The following are the evidence of continental drift theory:
- The Matching of Continents: The shorelines of Africa and South America facing each other have a remarkable and unmistakable match.
- Rocks of Same Age Across the Oceans: The belt of ancient rocks of 2,000 million years from Brazil coast matches with those from western Africa.
What are four pieces of evidence supporting continental drift?
The four pieces of evidence for the continental drift include continents fitting together like a puzzle, scattering ancient fossils, rocks, mountain ranges, and the old climatic zones’ locations.
What evidence did Alfred Wegener use to support continental drift?
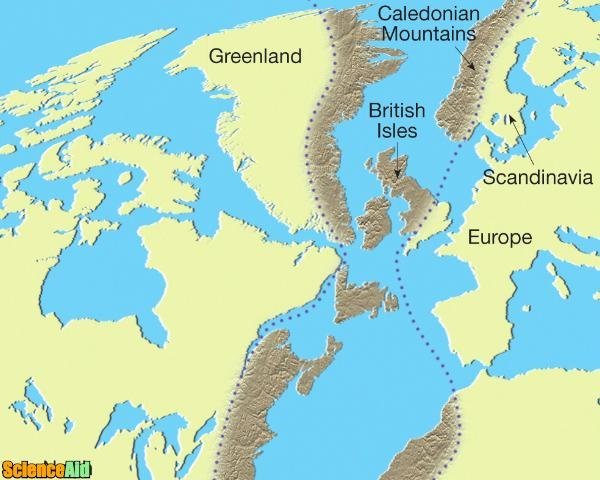
Wegener used geologic, fossil, and glacial evidence from opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean to support his theory of continental drift. For example, he said that there were geological similarities between the Appalachian Mountains in North America, and the Scottish Highlands.
What evidence supported the hypothesis of continental drift?
Wegener used fossil evidence to support his continental drift hypothesis. The fossils of these organisms are found on lands that are now far apart. Grooves and rock deposits left by ancient glaciers are found today on different continents very close to the equator.
Which features were considered evidence of continental drift?
Evidence in Support of the Continental Drift
- Evidence in Support of the Continental Drift
- The Matching of Continents (Jig-Saw-Flt) The shorelines of Africa and South America facing each other have an extraordinary and unmistakable match.
- Rocks of Same Age Across the Oceans. ...
- Placer Deposits. ...

What climate evidence supports continental drift?
The evidence for continental drift included the fit of the continents; the distribution of ancient fossils, rocks, and mountain ranges; and the locations of ancient climatic zones.
How does the continental drift impact on climate?
This drift also had an impact on the climate because it changed the physical features of the landmass, their position and the position of water bodies. The separation of the landmasses changed the flow of ocean currents and winds, which affected the climate.
What evidence is there for climate change on continents?
The 'same animal fossils' found on different continents provide evidence climatic change on continent supporting the theory of 'continental drift'. Explanation: The continental drift is actually a theory that has been made how the continents are shifted their position on the surface of the earth.
What were the 4 main evidence of continental drift?
They based their idea of continental drift on several lines of evidence: fit of the continents, paleoclimate indicators, truncated geologic features, and fossils.
What is the continental type of climate?
There are three types of continental climate—warm summer, cool summer, and subarctic. All these climates exist only in the Northern Hemisphere. Usually, continental climates are found in the interior of continents. Warm summer climate regions often have wet summer seasons, similar to monsoon climates.
What are the causes of climate changes?
Human activity is the main cause of climate change. People burn fossil fuels and convert land from forests to agriculture. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, people have burned more and more fossil fuels and changed vast areas of land from forests to farmland.
What are three examples of evidence that support the theory of climate change?
We also know that climate change is happening because we see the effects everywhere. Ice sheets and glaciers are shrinking while sea levels are rising. Arctic sea ice is disappearing. In the spring, snow melts sooner and plants flower earlier.
How do we know the climate is changing?
What are some of the signs of climate change? Temperatures are rising world-wide due to greenhouse gases trapping more heat in the atmosphere. Droughts are becoming longer and more extreme around the world. Tropical storms becoming more severe due to warmer ocean water temperatures.
What is climate change examples?
