
Temperate Rainforest Biome: Climate, Precipitation, Location, Seasons, Plants and Animals
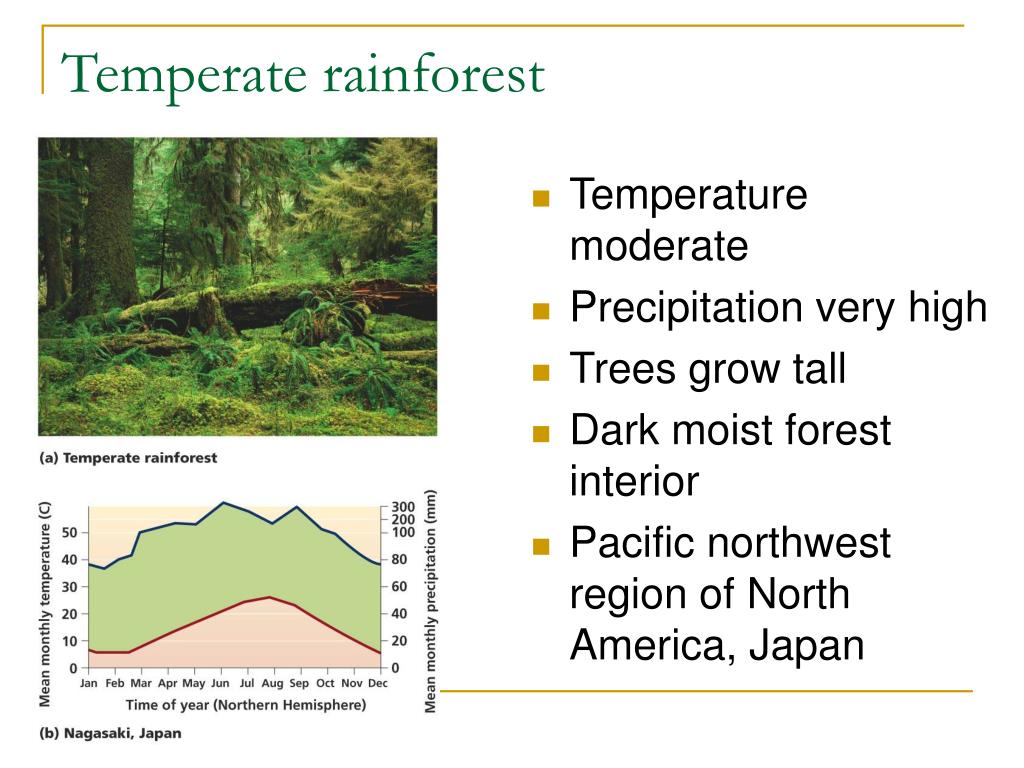
- Climate Temperate rainforests are characterized by mild climates or temperatures. ...
- Precipitation Considering the word ‘’rain” is found in the word ‘’rainforest,” it tells you right off that this biome receives plenty of rainfall. ...
- Location Temperate rainforests are located along some coasts in temperate zones. ...
- Seasons Temperate rainforests experience an extended growing season. ...
- Plants ...
- Animals ...
What are the threats to the temperate forest?
Threats to Biodiversity. Over-harvesting trees in the temperate forest is using up most of the natural resources in this biome. With that, habitat destruction occurs and this is home to the wildlife species of the temperate forest. Another major threat is the usual water and air pollution and also soil depletion.
What is the average weather in a temperate coniferous forest?
Weather and Water. Weather and Water Winters in most coniferous forests are long, cold, and snowy. Summers are usually short and warm. The temperature ranges from about −40 degrees Fahrenheit to about 68 degrees Fahrenheit (−40 degrees Celsius to 20 degrees Celsius). Some forests get as much as 79 inches (200 cm) of rain a year.
What are the disadvantages of a temperate climate?
• The disadvantage is: Although this temperate/mild climate brings a lot of advantages, however, this climate brings a problem, too. Since the temperature is relatively moderate, it will cause a problem for agricultural sector.
