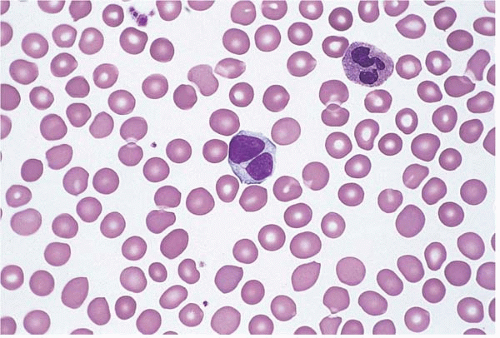
A peripheral blood smear test is a technique healthcare providers use to examine your red and white blood cells and your platelets. This test gives them a clear picture of changes in your blood cells and platelets that may be a sign of disease. A peripheral blood smear test is an important part of diagnosing disease.
What are the signs of peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral Vascular Disease Symptoms. PVD symptoms usually begin slowly and irregularly. You may feel a general level of discomfort like cramping in your legs that gets worse with physical activity and fatigue. The most common symptom of PVD is claudication, which is lower limb muscle pain experienced when walking.
What is the most common symptom of peripheral artery disease?
- Sores or wounds on the feet or toes that aren’t healing well
- Pain, burning or aching in the toes and feet at night or when lying down
- Color changes (especially redness or darkening) of the limbs
- Skin that is cooler to the touch on the feet or lower legs
- An increase in the number of infections
- Shiny skin or skin that becomes hairless on your lower legs
What are the signs of peripheral arterial disease?
Symptoms can range from:
- Pain in the legs and feet
- Fatigue, especially during exercise
- Cold feet
- Thickened, opaque toenails
- Bluish discoloration of the skin
- Gangrene
- Restricted mobility
- Impotence
Do smudge cells always indicate CLL?
The presence of smudge cells on peripheral-blood smears of CLL patients is a constant feature of CLL with significant interpatient variability. The median smudge cell percentage was 28% (range, 1% to 75%) in our study. Only four patients (4%) had a smudge cell percentage within the 1% to 5% range.

What is the clinical importance of blood smears?
A blood smear is used to help diagnose and monitor many conditions, such as blood disorders, sudden kidney failure, and treatment for certain cancers.
What is the purpose of peripheral blood smear?
A procedure in which a sample of blood is viewed under a microscope to count different circulating blood cells (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, etc.) and see whether the cells look normal.
What diseases require a peripheral blood smear and why?
A blood smear can be used to help diagnose or check on many conditions, such as:Anemia.Jaundice.Sickle cell disease.Thrombocytopenia.Malaria.Sudden kidney failure.G6PD deficiency.Certain cancers.
What can you diagnose from blood smear?
The Blood Smear as Part of the Medical Record Sometimes the blood smear provides the primary or the only evidence of a specific diagnosis, such as myelodysplastic syndrome, leukemia, lymphoma, or hemolytic anemia.
What cells are seen in a peripheral blood smear?
In the peripheral blood, the proportion of polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells to mononuclear cells varies with age but in adults' neutrophils is the most abundant. They constitute about 40 to 75% of entire leucocytes, lymphocytes about 20-45%, eosinophils 1 to 6%, monocytes 2- 10% and basophils <1%.
What's the advantage of a blood smear compared to a CBC?
A blood smear is sometimes prepared when red blood cell and/or white blood cell abnormalities are suspected when an automated Complete Blood Count (CBC) is performed. Visual examination of a blood smear provides a clearer picture of these abnormalities prompting further testing to determine the cause.
What is a normal peripheral smear?
A normal peripheral blood smear indicates the appropriate appearance of red blood cells, with a zone of central pallor occupying about 1/3 of the size of the RBC.
What infections can a smear test pick up?
Screening will pick up human papilloma virus (HPV) infection, which causes the cell changes that could lead to cervical cancer. Even if you haven't had sex for years, you should still attend screening because you may have come into contact with HPV from a previous partner, months or even years ago.
Can a blood smear detect leukemia?
For the peripheral blood smear (sometimes just called a smear), a drop of blood is smeared across a slide and then looked at under a microscope to see how the cells look. Changes in the numbers and the appearance of the cells often help diagnose leukemia.
What is the purpose of the smear preparation?