Our changing climate Global temperatures rose about 1.8°F (1°C) from 1901 to 2020. Sea level rise has accelerated from 1.7 mm/year throughout most of the twentieth century to 3.2 mm/year since 1993. Glaciers are shrinking: average thickness of 30 well-studied glaciers has decreased more than 60 feet since 1980.
What caused continental drift?
Continental drift over millions of years was caused by plate tectonics. And plate tectonics also explained how the movement of the plates create volcanoes and earthquakes, and how the collision between continents gave rise to huge mountain ranges.
How does continental drift occur?
The Earth's crust is broken up into a series of massive sections called plates. These tectonic plates rest upon the convecting mantle, which causes them to move.
How did continental drift happen?
He argued that the continents had once formed a singular supercontinent that he called Pangea, which means "all lands." Over millions of years Pangea broke into several fragments, which began moving away from each other, slowly drifting to their current positions on Earth's surface.
What are the impacts of continental drift?
Continental drift has impacted the universe in many ways. It has affected the global climate, the world's geographical positions and the evolution of animals. Continental drift also comes along with grave effects such as Volcanoes, Earthquakes, and Tsunamis.
How did Pangea affect climate change?
The destruction of Pangaea triggered warming carbon dioxide levels. Greenhouse climate conditions that enveloped the Earth for long periods in the deep past – millions of years before humans added their current substantial contribution – were caused by the break-up of the supercontinent Pangaea.
What does continental drift cause?
These tectonic plates rest upon the convecting mantle, which causes them to move. The movements of these plates can account for noticeable geologic events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and more subtle yet sublime events, like the building of mountains.
How do ocean currents affect climate?
Ocean currents act much like a conveyer belt, transporting warm water and precipitation from the equator toward the poles and cold water from the poles back to the tropics. Thus, currents regulate global climate, helping to counteract the uneven distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth's surface.
Who is most associated with the theory of continental drift?
The theory of continental drift is most associated with the scientist Alfred Wegener. In the early 20th century, Wegener published a paper explaining his theory that the continental landmass es were “drifting” across the Earth, sometimes plowing through oceans and into each other.
What did Wegener's theory of continental drift not accept?
Scientists did not accept Wegener’s theory of continental drift. One of the elements lacking in the theory was the mechanism for how it works—why did the continents drift and what patterns did they follow? Wegener suggested that perhaps the rotation of the Earth caused the continents to shift towards and apart from each other. (It doesn't.)
What are the most dynamic sites of tectonic activity?
Some of the most dynamic sites of tectonic activity are seafloor spreading zones and giant rift valleys. In the process of seafloor spreading, molten rock rises from within the Earth and adds new seafloor ( oceanic crust) to the edges of the old. Seafloor spreading is most dynamic along giant underwater mountain ranges known as mid-ocean ridge s.
What are the continents resting on?
Today, we know that the continents rest on massive slab s of rock called tectonic plate s. The plates are always moving and interacting in a process called plate tectonics. The continents are still moving today. Some of the most dynamic sites of tectonic activity are seafloor spreading zones and giant rift valleys.
How are the North American and Eurasian plates separated?
The North American and Eurasian tectonic plates, for example, are separated by the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The two continents are moving away from each other at the rate of about 2.5 centimeters (1 inch) per year. Rift valley s are sites where a continental landmass is ripping itself apart.
How long ago did Pangaea exist?
Pangaea existed about 240 million years ago. By about 200 million years ago, this supercontinent began breaking up. Over millions of years, Pangaea separated into pieces that moved away from one another. These pieces slowly assumed their positions as the continent we recognize today.
How long have supercontinents been around?
These include Pannotia, which formed about 600 million years ago , and Rodinia, which existed more than a billion years ago.
How long have continents been apart?
Today’s continents were once part of a huge supercontinent known as Pangaea, which began to break apart around 175 million years ago .
Which plate is responsible for the monsoon season?
For example, around 35 million years ago the plate carrying modern-day India started pushing under the Asia plate to create the Himalayas, which affect global wind patterns and drive the monsoon season to this day. Geological faults can clearly be seen on this rocky outcrop in Devon.
Tectonic causes, climatic effects
One explanation for the change is the steadily and substantially decreasing levels of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (at least until the anomalous and very recent post-Industrial Revolution era). Less greenhouse gas means that less heat is trapped in Earth’s atmosphere.
Rising mountains, closing gateways
The following articles outline two theories that link tectonic and climatic changes.