What climate and rainfall is in the forest?
Climate of tropical wet and dry or forest In summer, the temperature ranges from 25 C to 30 C, while in winter, it is between 20 C and 30 C. There is a precipitation rate of 700 to 1000 mm per year. There is less than 60 mm of rain in the driest months, which are November to March.
Where are temperate forests climate?
Description. Temperate deciduous forests are located in the mid-latitude areas which means that they are found between the polar regions and the tropics. The deciduous forest regions are exposed to warm and cold air masses, which cause this area to have four seasons.
Are temperate forests hot or cold?
It's warm in the summer, but it gets cool in the fall, and cold in the winter. Most temperate forests don't get as much rainfall as tropical rainforests, but they do get enough rain—about 30 to 60 inches each year—to grow big trees.
What is the climate of temperate biomes?
A temperate climate is a moderate climate that is neither extremely hot nor extremely cold. A temperate climate can be either continental or coastal. Continental temperate climates are found inland, and they tend to have cold winters, hot summers, and moderate precipitation.
What is the climate in a temperate deciduous forest?
Winters are cold and summers are warm. Temperate deciduous forests get between 30 and 60 inches of precipitation a year. Precipitation in this biome happens year round. Because the soil is very fertile and hardwood trees are good for building, this biome has some of the world's largest population centers in it.
Do temperate forests have snow?
Following rainforests, temperate deciduous forests are the second-rainiest biome. The average yearly precipitation is 30 - 60 inches (75 - 150 cm). This precipitation falls throughout the year, but in the winter it falls as snow. The average temperature in temperate deciduous forests is 50°F (10°C).
What are 5 characteristics of a temperate forest?
Key Characteristics of Temperate Deciduous "Broadleaf" ForestDeciduous forests have a long, warm growing season as one of four distinct seasons.There is abundant moisture.The soil typically is rich. ... Tree leaves are arranged in strata: canopy, understory, shrub, and ground.More items...
What are the 4 types of temperate climates?
These include subtropical zone humid subtropical climate and Mediterranean climate, and middle latitude zone oceanic, and continental climate.
What is temperate climate example?
Examples are Western Europe, and western North America at latitudes between 40° and 60° north (65°N in Europe). Some parts of the temperate zone have a Mediterranean climate, which have a dry summer – for example Rome, Cape Town, Santiago or Adelaide.
What are the three temperate climates?
The Mediterranean climate has wet winters and dry summers. The marine west coast climate gets lots of rain from the nearby ocean. In the humid subtropical climate, summers are wet but winters are very cold.
What are 3 facts about the temperate deciduous forest?
The coldest temperatures in temperate deciduous forests range from about 37°F to 64°F. Deciduous trees in these forests drop their leaves in fall and regrow them in spring. The trees in temperate deciduous forests are angiosperms, meaning they have flowers and produce seeds.
What are 5 facts about the temperate deciduous forest?
Deciduous Forest Facts Infographics.Deciduous Forests Change with the Seasons. ... Animals in Deciduous Forests Use Camouflage. ... Insects Lay Eggs Before Perishing in the Winter. ... Animals in Deciduous Forests Have to Adapt to the Seasons to Survive. ... There Are Five Layers of Vegetation in Deciduous Forests.More items...•
Is the temperate deciduous forest cold?
On average, these types of forests have cold winters and hot, wet summers. The temperature in temperate deciduous forest can range from -20°F in the winter to over 90°F in the summer, with a yearly average temperature of 50°F.
Are temperate rainforests hot?
Temperate rainforests are characterized by mild climates or temperatures. Essentially, these areas do not experience extremely cold or extremely hot temperatures. Temperate rainforests have two different seasons. One season (winter) is quite long and wet, and the other (summer) is short, dry and foggy.
What type of forest is cold?
The boreal forest climate is characterized by short summers and long winters with incredibly cold temperatures (reaching -65°F in some places). Boreal forests have poor, acidic soils and short growing seasons (only 130 days).