The preparation of a smear is required for many laboratory procedures, including the Gram-stain. The purpose of making a smear is to fix the bacteria onto the slide and to prevent the sample from being lost during a staining procedure. A smear can be prepared from a solid or broth medium.
What is the purpose of staining blood smears quizlet?
What is the purpose of staining blood smears? Smears are stained so that formed elements can be preserved for microscopic viewing and identifying and evaluating blood cell morphology.
How to determine morphology of peripheral blood cells?
Morphologic abnormalities of peripheral blood cells are discovered by microscopic examination with the oil immersion lens of well-prepared films of peripheral blood stained with Wright's stain . For appropriate interpretation of the morphology of erythrocytes, one concentrates on areas of the slide where the red cells appear singly and have central pallor. Examination of erythrocytes far out on the feathered edge discloses erythrocytes lacking central pallor, whereas in thick areas of the slide the morphology of the erythrocytes is distorted by contact between cells.
What is the diagnosis of leukemia?
The diagnosis of leukemia is commonly obvious by recognition of abnormal numbers and stages of development of myeloid or lymphoid cells in the blood. Immature monocytes suggest either leukemia or myelodysplasia. A significant increase in the number of basophils usually indicates a myeloproliferative disorder.
Why do spherocytes form?
Spherocytes can be due to an inherited membrane abnormality of erythrocytes (hereditary spherocytosis) or can result from the action of phagocytes on erythrocytes sensitized with antibodies wherein the phagocytes remove portions of the red cell membrane, creating spherocytes.
What causes erythrocytes to become artifacts?
Artifactual changes of erythrocytes occur commonly on peripheral blood films. Cytoplasmic vacuolization of red cells is an artifact. Echinocytes (crenated red cells) are frequently caused by hypertonicity or alkalinity of the staining solution. Stomatocytes may form when the staining solution is too acidic. When target cells appear in one area of the slide and not in another, they are artifacts because naturally occurring target cells will be distributed evenly throughout the slide.
What are the two abnormalities of erythrocytes?
Two abnormalities of erythrocytes can be recognized by low-power microscopic examination of the blood. Rouleaux of erythrocytes is related to very high serum protein concentrations, generally due to multiple myeloma or to macroglobulinemia. Agglutination of red cells on the slide is usually due to cold agglutinins.
What are normal red blood cells?
Normal human red blood cells are biconcave disks (diskocytes) with a mean diameter of about 7.5 μm. Erythrocytes are slightly smaller than small lymphocytes. The hemoglobin of red cells is located peripherally, leaving an area of central pallor equal to approximately 30 to 45% of the diameter of the cells. Cells of normal size and hemoglobin content (color) are termed normocyticand normochromic. Larger than normal erythrocytes are macrocytes(diameter greater than 9 μm); small red cells are microcytes(diameter less than 6 μm); and those with central pallor greater than 50% of the diameter are hypochromic. Abnormal variability in size is termed anisocytosis;unusual variation in shape is called poikilocytosis;and significant differences among erythrocytes in the amount of central pallor is referred to as anisochromia. Polychromatophiliameans the erythrocytes have a blue-gray hue to the color of their cytoplasm.
How big are platelets?
Most platelets in the peripheral blood have diameters between 1 and 3 μm. Platelets greater than 3 μm in diameter are "large" (megathrombocytes). In a normal person usually less than 5% of the platelets appear large. Figure 155.1shows examples of morphologically normal and abnormal erythrocytes. Figure 155.1.
What is a peripheral blood smear test?
A peripheral blood smear test is usually ordered as a follow-up test when the complete blood count (CBC) reveals abnormal results. A peripheral smear test can be used to diagnose, monitor numerous conditions and blood diseases that affect population of blood cells.
What is the purpose of a blood smear?
The blood smear test or peripheral smear test is a type of blood test that is done to procure detailed information about the number and shape of blood cells. This test focuses on the red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. This test provides information about the number and shape of these cells.
How do you know if your platelets are low?
An abnormally low or high number of platelets are evaluated through the blood smear test that helps to visualize any abnormalities in the shape or size of the platelets.
How many WBCs are there in a smear?
