artery disease
Brand Names: Tenormin · Senormin · Tenormin Calendar Pak
Drug Class: Beta Blockers Cardiac Selective
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Do not use. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
May Treat: Hypertension · Acute myocardial infarction · Acute coronary syndrome · Anginal pain in coronary artery disease
Brand Names: Tenormin · Senormin · Tenormin Calendar Pak
Drug Class: Beta Blockers Cardiac Selective
Availability: Prescription Required
Pregnancy: Do not use. This medication may be harmful to an unborn child.
Lactation: Consult a doctor before using
Driving: May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Use caution
Medical uses
Side effects
Overdose
Society and culture
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart-associated chest pain. Atenolol, however, does not seem to improve mortality in those with high blood pressure. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain irregular heart beats. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. It can also be used with other blood pressure medicatio…
External links
Atenolol is used for a number of conditions including hyperthyroidism, hypertension, angina, long QT syndrome, acute myocardial infarction, supraventricular tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia, and the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal.
The role for β-blockers in general in hypertension was downgraded in June 2006 in the United Kingdom, and later in the United States, as they are less appropriate than other agents such as A…
Medical uses
Hypertension treated with a β-blocker such as atenolol, alone or in conjunction with a thiazide diuretic, is associated with a higher incidence of new onset type 2 diabetes mellitus compared to those treated with an ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker.
β-blockers, of which atenolol is mainly studied, provides weaker protection against stroke and mortality in patients over 60 years old compared to other antihypertensive medications. Diuretics may …
Usage
Symptoms of overdose are due to excessive pharmacodynamic actions on β1 and also β2-receptors. These include bradycardia (slow heartbeat), severe hypotension with shock, acute heart failure, hypoglycemia and bronchospastic reactions. Treatment is largely symptomatic. Hospitalization and intensive monitoring is indicated. Activated charcoal is useful to absorb the drug. Atropine will counteract bradycardia, glucagon helps with hypoglycemia, dobutamine can be …
Results
Atenolol has been given as an example of how slow healthcare providers are to change their prescribing practices in the face of medical evidence that indicates that a drug is not as effective as others in treating some conditions. In 2012, 33.8 million prescriptions were written to American patients for this drug. In 2014, it was in the top (most common) 1% of drugs prescribed to Medicare patients. Although the number of prescriptions has been declining steadily since limite…
Prevention
• "Atenolol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Diagnosis
- Atenolol is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure. It also is used to prevent angina (chest pain) and improve survival after a heart attack. Atenolol is in a class of medications called beta blockers. It works by relaxing blood vessels and slowing heart rate to improve blood flow and decrease blood pressur...
Preparation
- Atenolol comes as a tablet to take by mouth. It is usually taken once or twice a day. To help you remember to take atenolol, take it around the same time(s) every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take atenolol exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more ofte…