What biome is hot cold?
Deserts can be either cold or hot, although most of them are found in subtropical areas. Because of their extreme conditions, there is not as much biodiversity found in deserts as in other biomes. Any vegetation and wildlife living in a desert must have special adaptations for surviving in a dry environment.
What describes a temperate forest?
Temperate forests are characterized as regions with high levels of precipitation, humidity, and a variety of deciduous trees Decreasing temperatures and shortened daylight hours in fall mean decreased photosynthesis for plants.
What is the climate of a tropical rainforest?
Climate. Temperate rainforests have two distinct seasons. One is long and wet, and the other is a short, dry and foggy summer. During the long wet season the temperature rarely drops below freezing (0°C and 32°F) and during the short, dry, foggy season the temperature rarely goes above 27°C and 80°F, this tells us why this biome is called ...
How much rain does fog produce in the rainforest?
Even in the summer, when it is dry, the weather is cool, the fog supplies enough moisture to sustain the rainforest. The fog actually yields 18-30 cm (7-12 in) of precipitation each summer.
What is the annual temperature of a tropical rainforest?
Temperature. - Annual temperature ranges from a low of 5 °C to a high of 25 °C. - Temperate rainforests are a lot cooler than tropical rainforests, however the temperatures are still mild. Hence the name given, temperate.
Why is moisture important in the temperate rainforest?
The ocean's. moisture helps protect the rainforest from extreme temperatures. - Weather is still cool and cloud covered with fog which provides moisture to nourish the forest.
Why is fog important to the forest?
trees. This fog supplies the forest with about 10 inches of rain each year. Along with this the fog is beneficial because. it provides moisture for plants. - The amount of rainfall in this biome creates a moist environment with long growing seasons.
Is the tundra hot or cold?
Not as hot as tropical rainforests and not as cold as the tundra. - Temperate forests are relatively wet, but not as rainy as tropical rainforests. trees. This fog supplies the forest with about 10 inches of rain each year. Along with this the fog is beneficial because. it provides moisture for plants.
Where is the Hoh River Valley?
Hoh River Valley Temperate Rain Forest located in Washington State's Olympic National Park. The fog that rolls into the temperate rain forest. The sunlight peaking through the tall trees, photo shows how some plants grow onto other trees, in this case moss. Moss covered trees in Olympic National Park, Washington State.
What are conifers in a forest?
Some temperate forests have trees with needles rather than leaves. Trees that have needles and cones , like pine cones, are called conifers. A forest with mostly conifers is called a coniferous forest. Because they stay green all year long, conifers are also called evergreens. Pines, firs, and spruce trees are conifers—and so are Christmas trees! A forest with both deciduous trees and conifers is called a mixed forest.
How to tell what season a forest is?
Unlike in a rainforest, where the temperature stays the same year-round, it’s easy to tell what season it is in a temperate forest. It’s warm in the summer, but it gets cool in the fall, and cold in the winter. Most temperate forests don’t get as much rainfall as tropical rainforests, but they do get enough rain—about 30 to 60 inches each year—to grow big trees. Certain trees in a temperate forest can grow up to 100 feet tall—that's as high as a seven-story building!
What trees drop their leaves in the fall?
Trees that drop their leaves in autumn are called deciduous trees. Oaks, elms, ash, and beeches are a few of the deciduous trees that can grow in temperate forests .
Where are maple trees found?
Unauthorized use is prohibited. Maples are broad-leaved deciduous trees found in temperate forests. Sap to make syrup is collected from maples in the late winter and early spring. Maples are broad-leaved deciduous trees found in temperate forests.
Why do animals live in temperate forests?
Because the weather changes with the seasons, the animals that live in temperate forests have adaptations that allow them to survive in different kinds of weather. Squirrels and chipmunks gather and store nuts in the fall, which they then eat in colder months when food is scarce.
How much rain does a temperate forest get?