A WBC differential is done as a part of the peripheral smear test. Usually, a minimum of 100 white blood cells arefound, counted and categorized according to the type. Then the percentage of each type is calculated and the morphology and stage of development of the white blood cells are recorded. White blood cells have a nucleus which is surrounded by cytoplasm. The white blood cells are derived from the stem cells of the bone marrow. The five distinct types of WBCs are:
Why do red blood cells have a pinkish color?
They have around and flattened appearance with a depression in the middle. The RBCs appear pink or red in colour because of the presence of hemoglobin in the cells. Abnormalities in the shape and size of red blood cells indicate diseases such as: Anemia.
What is a blood smear test?
The blood smear test is a simple procedure in which your health care provider draws a blood sample from the vein in your arm. The blood sample is sent to the lab where a drop of blood is spread thinly onto a glass slide and it is then treated with a special strain. This procedure is known as a blood film.
What medications affect blood smear results?
Some medications that can affect the test results are warfarin, atromentin and acenocoumarol. Tell your doctor about any existing medical conditions such as hemophilia. Certain disorders such as cancer and procedures like regular blood transfusions can give abnormal results of the blood smear.
What is blood smear?
The blood smear is a simple blood test. A phlebotomist, a person specifically trained to draw blood, first cleans and sterilizes the injection site with an antiseptic. They then tie a band above the venous site where your blood will be drawn. This causes your veins to swell with blood.
Why are platelets important?
platelets, which are important for blood clotting . The test provides information on the number and shape of these cells, which can help doctors diagnose certain blood disorders or other medical conditions. Irregularities in the number or shape of your red blood cells can affect how oxygen travels in your blood.
What does it mean when your white blood cells are abnormal?
Abnormalities in the shape or number of white blood cells may be signs of a platelet disorder. Platelet disorders affect your blood’s ability to clot, which can lead to excessive or prolonged bleeding or blood clotting. They often occur when the body produces too many or too few platelets.
What diseases affect platelets?
other lymphoproliferative diseases, including multiple myeloma. Disorders affecting platelets include: myeloproliferative disorders, a group of disorders that cause blood cells to grow abnormally in the bone marrow.
What is the disorder that occurs when the body produces an excessive number of red blood cells?
polycythemia rubra vera, a disorder that occurs when the body produces an excessive number of red blood cells. Disorders related to white blood cells include: acute or chronic leukemia, a type of blood cancer. lymphoma, a form of cancer that affects the immune system. HIV, a virus that infects white blood cells.
What causes abnormalities in the red blood cells?
These abnormalities are often caused by a mineral or vitamin deficiency, but they can also be caused by inherited medical conditions, such as sickle cell anemia.
What is the disorder in which the body doesn't produce enough red blood cells?
iron-deficiency anemia, a disorder in which the body doesn’t produce enough normal red blood cells due to iron deficiency. sickle cell anemia, an inherited disease that occurs when red blood cells have an abnormal crescent shape. hemolytic uremic syndrome, which is commonly triggered by an infection in the digestive system.
What is the purpose of a blood smear?
A blood smear involves looking at a sample of blood under the microscope after applying special stains and looking for abnormalities or changes in red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. There are many reasons why your doctor may order a blood smear. Some of these include: 1 .
Why do doctors look at blood smears?
Unlike automated tests (such as a CBC), a technician or healthcare provider looks at a blood smear under the microscope in order to detect a wide range of changes that give clues to underlying diseases.
What is a good measure of bone marrow?
In addition to information about the different types of blood cells, a blood smear (especially when combined with a reticulocyte count) can often be a good measure of how well the bone marrow is functioning.
What are the findings of the study of white blood cells?
Findings that are noted include: 1 . The number of the type of blood cells. With white blood cells, the number and proportion of the different subtypes of white blood cells, including lymphocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes. The relative size of the cells, as well as a variation in size.
What does it mean to evaluate an infection?
to evaluate an infection (identifying the types of white blood cells present can help determine if an infection is viral, bacterial, or parasitic, as well as the severity)
Which type of white blood cell can be elevated with many conditions?
Monocytes : This type of white blood cell can be pictured as a garbage can and can be elevated with many conditions.
Can a blood smear include native blood cells?
There are a few limitations to a blood smear. If a person has received a blood transfusion, the smear will include a combination of native and donated blood cells. 2 . There are several potential ways in which error can enter into a blood smear.