Most temperate forests don’t get as much rainfall as tropical rainforests, but they do get enough rain—about 30 to 60 inches each year —to grow big trees. Certain trees in a temperate forest can grow up to 100 feet tall—that's as high as a seven-story building!
What are the flat leaves and needles?
In regions of the world where it's not extremely hot or cold (called temperate regions), the forests are full of trees with wide, thin leaves. These leaves absorb sunlight during the summer.
What are the two main types of temperate forests?
There are many ways temperate forests can be further divided, but the two main types are deciduous and coniferous forests. Deciduous forests have deciduous trees like maples, which lose their leaves in the winter. Coniferous forests are have lots of conifers like Lodgepole Pine, which keep their needles (special leaves) all year long. Generally, coniferous forests receive less rain than deciduous forests and they grow more slowly. In the United States, most western temperate forests are coniferous and most eastern temperate forests are deciduous.
How many seasons do temperate forests have?
Changing Seasons. Temperate forests have four seasons: spring, summer, winter, and fall. Because they are in the mid latitudes of the Earth — not too far south or north — they have a mild climate. Deciduous trees, like the one the red oak leaf (left) came from, lose their leaves each winter.
How much precipitation does a temperate forest receive?
Temperate forests receive about 30 to 60 inches of precipitation a year. The temperatures are rarely below -20 F (-29 C) or above 90 F (32 C).
What does it feel like to walk through a tree?
Leaves slide under your feet and thick tree trunks surround you. Above your head everything is green, as leaves block the sky. You feel twigs crunch under your feet , and mushrooms peek out from under beds of leaves. Somewhere off in the trees you hear the pecking of a woodpecker. All sorts of birds call or fly off as you walk by. You stay quiet and see a deer pass by in the distance. Chances are, you’re in a temperate forest.
Which forest receives less rain?
Generally, coniferous forests receive less rain than deciduous forests and they grow more slowly. In the United States, most western temperate forests are coniferous and most eastern temperate forests are deciduous. Images via Wikimedia Commons. Autumn forest image by ForestWander.
What is the term for the weather patterns in a region over long periods of time?
Climate: the weather patterns in a region over long periods of time. Hibernate: the act of sleeping through the cold winter months, like some animals do to survive the winter... more (link is external) Mid latitudes: the areas of the Earth between about 24 and 66 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator.
What is the mid latitude?
Mid latitudes: the areas of the Earth between about 24 and 66 degrees latitude, both north and south of the equator. Migration: movement of an animal or a group of animals from one place to another. Old growth forest: A mature forest that has never been cut down by humans.
How did temperate forests evolve?
Temperate forests originated during the period of cooling of world climate that began at the start of the Cenozoic Era (65.5 million years ago). As global climates cooled, climatic gradients steepened with increasing latitude, and areas with a hot, wet climate became restricted to equatorial regions. At temperate latitudes, climates became progressively cooler, drier, and more seasonal. Many plant lineages that were unable to adapt to new conditions became extinct, but others evolved in response to the climatic changes, eventually dominating the new temperate forests. In areas that differed least from the previously tropical environments—where temperate evergreen forests now grow—the greatest numbers of plant and animal species survived in forms most similar to those of their tropical ancestors. Where conditions remained relatively moist but temperatures dropped in winter, deciduous trees evolved from evergreen rainforest ancestors. In areas that became much more dry—though not to the extent that tree development was inhibited and only scrubland or desert environments were favoured—sclerophyllous trees evolved.
What is a temperate forest?
Temperate forest, vegetation type with a more or less continuous canopy of broad-leaved trees. Such forests occur between approximately 25° and 50° latitude in both hemispheres. Toward the polar regions they grade into boreal forests, which are dominated by evergreen conifers, so that mixed forests containing both deciduous ...
How did humans affect temperate forests?
Human activities have had pronounced effects on the nature and extent of modern temperate forests. As long ago as 8,000 years, most sclerophyllous forests of the Mediterranean region had been cut over for timber or cleared to make space for agricultural pursuits. By 4,000 years ago in China the same process led to the removal of most broad-leaved and deciduous forests. In Europe of 500 years ago the original deciduous forests had disappeared, although they are remembered in nursery tales and other folklore as the deep, wild woods in which children and princesses became lost and in which dwarfs and wild animals lived.
How did the character of the Australian sclerophyllous forests change?
The character of the Australian sclerophyllous forests changed in response to more than 38,000 years of burning by the Aboriginal people, and the range of these forests was expanded at the expense of broad-leaved forests.
Where are deciduous forests found?
Deciduous forests are found in regions of the Northern Hemisphere that have moist, warm summers and frosty winters—primarily eastern North America, eastern Asia, and western Europe. In contrast, evergreen forests—excepting boreal forests, which are covered in boreal forest —typically grow in areas with mild, nearly frost-free winters. They fall into two subcategories— broad-leaved forests and sclerophyllous forests. (Sclerophyllous vegetation has small, hard, thick leaves.) The former grow in regions that have reliably high, year-round rainfall; the latter occur in areas with lower, more erratic rainfall. Broad-leaved forests dominate the natural vegetation of New Zealand; they are significantly represented in South America, eastern Australia, southern China, Korea, and Japan; and they occur in less well-developed form in small areas of southeastern North America and southern Africa. Sclerophyllous forests occur particularly in Australia and in the Mediterranean region.
Where do sclerophyllous forests occur?
Sclerophyllous forests occur particularly in Australia and in the Mediterranean region. trees, deciduous and coniferous. Prominent structural differences between coniferous and deciduous trees. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What is the food web in a deciduous forest?
In the temperate deciduous forest, there is a food web that consists of several trophic (food) levels. Each trop hic level has organisms that have the same role in the food web. They also share the same energy sources. The trophic levels and the organisms living in each of them are shown in the image below. At the lowest level, the soil is full of ...
What are the insects that live in the temperate deciduous forest?
Insects inhabiting temperate deciduous forests include ants, flies, bees, wasps, cicadas, walking sticks, moths, butterflies, dragonflies, mosquitoes and praying mantises. Frogs, toads, snakes and salamanders are some of the reptilian residents of the temperate deciduous forest. Common birds found in this biome include woodpeckers, robins, jays, cardinals, owls, turkeys, hawks and eagles. Smaller mammals in the temperate deciduous forests include rabbits, otters, monkeys, beavers, raccoons, porcupines and squirrels. Bears, white-tailed deer, moose, tigers, elephants, giraffes, leopards, pandas and humans are some of the larger mammals that live in this biome.
What type of forest has dense canopy?
This creates more plant and animal diversity than is found in tropic or subtropical deciduous forests, both of which have dense canopies.
How much rain does a deciduous forest get?
Temperate deciduous forests have temperatures ranging from -22°F to 86°F. The average annual rainfall is 30 to 60 inches, with added precipitation falling in the form of snow. Temperate deciduous forests need at least 120 days without frost.
Why are deciduous forests called broad leaf forests?
These forests are also known as broad- leaf forests because the trees have wide, flat leaves. Temperate deciduous forests lie in the mid-latitude areas of the Earth, between the Arctic poles and the tropics. These biomes are exposed to warm and cold air masses, causing them to have four seasons: winter, spring, summer and fall.
What is the last layer of the forest?
These plants must be shade-tolerant to live this far down in the forest. The last layer is the forest floor. This area of the biome has rich soil from decayed leaves, twigs, moss and animal waste, also called litter; this is the recycling area of the temperate deciduous forest. Earthworms, bacteria, fungi and insects are resident here, ...
What is the uppermost level of the trophic food web?
The uppermost level of the trophic food web is home to the top carnivores, also called tertiary consumers. In addition, there can be a quaternary trophic level in more complex food webs. The food web ends when the animals at the top have no natural predators.
